Packet scheduling based on message length
a packet scheduling and message technology, applied in the field of multi-hop networks, can solve problems such as minimal delays
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
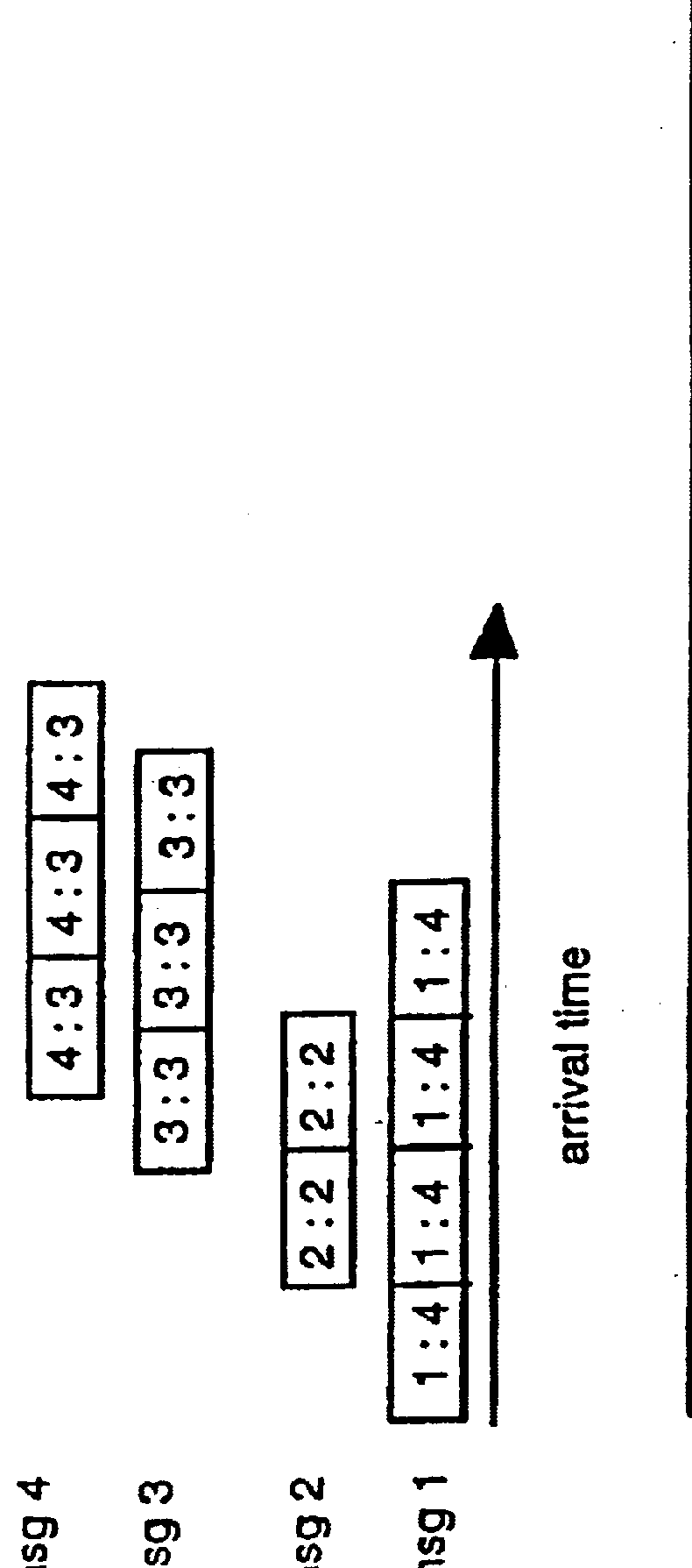
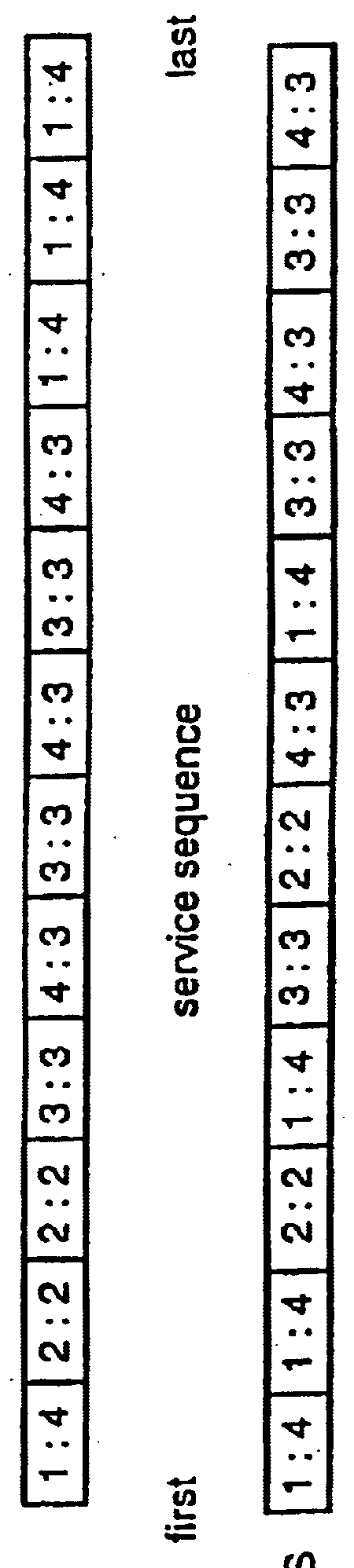
The present invention is a system for scheduling packets in a network. This new mechanism schedules the packets based on the length of the original (application layer) message, with the objective of reducing end-to-end message delays.
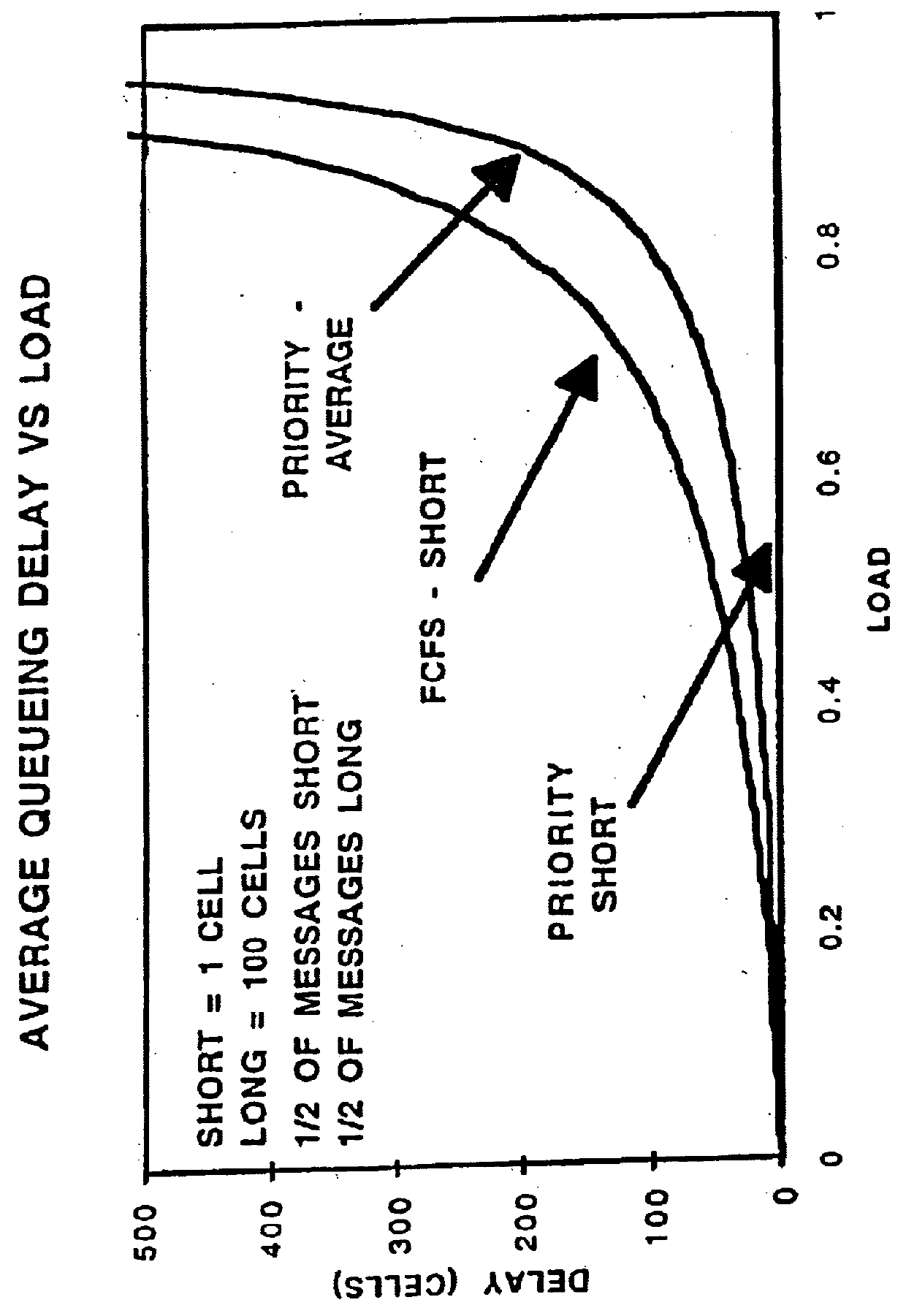
In considering the scheduling of messages at a single node, it is clear that when message sizes vary widely the scheduling of messages based on their size reduces average message delays considerably. As an example, in FIG. 1 we show the average queuing delay for a single node system with messages arriving randomly with exponential inter-arrival times. Half of the arriving messages are one cell in length and the other half are 100 cells in length. Shown in the figure is the queuing delay for two scheduling algorithms. One algorithm serves the messages preemptive priority over the long messages. As can be seen from the figure the average delay for the priority system is much lower than the corresponding delays for the FCFS system.
In general, it is known t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com