Lock
a technology of locking and assembly, applied in the direction of ropes and cables for vehicles/pulleys, mechanical machines/dredgers, shackles, etc., can solve the problems of needing to replace the whole device, the operation of the digging device is typically subject to harsh conditions, and the excavating bucket or other digging device or equipment is typically subject to large forces, so as to achieve good retention performance in the operation of the equipment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
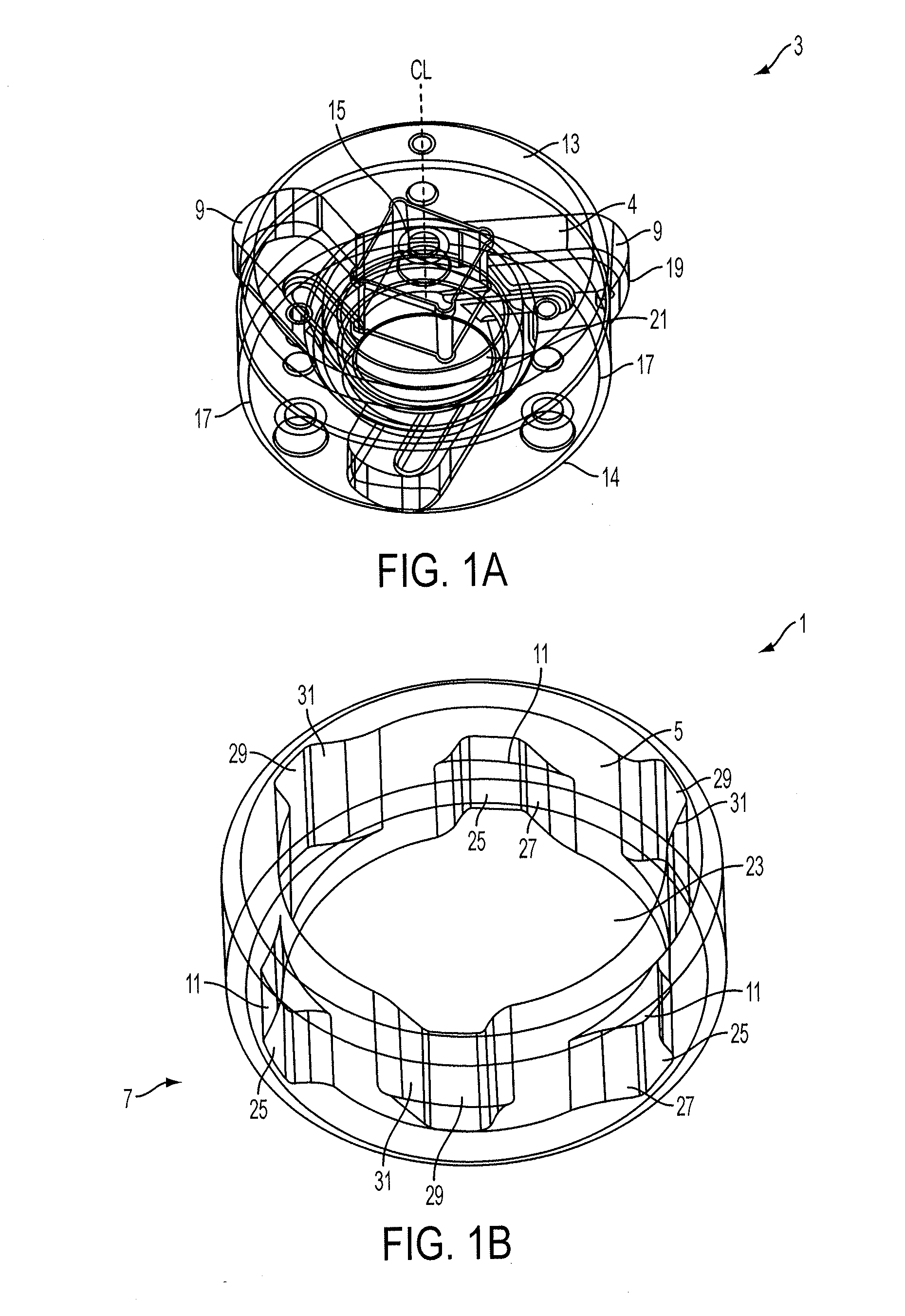
[0055]FIGS. 1A and 1B are exploded perspective views of a lock assembly according to a
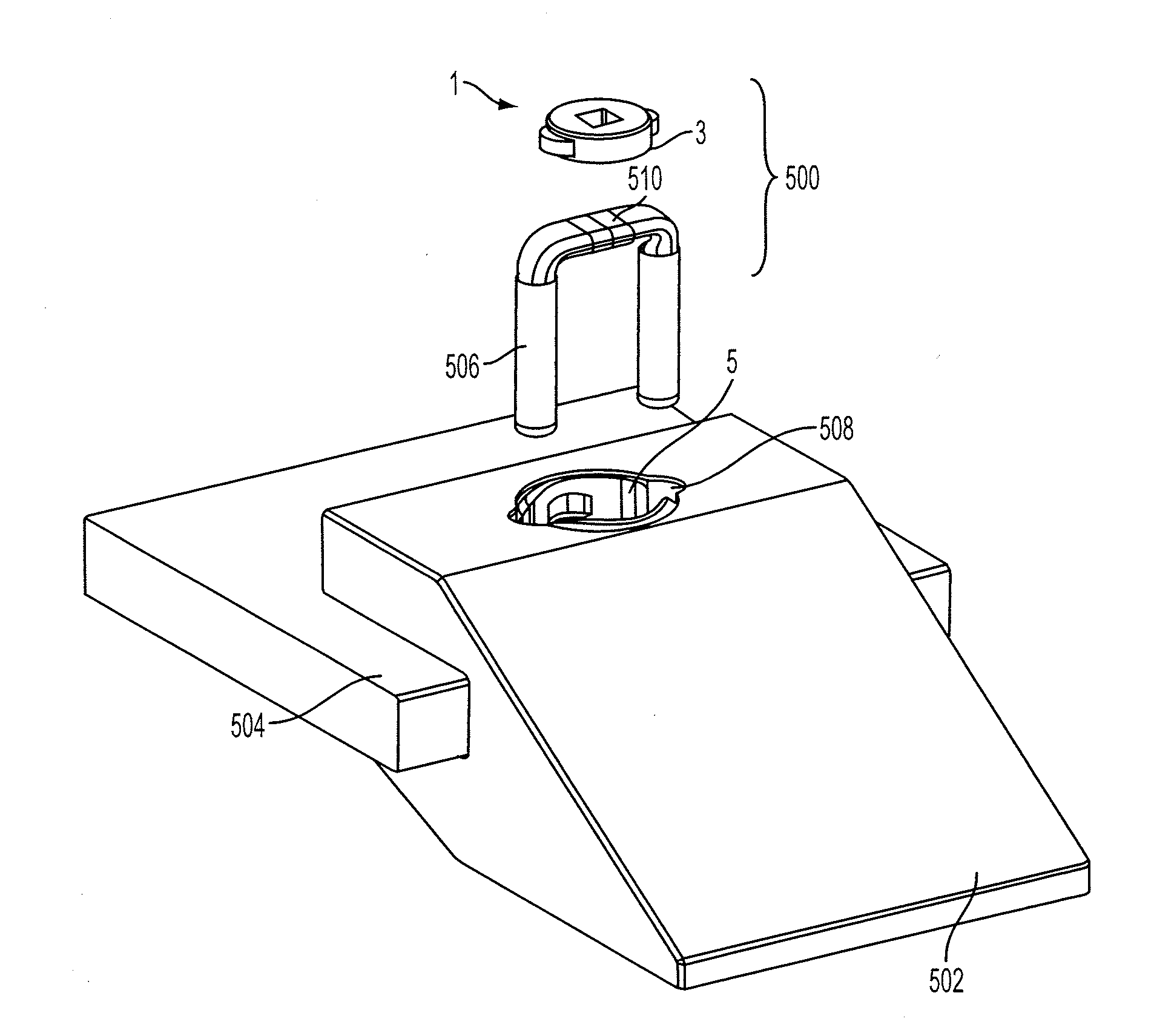
[0056]FIG. 1B illustrates a lock assembly 1 comprising the locking element 3 of FIG. 1A and a retaining member which in the illustrative form is a locking ring 7 of FIG. 1B. The locking ring 7 incorporates a cavity 23 having an interior locking surface 5 and the locking element is received in the cavity and engagable with the locking surface as will be described in more detail below.
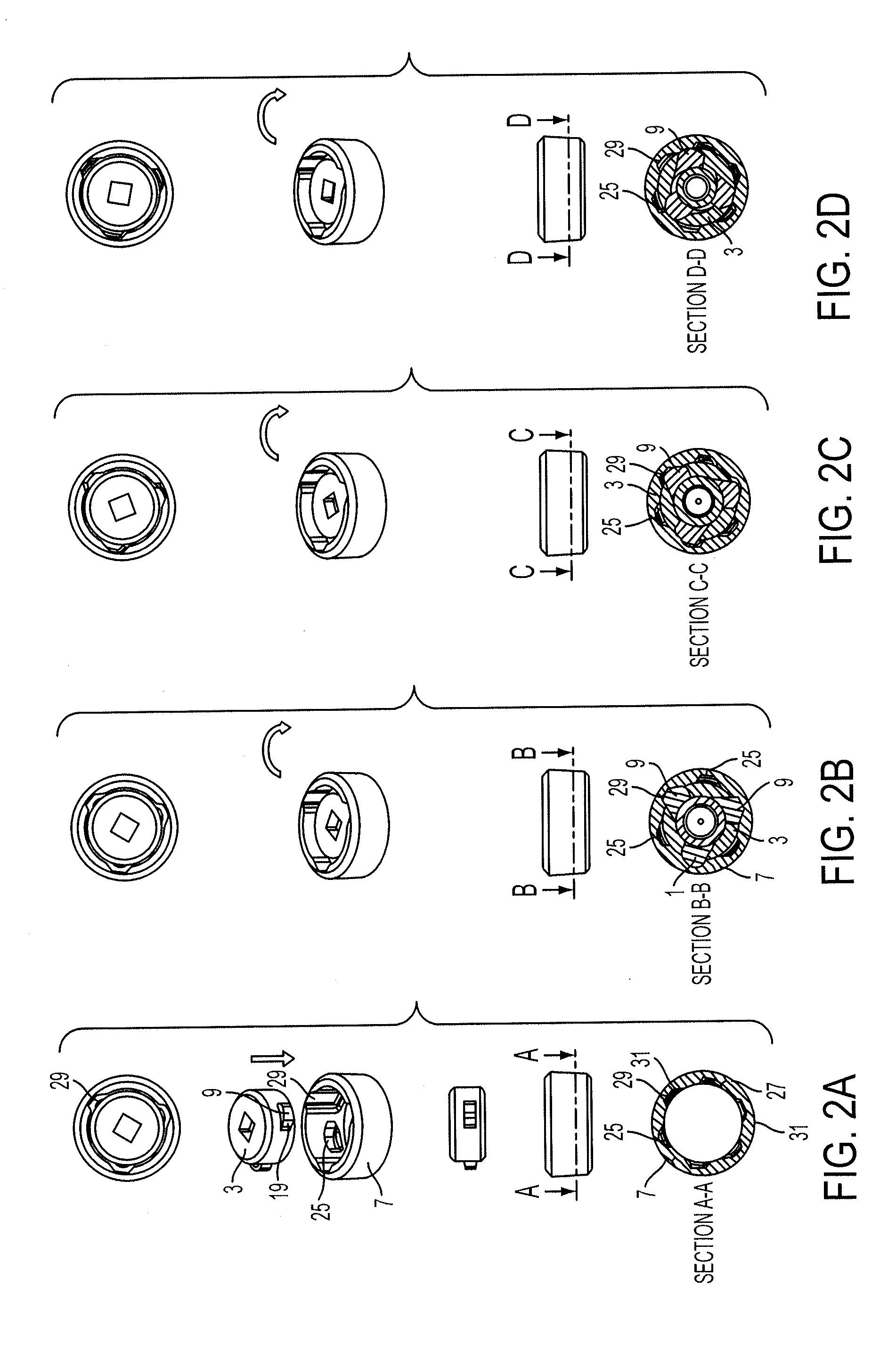
[0057]In the illustrative form, the locking element 3 has a body 4 which is generally cylindrical having an axis CL which forms a first locking axis of the body 4 and about which the locking element is arranged to rotate in use. The locking element 3, as illustrated, also has three tabs 9 movable between an extended position and a retracted position relative to the first locking axis. The locking surface 5 has three retaining elements 11, which when engaged with the respective tabs 9, prevent relative movement between t...
second embodiment
[0082]the locking element will now be described with reference to FIGS. 3 to 5C. The locking element 103 has tabs 109, that has a movement axis extending radially from the first locking axis of the body 104 of the locking element 103. FIGS. 5A to 5C illustrate various positions of the tabs 109 as they move radially between their extended and retracted positions.
third embodiment
[0083]the locking element will now be described with reference to FIGS. 6 to 8C. The locking element 203 has tabs 209, that are pivotally attached by pivots 210 to the body 204. The pivots 210 allow the tabs to swing outwardly between an extended position and a retracted position. A resilient element 221 is provided for each tab 209 to bias the tabs to the extended position. FIGS. 8A to 8C illustrate various positions of the tabs 209 from an extended position to a retracted position.
[0084]A further embodiment of the locking element (not shown) may have tabs with additional camming surfaces on the tabs. In one form, the additional camming surfaces may allow the lock assembly to be locked and unlocked in both directions (i.e. clockwise and anti-clockwise when viewed from the top view). A further alternative is to have camming surfaces on the underside of the tabs (i.e. the face when viewing towards the bottom surface 14 of the body), thereby allowing the lock element 3 to be push fit ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com