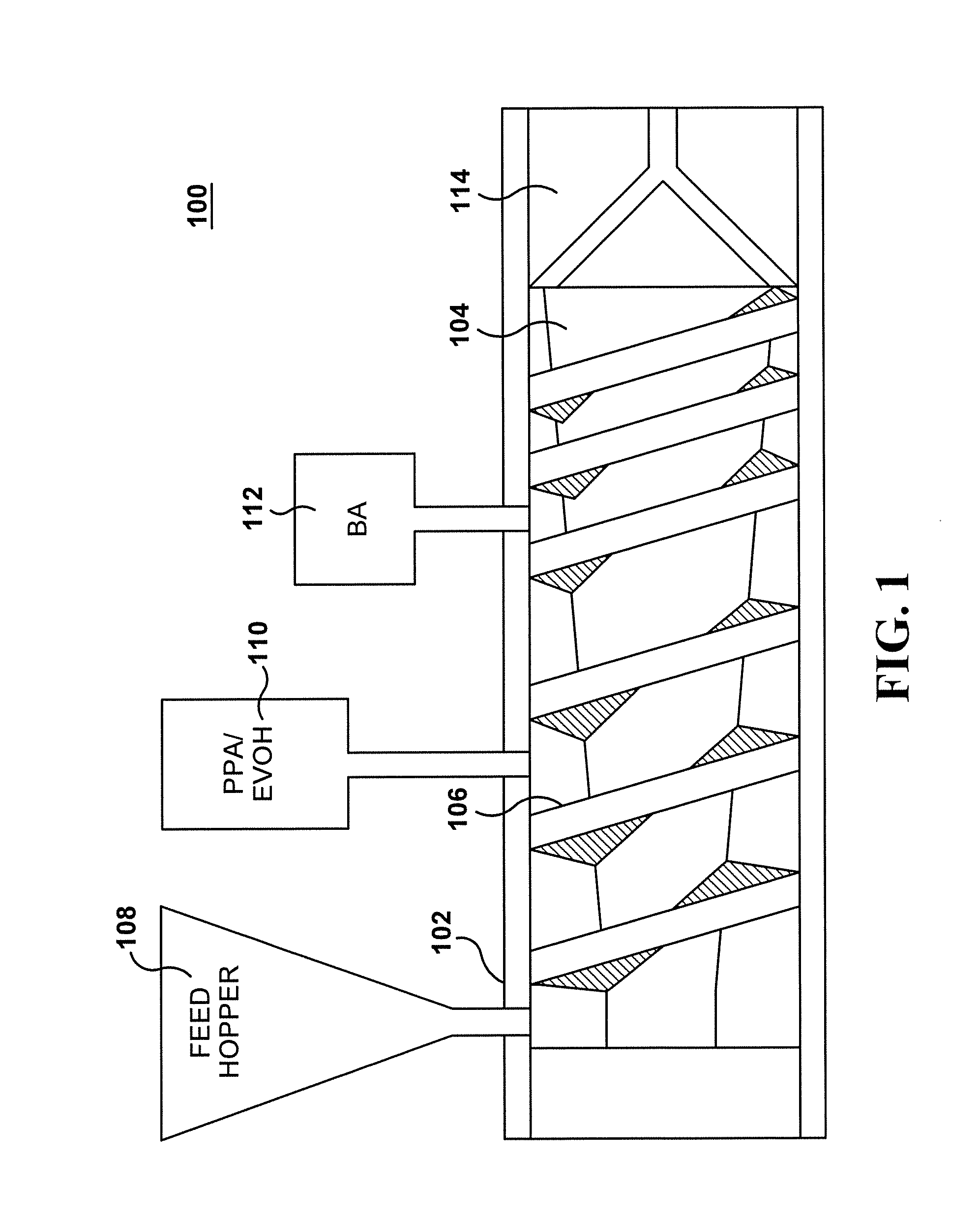
Processing aids for use in manufacturing extruded polystyrene foams using low global warming potential blowing agents
a technology of extrusion aids and blowing agents, which is applied in the field of polymeric foam manufacturing processes, can solve the problems of ozone depletion potential, and achieve the effect of increasing the prevalence of global warming
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Operating Window Expansion with Phase Changing Materials in CO2 Foaming
[0057]One percent of PT24 microencapsulated powder containing 80% phase changing material and 20% encapsultion wall material was applied for XPS foaming using about 3.7-4.3% CO2 blowing agent. A foam board with a 1 inch thickness was produced smoothly and the properties of the resulting foam board are shown as Samples 1 & 2 in Table 2 below. The foam board properties are each within the acceptable range for traditional foam borads. Particulalry, the boards have a density between about 1.4 and 3 psi, an R-value of 4-7 per inch. a cell size between about 0.005 and 0.6 mm, a compressive strength between about 6 and 80 psi, and an open cell content of less than 30 percent. On the contrary, without the phase changing material, the process could not be continued under the similar processing conditions due to the overshooting of die pressure (Sample #3). This observation indicates that phase changing materials are neces...
example 2
Application of PT24 Liquid in CO2 Foaming
[0058]A liquid processing aid, PT24, was injected directly into the extruder with 3.5% CO2 as the blowing agent. An XPS foam board with good surface quality was produced without any modification to the traditional foaming conditions. The foam board properties are illustrated below, in Table 3. This further proves the benefit of using the subject phase changing materials as a processing aid when using CO2 as the blowing agent.
TABLE 3Application of PT24 liquid for CO2 XPS foamingFoamCellCompressiveSamplePT24 liquiddensityRsizeOpen cellstrength#(wt %)(pcf)value(mm)(%)(psi)40.82.814.410.161.9936.651.22.774.390.175.9432.661.62.784.410.176.3132.8
example 3
Design of Experiment (DOE) of Using PT24 Microencapsulated Powder in CO2 Foaming
[0059]A Design of Experiment (“DOE”) was developed to understand the influence that phase changing processing aids have on foam properties. A DOE is an information gathering exercise where one or more variations are present. The particular DOE designed was based on three key parameters: phase changing material usage level (between 1 and 3 weight %), polystyrene melt flow index, and CO2 concentration. A single DOE having three factors and two levels (low and high) was performed.
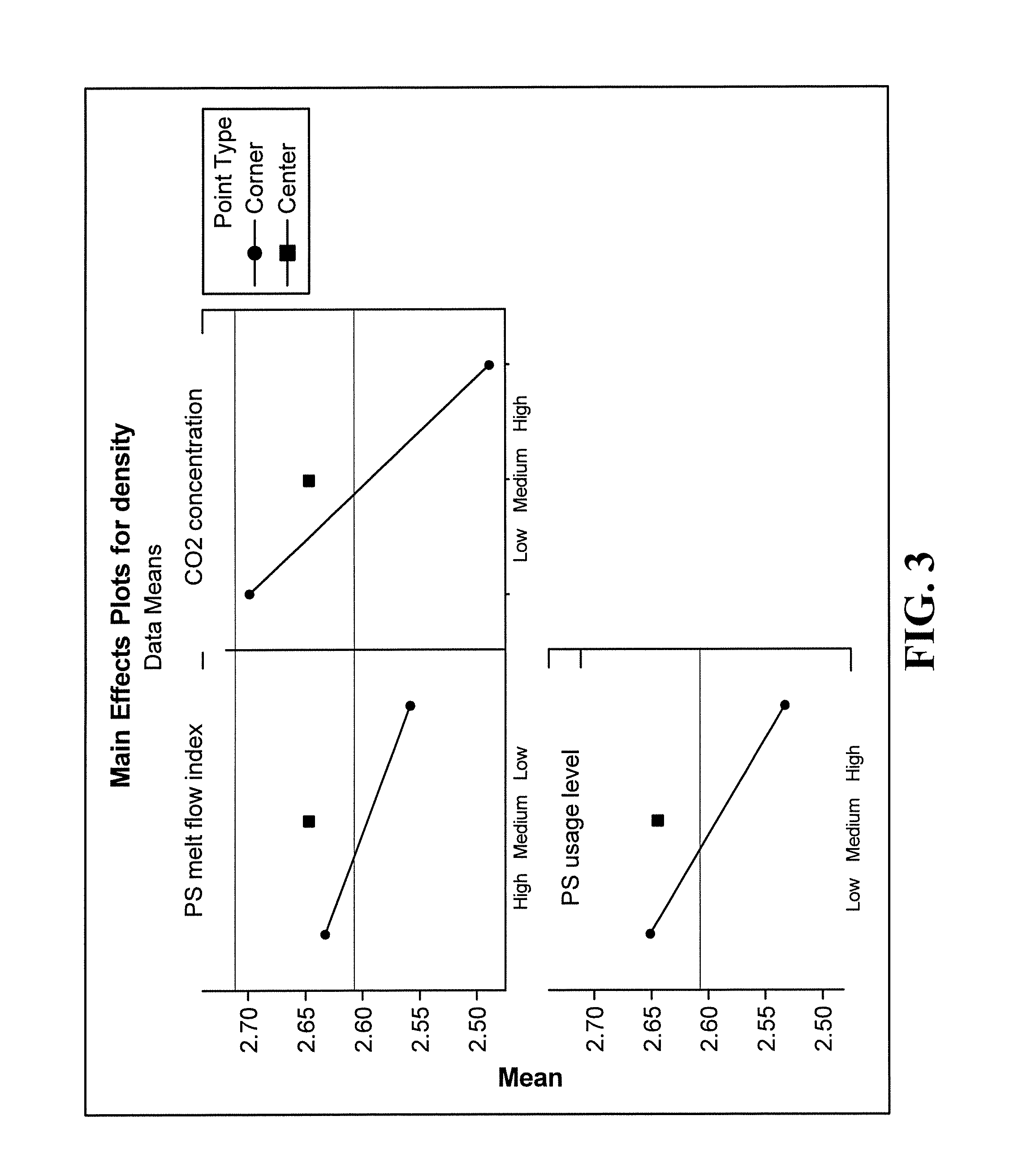
[0060]The main effects from the three key parameters to foam density, foam cell size, and compressive strength are summarized in FIGS. 3, 4, &5, respectively. FIG. 3 illustrates the effects the various parameters have on foam density when exposed to both low and high levels. For instance, at a high polystyrene melt flow index, the foam density is also high. Conversely, as the CO2 or phase changing material concentration increases, ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pressure | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pressure | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| weight percent | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com