Robotic Drowning Rescue System
a robotic and rescue technology, applied in the field of robotic drowning rescue systems, can solve the problems of ineffective “active lost motor functions, and erroneous targetting of “passive” drowning detection methods known in the ar
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
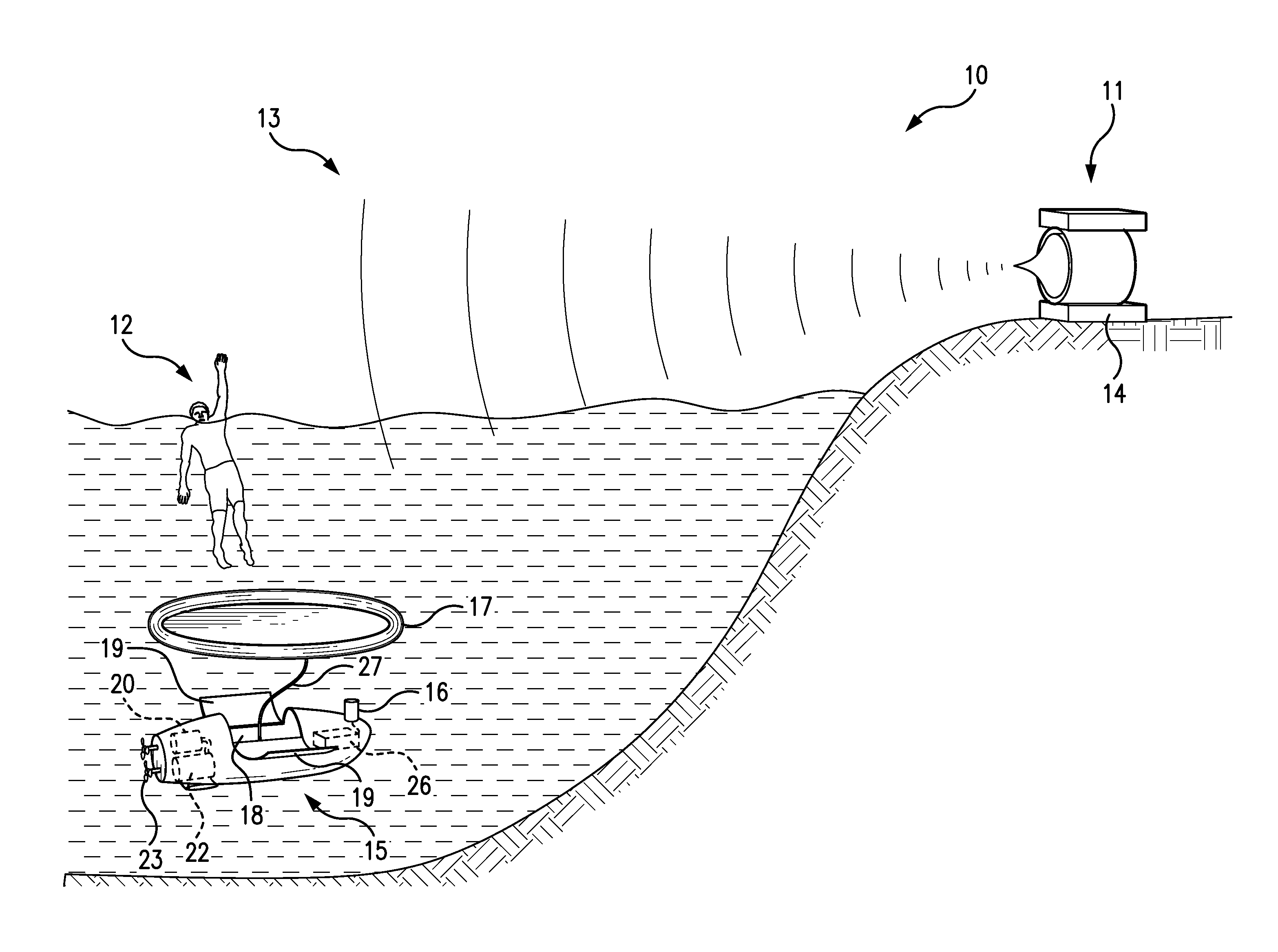
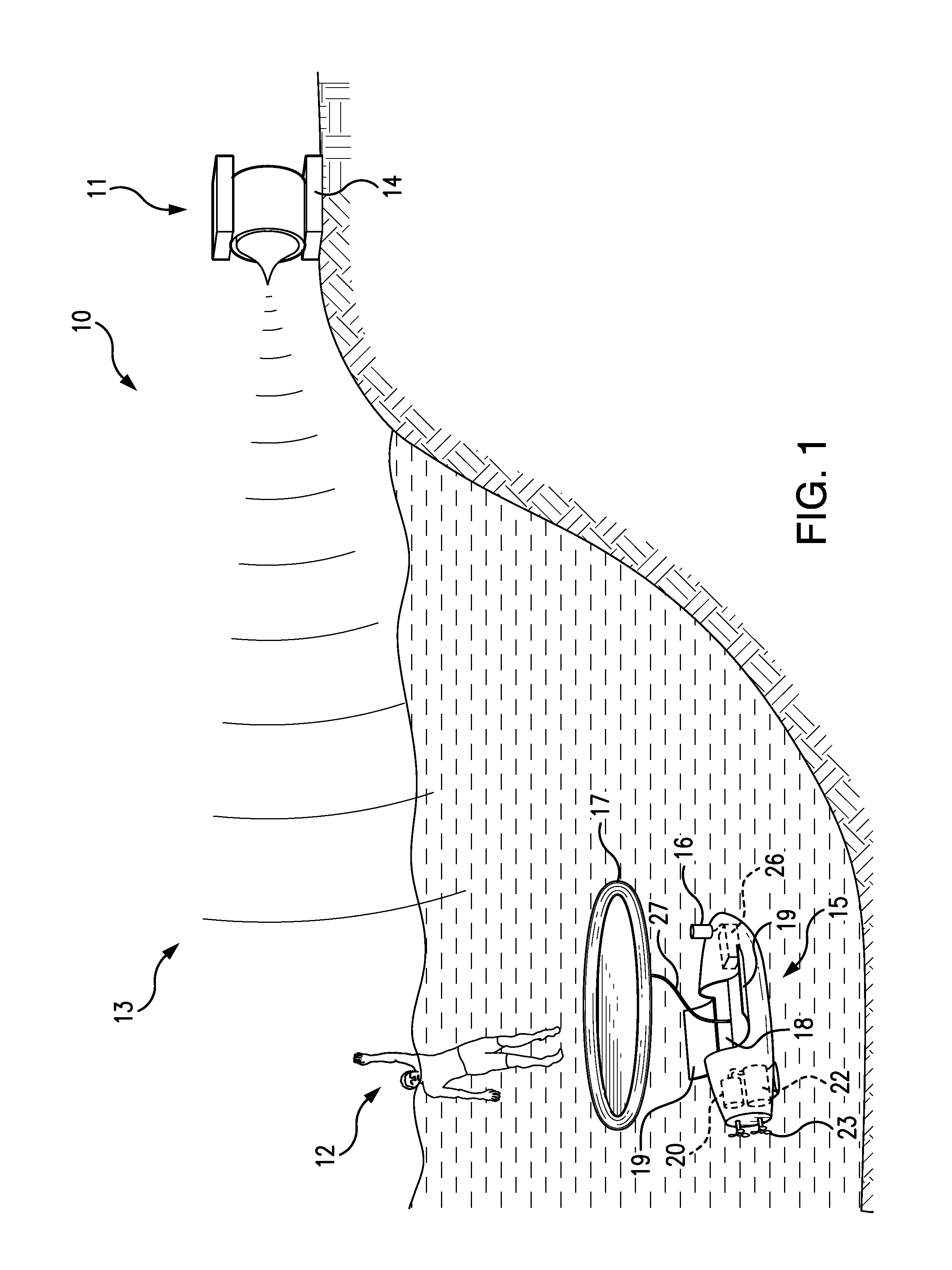
[0038]Referring to FIGS. 1, 2A and 2B, one embodiment of the present invention 10 comprises a detection device 11, which monitors the victim 12 and remotely and passively acquires victim data 13, comprising behavioral and / or biometric data. The detection device compares the victim data 13 with a compiled set of documented drowning indicia. This comparison is implemented by a computer system 14 in the detection device 11, using software to match the victim data 13 with the drowning indicia. The detection device 11 remotely and passively acquires the victim data 13 using microwave, infrared, optical, sonic and / or ultrasonic observations and / or measurements.
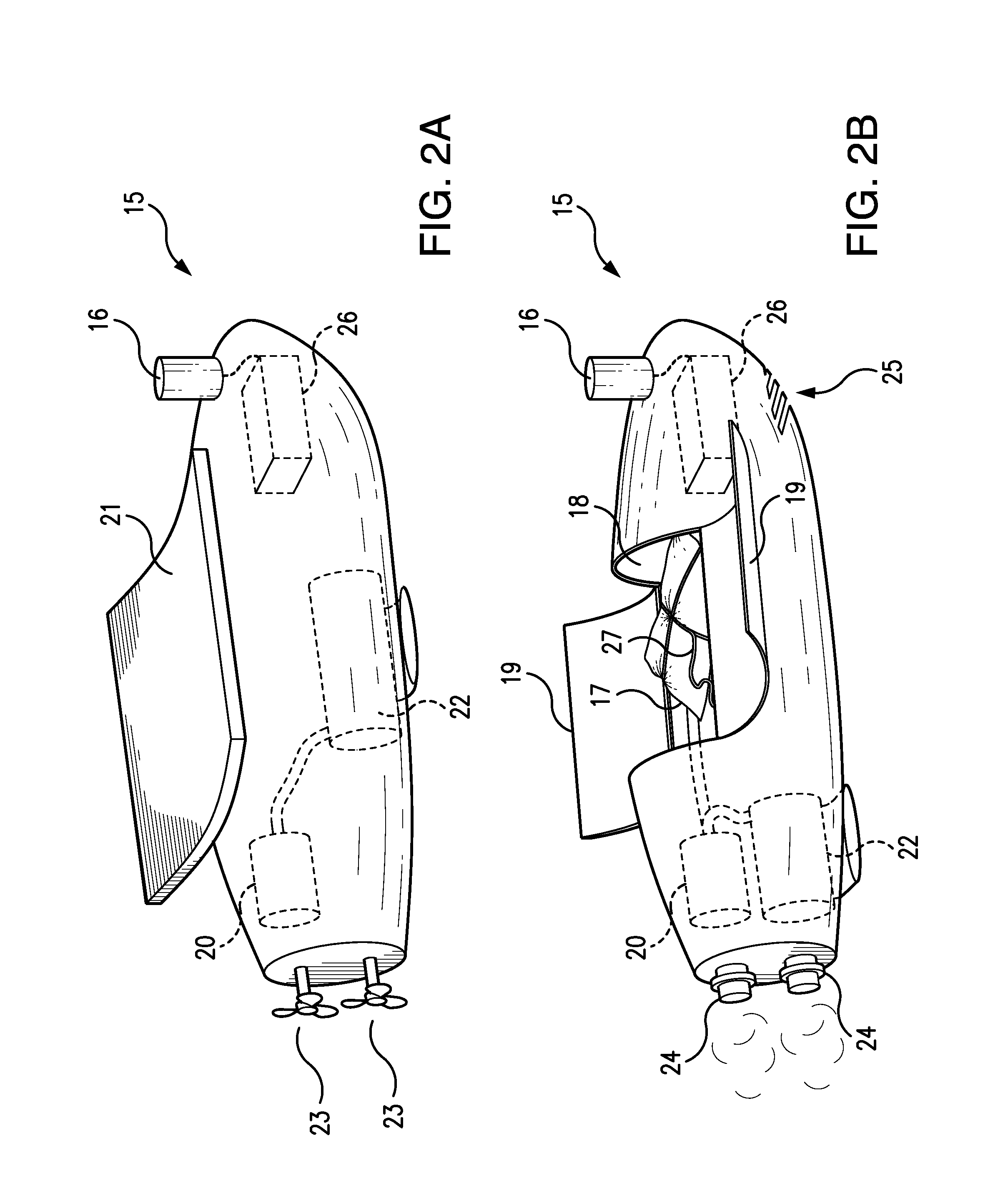
[0039]Upon detecting one or more drowning indicia, the detection device 11 acquires location coordinates of the victim 12 and wirelessly communicates the victim's location coordinates to a self-propelled robotic submersible 15. The robotic submersible 15 thereupon travels to the victim's location and uses a positioning sensor 16 to ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com