Cellular therapeutic agent for incontinence or urine comprising stem cells originated from decidua or adipose
a technology of adipose stem cells and a cell therapy agent, which is applied in the direction of skeletal/connective tissue cells, drug compositions, biocide, etc., can solve the problems of difficult culture, weakening of pelvic floor muscles, and difficult to maintain isolated stem cells in vitro, so as to prevent or treat urinary incontinence
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Isolation and Culture of Stem Cells According to the Present Invention
(1) Isolation and Culture of Placental Decidua-Derived Stem Cells
[0090]The decidua was isolated from the placenta in the following manner according to the method described in Korean Patent Publication No. 10-2007-0101756A filed in the name of the applicant. Specifically, the placentas were collected from normal births and premature births in Guro Hospital, Korea University Medical Center, according to the Institutional Review Board Guidelines of Korea University Medical Center and used for research purposes. The placenta tissues were transferred to the laboratory in a state in which it was contained in physiological saline containing an antibiotic. The placenta tissues transferred to the laboratory were washed with PBS to remove blood cells and various other tissues, or the tissues were treated with hemolysis buffer to remove blood cells, or each of amnion, chorion, decidua and placental bed tissues constituting t...
example 2
Examination of Proliferation Rate of Placental Decidua-Derived Stem Cells
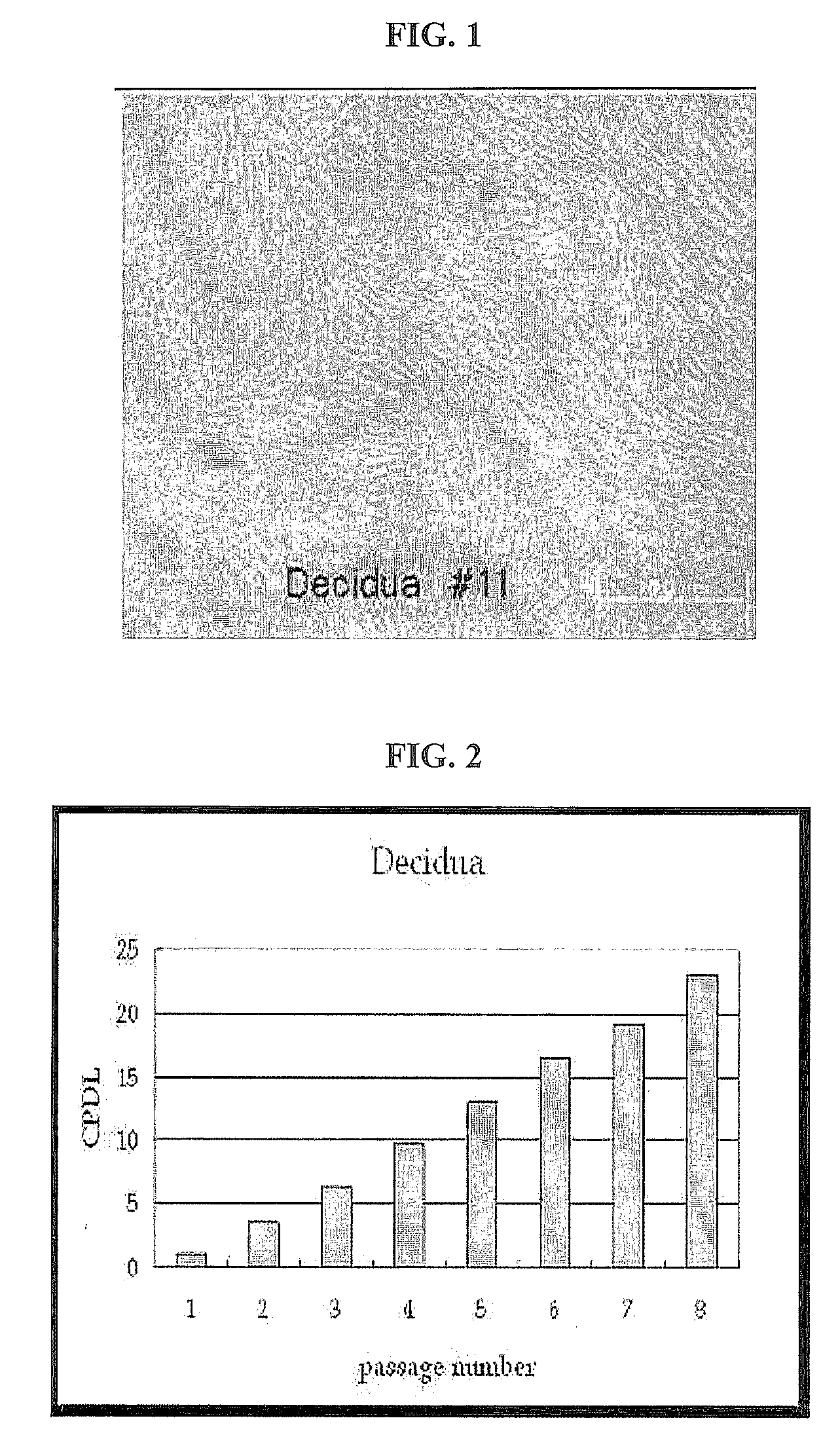
[0093]The proliferation rate of the stem cells obtained according to the above-described method of proliferating the human placental decidua tissue-derived multipotent stem cells, was examined. Placental decidua-derived stem cells resulting from the placental decidua tissue samples of different human individuals were obtained through the isolation method described in Example 1, and then seeded into a 75-flask at a density of 2×105 cells.
[0094]CPDL is an index indicative of the proliferation rate of cells and expressed as the following equation:
CPDL=ln(Nf / Ni) / ln2
wherein, Ni: the initial number of seeded cells; and Nf: the final number of cells.
[0095]The CPDL of the decidua-derived stem cells and was observed according to passage number and, as a result, the cells showed a CPDL value of about 30 at passage 12. This CPDL value was similar to that of human adipose tissue-derived stem cells (Lin et al., stem cells a...
example 3
Immunological Characteristics of Placental Decidua-Derived Multipotent Stem Cells
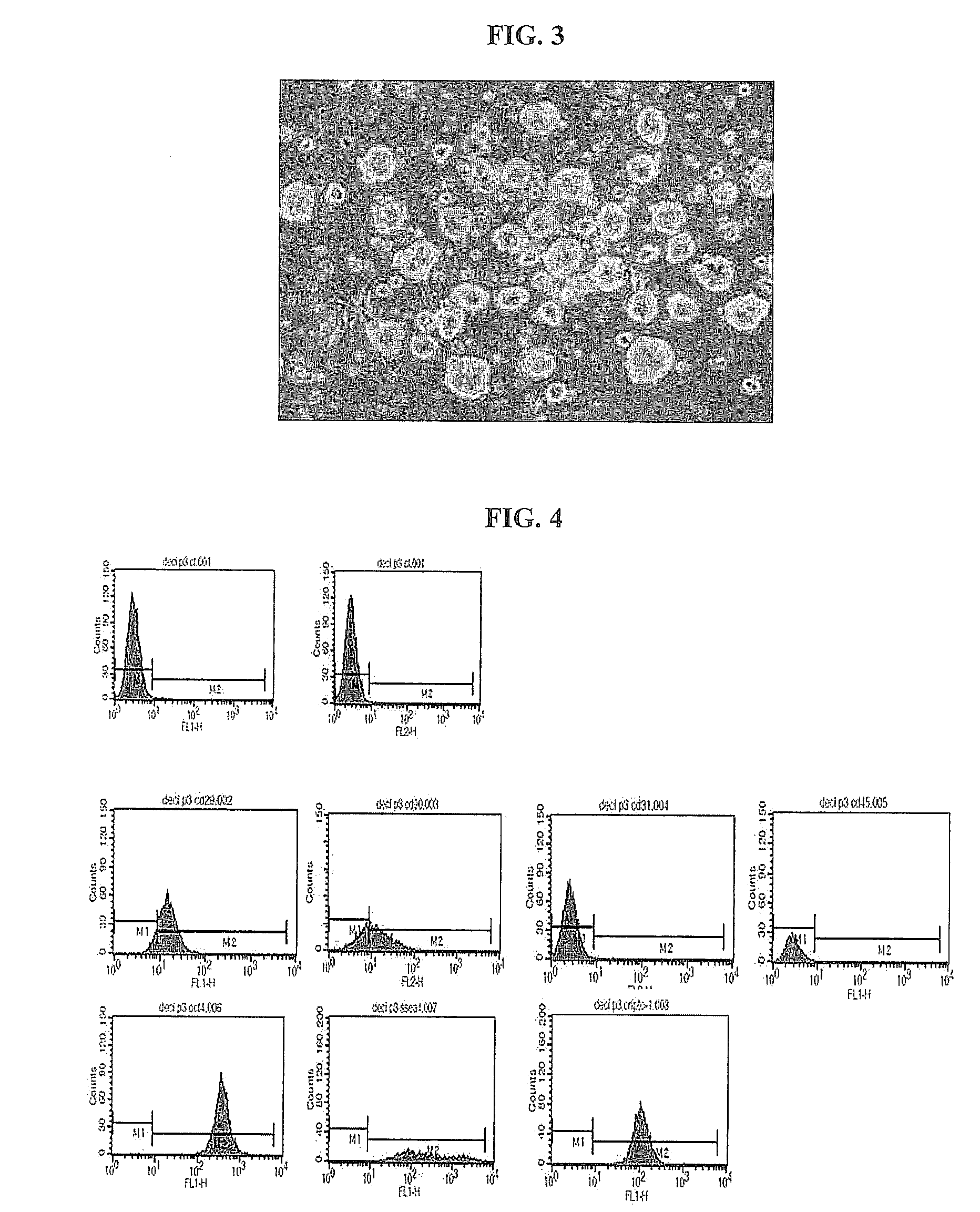
[0096]The placental decidua-derived multipotent stem cells obtained in Example 1 were washed with PBS and treated with trypsin. Then, the cells were collected and centrifuged at 1000 rpm for 5 minutes. After the supernatant was discarded, the cells were suspended in PBS and dispensed into each well at a cell density of 1×105 cells. An antibody (R-phycoerythrin-conjugated mouse anti-human monoclonal antibody) was placed into each well, and the cells were incubated at 4° C. for 40 minutes. After the incubation, the cell broth was centrifuged at 1000 rpm for 5 minutes. After the supernatant was removed, the cells were washed with PBS and centrifuged at 1000 rpm for 5 minutes. Then, after the supernatant was removed, the cells were washed with PBS and centrifuged at 1500 rpm for 5 minutes. After the supernatant was removed, the cells were fixed with 1% paraformaldehyde and analyzed using a flow cytometer. A...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com