Structure of power transmission apparatus
a technology of power transmission apparatus and structure, which is applied in the direction of engine starters, machines/engines, and gears, etc., can solve the problems of slipping of the endless transmitting member on each pulley, difficulty in keeping the output, and difficulty in increasing the tension of the endless transmitting member to a required degree, so as to minimize the slippage increase the tension, and increase the tension of the endless transmitting member
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
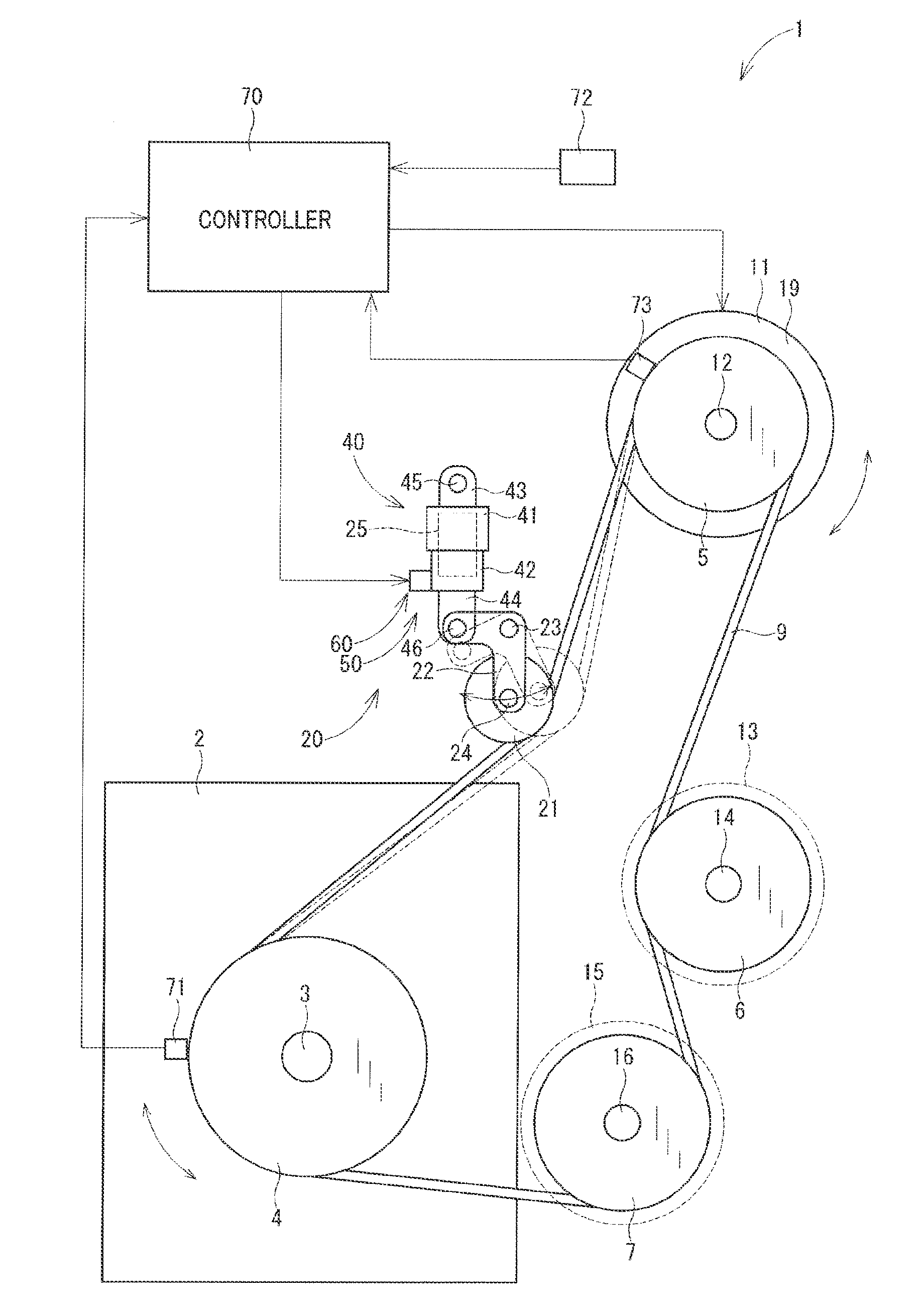
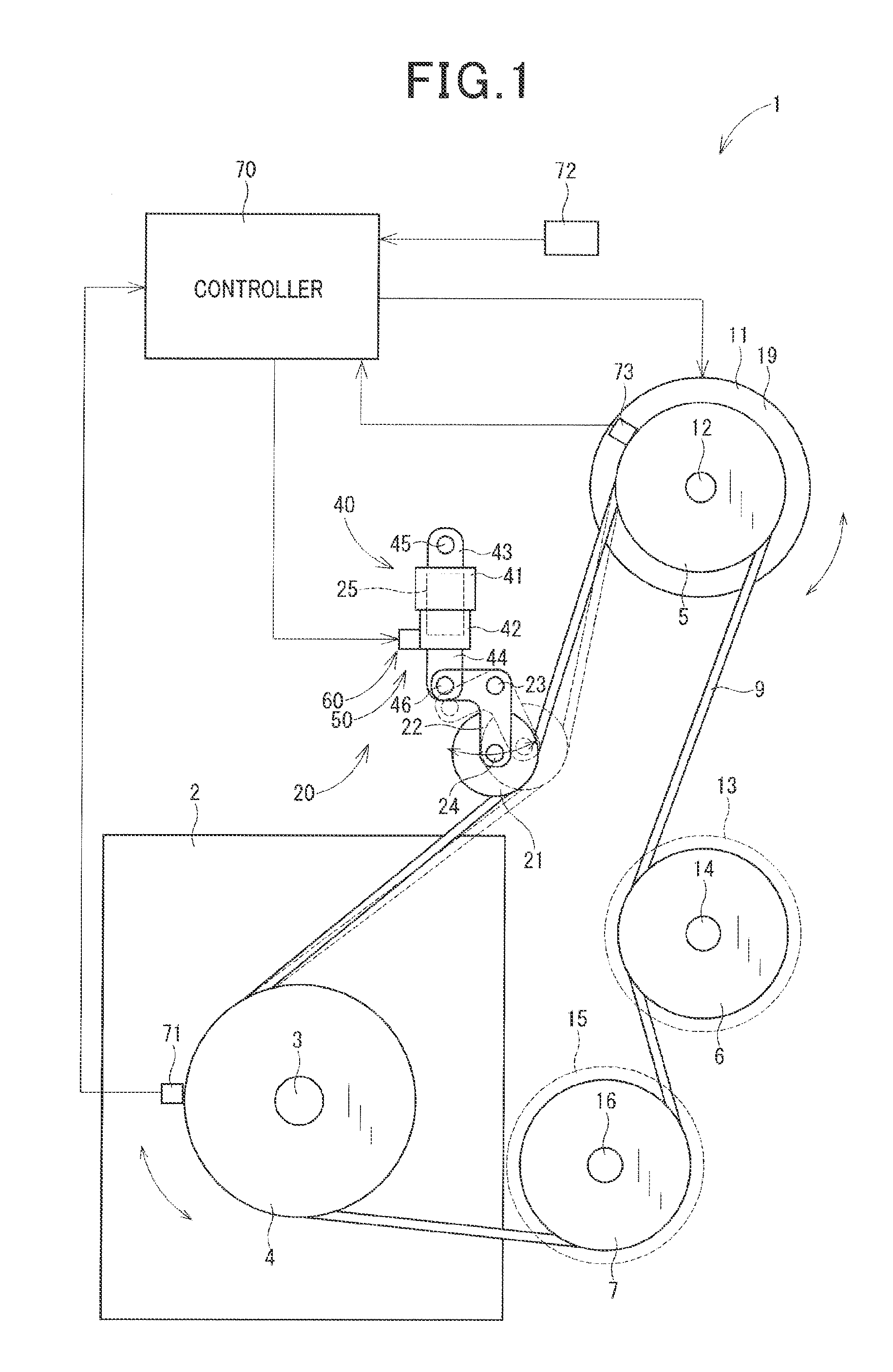
[0026]FIG. 1 illustrates a power transmission system 1 according to the first embodiment. The power transmission system 1, as referred to herein, is installed in an automotive vehicle, not shown, which is equipped with an internal combustion engine 2. The power transmission system 1 works to transmit output power (i.e., torque), as produced by the engine 2, to a given accessory 11 and other accessories 13 and 15 mounted in the vehicle. The accessories 11, 13, and 15, as referred to herein, are auxiliary electric or mechanical devices which are supplied with or transmit power or torque from or to the internal combustion engine 2. The given accessory 11 will also be referred to below as a first auxiliary device. The accessories 13 and 15 will also be referred to below as second auxiliary devices.
[0027]The power transmission system 1 is, as clearly illustrated in FIG. 1, disposed near the engine 2. The power transmission system 1 includes a driving pulley 4, a given accessory pulley 5,...
second embodiment
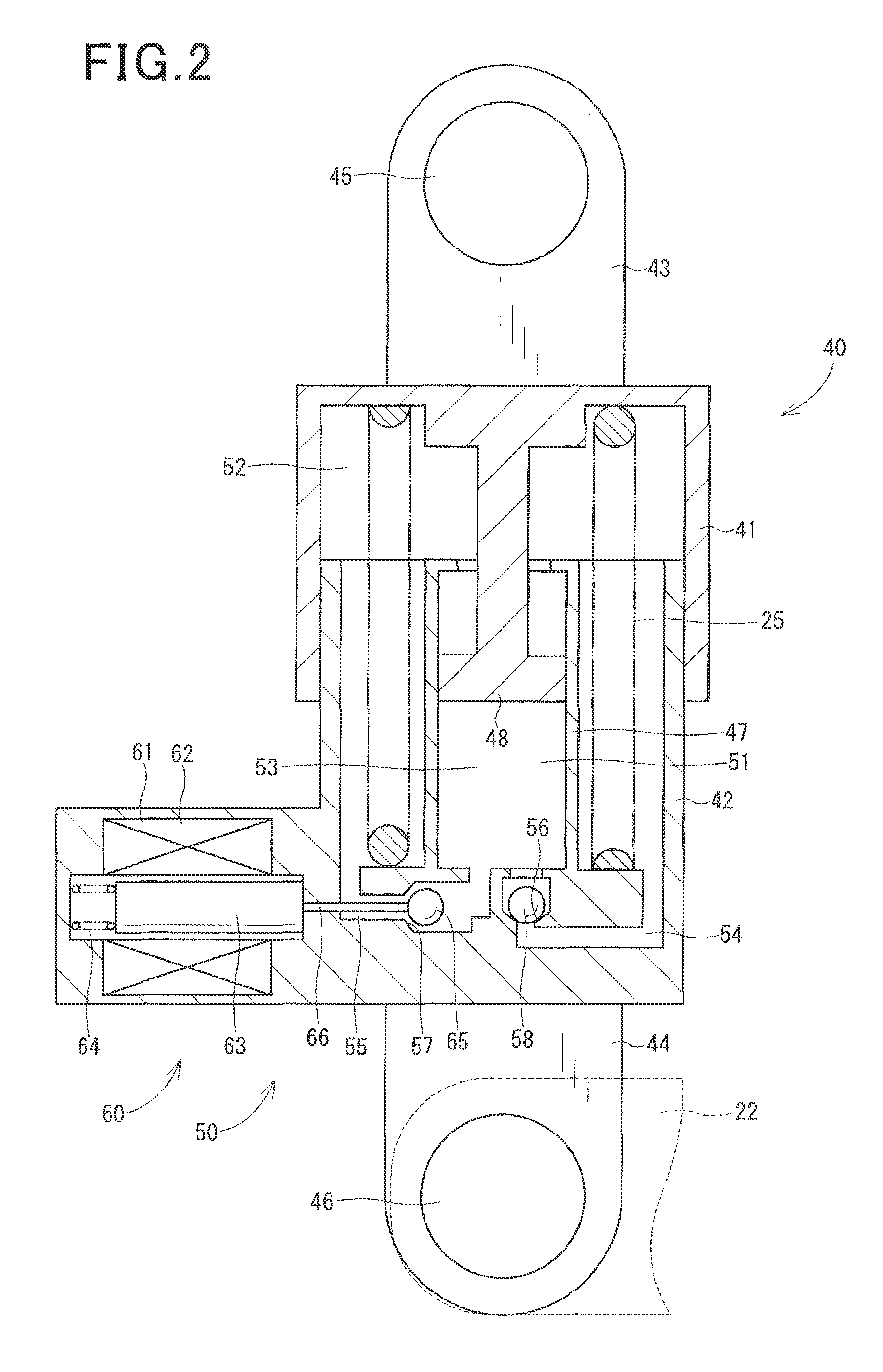
[0111]FIG. 5 illustrates the power transmission system 1 according to the second embodiment which is different in physical structure thereof and operation of the reverse rotation step made by the ECU 70 from the first embodiment.
[0112]The power transmission system 1 is also equipped with a position sensor 74 installed on the tensioner body 40. The position sensor 74 measures the distance between the upper body 41 and the lower body 42, that is, an extended / contracted position of the tensioner body 40. The position sensor 74 outputs a signal indicative of the position of the tensioner body 40 to the ECU 70. The ECU 70 analyzes the output from the position sensor 74 and determines the extended / contracted position of the tensioner body 40.
[0113]The prediction of the reversing timing, as made by the ECU 70, will be described below with reference to FIG. 6.
[0114]FIG. 6 is a flowchart of a sequence of logical steps or reversing timing determination program executed by the ECU 70 when or a...
third embodiment
[0133]The power transmission system 1 according to the third embodiment will be described below which is different in how the ECU 70 determines the reversing timing from the first embodiment. Other arrangements are identical, and explanation thereof in detail will be omitted here.
[0134]When it is required to predict the reversing timing when the drive shaft 3 is expected to reverse, the ECU 70 analyzes the output from the angular position sensor 73 to determine the angular position of the given accessory pulley 5 and calculates the reversing timing as a function of the angular position of the given accessory pulley 5 and a target angular position θISG of the given accessory pulley 5 to be achieved in the reverse rotation control step. The target angular position θISG is given by
θISG=(Lb−La) / 2πRISG (5)
[0135]Specifically, when the reversing timing is reached, that is, the angular position of the given accessory pulley 5, as measured by the position sensor 73, reaches the target angul...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com