Monopolar fuel cell stack coupled together without use of top or bottom cover plates or tie rods
a fuel cell and stack technology, applied in the field of fuel cells, can solve the problems of dismantling the entire stack, achieve the effects of improving power density, simple troubleshooting and assembly, and improving the commercialization of portable direct methanol fuel cell power sources
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
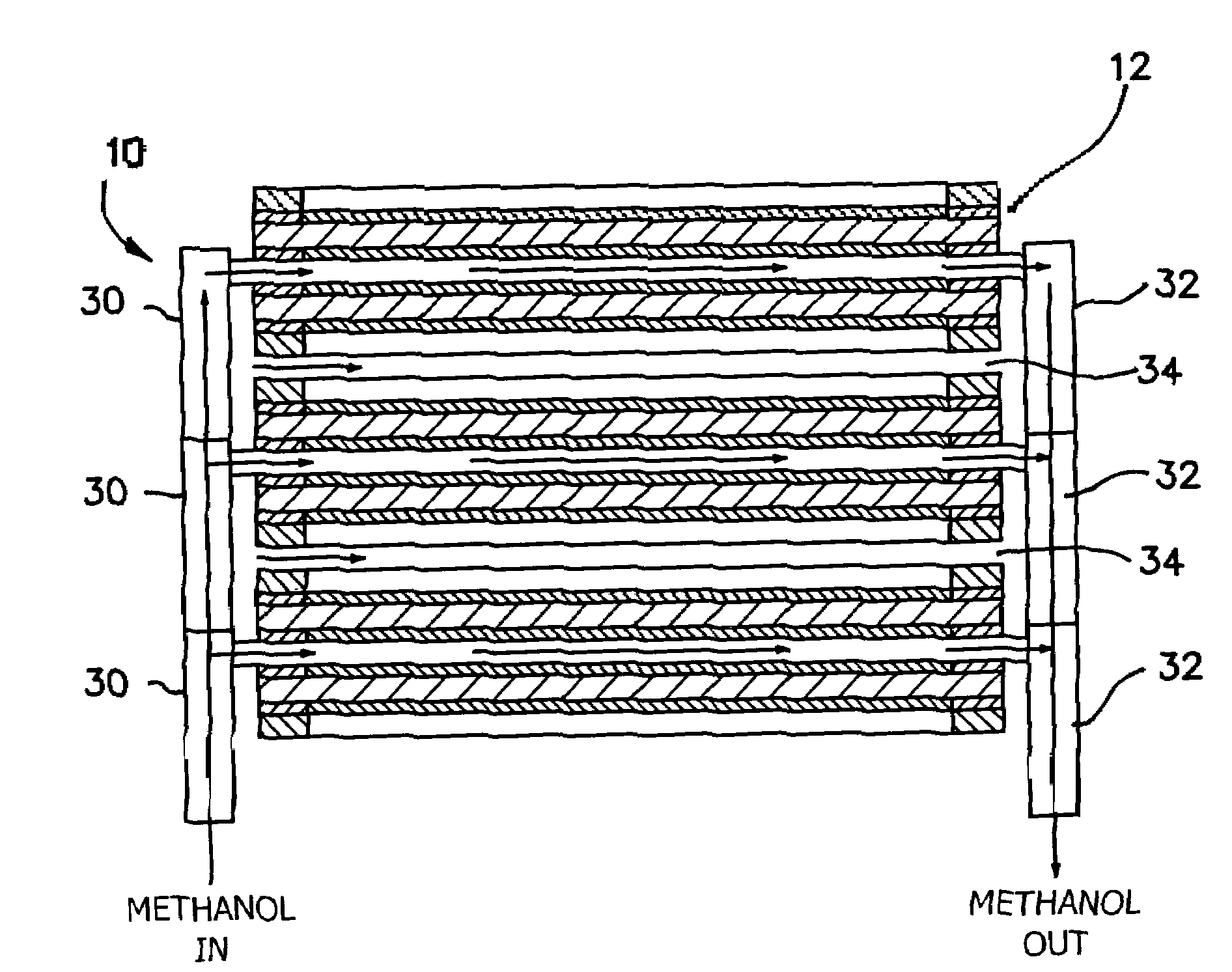
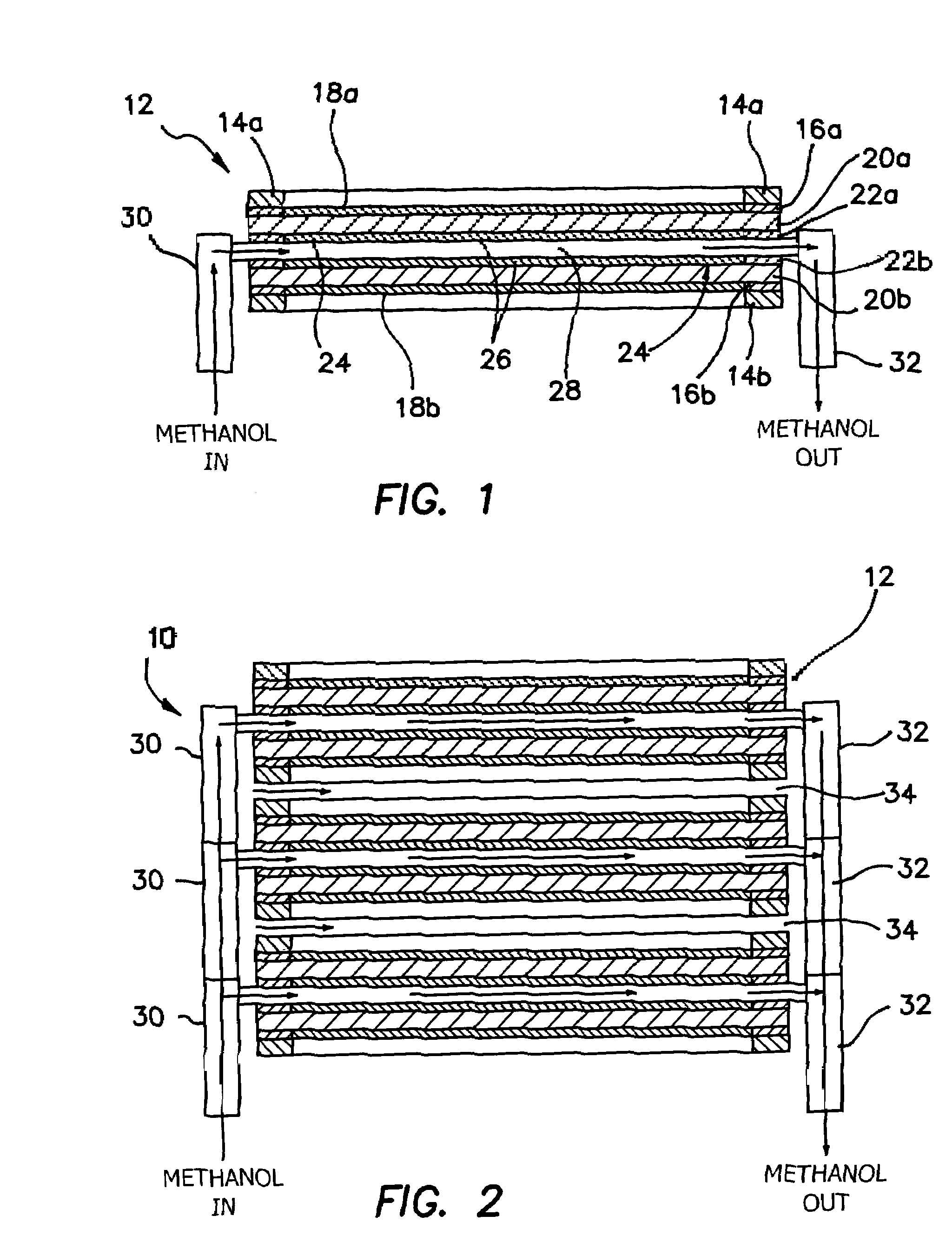
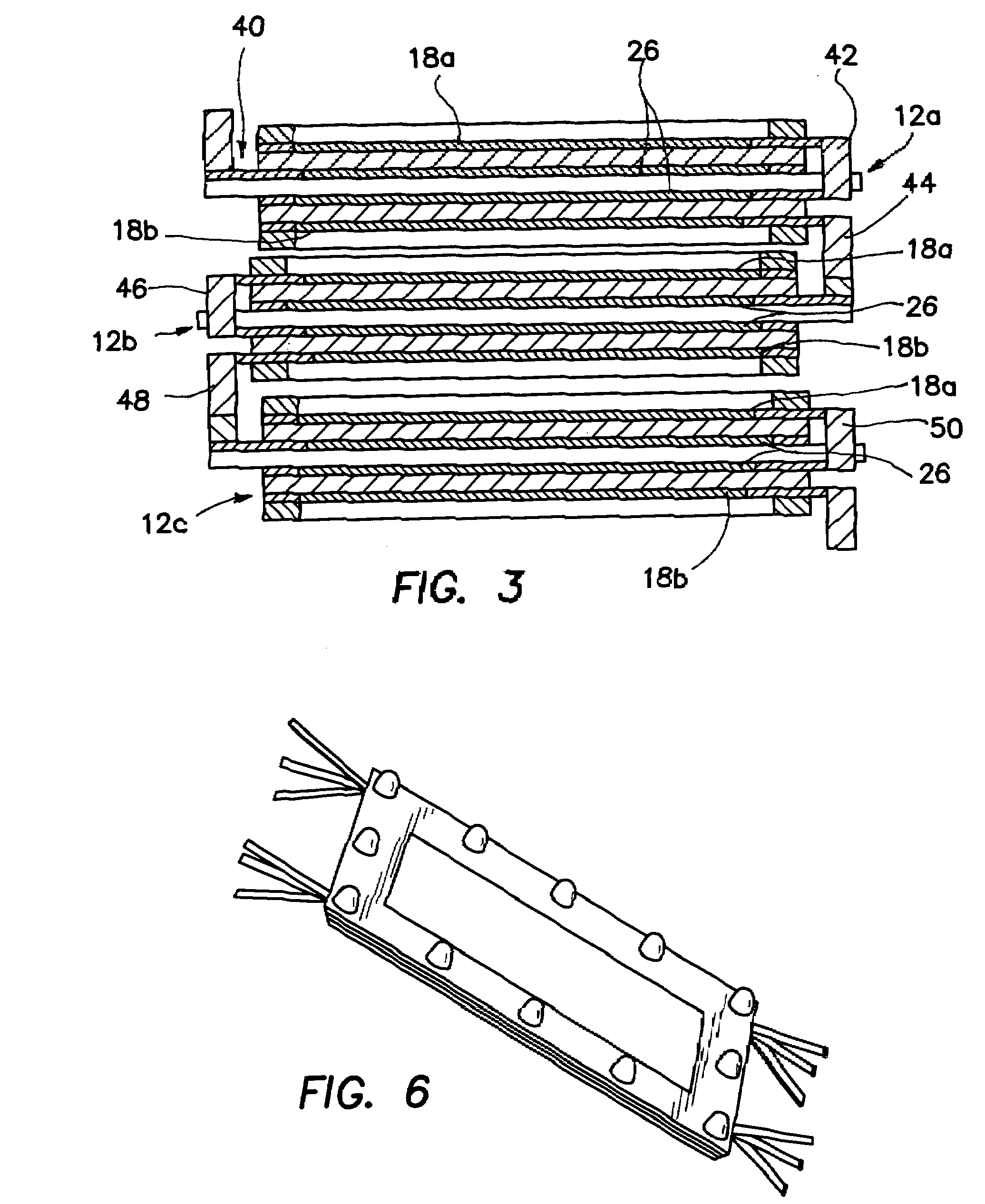
[0024]The invention is a stack 10 as shown in cross-sectional side view in FIG. 2 used in a methanol fuel cell, although it could be used with other types of fuels as well. Such a methanol fuel cell is described in detail in Surampudi et.al., “Direct Methanol Feed Fuel Cell and System,” U.S. Pat. No. 6,303,244 (2001), U.S. Pat. No. 5,599,638 (1997), and U.S. Pat. No. 6,485,851 (2002), each of which are incorporated herein by reference. The stack design of the invention offers a two-to-three fold improvement in power densities, suitable for manufacturing, uses inexpensive plastic materials, and is straightforward to troubleshoot and assemble. Such a stack design brings portable direct methanol fuel cell power sources one big step closer to commercialization. The design achieves the functions and performance of a conventional stack and has the potential to be just 30% of the weight of the conventional bipolar stack.
[0025]An “all-plastic” monopolar stack design is disclosed. By departi...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| power output | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| electrical current | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| chemical reaction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com