Polyvalent vaccine
a polyvalent, vaccine technology, applied in the field of immunogenic compositions, can solve the problems of limited response potential to any single vaccine antigen, limited coverage, and variability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example
Experimental Details
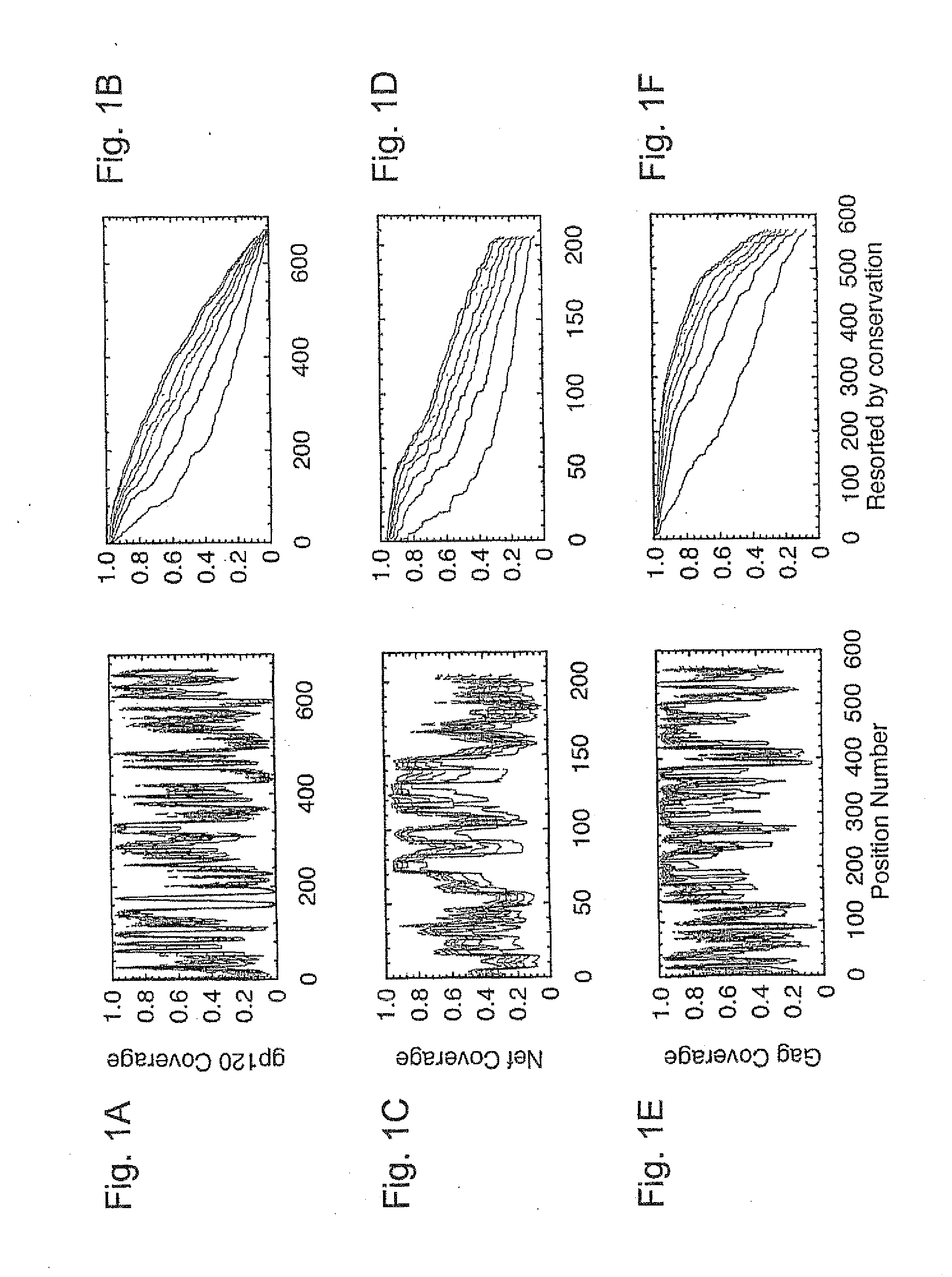
[0045]HIV-1 sequence data. The reference alignments from the 2005 HIV sequence database (http: / / hiv.lanl.gov), which contain one sequence per person, were used, supplemented by additional recently available C subtype Gag and Nef sequences from Durban, South Africa (GenBank accession numbers AY856956-AY857186) (Kiepiela et al, Nature 432:769-75 (2004)). This set contained 551 Gag and 1,131 NefM group sequences from throughout the globe; recombinant sequences were included as well as pure subtype sequences for exploring M group diversity. The subsets of these alignments that contained 18 A, 102 B, 228 C, and 6 G subtype (Gag), and 62 A, 454 B, 284 C, and 13 G subtype sequences (Nef) sequences were used for within- and between-single-clade optimizations and comparisons.
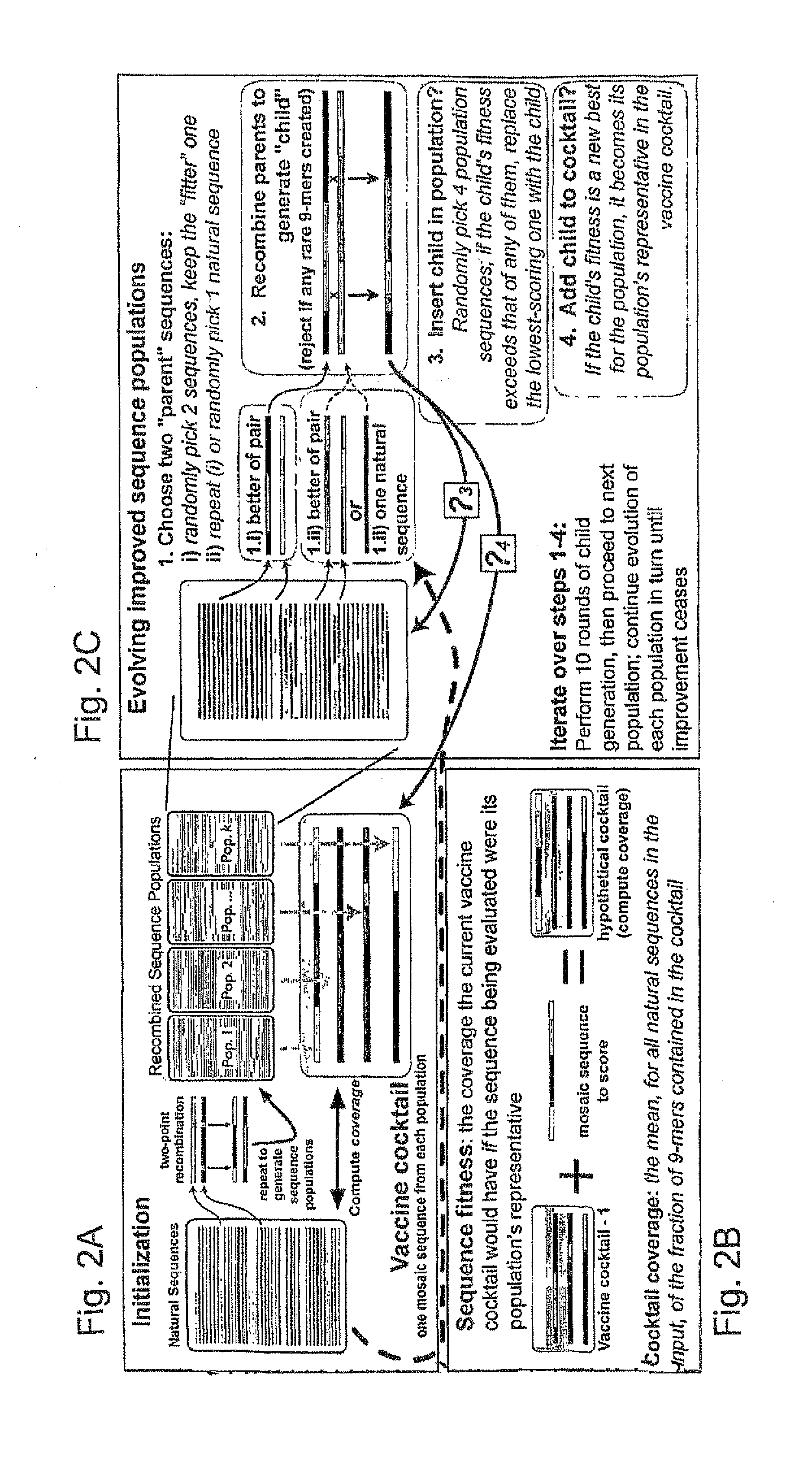
[0046]The genetic algorithm. GAs are computational analogues of biological processes (evolution, populations, selection, recombination) used to find solutions to problems that are difficult to solve a...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| nucleic acid | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| immunogenic composition | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com