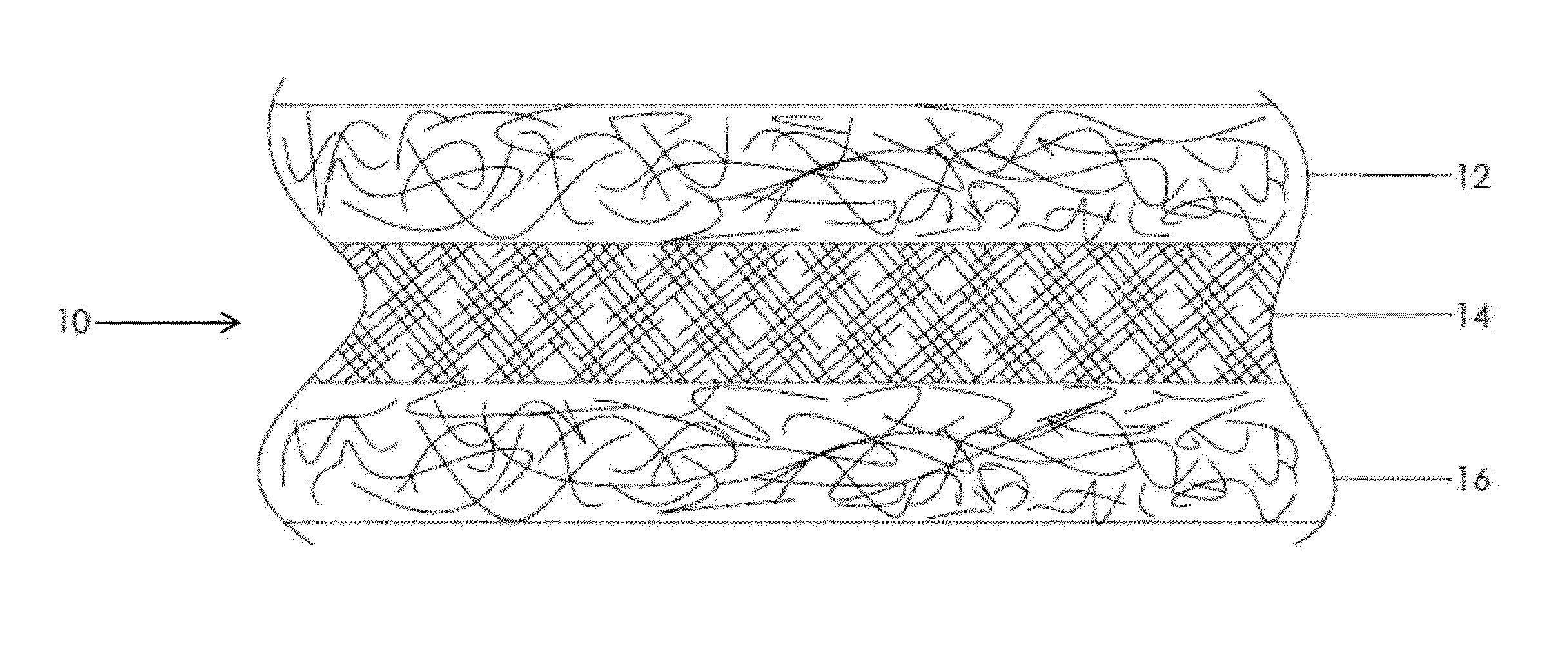
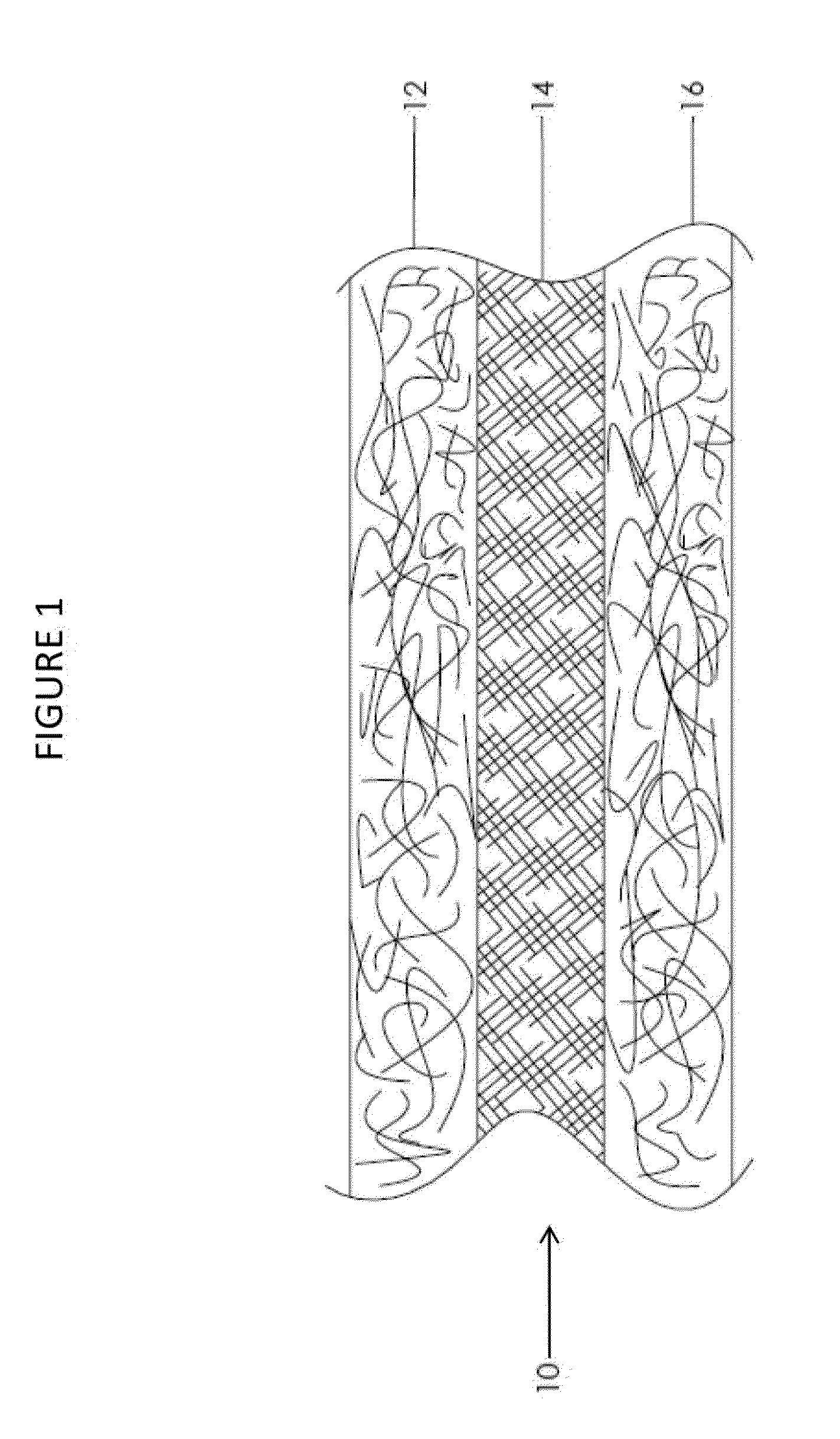
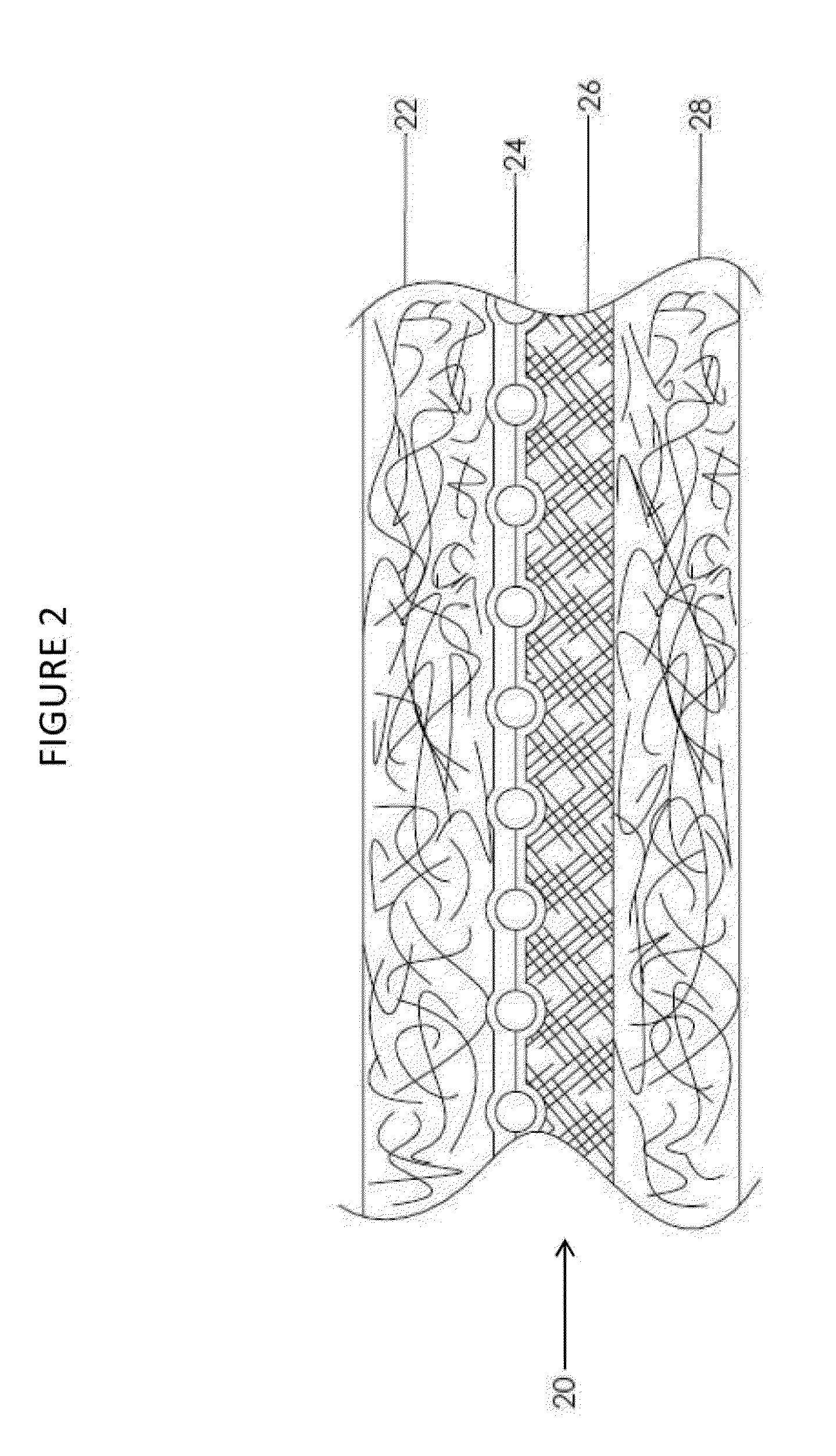
Composite prosthetic devices
a prosthetic device and composite technology, applied in the field of prosthetic devices, can solve the problems of difficult to cover the geometries of stents, mechanical properties, and difficulty in manipulating certain properties of conventional devices,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Espun PTFE / Espun PTFE / Espun PTFE
[0116]An espinning dispersion based on a mixture of 5.2% (PEO / PTFE) 300,000 amu polyethylene oxide and Daikin DX-9030, 60% PTFE dispersion in water is prepared, allowed to homogenize, and turned and filtered to achieve a smooth consistency. A 0.002″ thick stainless steel foil sheet (15.5″×17.5″) is mounted on a conductive fabric. The stainless foil is passed into the espinning chamber where PTFE fibers are to be deposited. The dispersion is espun using a total potential of 80 kV to facilitate formation of PTFE fibers, which collect in random formation on the stainless steel foil. The stainless steel foil containing the PTFE membrane is removed from the fabric and sintered at 385° C. until fully sintered (e.g., about 5 minutes).
[0117]The 0.0008″ sintered espun PTFE sheet, removed from the stainless foil, is wrapped twice around a 0.50″ exterior diameter (OD) stainless steel hypotube. The electrospinning process is repeated to give a second espun PTFE s...
example 2
Espun PTFE / Stent / Espun PTFE / Espun PTFE
[0118]Example 2 is made similarly to Example 1 with the addition of a wire stent frame as an additional layer of the composite. An espinning dispersion based on a mixture of 5.2% (PEO / PTFE) 300,000 amu polyethylene oxide and Daikin DX-9030, 60% PTFE dispersion in water is prepared, allowed to homogenize, and turned and filtered to achieve a smooth consistency. A 0.002″ thick stainless steel foil sheet (15.5″×17.5″) is mounted on a conductive fabric. The stainless foil is passed into the espinning chamber where PTFE fibers are to be deposited. The dispersion is espun using a total potential of 80 kV to facilitate formation of PTFE fibers, which collect in random formation on the stainless steel foil. The stainless steel foil containing the PTFE membrane is removed from the fabric and sintered at 385° C. for 5 minutes.
[0119]The 0.0008″ sintered espun PTFE sheet, removed from the stainless foil, is wrapped twice around a 0.50″ exterior diameter (OD...
example 3
Espun PTFE / Espun PVDF / Espun PTFE
[0120]An espinning dispersion based on a mixture of 5.2% (PEO / PTFE) 300,000 amu polyethylene oxide and Daikin DX-9030, 60% PTFE dispersion in water is prepared, allowed to homogenize, and turned and filtered to achieve a smooth consistency. A 0.002″ thick stainless steel foil sheet (15.5″×17.5″) is mounted on a conductive fabric roll with a payoff and take-up mounted above a spinning electrode. A total potential of 80 kV is employed to facilitate formation of PTFE fibers, which collect in random formation on the stainless steel foil. The stainless steel foil containing the PTFE membrane is removed from the fabric and sintered (if desired) at 385° C. for 5 minutes.
[0121]A 0.0015″ thick stainless foil sheet 17″×18.5″ is wrapped around a rotating drum. The drum assembly is placed into a rotating chuck such that it is positioned to allow espinning along the entire length of the turning drum assembly. An espinning solution based on a mixture of 25% Atofina...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameters | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com