Configurable reset circuit for a phase-locked loop
a phase-locked loop and reset circuit technology, applied in the field of electrical and electronic arts, can solve the problems of not allowing the pll to maintain synchronization with the incoming signal, the performance the circuit of the pll is not good, so as to achieve the effect of eliminating the occurren
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
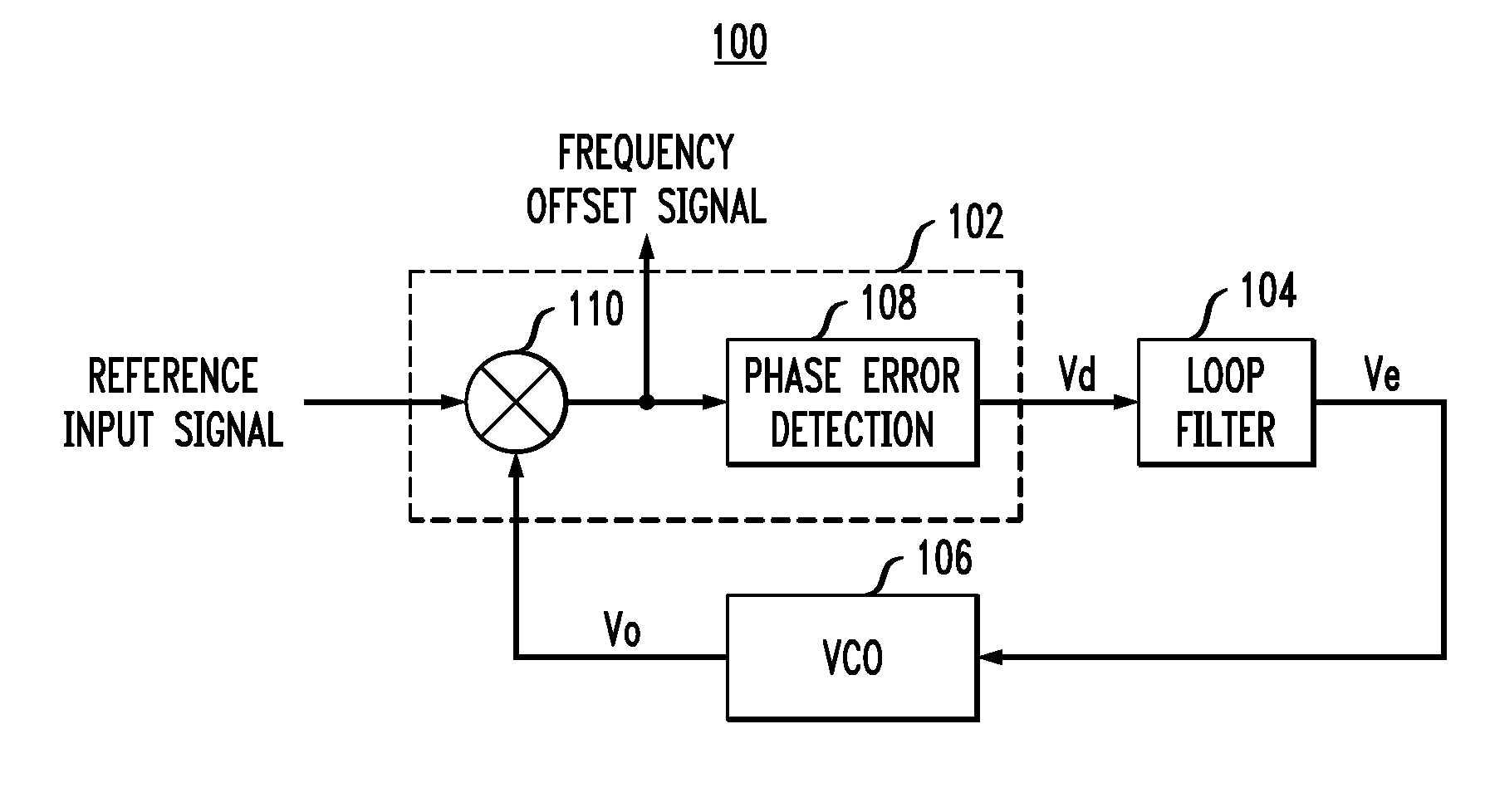
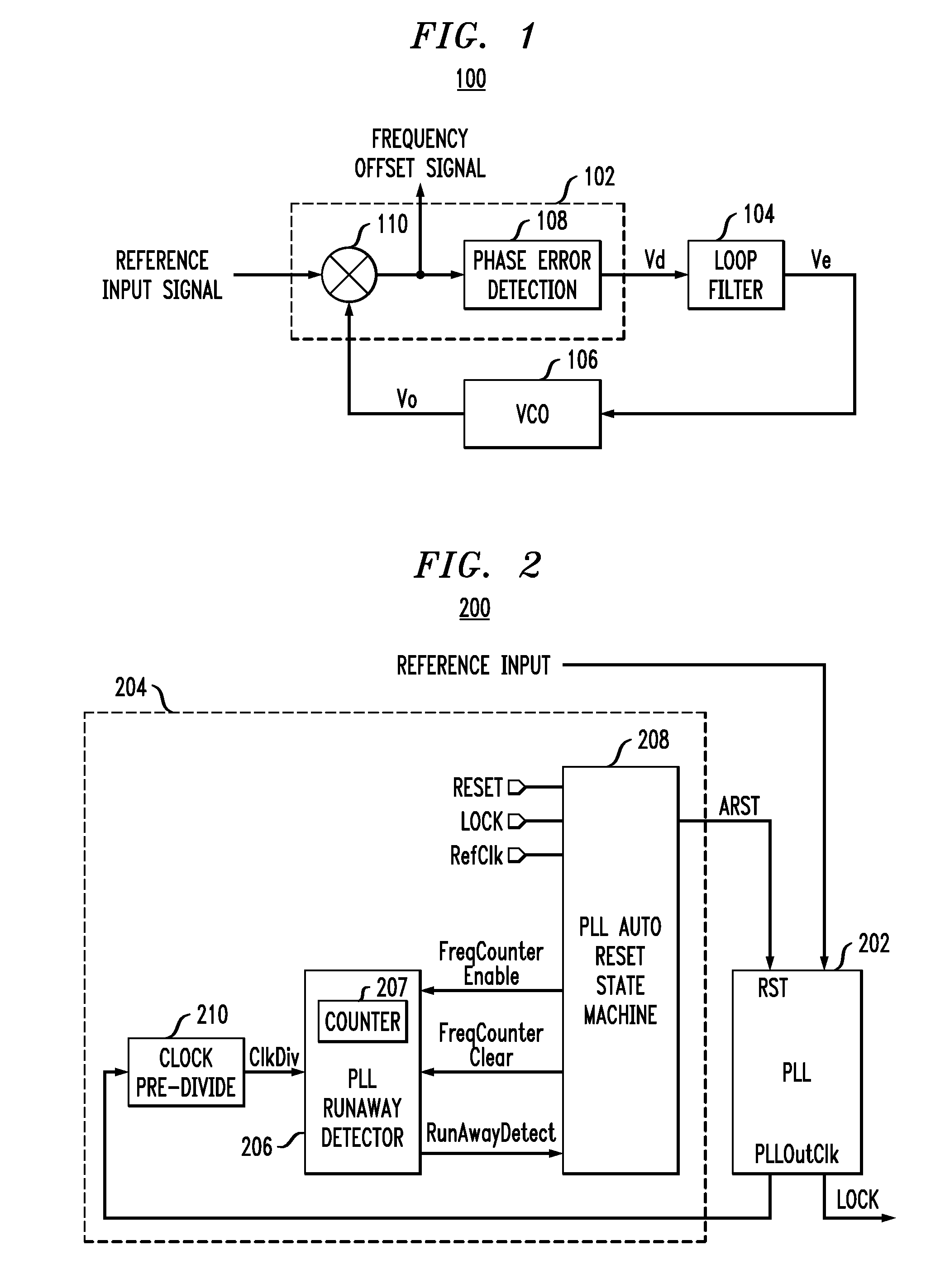
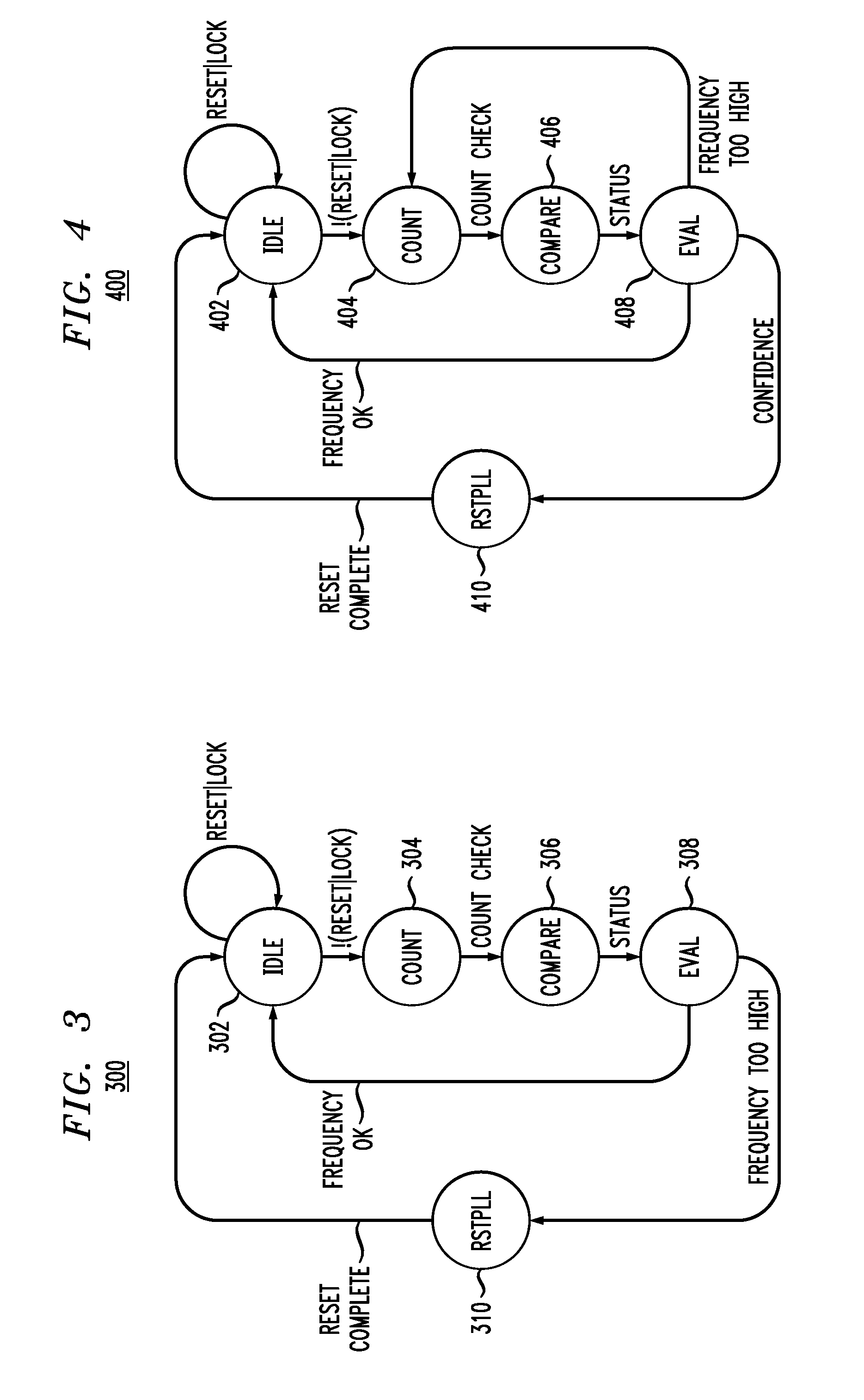
[0016]The present invention will be described herein in the context of an illustrative PLL circuit. It is to be appreciated, however, that the techniques of the present invention are not limited to the specific circuit shown and described herein. Rather, embodiments of the invention are directed broadly to improved techniques for detecting and eliminating runaway in a PLL circuit. For this reason, numerous modifications can be made to these embodiments and the results will still be within the scope of the invention. No limitations with respect to the specific embodiments described herein are intended or should be inferred.
[0017]FIG. 1 is a block diagram depicting an exemplary PLL 100 in which techniques of the present invention may be implemented. The basic functional blocks of PLL 100 include a phase detector 102, or an alternative phase-frequency comparator, a loop filter 104 (e.g., low-pass filter, band-pass filter, etc.), and a voltage controlled oscillator (VCO) 106, or alterna...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com