Cooling apparatus and frost detecting method thereof
a technology of cooling apparatus and frost detection, which is applied in the direction of domestic cooling apparatus, refrigeration machines, defrosting, etc., can solve the problems of excessive power consumption, inefficient removal method of frost formed on the evaporator, and inability to detect so as to accurately determine the amount of frost formed, accurately determine the noise contained in the signal received, and achieve the effect of easy and accurate determination
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0053]Hereinafter, exemplary embodiments will be described in order to explain the present invention by referring to the figures.
[0054]Exemplary embodiments are adapted to enhance the defrosting efficiency of a cooling apparatus and thus to reduce power consumption by accurately detecting whether or not frost has been formed on an evaporator of the cooling apparatus and the amount of frost formed, and controlling driving of a heater based on the results of the detection, thereby controlling a defrosting operation.
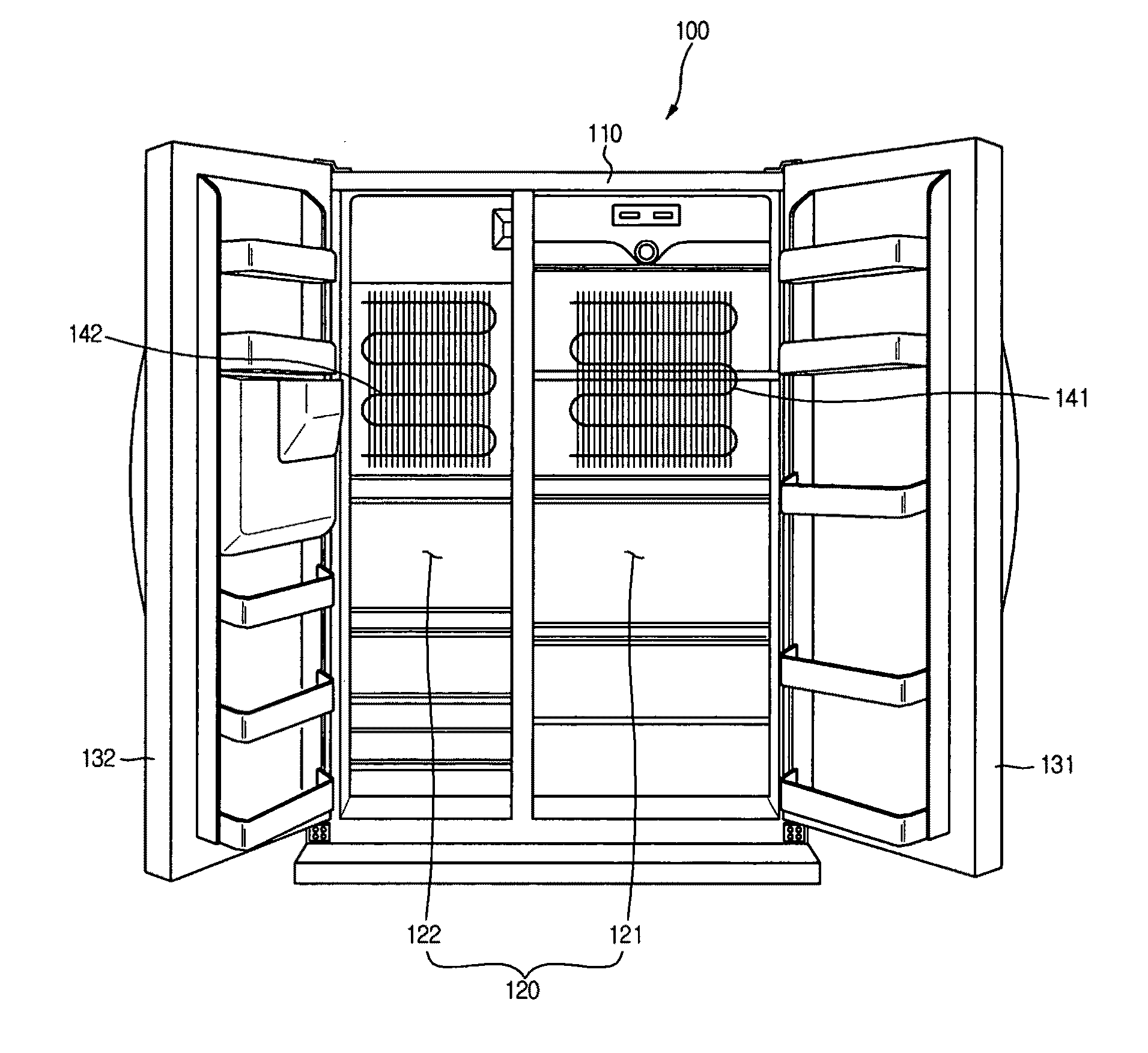
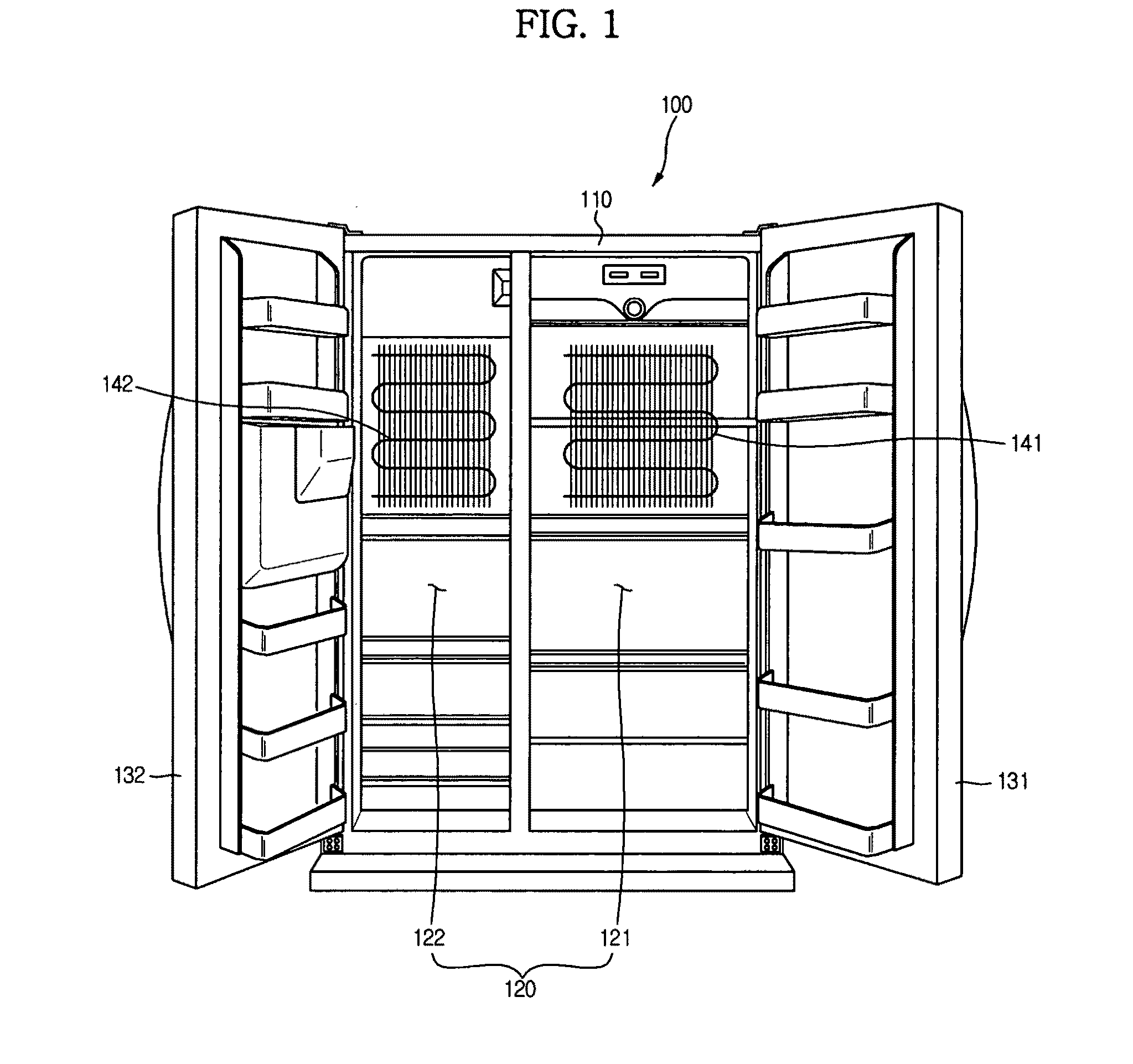
[0055]The exemplary embodiments are described in conjunction with an example in which the cooling apparatus is applied to a refrigerator.
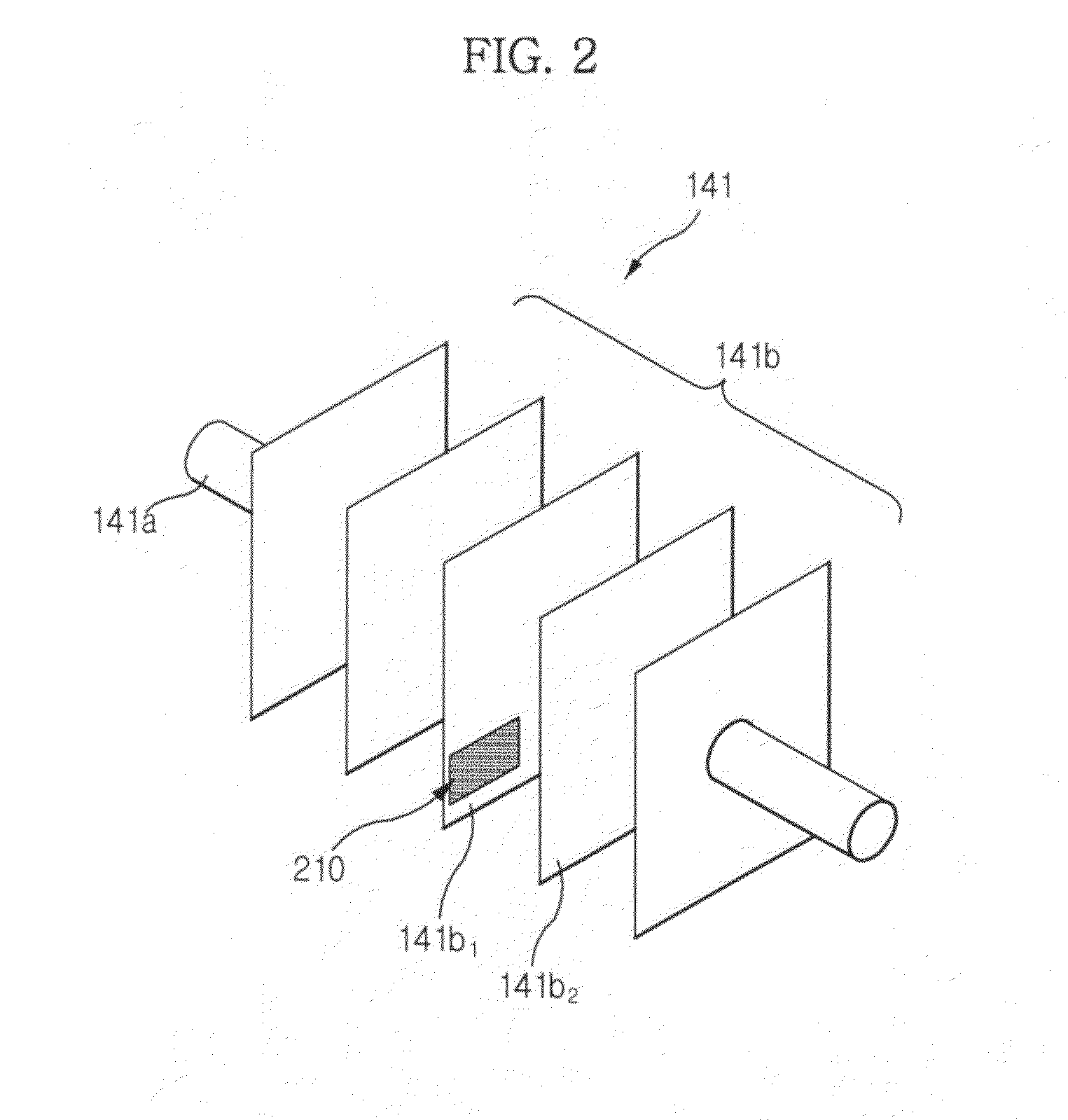
[0056]FIG. 1 is a view illustrating a refrigerator according to an exemplary embodiment. FIG. 2 is a view illustrating a detailed configuration of an evaporator provided at the refrigerator according to the illustrated embodiment. FIG. 3 is a block diagram illustrating a control configuration of the refrigerator according to an exemplary e...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com