Driving assistance method for motor vehicle
a technology for motor vehicles and assistance methods, applied in brake systems, instruments, braking systems, etc., can solve problems such as inability to function, driver failure to realize, and obstacle will be struck at full speed, so as to reduce noise and vibration of motor vehicles, reduce the risk of collision, and improve the braking reaction time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
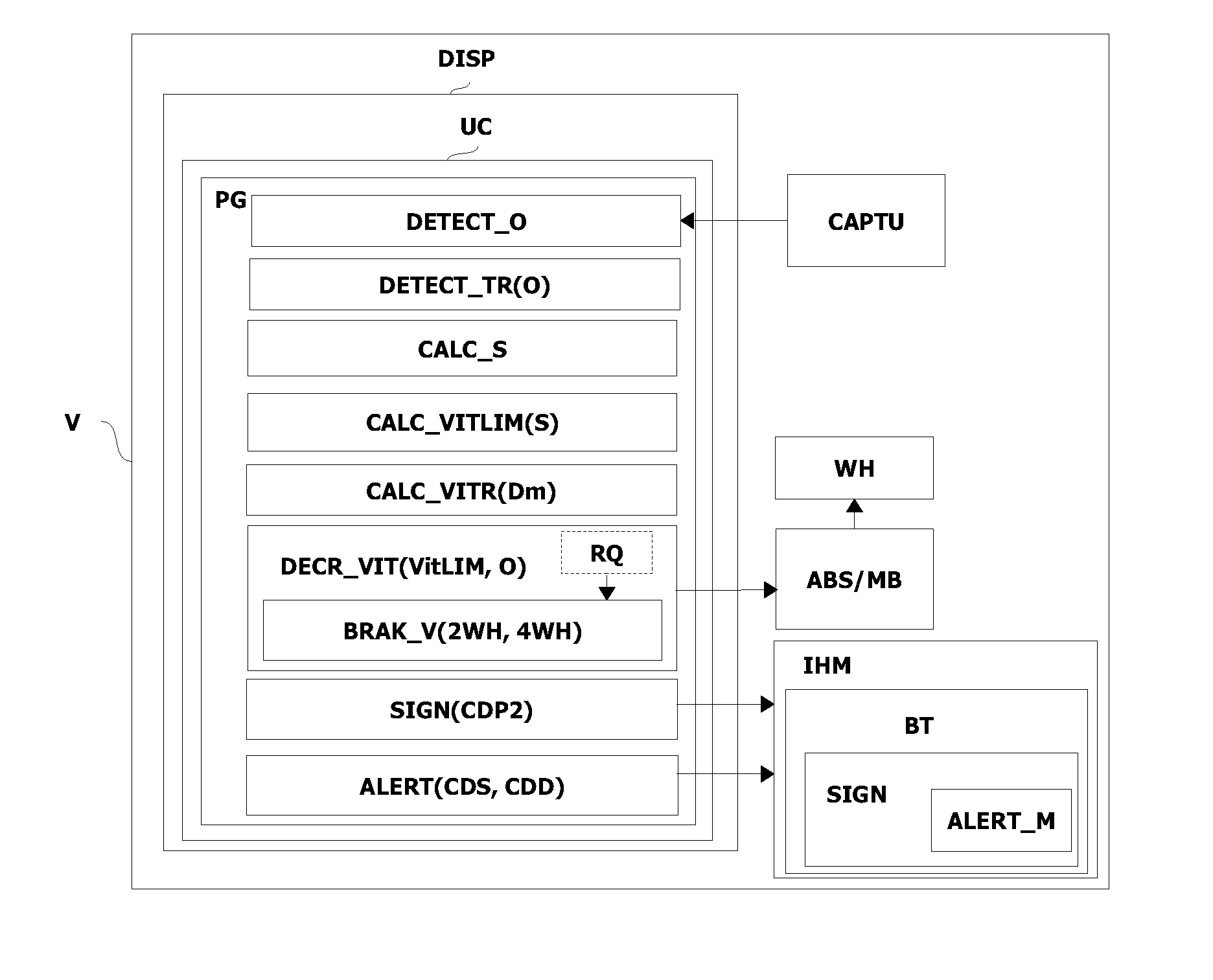
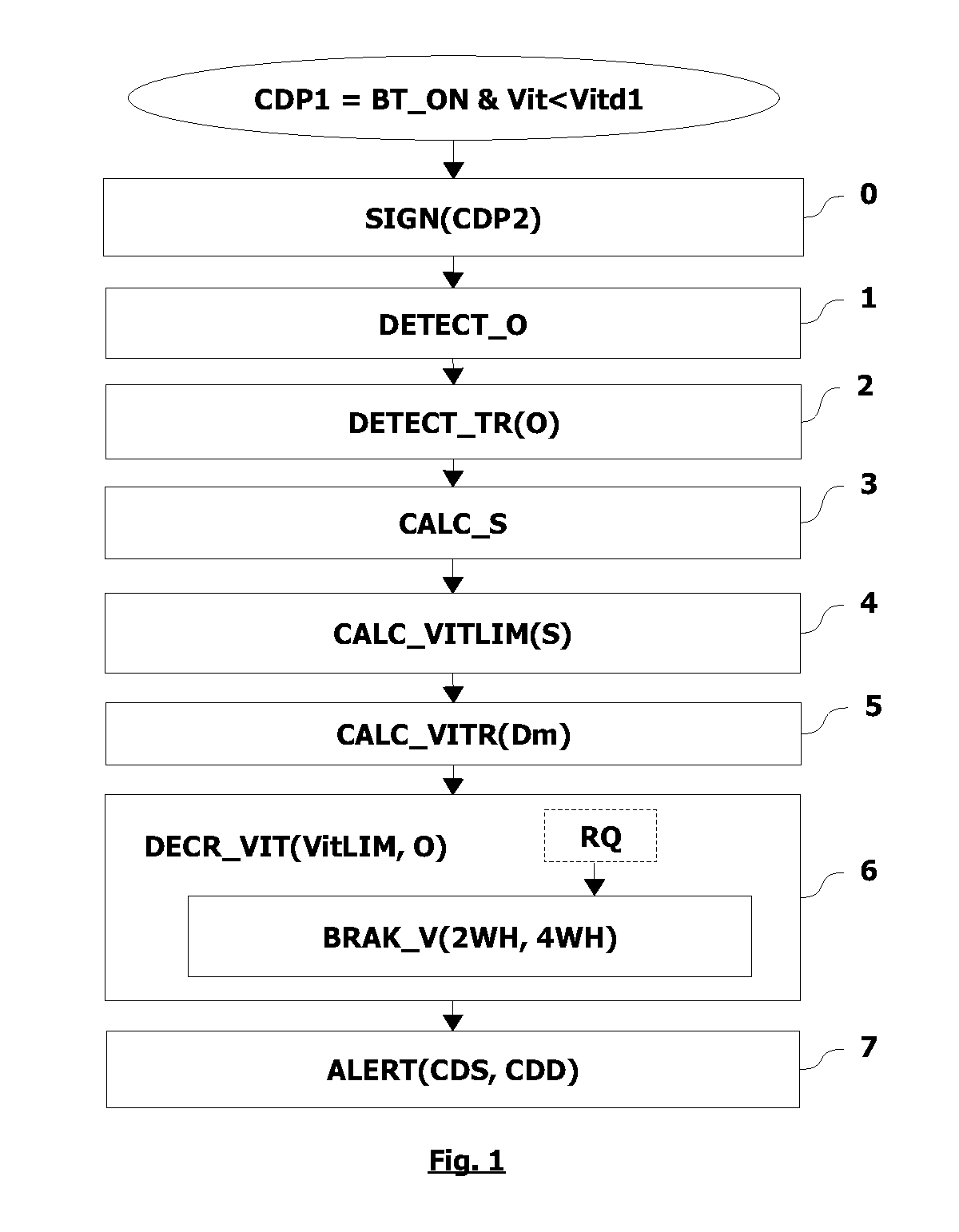
[0175]In a first embodiment, the alert function ALERT generates a first level of alert when safe conditions CDS are attained.
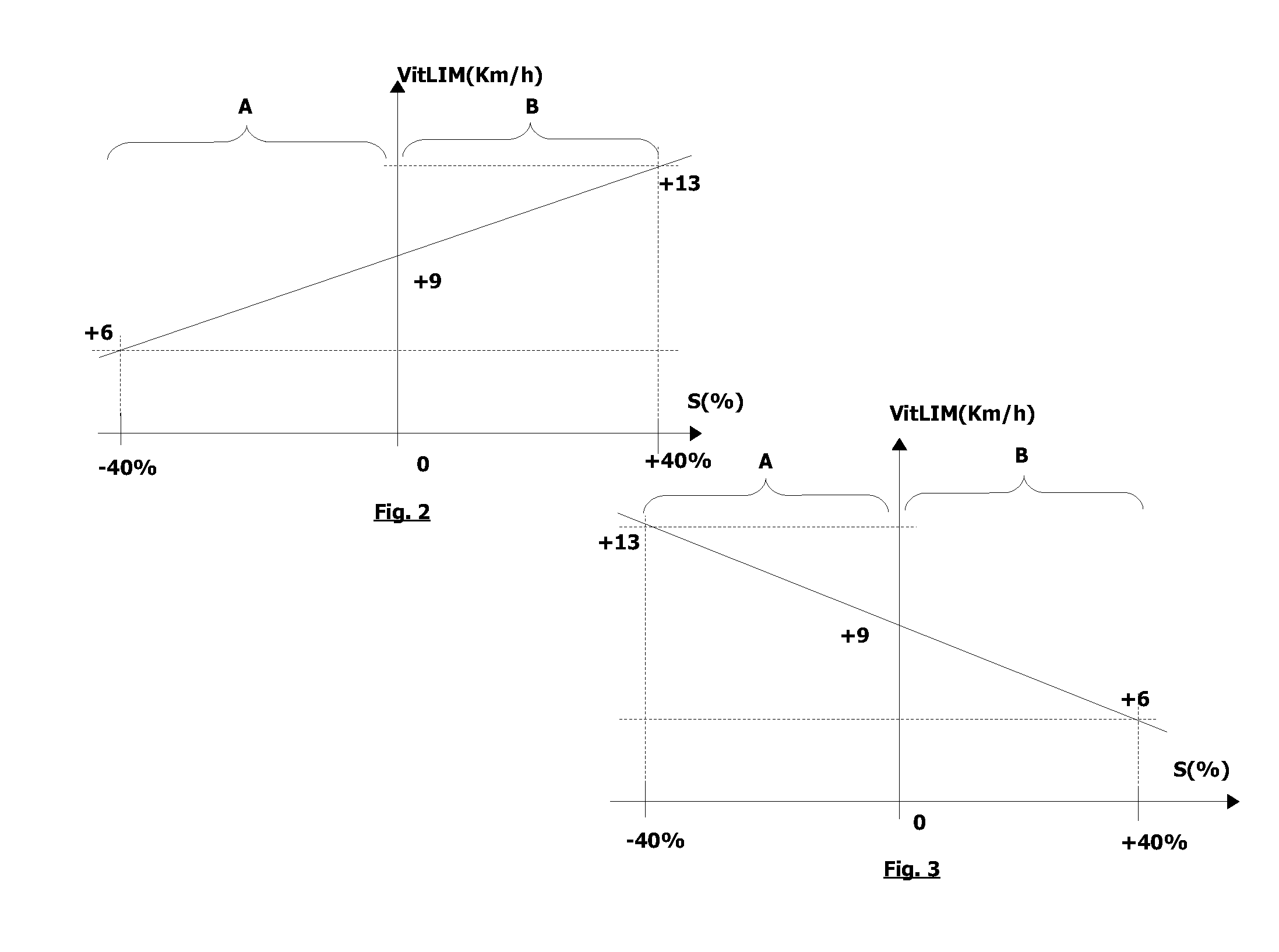
[0176]In one non-limitative variant, the safe conditions CDS are:[0177]a vehicle speed Vit which lies within a first interval of speeds allowing the motor vehicle V to be stopped without striking an obstacle O which has been detected. In one non-limitative example, the interval lies between 3 and 7 km / h; and[0178]the observation of internal control parameters PIC forecasting a potential danger of colliding with the obstacle O; thus, the alert function ALERT warns the driver so that he can increase the braking request by foot via the brake pedal in addition to the automatic reduction of the vehicle speed Vit.
[0179]In one non-limitative example, the internal control parameters PIC are:[0180]a predicted distance Dp from the obstacle O evaluated depending on the acceleration / deceleration of the motor vehicle V. In one non-limitative example, Dp=Vit2 / (2×deceleratio...
second embodiment
[0186]In a second embodiment, the alert function ALERT generates a second level of alert when dangerous conditions CDD are reached.
[0187]In one non-limitative variant, the dangerous conditions CDD are:[0188]a vehicle speed Vit which lies in a second interval of speeds which do not allow the motor vehicle V to stop without colliding with an obstacle O detected. In one non-limitative example, the interval lies between 7 and 20 km / h; and[0189]the observation of the internal control parameters, described above, forecasting a danger of colliding with the obstacle O.
[0190]In this case, the driving assistance causes the speed of the motor vehicle V to diminish, but the obstacle O will be struck before the motor vehicle V has stopped.
[0191]Obviously, these two embodiments are used in combination.
[0192]Thus, the method described enables the damage caused to an obstacle to be reduced if there is a collision, by reducing the speed of the motor vehicle before the collision takes place, and when...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com