Detection of objects in an image using self similarities
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
FIGS. 1, 2 a First Embodiment
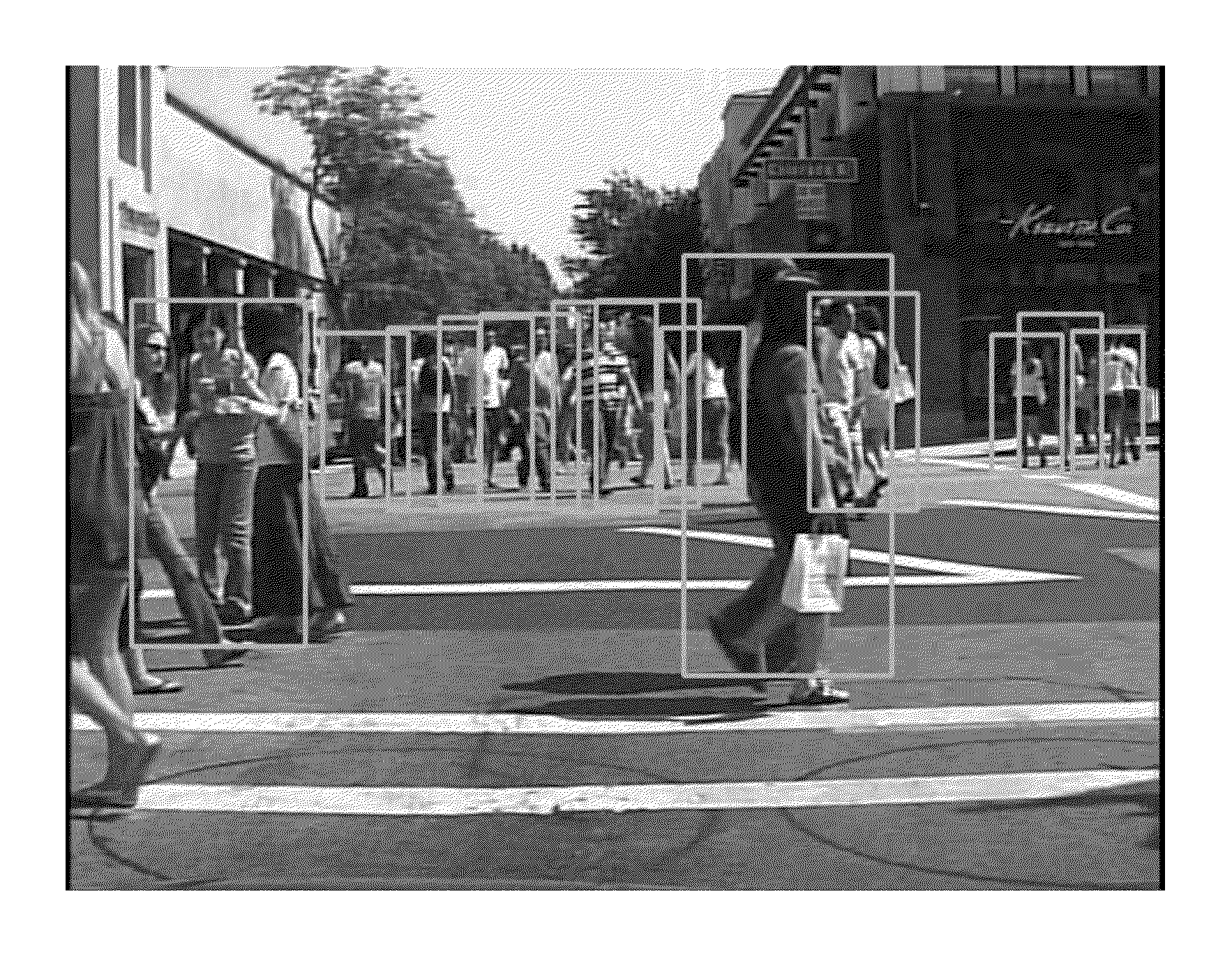
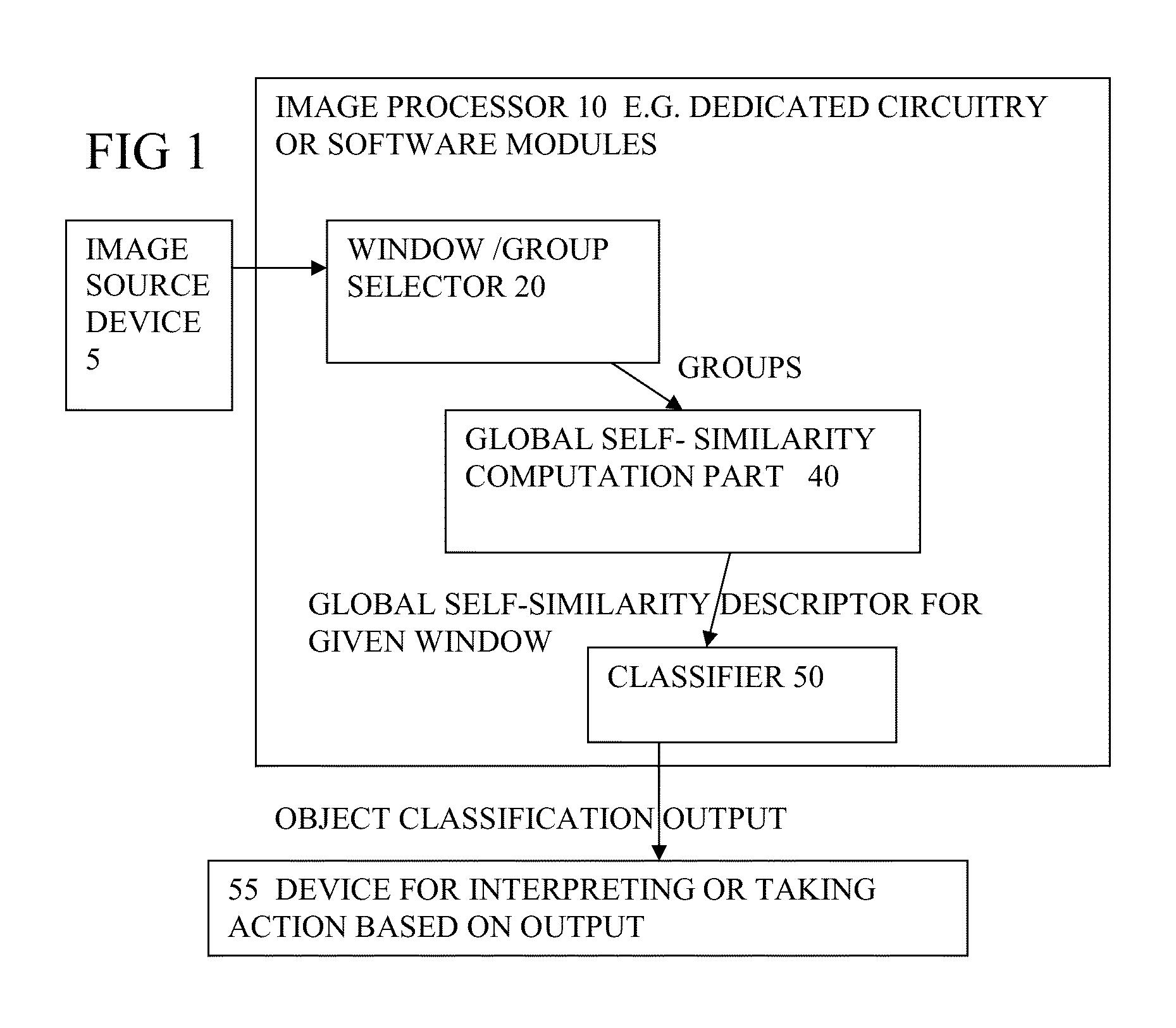
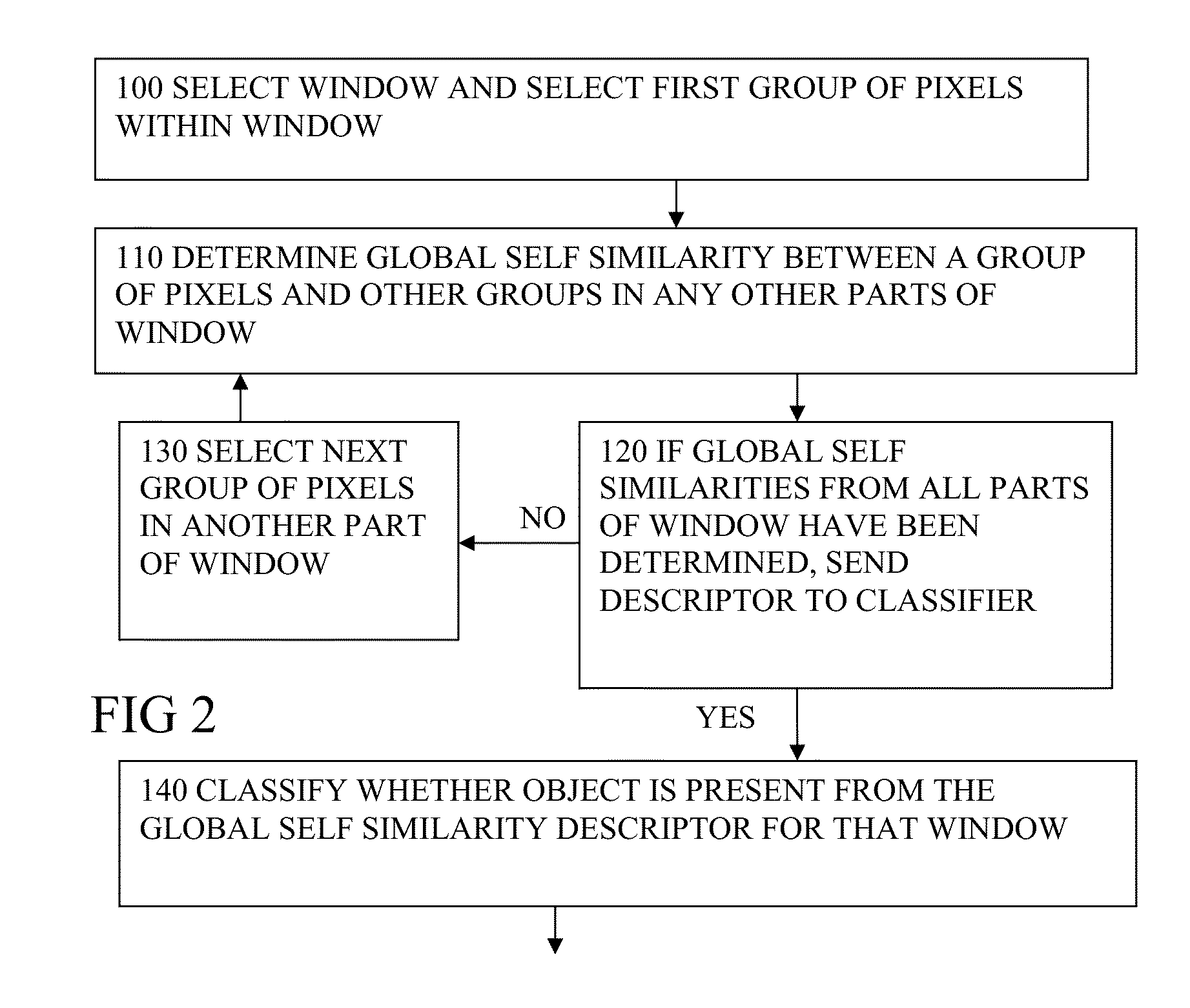
[0063]FIG. 1 shows an image processor according to an embodiment. FIG. 2 shows steps carried out by this or other embodiments. The image processor can be implemented as for example one or more integrated circuits having hardware such as circuit blocks dedicated to each of the parts shown, or can be implemented for example as software modules executed by a general purpose processor in sequence, as in a server. The parts shown include a selector 20 for receiving an input image or image stream (such as frames of a video, in real time or non real time) from an image source device 5, and selecting a detection window, and within that window, selecting groups of pixels to be processed. The groups can be e.g. 6×6 or 8×8 pixels or different sizes. They need not be square, and can be rectangular or other regular or irregular shape. Groups are processed by a global self similarity computation part 40. The self similarity computation part determines self similarity ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com