Solid-state imaging device, method of driving the device, and camera system with varied timing of sampling period for sampling a bias voltage during pixel readout
a solid-state imaging and bias voltage technology, applied in the field of solid-state imaging devices, can solve the problems of reducing the image quality of the image, affecting the image quality, so as to prevent noise and reduce the image quality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
1. First Embodiment
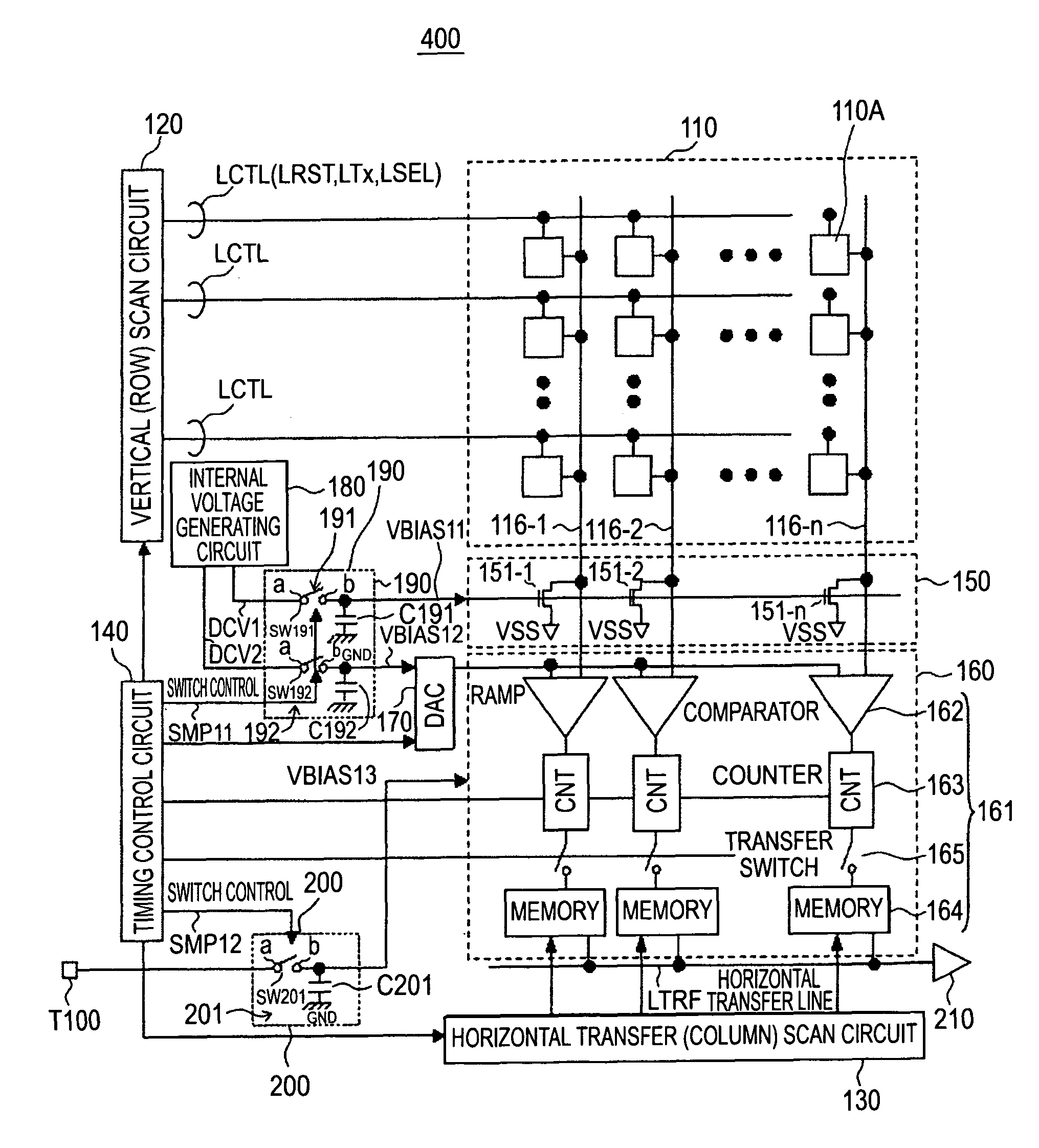
[0065]FIG. 3 is a block diagram showing an exemplary configuration of a solid-state imaging device (CMOS image sensor) having column-parallel ADCs incorporated therein according to an embodiment of the invention.
[0066]FIG. 4 is a block diagram which more specifically shows major parts of the solid-state imaging device (CMOS image sensor) having column-parallel ADCs incorporated therein according to the first embodiment shown in FIG. 3, the illustrated parts including a pixel section and a column circuit.
[Exemplary General Configuration of Solid-State Imaging Device]
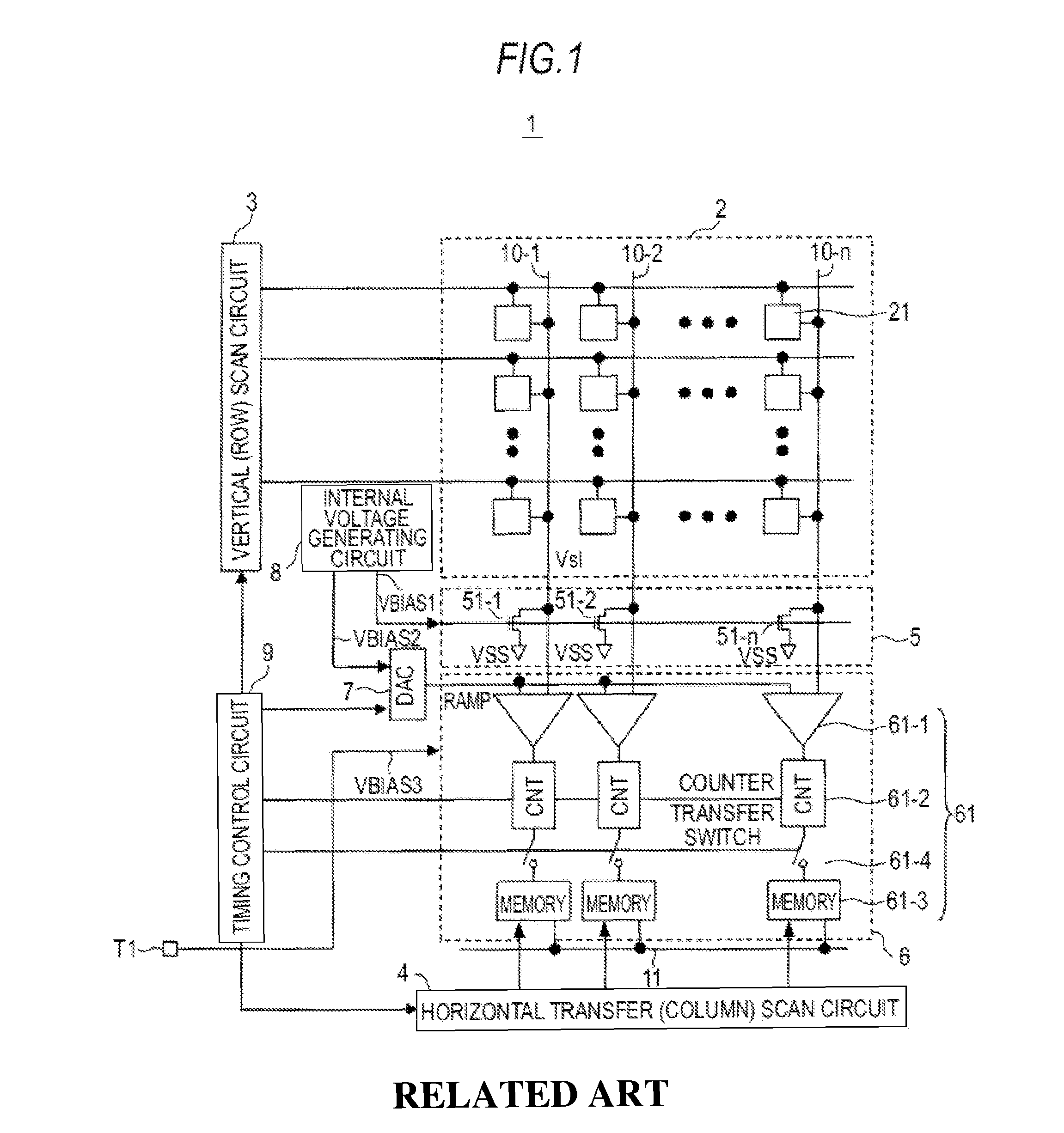
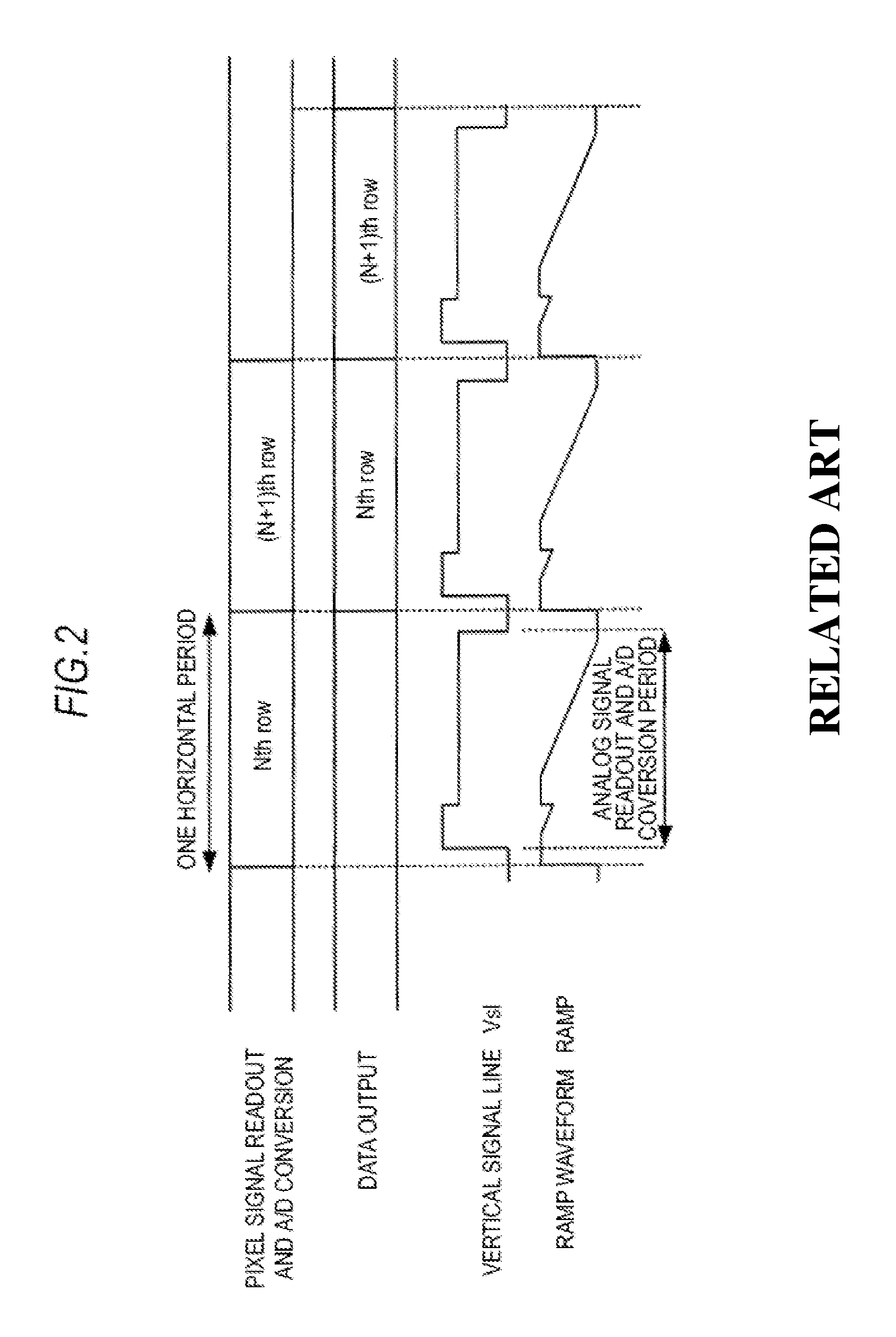
[0067]As shown in FIGS. 3 and 4, a solid-state imaging device 100 includes a pixel section 110, vertical scan circuit (row scan circuit) 120, a horizontal transfer scan circuit (column scan circuit) 130, and a timing control circuit 140.
[0068]Further, the solid-state imaging device 100 includes a load circuit 150 serving as a column circuit, a column-parallel processing section 160 which is a group of A...
second embodiment
2. Second Embodiment
[0233]FIG. 9 is a block diagram of a solid-state imaging device (CMOS image sensor) 100A having column-parallel ADCs in FIG. 3 according to a second embodiment of the invention, the diagram showing major parts of the device including a pixel section and a column circuit.
[0234]The solid-state imaging device 100A according to the second embodiment is different from the solid-state imaging device 100 according to the first embodiment in the following points.
[0235]In the solid-state imaging device 100 according to the first embodiment, the sample / hold portion 191 of the sample / hold circuit 190 is provided to supply a common bias voltage to the load circuit 150.
[0236]On the contrary, the solid-state imaging device 100A according to the second embodiment includes individual sample / hold portions 191A-1 to 191A-n provided in one-to-one association with load MOS transistors 151-1 to 151-n of a load circuit 150A.
[0237]The sample / hold portion 191A-1 includes a sampling swit...
third embodiment
3. Third Embodiment
[0266]FIG. 11 is a diagram showing an exemplary configuration of a camera system employing a solid-state imaging device according to a third embodiment of the invention.
[0267]As shown in FIG. 11, a camera system 400 includes an imaging device 410 which may be a solid-state imaging device 100 or 100A according to the above-described embodiments.
[0268]The camera system 400 includes an optical system for guiding incident light to a pixel region of the imaging device 410 (for forming an image of an object). For example, the optical system may be a lens 420 which forms an image of incident light (image light) on an imaging surface.
[0269]Further, the camera system 400 includes a driving circuit (DRV) 430 for driving the imaging device 410 and a signal processing circuit (PRC) 440 for processing signals output from the imaging device 410.
[0270]The driving circuit 430 includes a timing generator (not shown) generating various timing signals including a start pulse and a c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com