Bi-directional bus circuitry executing bi-directional data transmission while avoiding floating state
a bus circuit and bi-directional technology, applied in the field of bi-directional bus circuitry, can solve the problems of increasing the time of signal transmission over the bus line, constant current, wasteful consumption, circuit breakage in the input and output buffers of the circuit blocks connected to the bus node, etc., to increase suppress the parasitic capacitance of the data bus
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
[First Embodiment]
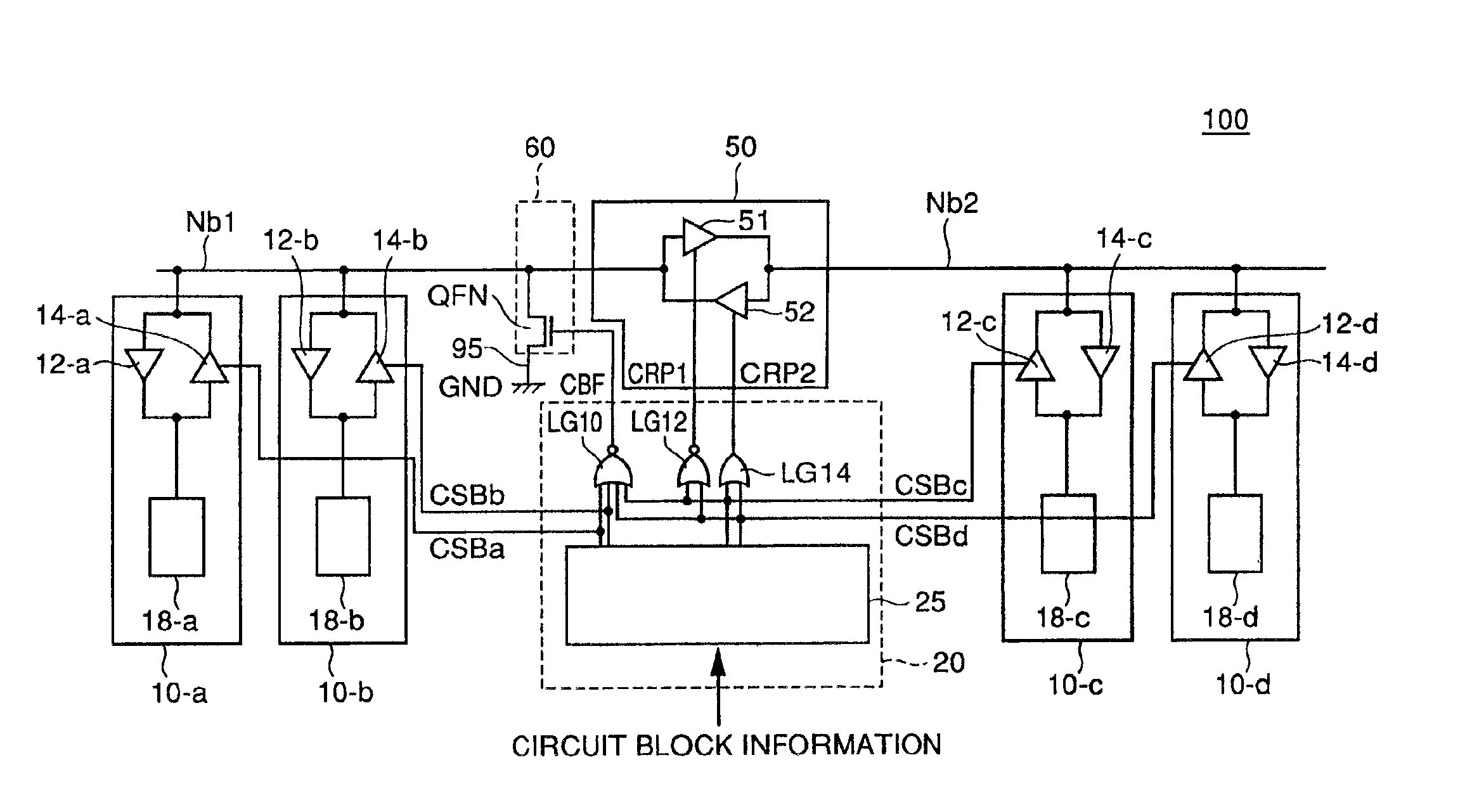
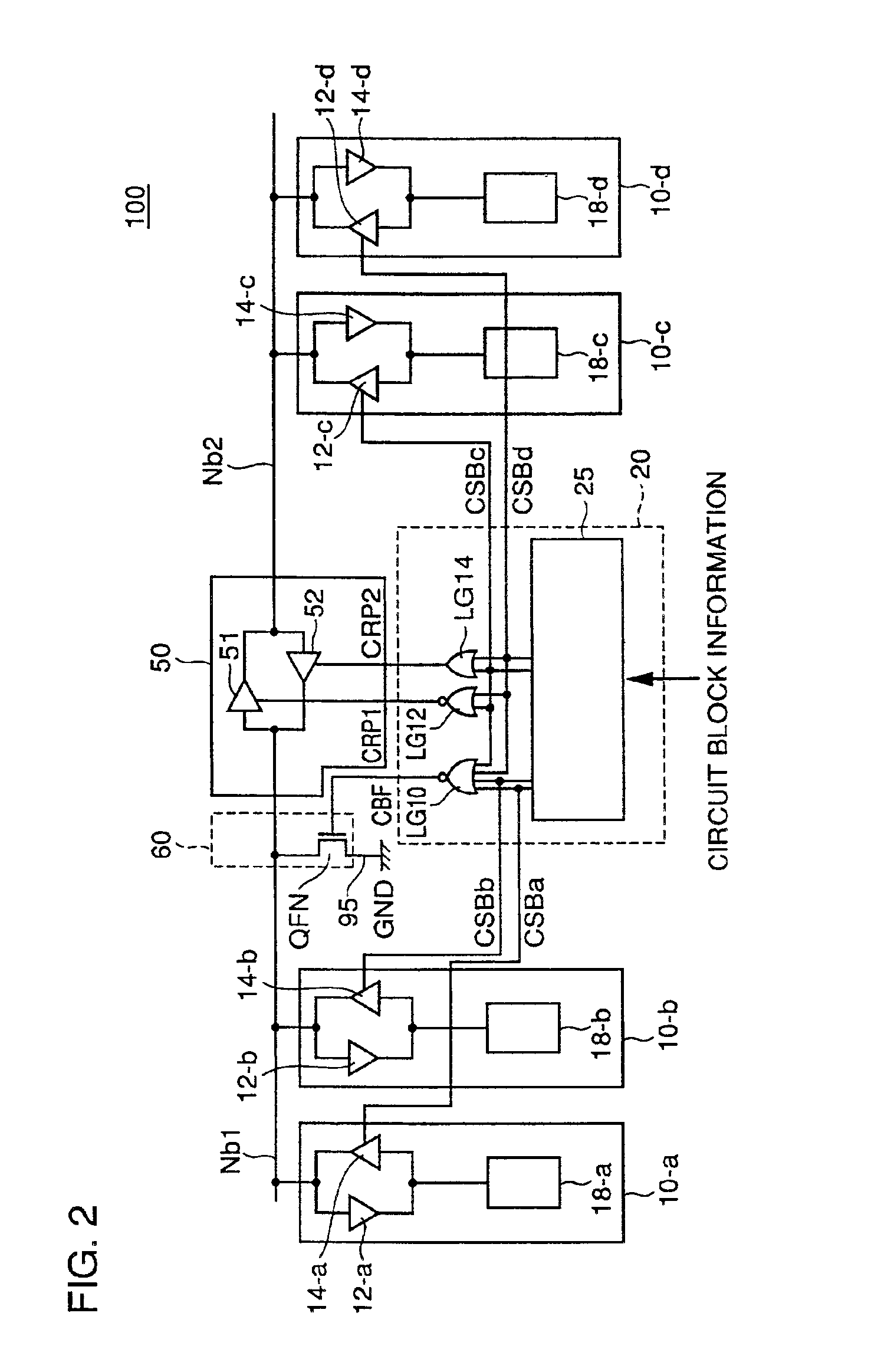
Referring to FIG. 2, the bi-directional bus circuitry 100 in accordance with the first embodiment includes a data bus divided into bus nodes Nb1 and Nb2 by a repeater circuit 50 for bi-directional signal transmission between bus nodes Nb1 and Nb2, a bus potential fixing circuit 60 for fixing the potential level of bus node Nb1 when the data bus is not used, and an arbiter circuit 20 controlling the operations of repeater circuit 50 and bus potential fixing circuit 60, based on circuit block information designating the circuit block on which data input / output is to be executed.
Bi-directional bus circuitry 100 transmits the data input to / output from circuit blocks 10-a to 10-d, by the data bus divided into bus nodes Nb1 and Nb2. Here, the four circuit blocks 10-a to 10-d are examples only, and the configuration of bi-directional bus circuitry 100 in accordance with the first embodiment is applicable to an arbitrary number of circuit blocks, as will be apparent from t...
second embodiment
[Second Embodiment]
The second embodiment is directed to a configuration of a bi-directional bus circuitry when provision of a number of repeater circuits is necessary as the data bus becomes longer.
Referring to FIG. 5, a bi-directional bus circuitry 200 in accordance with the second embodiment includes, in addition to repeater circuit 50, repeater circuits 70 and 90. Thus, the data bus of the bi-directional bus circuitry 200 comes to be divided into four bus nodes, that is, bus nodes Nb1 to Nb4.
Repeater circuits 70 and 90 have similar configurations as repeater circuit 50 described with the reference to the first embodiment. More specifically, repeater circuits 70 and 90 include tristate buffers 71 and 91 transmitting a signal in the same direction as tristate buffer 51, and tristate buffers 72 and 92 transmitting a signal in the same direction as tristate buffer 52, respectively.
Repeater circuits 70 and 90 are controlled by the repeater control signals CRP1 and CRP2 common to repea...
third embodiment
[Third Embodiment]
In the third embodiment, a configuration will be described in which each repeater circuit is used as a latch circuit when the data bus is not used, so as to enable fixing of the potential level when the data bus is not used, without providing any potential fixing circuit.
Referring to FIG. 7, a bi-directional bus circuitry 300 in accordance with the third embodiment is different from the bi-directional bus circuitry 100 in accordance with the first embodiment in that an arbiter circuit 320 is provided in place of arbiter circuit 20, and that bus potential fixing circuit 60 is not provided.
Arbiter circuit 320 has logic gates LG12 and LG16 generating repeater control signals CRP1 and CRP2, respectively. Logic gate LG12 provides the repeater control signal CRP1 as a result of an NOR logic operation of circuit block designating signals CSBc and CSBd. Logic gate LG16 provides the repeater control signal CRP2 as a result of an NOR logic operation of circuit block designat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com