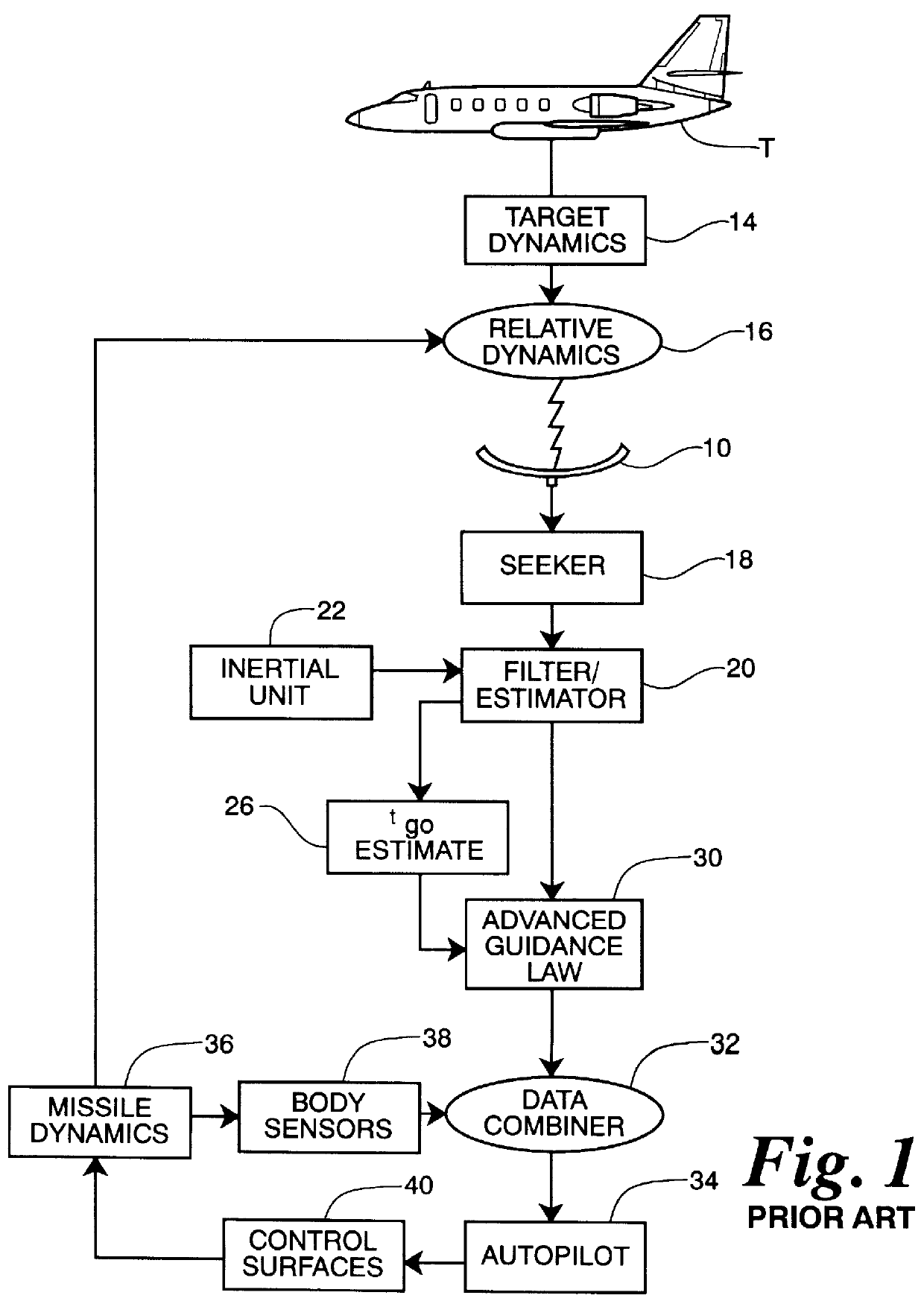
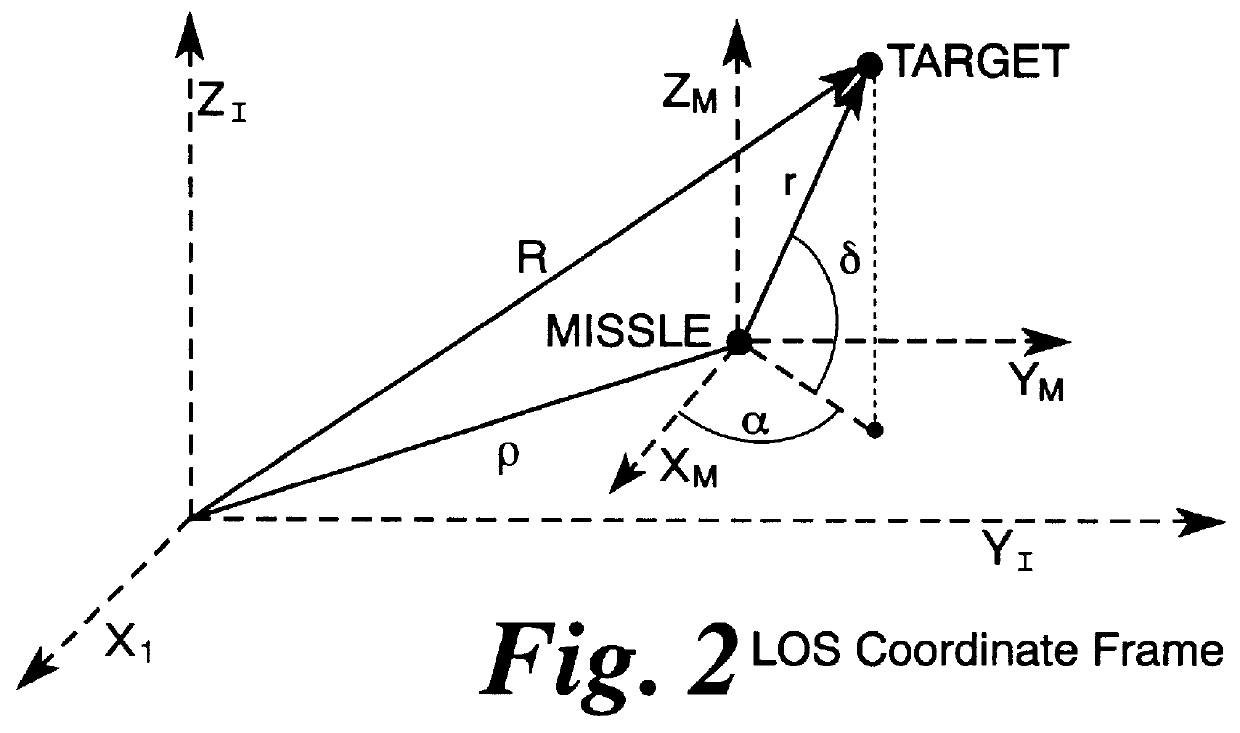
Adaptive matched augmented proportional navigation
a proportional navigation and adaptive matching technology, applied in the field of missile guidance, can solve the problem of inability to obtain a consistent accurate estimate of t.sub.go
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
The invention is disclosed in a WL / MN Interim Report dated Dec 1993, to the advanced medium range air-to-air missile (AMRAAM) System Program Office, entitled "Bank-To-Turn In-House Control Study", with limited distribution authorized for Dec. 17, 1993, and in a paper entitled "Adaptive Matched Augmented Proportional Navigation" which is in the restricted Proceedings of the AIAA Missile Sciences Conference, Monterey, Calif., Nov 1994. Copies of the report and paper are included herewith as part of the application as filed, and are hereby incorporated by reference.
Perhaps the most challenging of all guidance and control problems is that of a modern tactical air-to-air missile in pursuit of a highly maneuverable aircraft. The problem consists of the estimation of target motion, the generation of guidance commands to optimally steer the missile toward target intercept, and the control of the coupled, nonlinear, multivariable, uncertain dynamics of the air-to-air missile. Each portion of...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com