Dextromethorphan and an oxidase inhibitor for treating intractable conditions
a technology of oxidase inhibitor and dextromethorphan, which is applied in the field of pharmaceuticals, can solve the problems of intractable coughing, inability to respond to safe, non-steroid, non-addictive medications, and difficulty in treating
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Urinary DM / DR Ratios
Six patients suffering from ALS were administered orally a single 60 mg dextromethorphan dose. Several hours later, a urine sample was collected, and the urine concentrations of dextromethorphan (DM) and dextrorphan (DR) were measured as described below to determine a DM / DR ratio. A low DM / DR ratio indicates that DM is being rapidly oxidized to the DR metabolite in that body of that patient. In a different week, 60 mg of DM and 150 mg of quinidine were orally administered to the same patients, and urinary DM and DR levels and DM / DR ratios were determined again.
DM and DR urinary levels without quinidine were determined by adding 40 mg of thebaine as an internal standard to 1 mL of urine. To this was added 2000 units of betaglucuronidase in 1 mL of acetate buffer (0.1M, pH 5.0). The mixture was incubated for 18 hours at 37.degree. C. and then extracted by adding 1 mL of phosphate buffer (pH 12, 0.10M) and 7 mL of n-butanol / hexane (10:90 v / v). After mixing and centr...
example 2
Plasma Concentrations of DM
Five patients were orally administered 120 mg of DM, with no co-administration of quinidine. Between 10 and 12 hours later, blood was sampled, blood plasma was isolated by centrifugation, and the plasma was analyzed to determine the DM concentration using the thebaine / HPLC method.
During a different week, the same patients were orally administered 60 mg of DM (half the control dosage) and 150 mg of quinidine. Between 10 and 12 hours later, blood was sampled and the plasma was analyzed for DM using thebaine / HPLC.
The results, in Table 2, indicate that quinidine causes a major increase in the concentration of DM in the blood plasma.
TABLE 2 Effects of 150 mg / day quinidine on plasma dextromethorphan levels DEXTRO- DEXTRO- QUINIDINE METHORPHAN METHORPHAN DOSE PATIENT DOSE PLASMA LEVEL (MG / DAY) 1 120 MG / DAY NOT DETECTABLE 0 60 MG ONCE 33 NG / ML 150 2 120 MG / DAY 9.3 NG / ML 0 60 MG ONCE 29.7 NG / ML 150 3 120 MG / DAY NOT DETECTABLE 0 60 MG ONCE 29.0 NG / ML 150 4 120 MG / DA...
example 3
Dose-Response Study
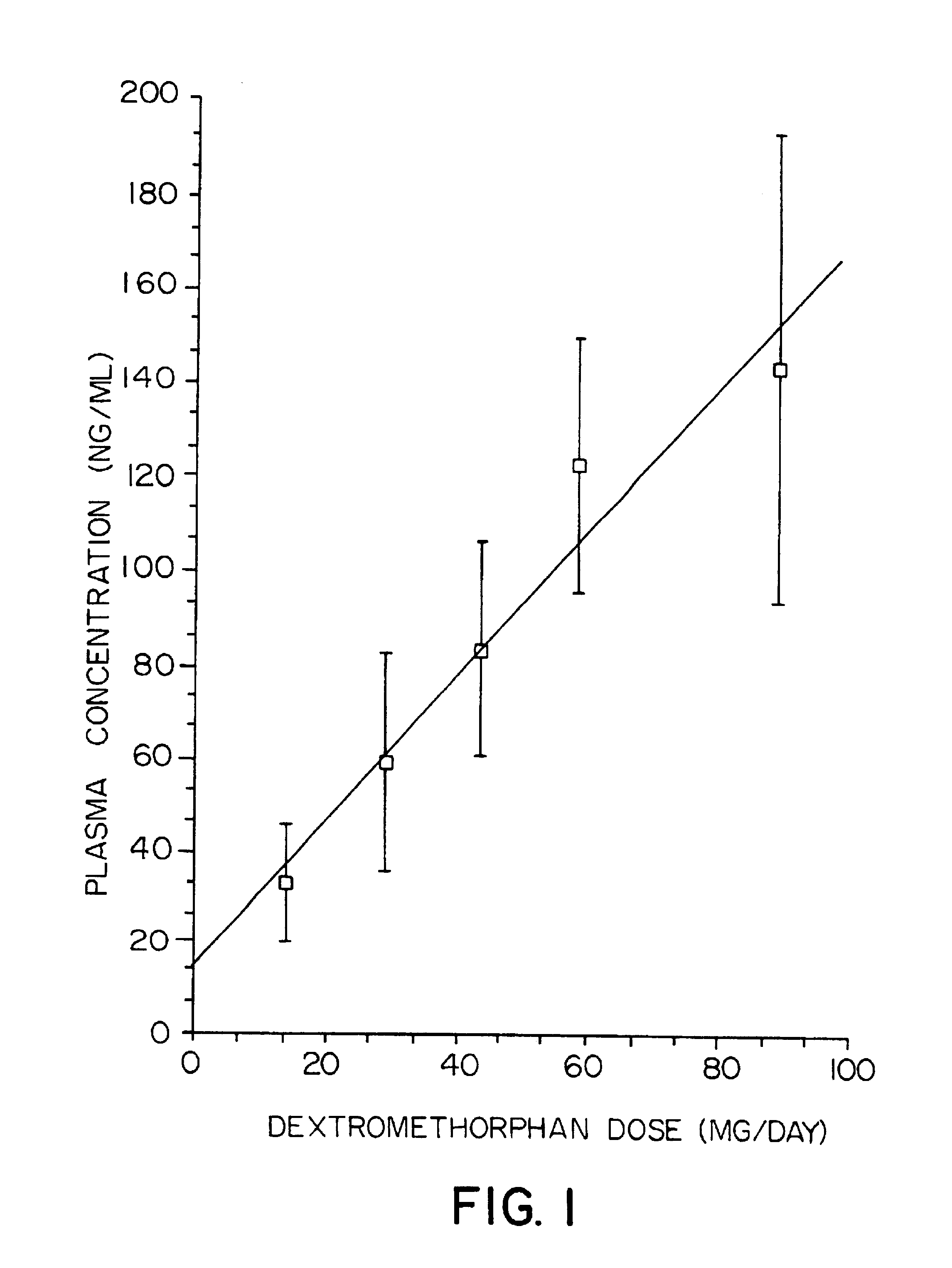
Additional studies were undertaken using a range of dosages of DM to establish a dose-response curve that correlates with plasma concentrations 10 to 12 hours later (determined as described in Example 2). All patients received 150 mg of quinidine daily. The results of those studies are shown in graphical form in FIG. 1, with mean values shown as open squares and standard deviation ranges shown by vertical bars. The ascending line through the median values is a linear approximation; a curve based on more extensive data would probably show a horizontal asymptote.
The results of the tests described in the foregoing Examples indicate that if quinidine is co-administered with DM, then DM circulation in the blood is increased and prolonged, without causing severe side effects. Accordingly, the co-administration of an antioxidant compound such as quinidine in conjunction with DM can increase the effectiveness of DM in any context that depends upon the concentration of DM ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Mass flow rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com