Methods and compositions for preventing ischemia reperfusion injury in organs
a technology of ischemia and reperfusion injury, applied in drug compositions, extracellular fluid disorders, cardiovascular disorders, etc., can solve the problem of imposing the risk of iri in the native organ by inhibiting or using the risk of iri, and achieve the effect of reducing the amount and duration of dialysis and improving clinical outcomes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Ischemia-Reperfusion Induced p53 Activation in Kidneys from Rat Donors
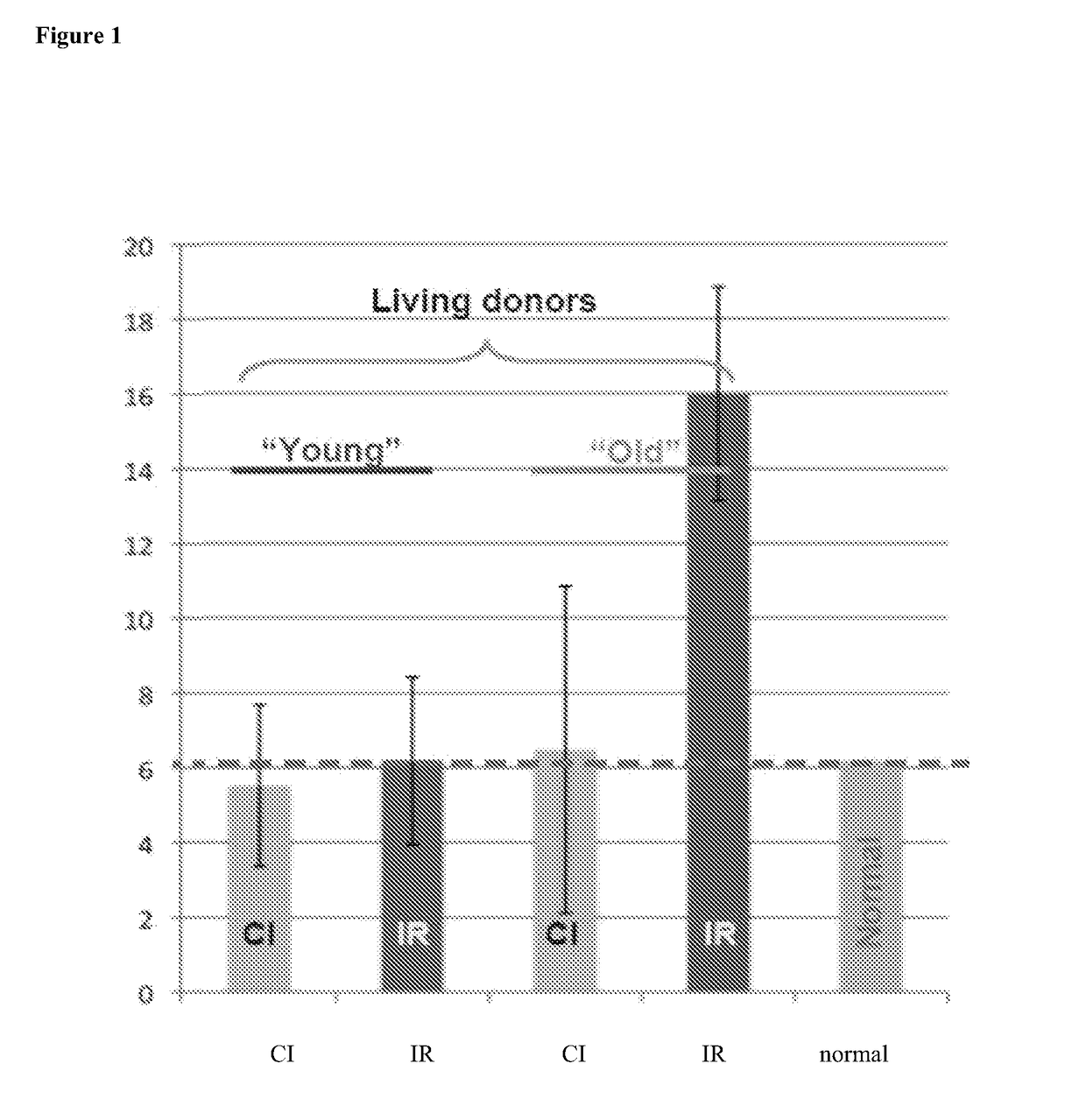
[0160]Kidneys were harvested from young (3-month old) and old (14-month old) SD rats (n=4-6) and subjected to cold ischemia (CI) for 5 hours. One kidney from each animal was processed for protein extraction whereas the second kidney was transplanted into 3-month old syngeneic rats. The transplanted kidneys were harvested 24 hours after the surgery and the resultant onset of ischemia-reperfusion injury (IR) and also processed for protein extraction. Protein extracts were analyzed in ELISA for p53 expression levels.
[0161]Results: In FIG. 1, the Y-axis shows arbitrary units corresponding to p53 protein levels measured in ELISA. FIG. 1 shows that the p53 protein level is significantly increased in transplanted kidneys from older rats, compared to transplanted kidneys from young rats (3 months old). Note that following p53 activation occurring via a variety of post-translational modifications, its steady-state levels a...
example 2
Use of an Inhibitor of a p53 Gene for Prophylaxis of Delayed Graft Function (DGF) in a Recipient of a Kidney from Donors of Various Ages.
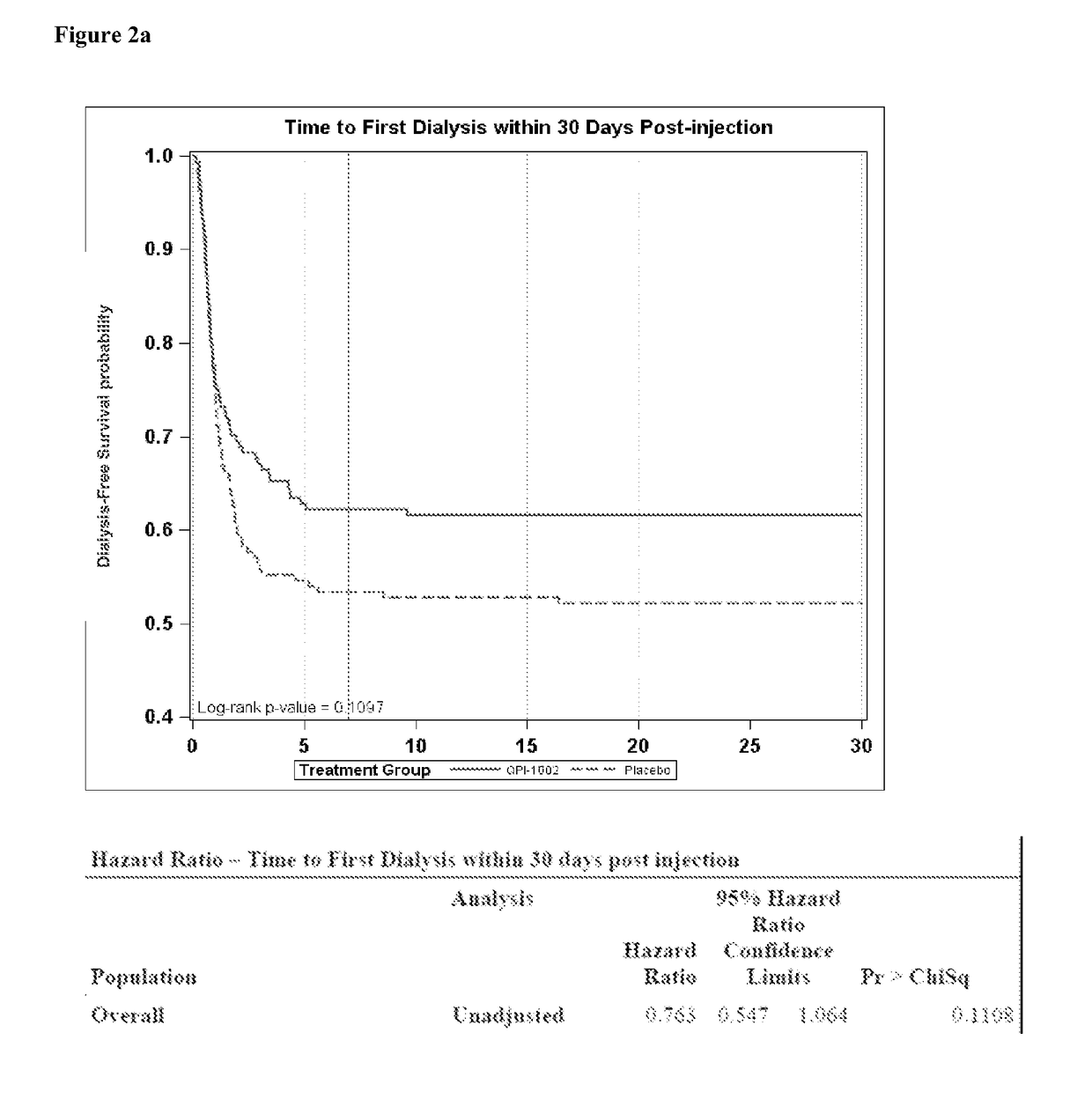
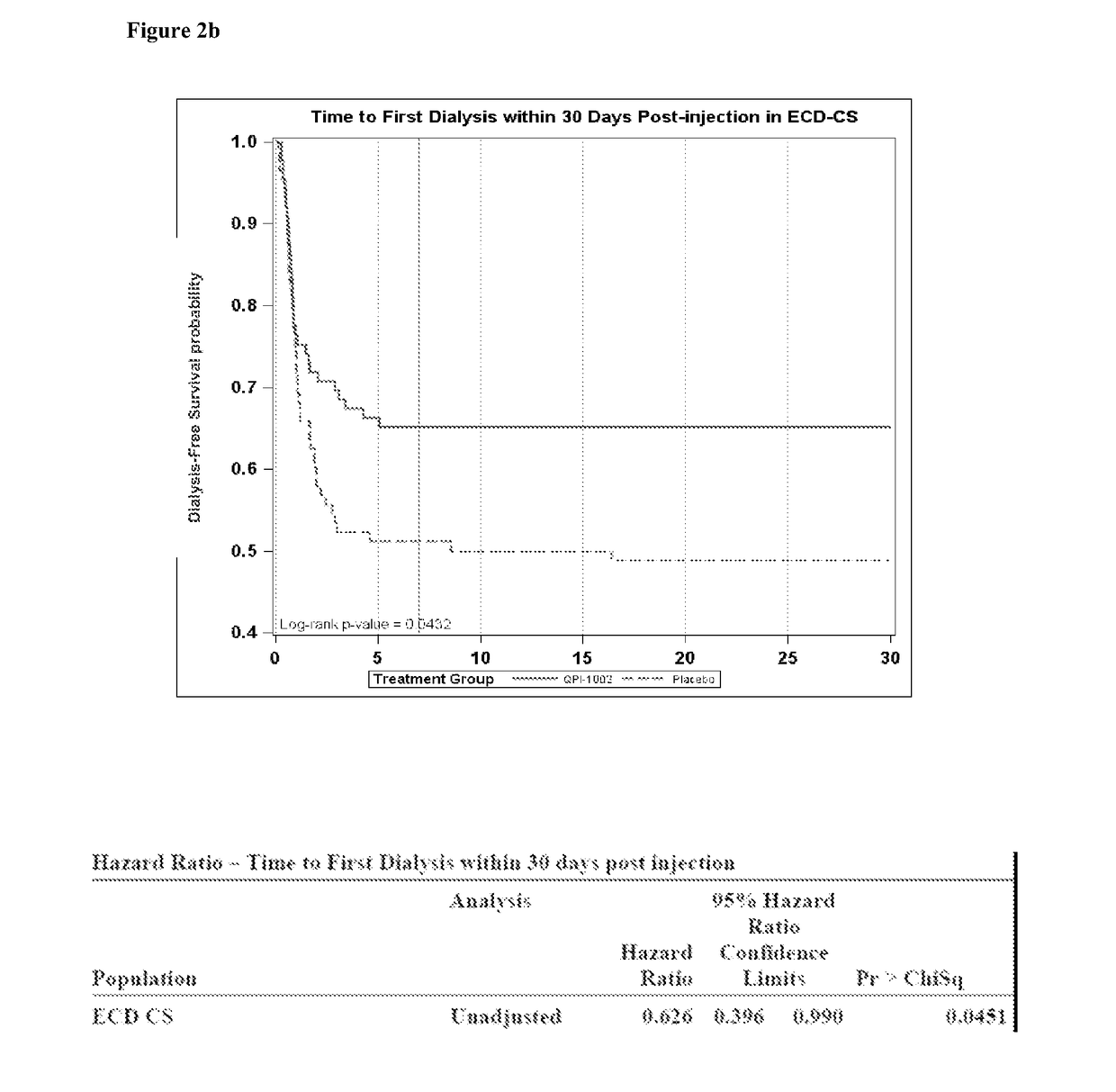
[0251]A study similar to Example 1 was performed to test the effectiveness of QPI-1002 using kidneys from donors of various ages that did not necessarily meet the criteria for ECD donors.
[0252]In the efficacy analysis, the best primary endpoint results were obtained for patients receiving kidneys from donors older than 45 years of age (regardless of their primary subgroup classification) that constituted 77% of all the evaluable patients in the study). Importantly, a threshold of 35 years of age (86% of all the evaluable patients in the study regardless of subgroup classification) yielded similar benefits (listed below):
[0253]Clinically meaningful and, in some subgroups, statistically significant reduction in the incidence of dialysis in the first week post-transplant—the primary endpoint of this study.
[0254]Clinically meaningful reductions in the ...
example 3
Dialysis Analysis in Phase II Study
[0257]Objective: Dialysis has a pharmacoeconomic impact as well as health consequences. Therefore, a comparison of the number of dialyses from day 0 to day 180 between treatment groups is of interest.
[0258]Statistical Methods: to compare between treatment groups (I5NP, Placebo)[0259]Zero-inflated Poisson regression model (ZIP), which is a statistical model based on a Poisson probability distribution that allows for frequent zero-valued observations. The dialysis count per patient variable is of such nature.[0260]Sensitivity analysis: Non-parametric test: Wilcoxon and Median[0261]Descriptive statistics: using counts, mean, standard deviation (SD), median, minimum and maximum
[0262]The analysis was not limited to the first course only or conditioned on DGF event.
[0263]Analysis scheme: The analysis was performed on the mitt(EE) population.[0264]Over all patients[0265]Donor age>35 years patient group[0266]Donor age>45 years patient group
[0267]Study Dura...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com