Corneal inlay design and methods of correcting vision
a technology of corneal inlay and design method, which is applied in the field of corneal inlay design and vision correction, can solve the problems of near-sightedness, vision impairment, and huang does not address the correction of presbyopia,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
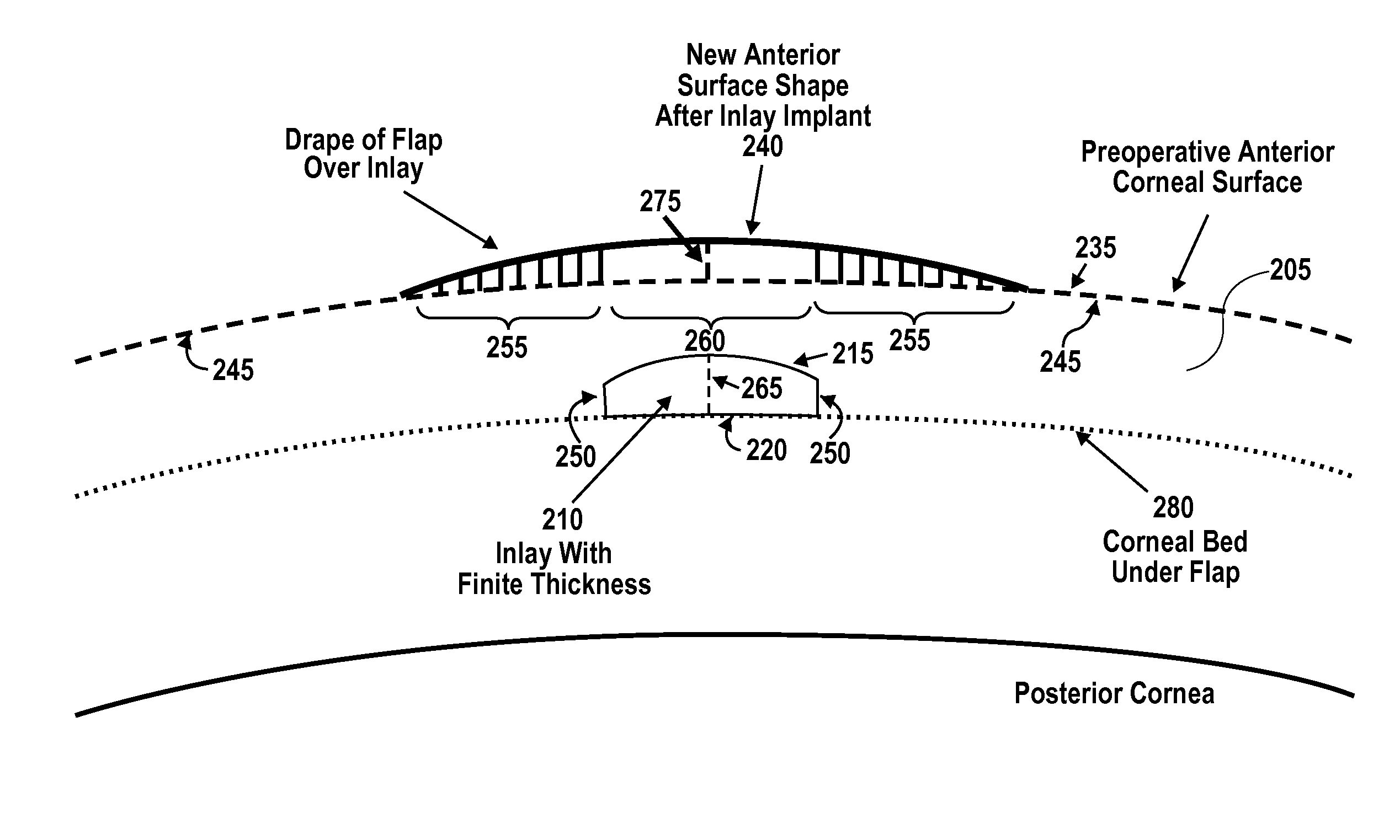
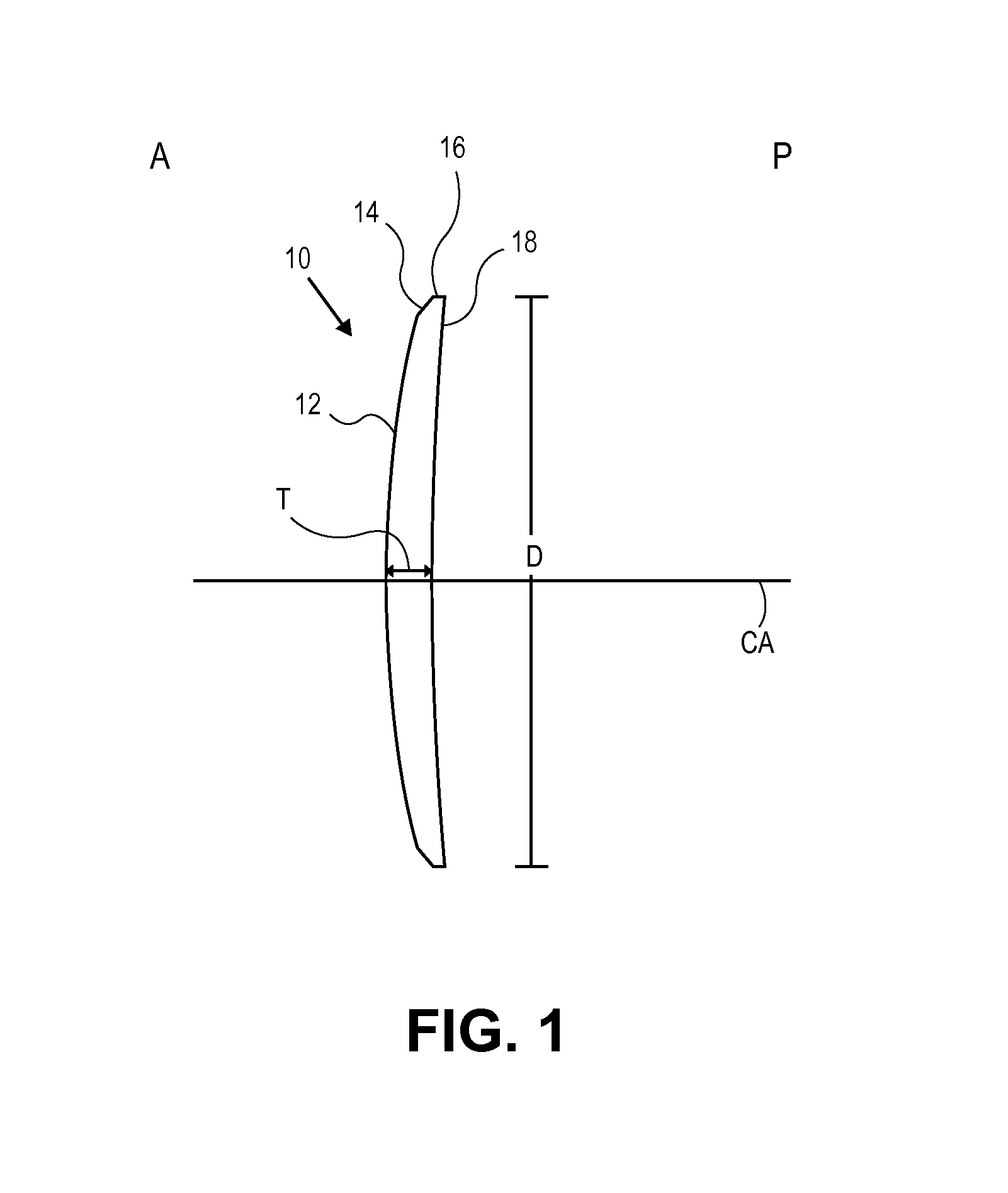
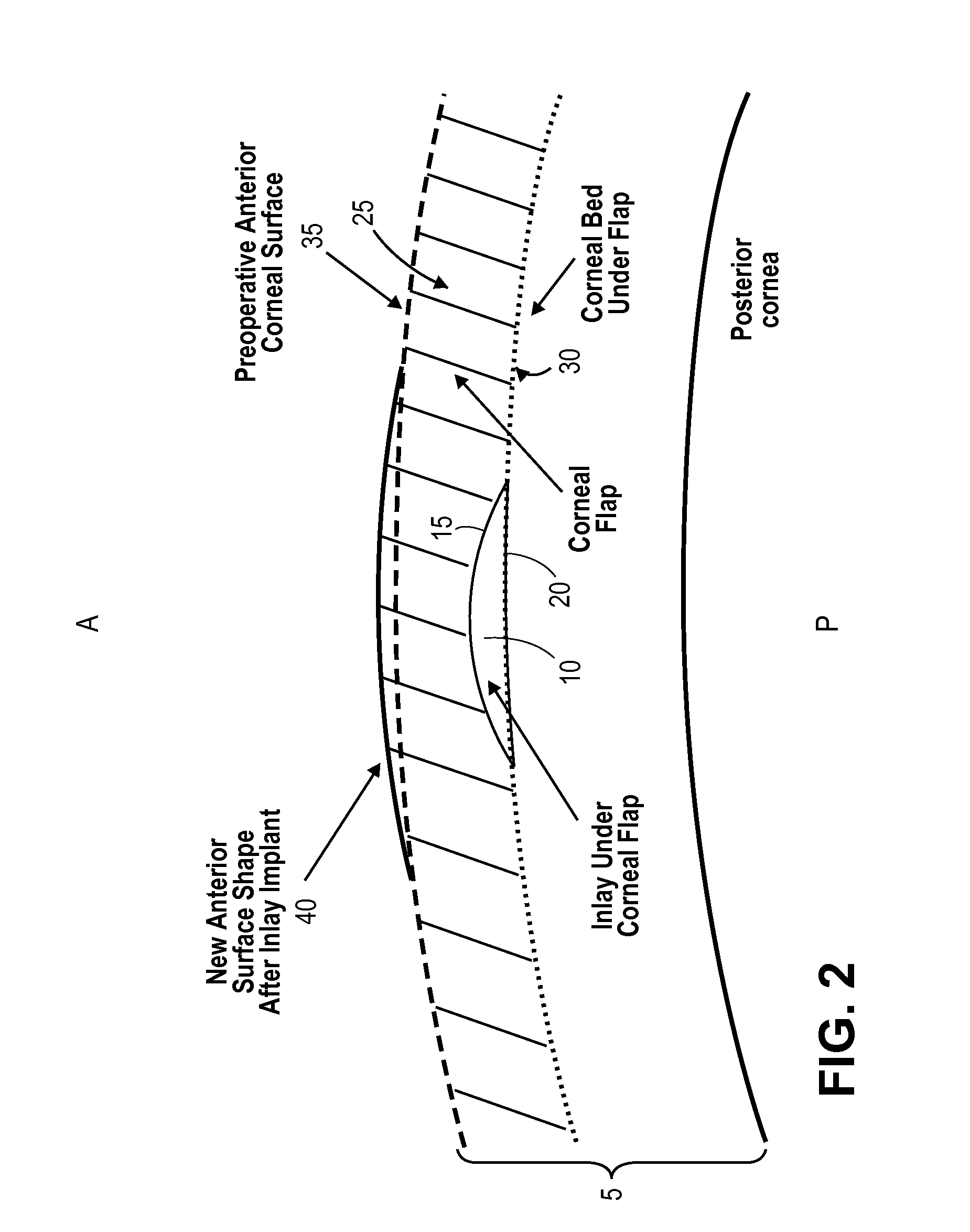
[0040]This disclosure relates to methods of vision correction and methods of compensating for a cornea's response to the vision correction procedure to invoke a desired corneal shape change. The disclosure includes methods of correcting presbyopia. In some embodiments the methods include implanting a corneal inlay within cornea tissue to correct for presbyopia while compensating for the inlay's presence within the cornea. The disclosure also provides methods of increasing the curvature of a central portion of the anterior surface of the cornea to provide near vision in the central portion while providing distance vision peripheral to the central portion. In some particular embodiments an inlay is implanted in the cornea to cause the central portion to increase in curvature to provide near vision.
[0041]The cornea can be generally considered to be comprised of, from the anterior A to posterior P direction, the epithelium, Bowman's layer, stroma, Descemet's membrane, and the endotheliu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com