Display device
a display module and liquid crystal technology, applied in static indicating devices, instruments, optical elements, etc., can solve the problems of unfavorable excess power consumption, low transmittance of display modules, and inability to properly drive liquid crystal molecules in the blue phase lcd, etc., to achieve low transmittance and high driving voltage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
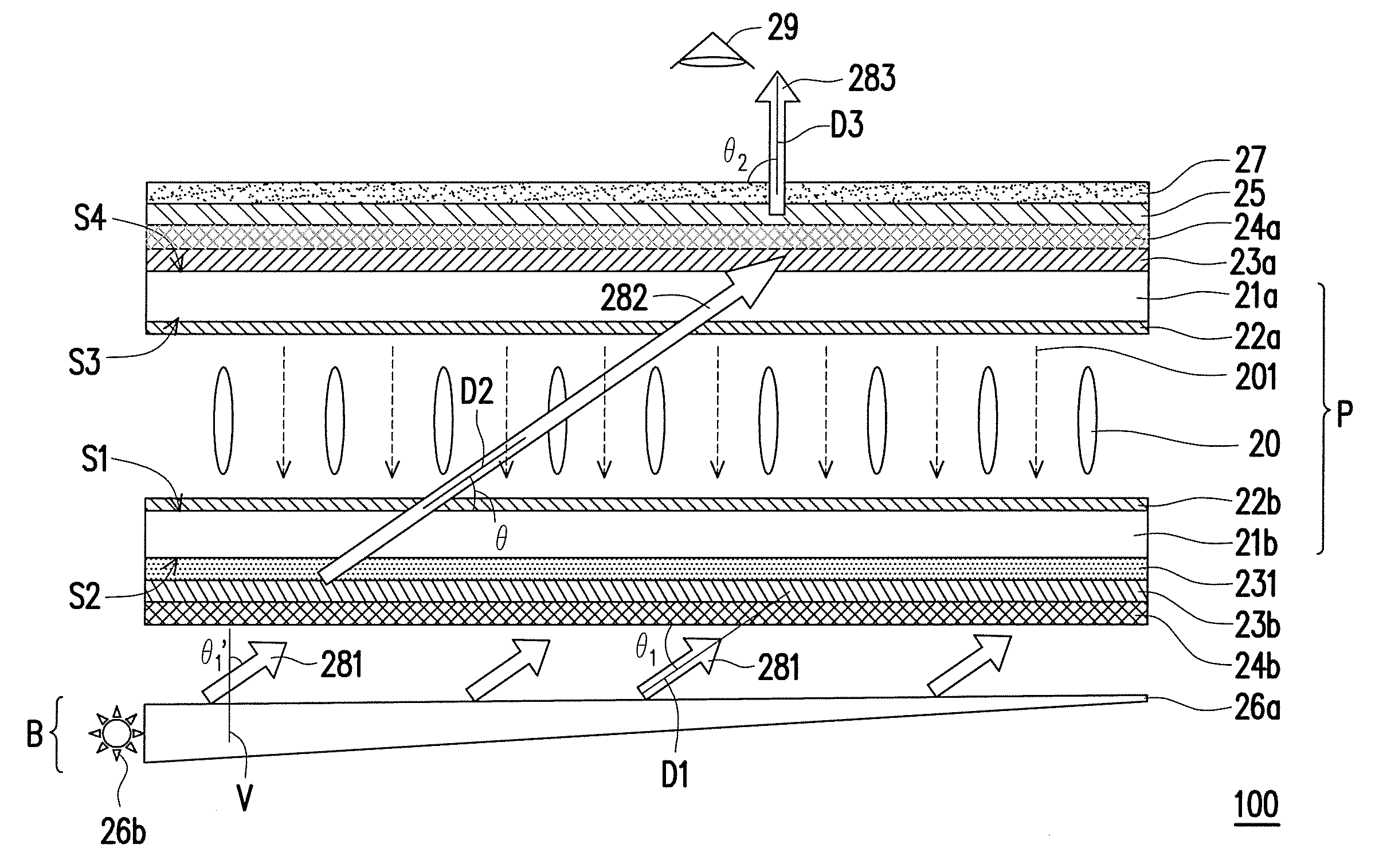
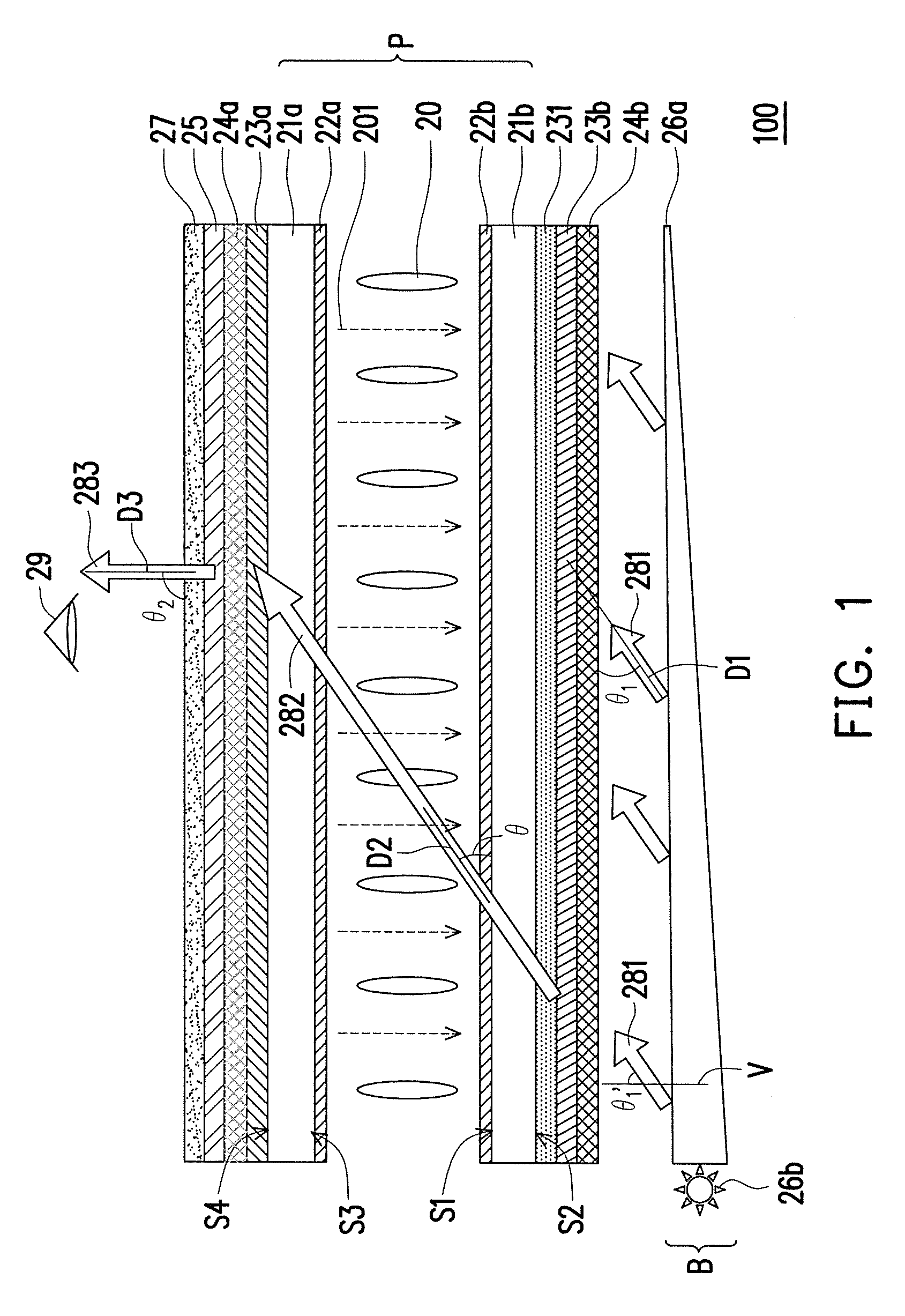
[0123]FIG. 21 is a schematic cross-sectional view of a display device according to a first embodiment of the invention. With reference to FIG. 21, a difference between a display device 100a and the embodiment of FIG. 1 lies in that, the display device 100a includes a first compensation film 28b and a second compensation film 28a, and does not include the compensation film 231. To be specific, the first compensation film 28b is disposed on the outer surface S2 of the first substrate 21b, and the second compensation film 28a is disposed between the second substrate 21a and the turning optical film 25.
[0124]In the present embodiment, the bottom polarizer 23b is disposed on the outer surface S2 of the first substrate 21b, and the top polarizer 23a is disposed on the outer surface S4 of the second substrate 21a. According to the present embodiment, the bottom polarizer 23b is disposed between the first compensation film 28b and the first optical film 24b. The top polarizer 23a is dispose...
second embodiment
[0138]FIG. 30 is a schematic cross-sectional view of a display device according to a second embodiment of the invention. With reference to FIG. 30, a display device 100b of the present embodiment is similar to the display device 100a of the first embodiment. A difference therebetween lies in that, the display device 100b further includes a third compensation film 31b and a fourth compensation film 31a. The third compensation film 31b is disposed between the first compensation film 28b and the bottom polarizer 23b, and the fourth compensation film 31a is disposed between the second compensation film 28a and the top polarizer 23a.
[0139]According to the present embodiment, the third compensation film 31b and the fourth compensation film 31a are respectively a biaxial compensation film, for example. The third compensation film 31b and the fourth compensation film 31a may be designed in accordance with different orientation angle Φ, so as to compensate for an angular difference between ...
third embodiment
[0142]FIG. 33 is a schematic cross-sectional view of a display device according to a third embodiment of the invention. With reference to FIG. 33, a display device 100c of the present embodiment is similar to the display device 100b of the second embodiment. A difference therebetween lies in that, in the display device 100c, the third compensation film 31b is disposed between the first compensation film 28b and the first substrate 21b, and the fourth compensation film 31a is disposed between and the second compensation film 28a and the second substrate 21a.
[0143]According to the present embodiment, the third compensation film 31b and the fourth compensation film 31a are respectively a biaxial compensation film, for example. The third compensation film 31b and the fourth compensation film 31a may be designed in accordance with different orientation angles Φ, so as to compensate for an angular difference between the top polarizer 23a and the bottom polarizer 23b. According to the pre...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| orientation angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| orientation angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| orientation angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com