Electric power source circuit and abnormality diagnosis system
a power source circuit and abnormality technology, applied in power supply testing, instruments, measurement devices, etc., can solve the problems of large current flowing from the battery, large size of the power supply relay, and difficulty in diagnosing the power supply relay with respect to the fixed closur
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
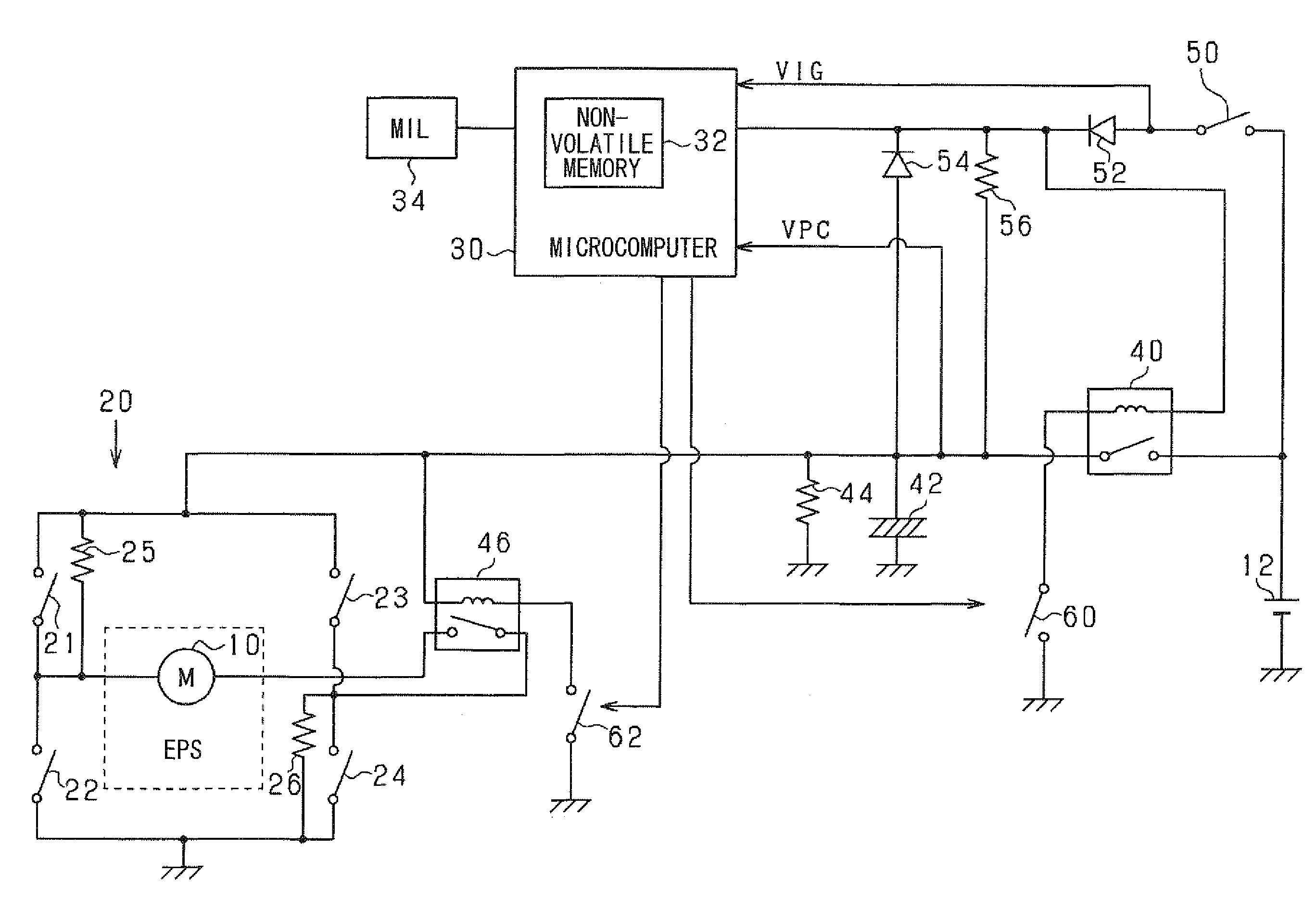
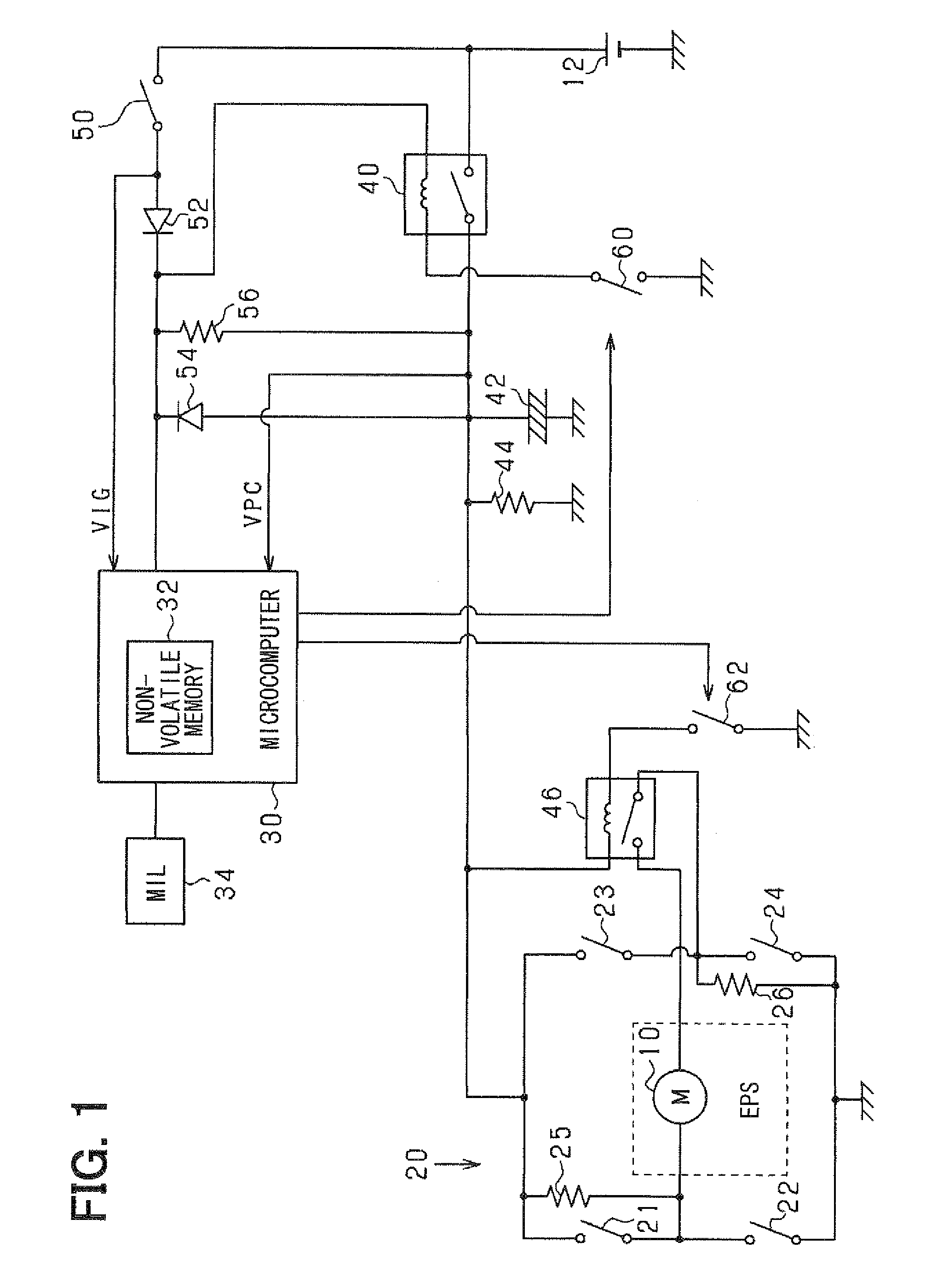
[0022]According to a first embodiment, an abnormality diagnosis system for an electric power source circuit of the present invention is applied to an abnormality diagnosis system for a power source circuit of an electric power steering apparatus mounted on a vehicle.
[0023]Referring to FIG. 1, an electric motor 10 is a DC motor with brushes. The motor 10 is an actuator provided in a steering apparatus, which power-assists steering operation of a driver. The motor 10 is supplied with electric power of a battery 12 through a H-bridge circuit 20.
[0024]The H-bridge circuit 20 is an electric power conversion circuit for supplying the electric power of the battery 12 to the motor 10. Specifically, the H-bridge circuit 20 has parallel-connected series arms. In one series arm, switching elements 21 and 22 are connected in series. In the other series arm, switching elements 23 and 24 are connected in series. The switching elements 21 to 24 may be transistors. A pair of terminals of the motor ...
second embodiment
[0052]A second embodiment is described next with respect to parts different from the first embodiment.
[0053]In the second embodiment, the power supply relay 40 is further diagnosed with respect to its fixed-open abnormality, in which the movable contact cannot be moved to close the input terminal and the output terminal in the power supply relay 40.
[0054]The principle of diagnosing the power supply relay 40 with respect to the fixed-open abnormality is shown in FIGS. 4A and 4B, in which the power supply relay 40 is assumed to be normal and abnormal, respectively. In FIGS. 4A and 4B, (a1) and (a2) indicate changes of the ignition switch 50, (b1) and (b2) indicate changes of the power supply relay 40, (c1) and (c2) indicate changes of the motor relay 46, (d1) and (d2) indicate changes of the output voltage VIG of the ignition switch 50, and (e1) and (e2) indicate changes of the charge voltage VPC of the capacitor 42.
[0055]If the power supply relay 40 is normal, as shown in FIG. 4A, wh...
third embodiment
[0064]A third embodiment is described next with respect to parts different from the second embodiment.
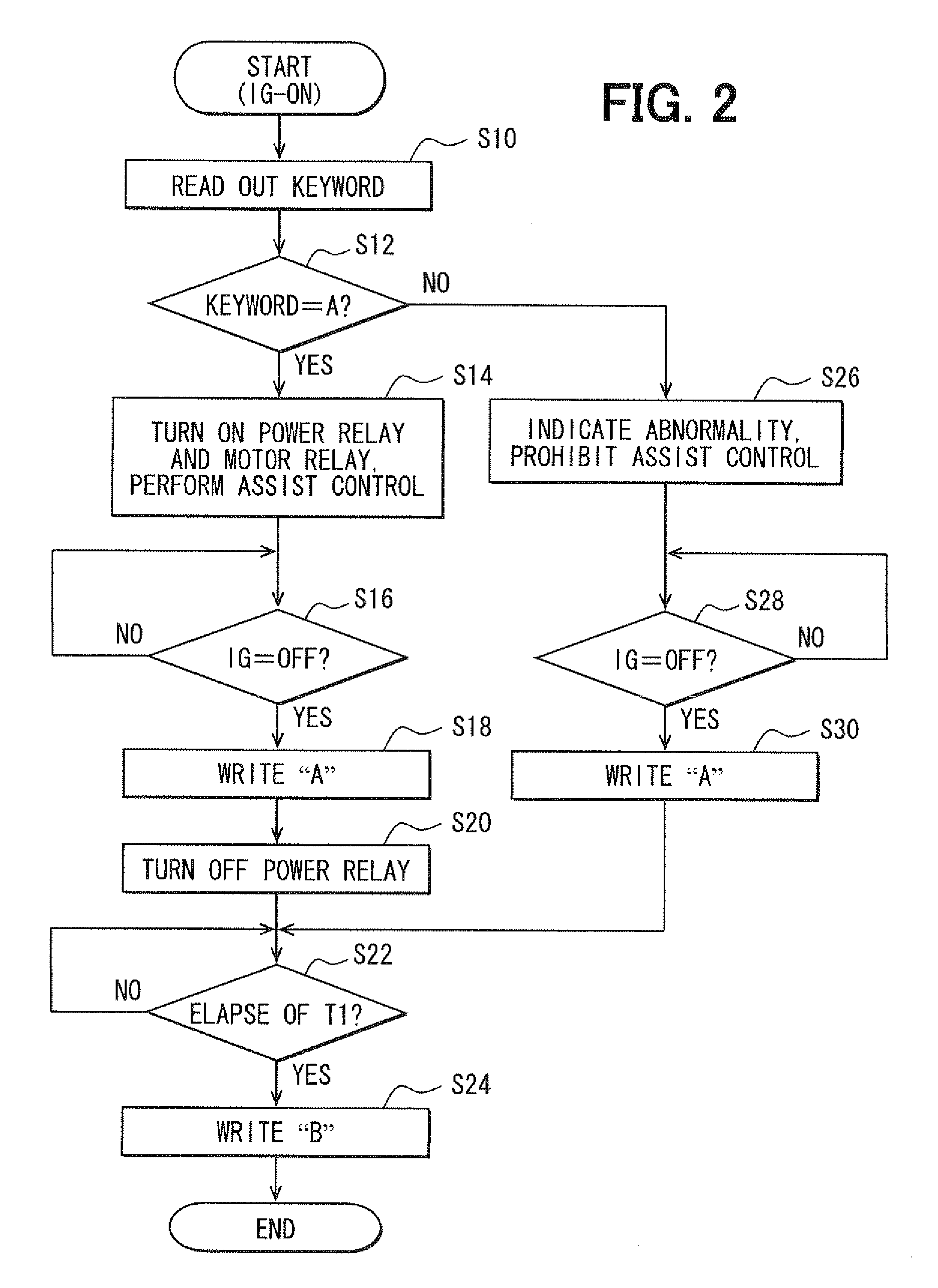
[0065]In the third embodiment, the abnormality diagnosis processing is executed as shown in FIG. 6 in response to the turn-on of the ignition switch 50 as a trigger. In FIG. 6, steps S60, S62, S64 and S66 are executed in addition to the steps executed in the second embodiment (FIG. 5).
[0066]If it is determined at step S42 that the fixed-closure abnormality is not present (NO), it is then checked at step S60 whether a predetermined time 13 has elapsed. The predetermined time 13 is set to correspond to a period required to charge the capacitor 42 to a predetermined voltage β by the ignition voltage VIG through the pre-charge resistor 56. If the predetermined time elapses (S62: YES), it is checked at step S62 whether the charge voltage VPC is greater than the predetermined voltage β. This step S62 is for checking whether the pre-charge path including the pre-charge resistor 56 has any ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com