Flat panel x-ray source
a flat panel x-ray source and x-ray technology, applied in the field of x-ray radiation, can solve the problems of low power efficiency of x-ray tubes, cathode x-ray tubes sharing limitations, and the production of x-rays by the electron beam striking the target also generates a considerable amount of heat, so as to achieve high power levels, improve heat dissipation, and efficient source of x-ray flux generation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
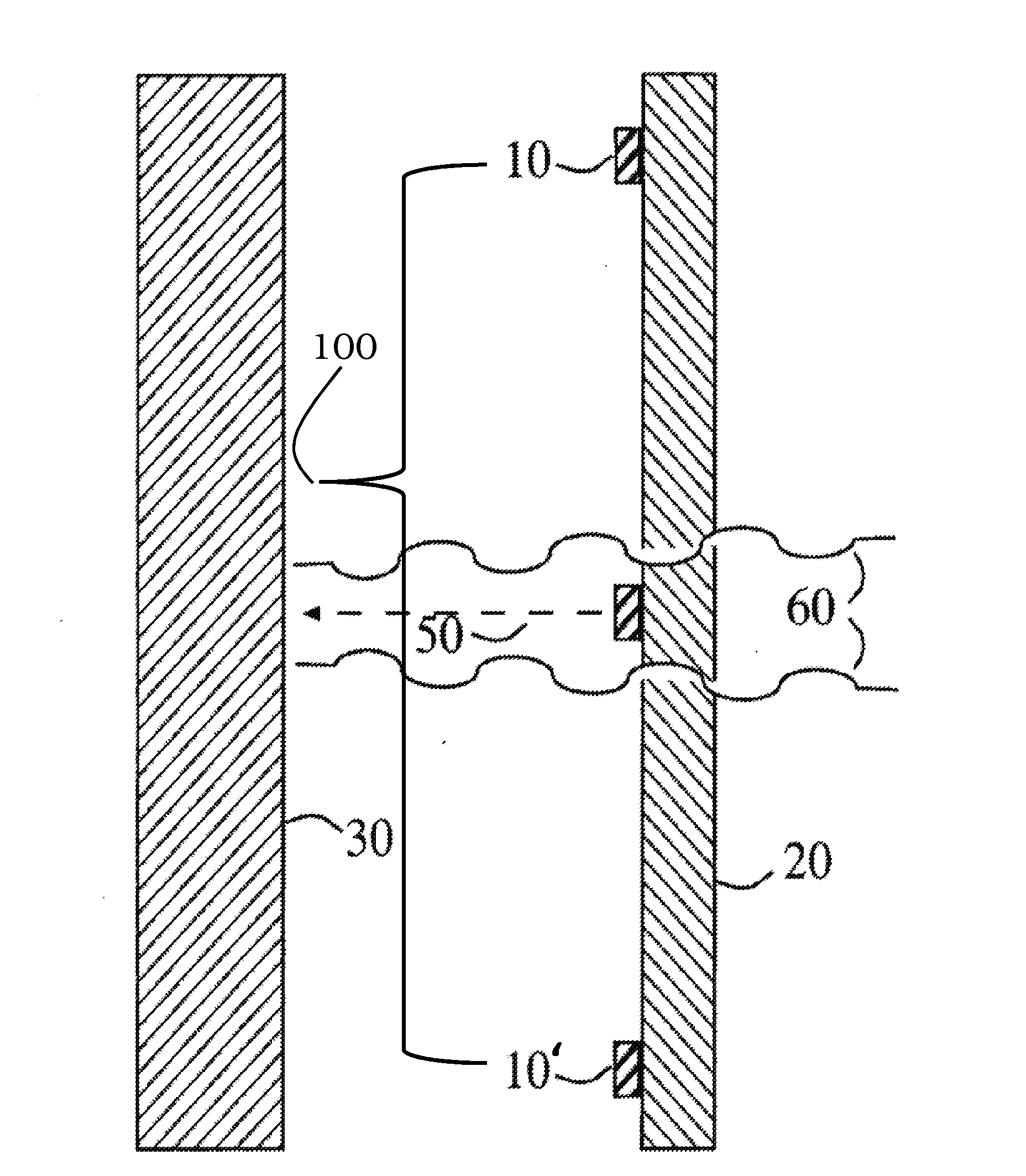
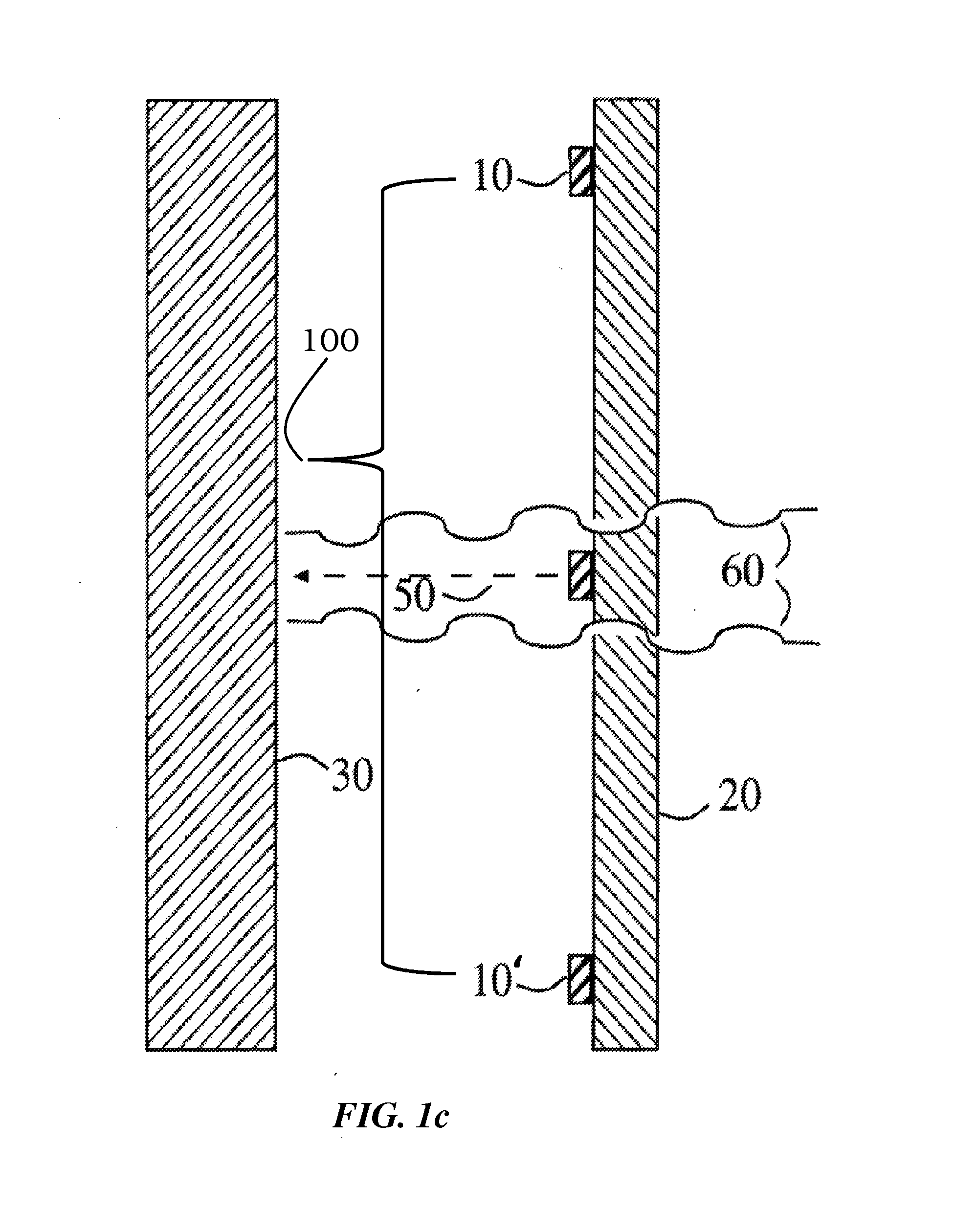
[0034]Although the following detailed description delineates specific attributes of the invention and describes specific designs and fabrication procedures, those skilled in the arts of microfabrication or radiation source production will realize that many variations and alterations in the fabrication details and the basic structures are possible without departing from the generality of the processes and structures. The most general attributes of the invention relate to the cathode array 100 formed on the exit window of the radiation source across from a metal X-ray target.
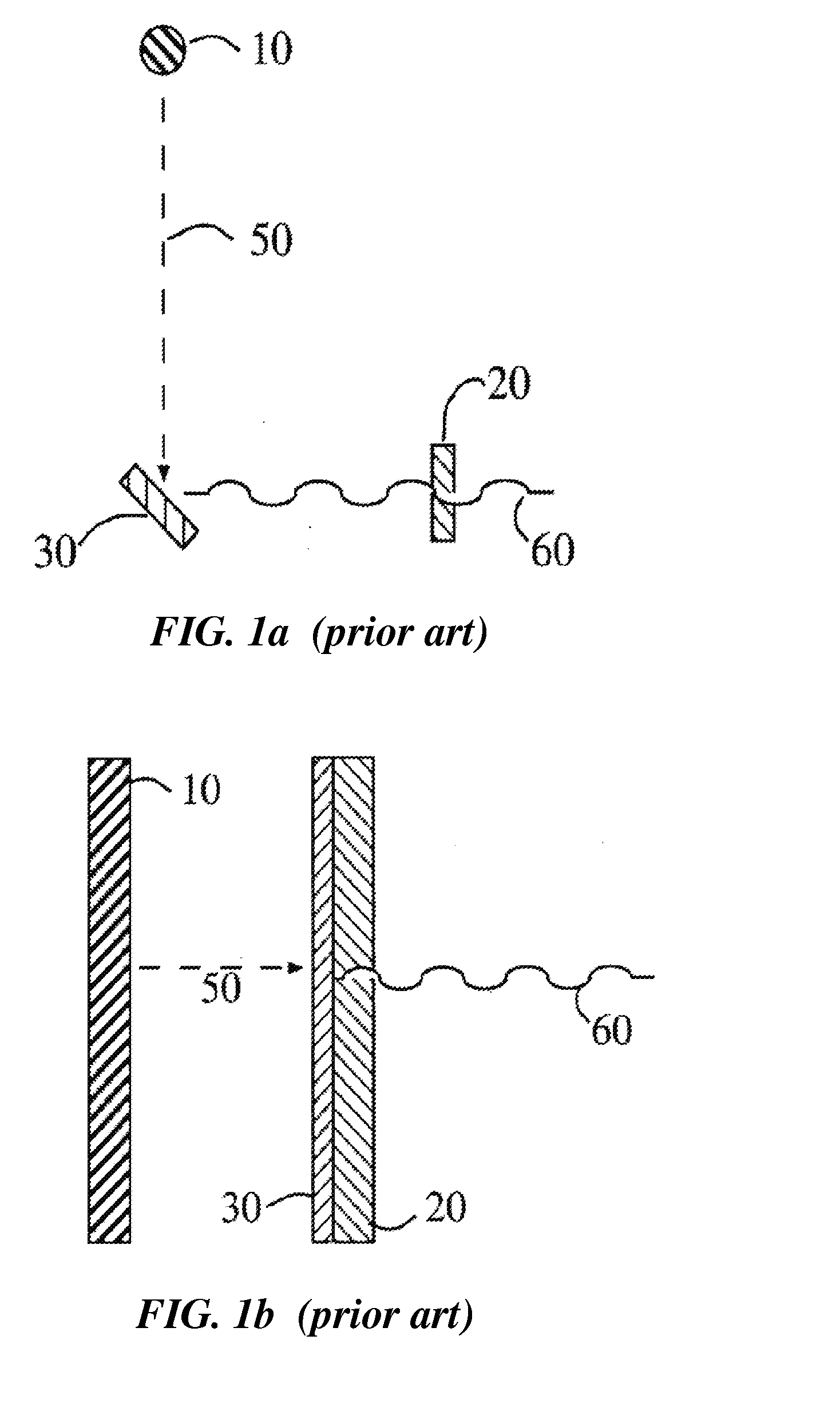
[0035]The general prior art method of producing X-ray flux is shown in FIG. 1a and FIG. 2. A cathode 10, commonly a hot filament cathode operated with an attached heater but more recently a field emission cold cathode, emits an electron beam current 50. An electrical potential established with respect to metal anode 30 directs this current at high velocity across a vacuum to impact the anode, which is disposed at ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com