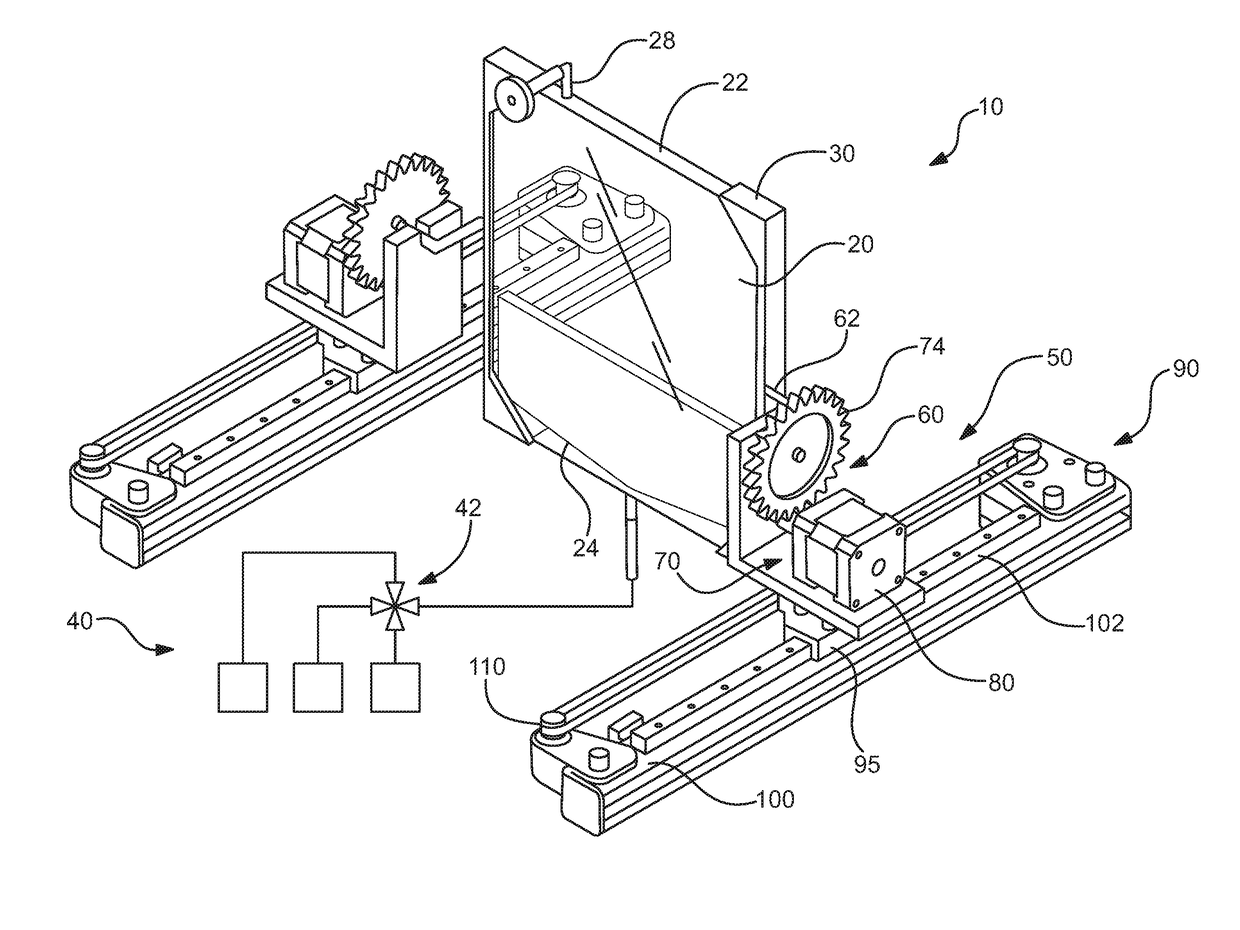
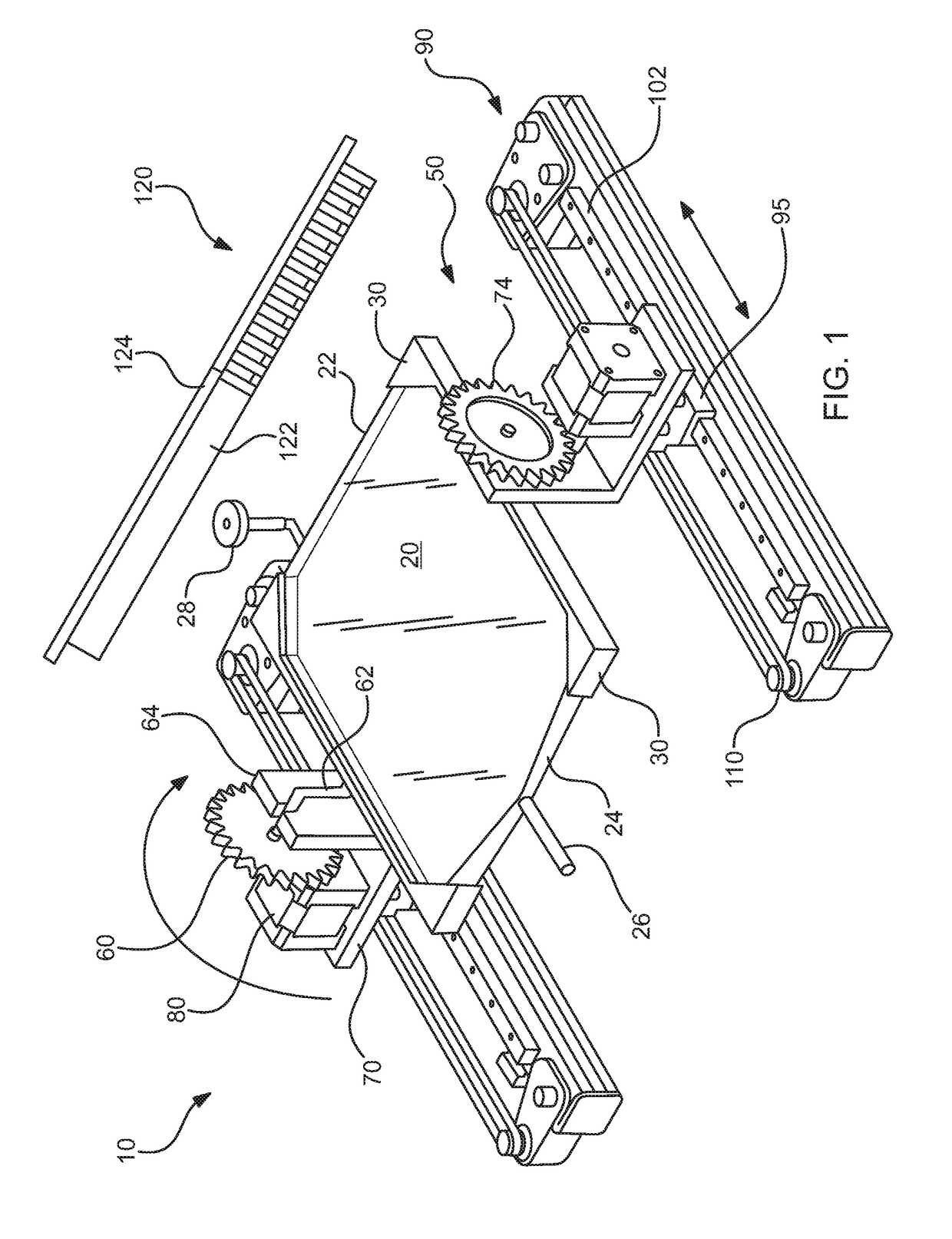
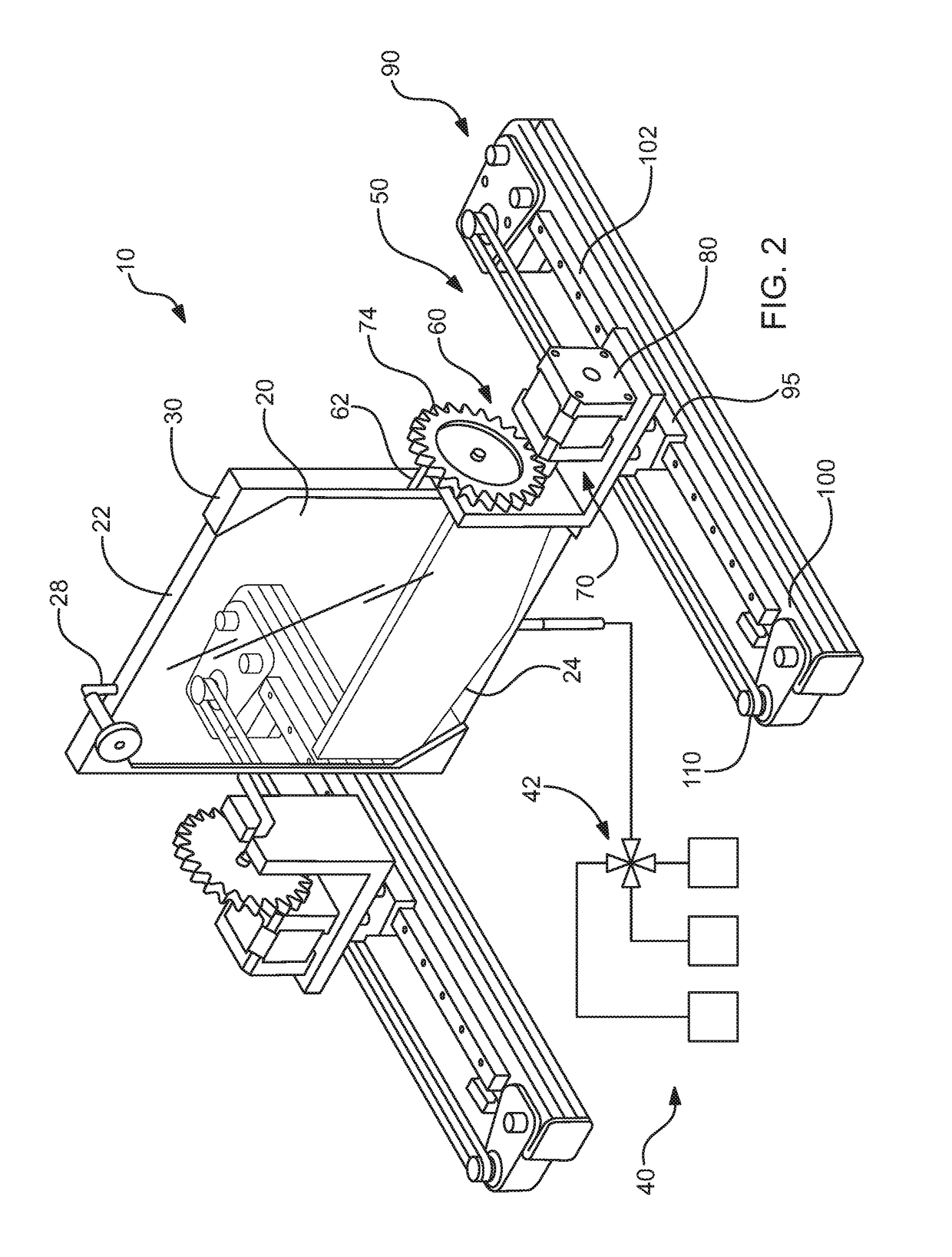
Apparatus and method for immunomagnetic cell separation
a technology of immunomagnetic cell and apparatus, applied in the field of magnetic separation device, can solve problems such as difficulty in obtaining sufficient enriched target populations
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
The Effect of Gravity on Entrapment of RBC During Magnetic Separation of Target Cells
[0080]For these experiments, CD3+ cells from a CEM cell line (T-lymphoblast, CD3+) were labeled at 108 cells / ml with biotinylated anti-CD3 mouse mAb (Tonbo biotech, San Diego, Calif.), unbound mAb was removed by washing and centrifugation, and cells were magnetically labeled with streptavidin ferrofluid by routine methods. All experiments were done at room temperature. To simulate separations from buffy coats, labeled cells were mixed with fresh bovine erythrocytes in a proprietary buffer. Those RBCs had been recovered from the pellet of centrifuged bovine blood that had been treated with EDTA. Contamination levels of RBC were simulated at 10, 20 and 30% hematocrit. Final volumes for these experiments were 2 ml and separations were done in acrylic cuvettes (1.0×1.0×4.0 cm). From the input numbers of target cells, the geometry of separation and the collection surface area used in these experiments, i...
example 2
The Effect of Gravity on RBC Contamination of CD3+ Cells Recovered from a Buffy Coat
[0086]As noted above, when target cells are isolated from buffy coats, ridding the product of RBCs can require multiple cycles of re-suspension and magnetic separation. To determine whether or not the methods disclosed, specifically separating against gravity and WWOR, are beneficial to the process of recovering CD3+ target cells from a buffy coat, blood of a young normal male was obtained and processed as described in Example 1.
[0087]The buffy coat total white blood cell content was determined by lysing red blood cells in a small buffy coat sample with distilled water and counting the white blood cells in a hemacytometer. The CD3+ cells in the buffy coat were labeled with biotinylated anti-CD3 mouse mAb, unbound mAb removed by centrifugation and cells magnetically labeled with streptavidin ferrofluid by routine methods. Two magnetically labeled cell samples, in duplicate, were separated against grav...
example 3
Isolation of CD3+ Cells from an Apheresis Product
[0091]Starting with an apheresis product of 1010 cells in a volume of about 1.0 L, platelets were initially removed as they are known to interfere with immunomagnetic separations. This can be accomplished by centrifugation or by well-known methods employing membrane technology (e.g., spinning-membrane filtration, Fresenius Kabi AG and Fresenius Kabi USA). The cells were then brought to a volume of approximately 80 ml with an appropriate buffer containing FcR blocking reagents that do not react with common-capture agents, DNAse, protein (e.g., human serum albumin), and other proprietary reagents known to reduce non-specific binding. This mixture was then introduced into the chamber while it was positioned vertically.
[0092]To the 80 ml cell suspension, an anti-CD3-conjugated magnetic particle (for direct labeling) or a common-capture magnetic particle (for indirect labeling) can be added from their respective vessels. Preferably, an ind...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com