Indirect measurement of tissue analytes through tissue properties
a tissue analyte and indirect measurement technology, applied in the field of biomedical testing, can solve the problems of limited technology state and complex alterations in the measured analytical signal, and achieve the effect of limiting the technology state and improving the accuracy and precision of noninvasive analyte measuremen
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
third embodiment
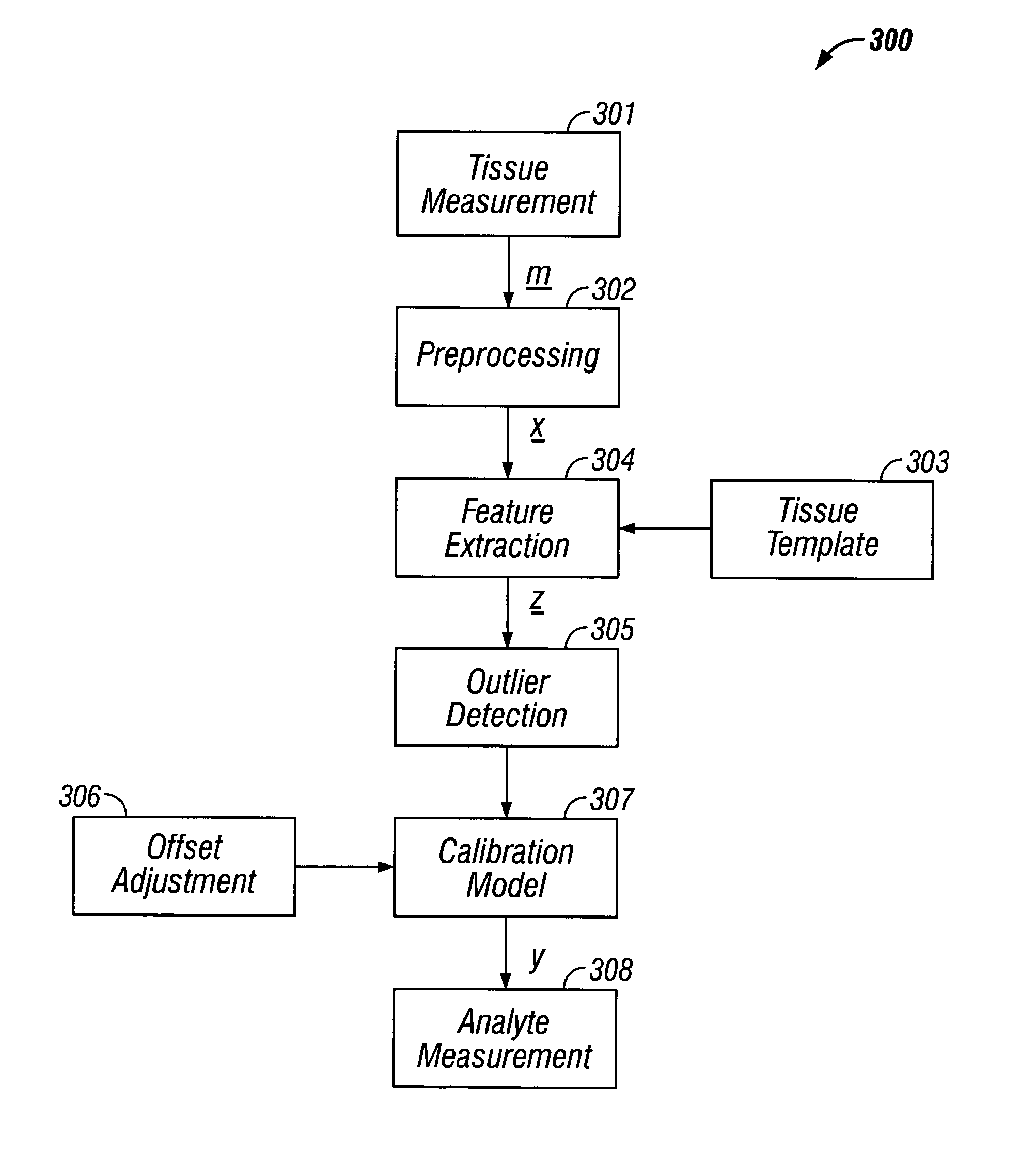
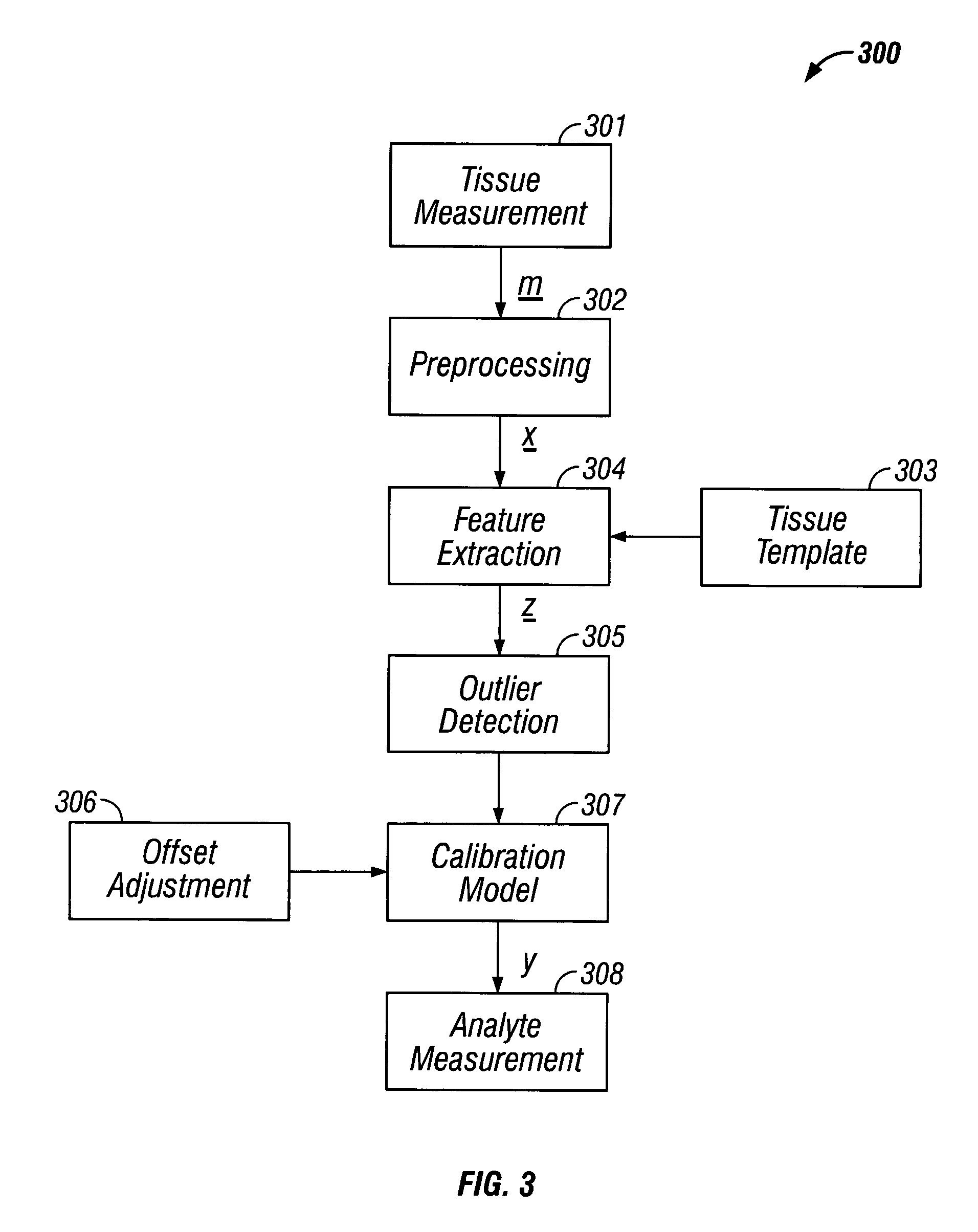
where y is the reference glucose concentration. In the third embodiment, when f(·) and g(·) are determined to be linear over the range of measurement, equation #6 reduces to:
ŷ=xpF−(mszG+mi)+b; (8)
where FεNx1 and GεMx1. In this embodiment, F and G are determined separately as described above using linear methods of calibration. This final realization of the supplemental use of features for glucose measurement is the preferred method.
[0151]In the second category of measurement, the extracted features are used to indirectly measure glucose through:
ŷ=(msg(z)+mi)+b; (9)
where g: M→1 is a model used to map the features to a variable correlated to the reference glucose level and ms and mi are slope and intercepts used to convert g(z) to the correct units. Determination of g(·) is through an exemplary set (calibration set) of tissue measurements, extracted features and reference glucose concentrations (from blood or interstitial measurements). A sub-set of features is selected based on the...
example 1
Bioimpedance and Bioelectrical Response
[0157]Bioimpedance and bioelectrical response measurements have been clearly demonstrated as an effective means for quantifying the water levels in various compartments of the body [see Siconolfi, supra]. As in the earlier discussion, a bioimpedance or bioelectrical response based meter is used as the apparatus shown in FIG. 2, with the tissue measurement and selected features including intracellular and extracellular fluid levels. The tissue template and related bias measurement are taken from the first bioimpedance tissue measurement of a particular measurement period (e.g., one day). A simple model is constructed via multiple linear regression on a calibration set to relate the two features to the reference glucose concentration. Non-invasive glucose measurement is made by first collecting a tissue template (the first tissue measurement of the day) and associated bias measurement (a single reference glucose concentration determined via an an...
example 2
Near-Infrared Diffuse Reflectance Spectroscopy
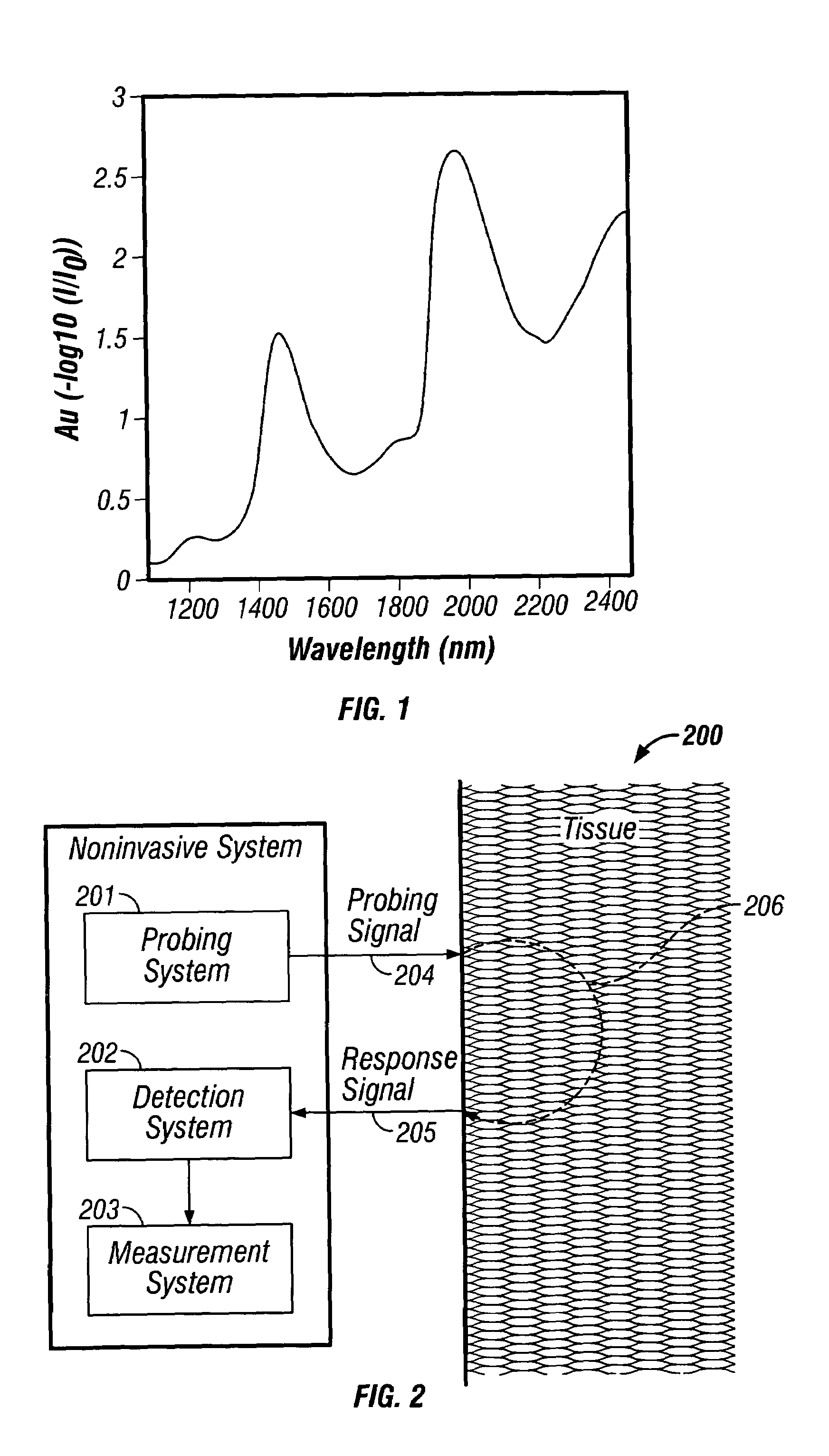
[0159]A calibration set of paired data points was collected on a particular subject whose glucose concentration spanned the range 70–350 mg / dL. Each data point included a near-infrared absorbance spectrum of the forearm and a reference glucose concentration determined from a blood draw and analysis. The near-infrared spectra were collected using a custom built scanning near-infrared spectrometer that collected intensity spectra in diffuse reflectance over the wavelength range 1100–1950 nm. The spectral sampling interval was 1 nm and the signal-to-noise ratio at the peak intensity was approximately 90 dB. The detector used in the study was Indium-Gallium-Arsenide (InGaAs) and the optical configuration consisted of a simple fiber-optic interface to the skin with a small (<2 mm) distance between the illumination and detection fibers. Reference spectra were recorded before each sample measurement by scanning an 80% SPECTRALON reflectance mat...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| wavelength range | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com