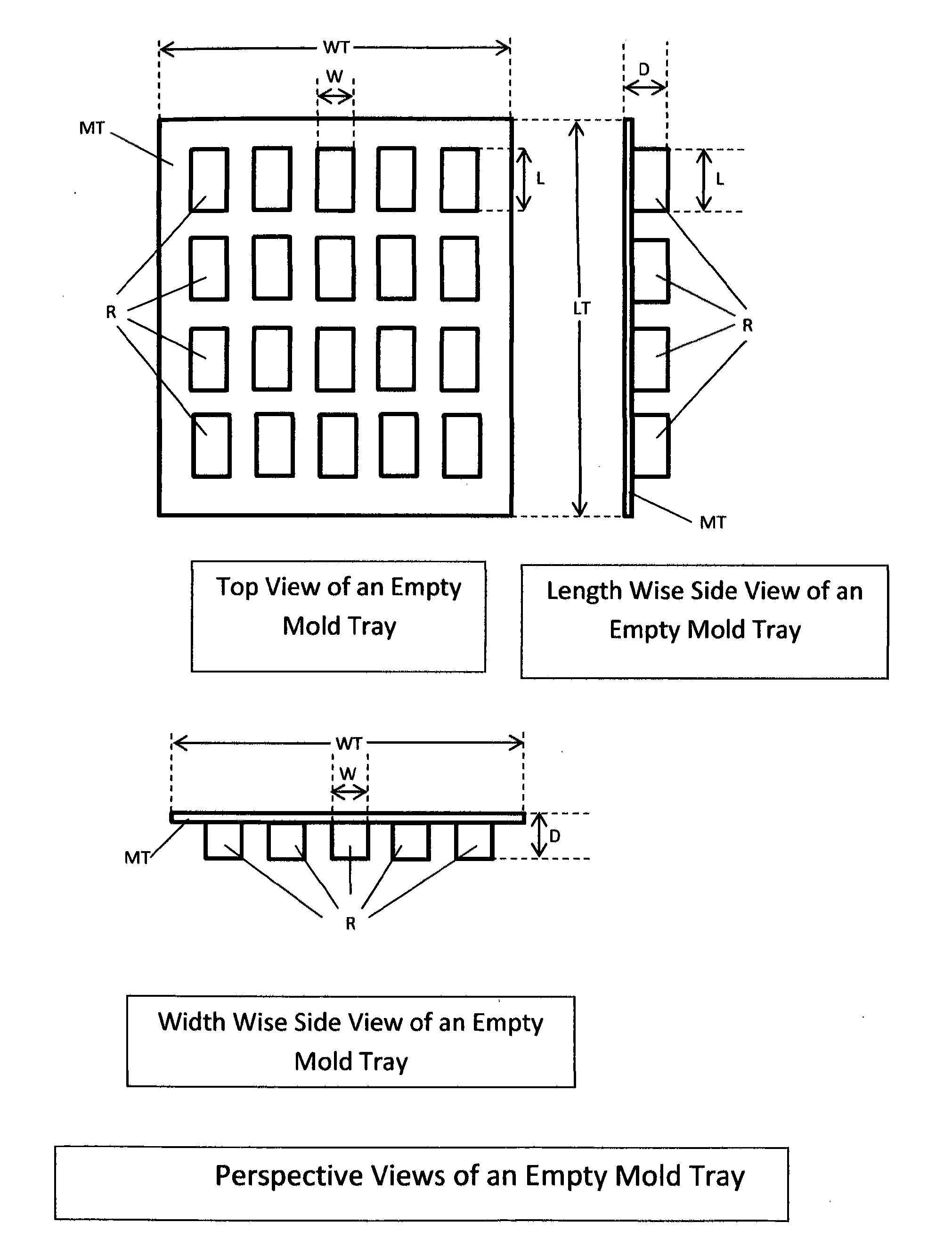
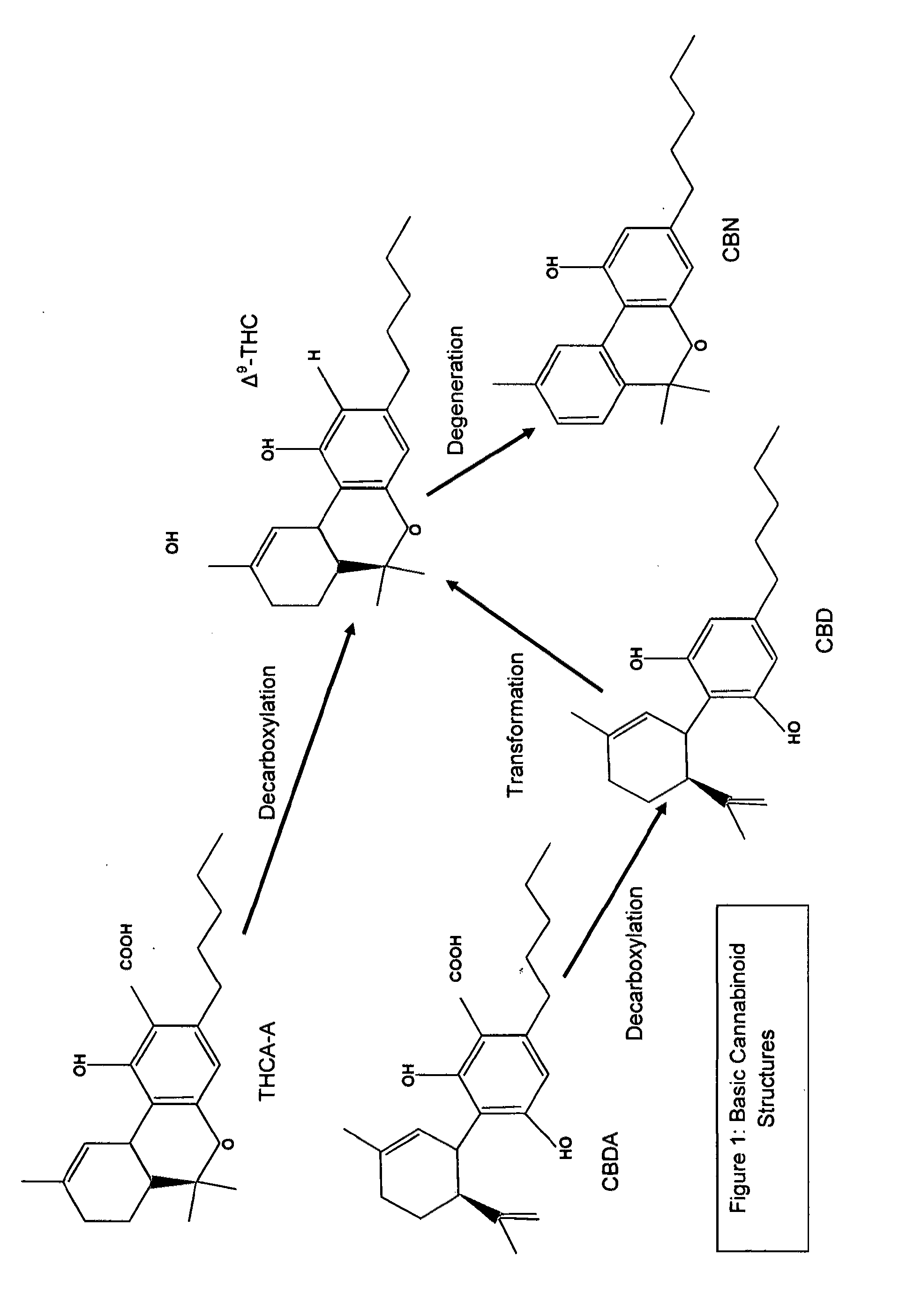
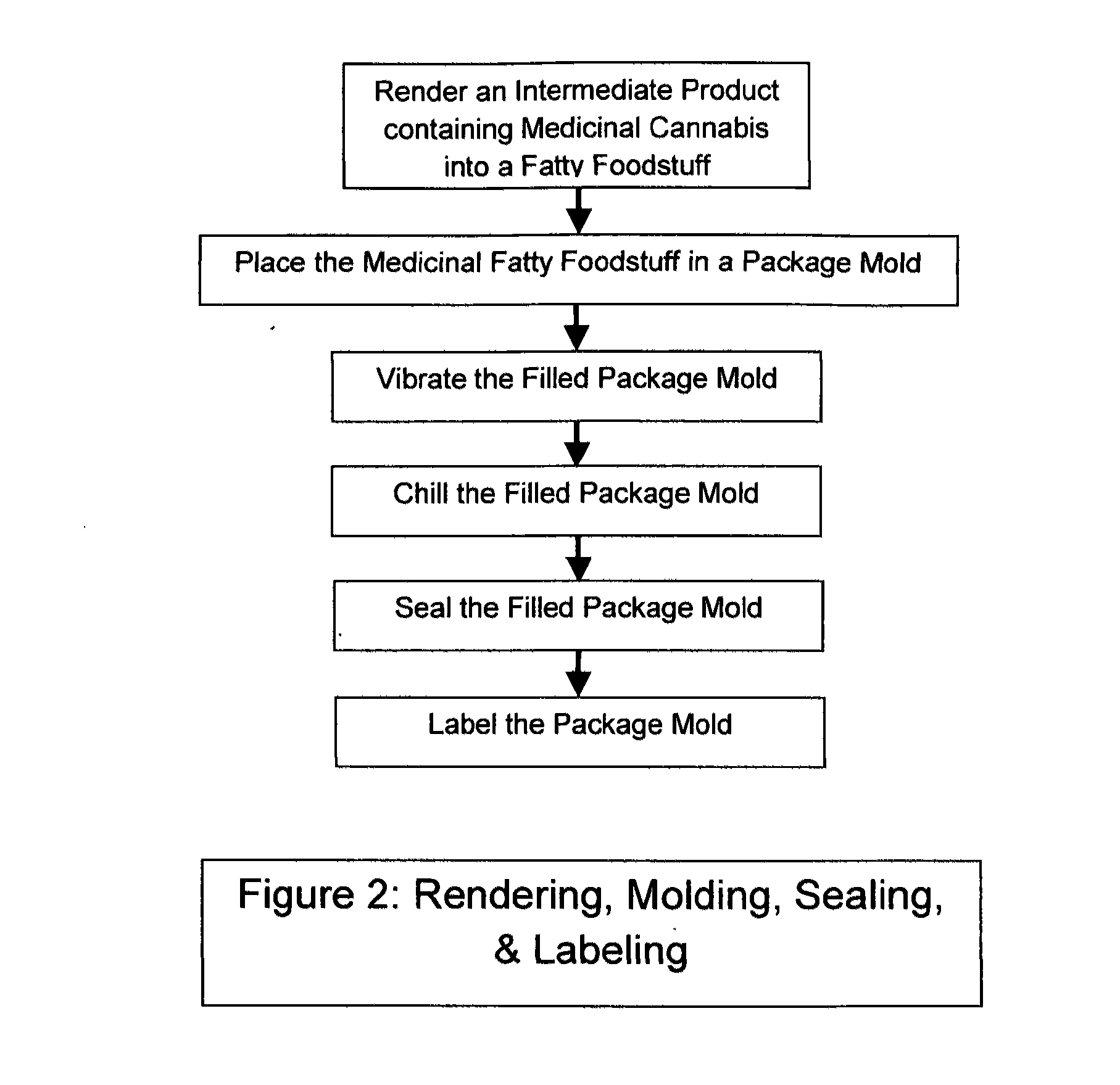
Medicinal cannabis fatty foodstuff
a technology of cannabis and food, applied in the field of fatty foodstuffs of cannabis, can solve the problems of uncontrollable crude processes that use no toxic chemicals, decarboxylated substances within cannabis will be lost to evaporation, and the “uncontrolled” processes that rely on temperature are truly uncontrollabl
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 2
of Mixing Extracts:
[0089]Extract 1: Volume 2 fluid oz comprised of 40% flavonoids & waxy materials: 60% total cannabinoids (95% of total cannabinoids are Δ9-THC, and 5% of total cannabinoids are CBN)
[0090]Extract 2: Volume 4 fluid oz, comprised of 40% flavonoids & waxy materials: 60% total cannabinoids (58% of total cannabinoids are Δ9-THC, and 42% of total cannabinoids are CBN)
[0091]Mixed cannabinoid content: Volume 6 fluid oz; (95*0.33333+58*0.66666) Δ9-THC; (5*0.33333+42*0.66666) CBN=(31.67+38.67) Δ9-THC; (1.66+28) CBN=70.34% Δ9-THC; 29.66% CBN.
[0092]Please note that the extracts do not consist of 100% cannabinoids, in the example above only 60% of the extracts consist of cannabinoids and 40% of the extracts above consist of flavonoids and waxy materials. Please also note that the calculations above have been normalized to a total cannabinoid content of 100%.
[0093]Therefore the total content of the mixed extract in Example 2 are 40% flavonoids and waxy materials; and 60% total ca...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com