Stabilized fabric seam for flat-woven continuous fabric belts
a fabric seam and continuous technology, applied in the field of continuous fabric belts, can solve the problems of reducing the tear strength, uneven drying and marking of the fibrous web, and increasing the strength of the seam only sub-proportionally with the seam length, and achieve the effect of increasing the tear resistance of the fabric seam
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
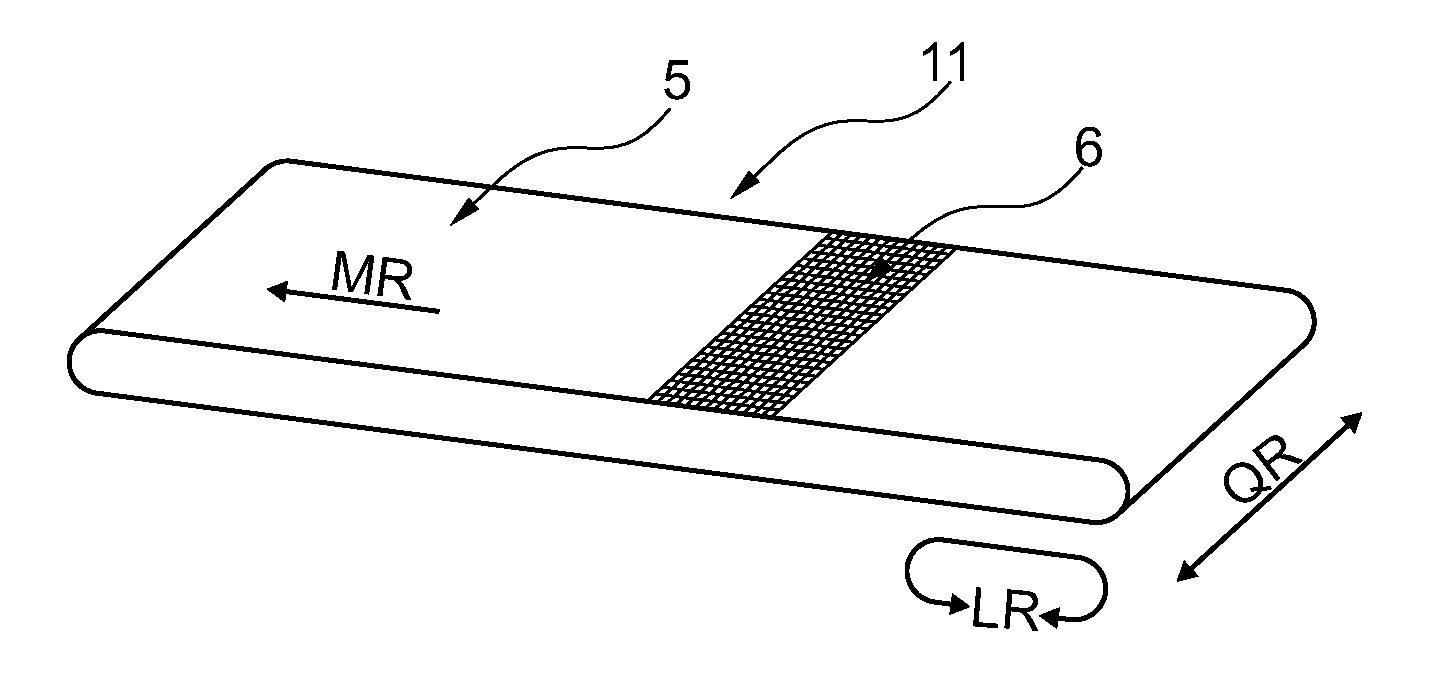
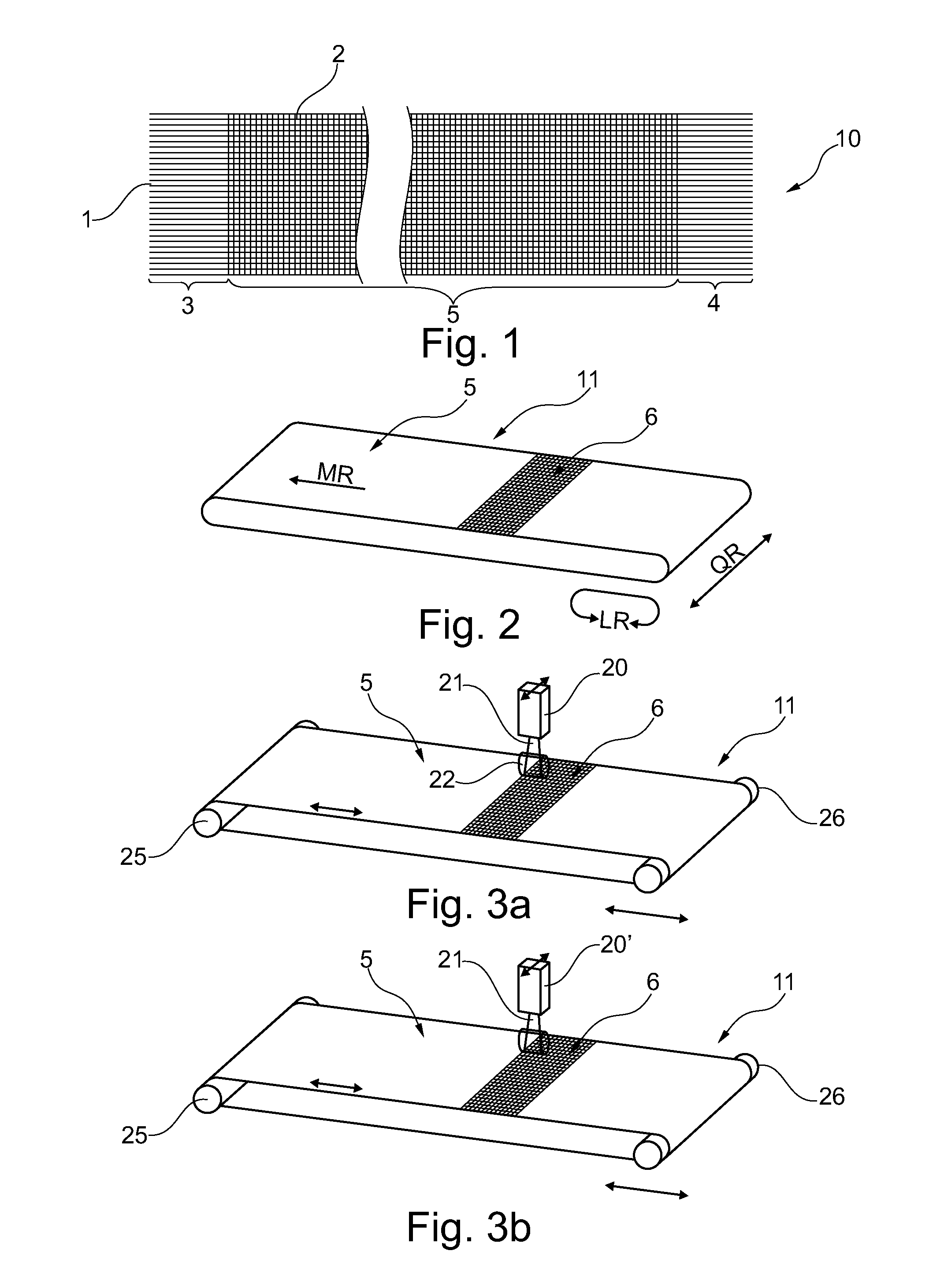
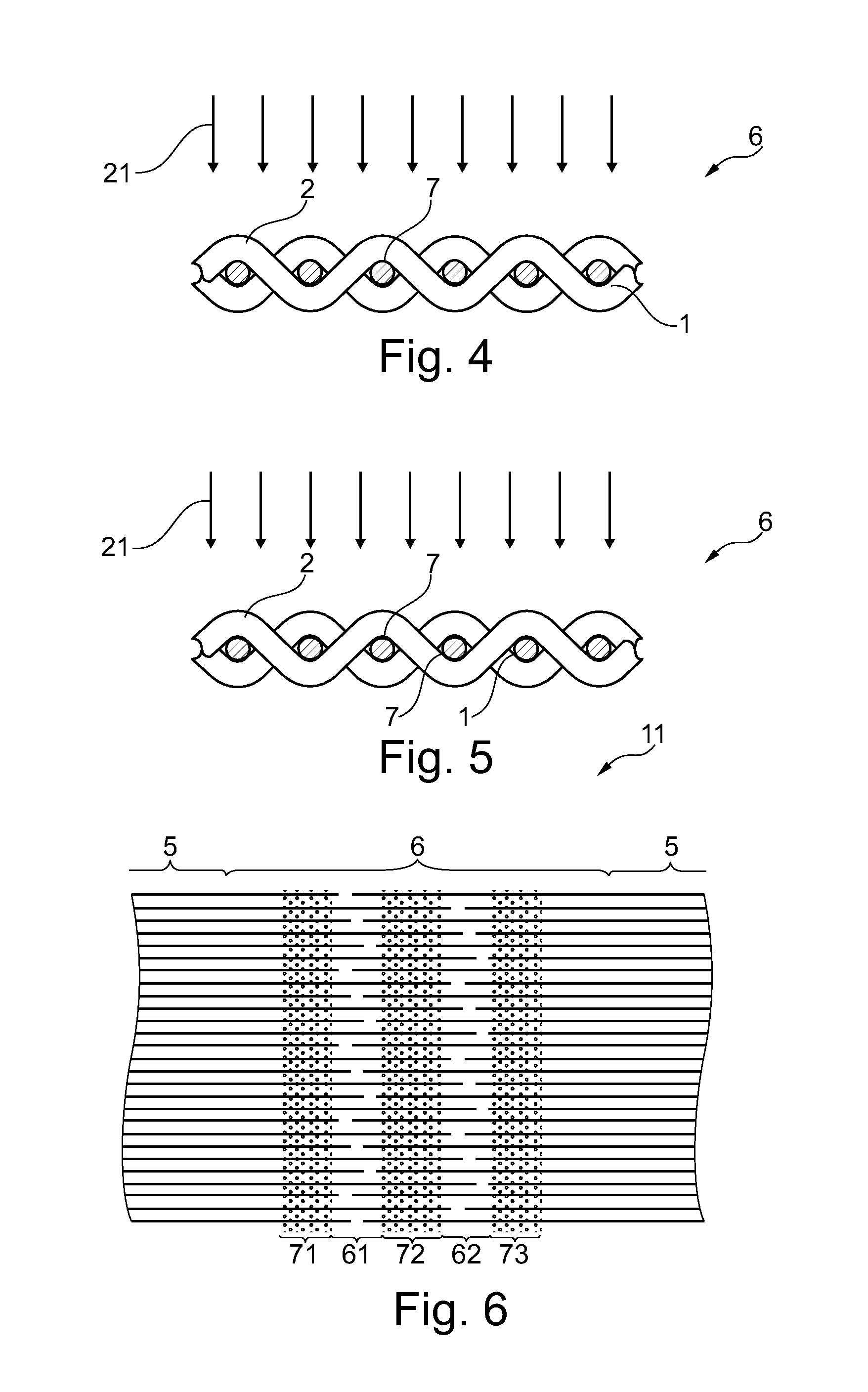
[0048]Referring now to the drawings, and more particularly to FIG. 1, there is shown a schematic illustration of a flat fabric belt 10 produced to length with ends 3 and 4 prepared for the formation of a fabric seam. The warp- or machine directional threads 1 of fabric 10 extending in the horizontal direction, cross in a defined pattern with weft- or cross-machine directional threads 2 illustrated in the vertical direction. For the purpose of a clear illustration always only one warp- or machine directional, or weft- or cross-machine directional thread is given an identification number.
[0049]Moreover, for better illustration of features, distance and number of warp- or machine directional threads and weft threads, as well as weave and dimensions of flat fabric belt 10 are selected without reference to concrete characteristics.
[0050]To produce a continuous flat fabric belt, ends 3 and 4 of flat fabric belt 10 must be joined with each other. So that the joint does not display a differ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| wavelength range | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com