Data classification based on point-of-view dependency
a data classification and dependency technology, applied in the field of automatic data classification, can solve the problems of difficult decisions, many machine learning algorithms display non-linear efficiency with respect to the number, and complex data classification systems have been developed, so as to improve accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
(a) Definitions and General Parameters
[0026]The following definitions are set forth to illustrate and define the meaning and scope of the various terms used herein.
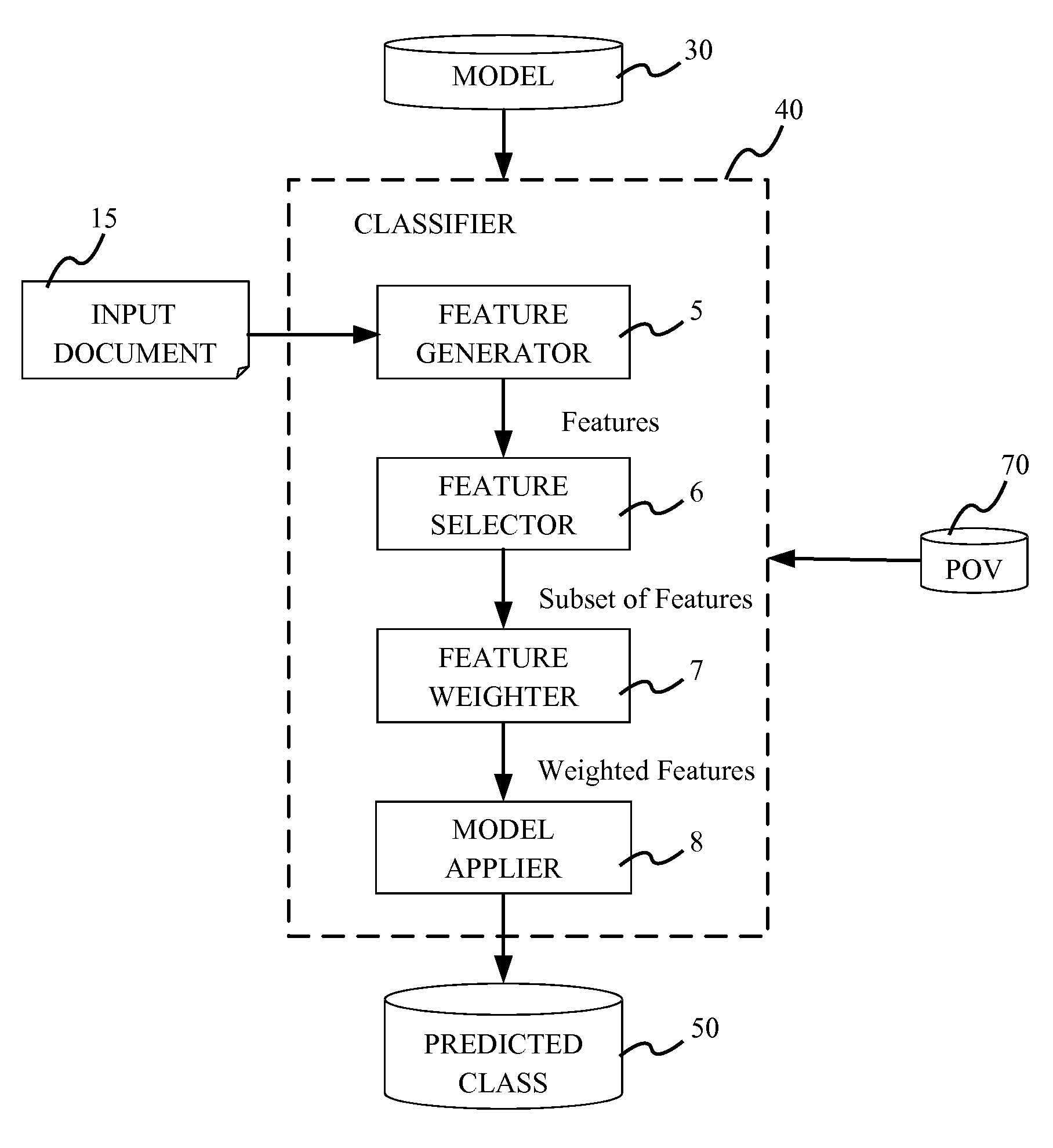
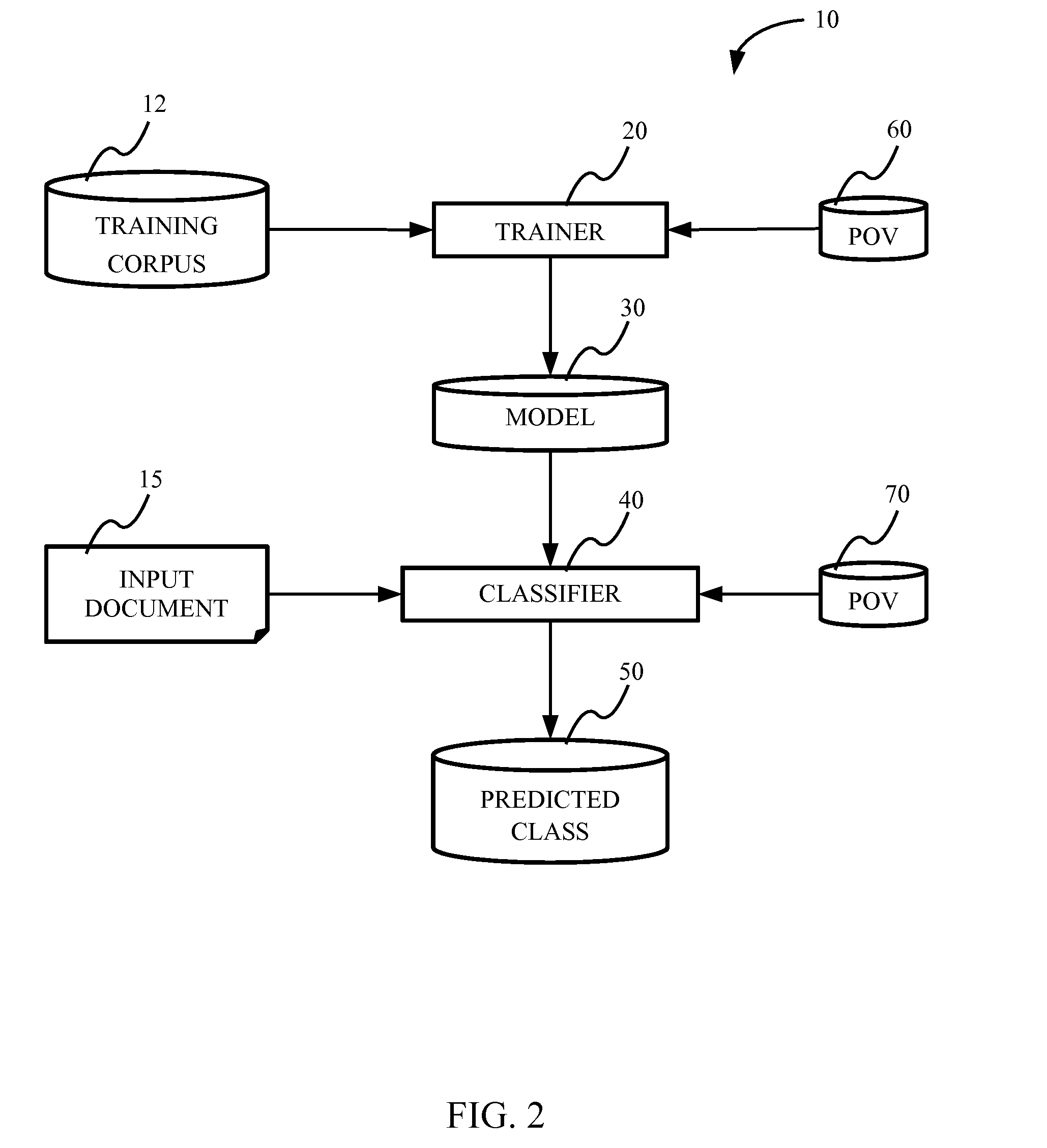
[0027]The terms “input item” and “document” are interchangeably used herein and refer to any item that can be used in conjunction with the present classification method. For example, an input item may include, but is not limited to, a word processing document, a file of a particular format (e.g., ASCII file, XML file, UTF-8 file, etc.), a collection of documents with some structural organization, an image, text, a combination of images and text, media, spreadsheet data, a collection of bytes, or other organizations of data or data streams.
[0028]The term “relevant feature” refers to a uniquely identifiable attribute that could affect the detection of patterns within a corpus. Relevant features might be domain specific, for example, in the case of English text classification, a relevant feature might be the presence of a un...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com