Methods for performing intelligent network services with an ISDN network terminator located at a subscriber's premise
a network terminator and subscriber technology, applied in special services for subscribers, data switching networks, time-division multiplexing selection, etc., can solve the problems of isdn subscriber, lack of basic electronic key telephone service (ekt) for analog phones, and inability to coexist between analog and digital terminal equipment at a customer's premise on a single subscription lin
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
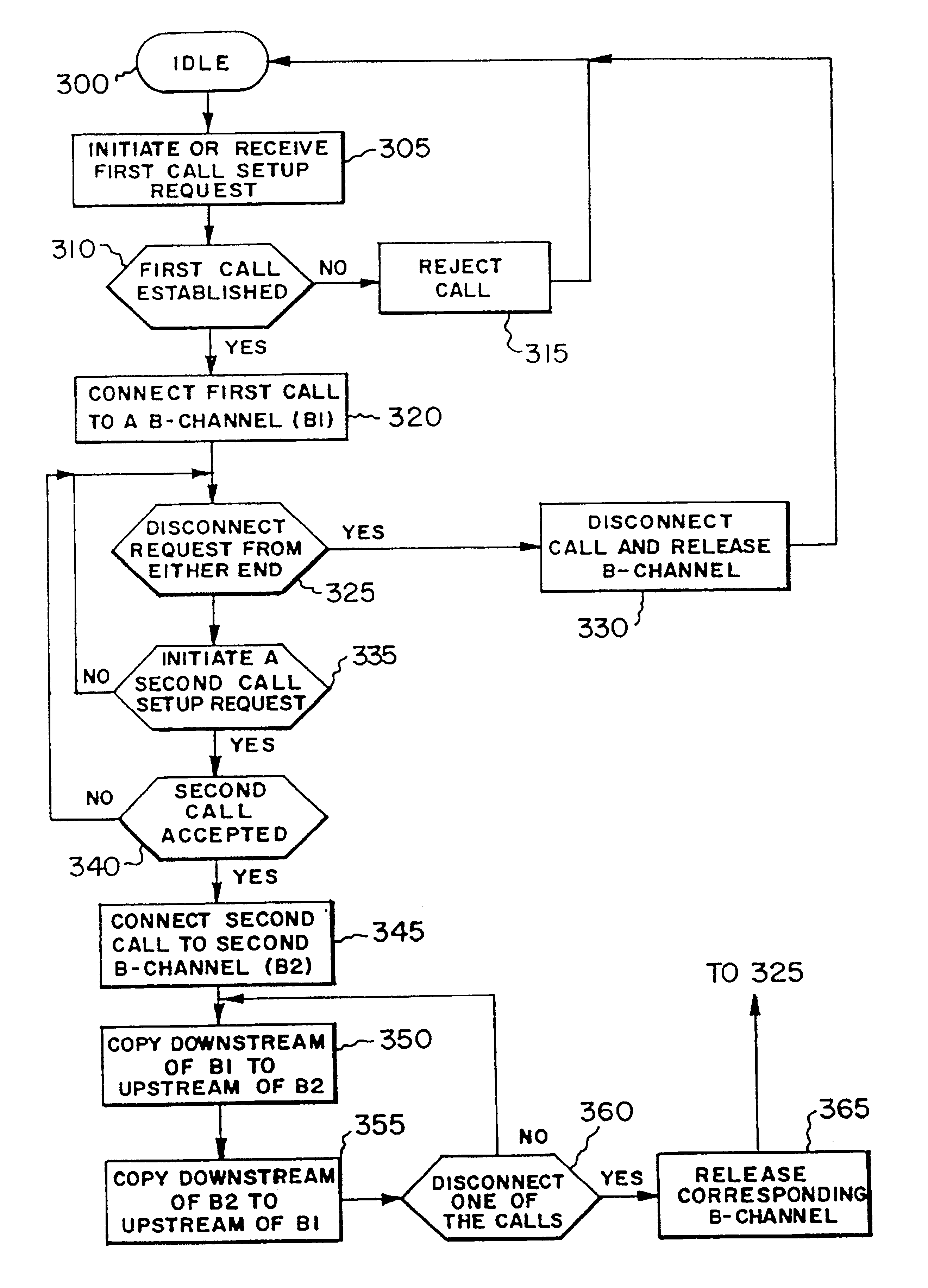
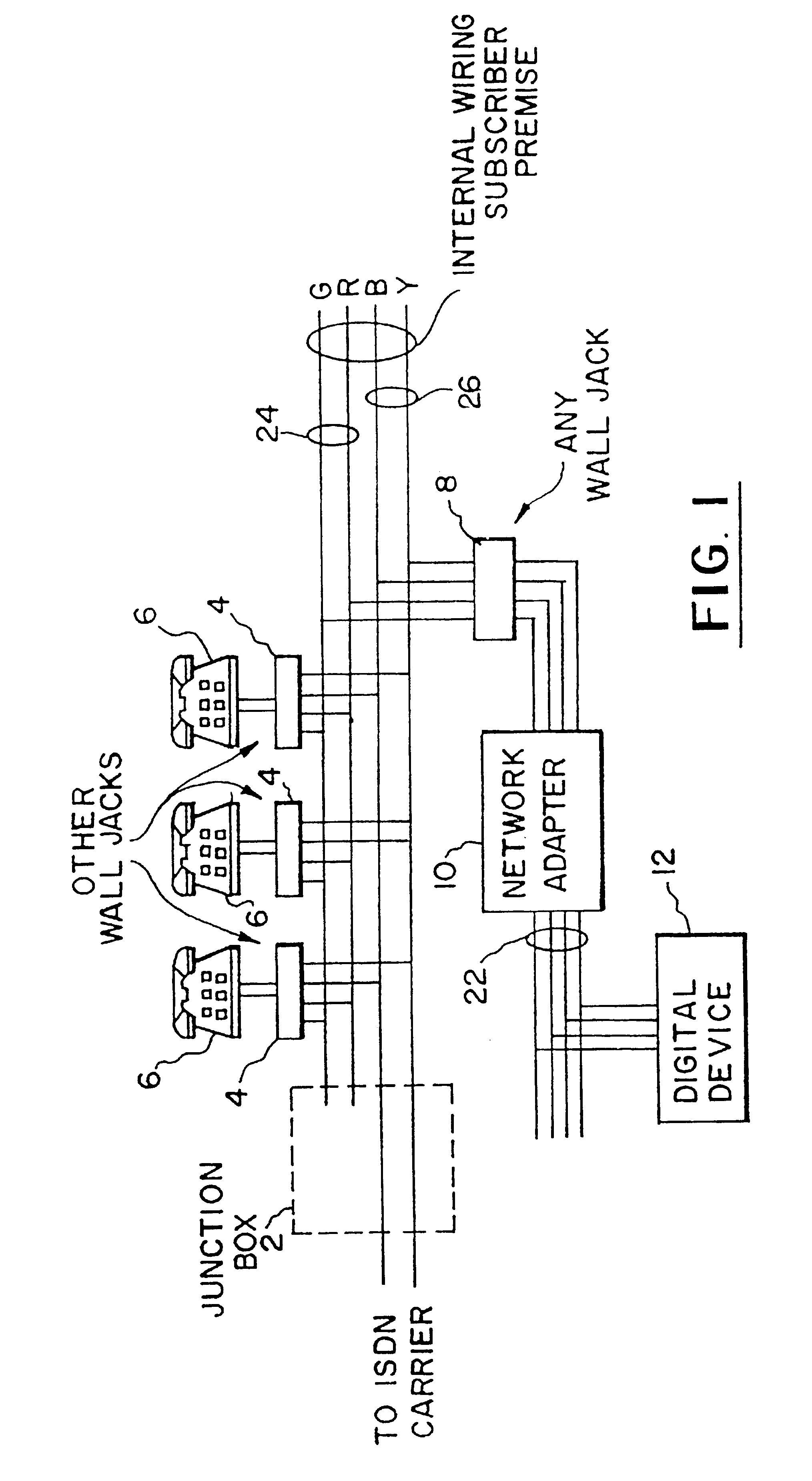
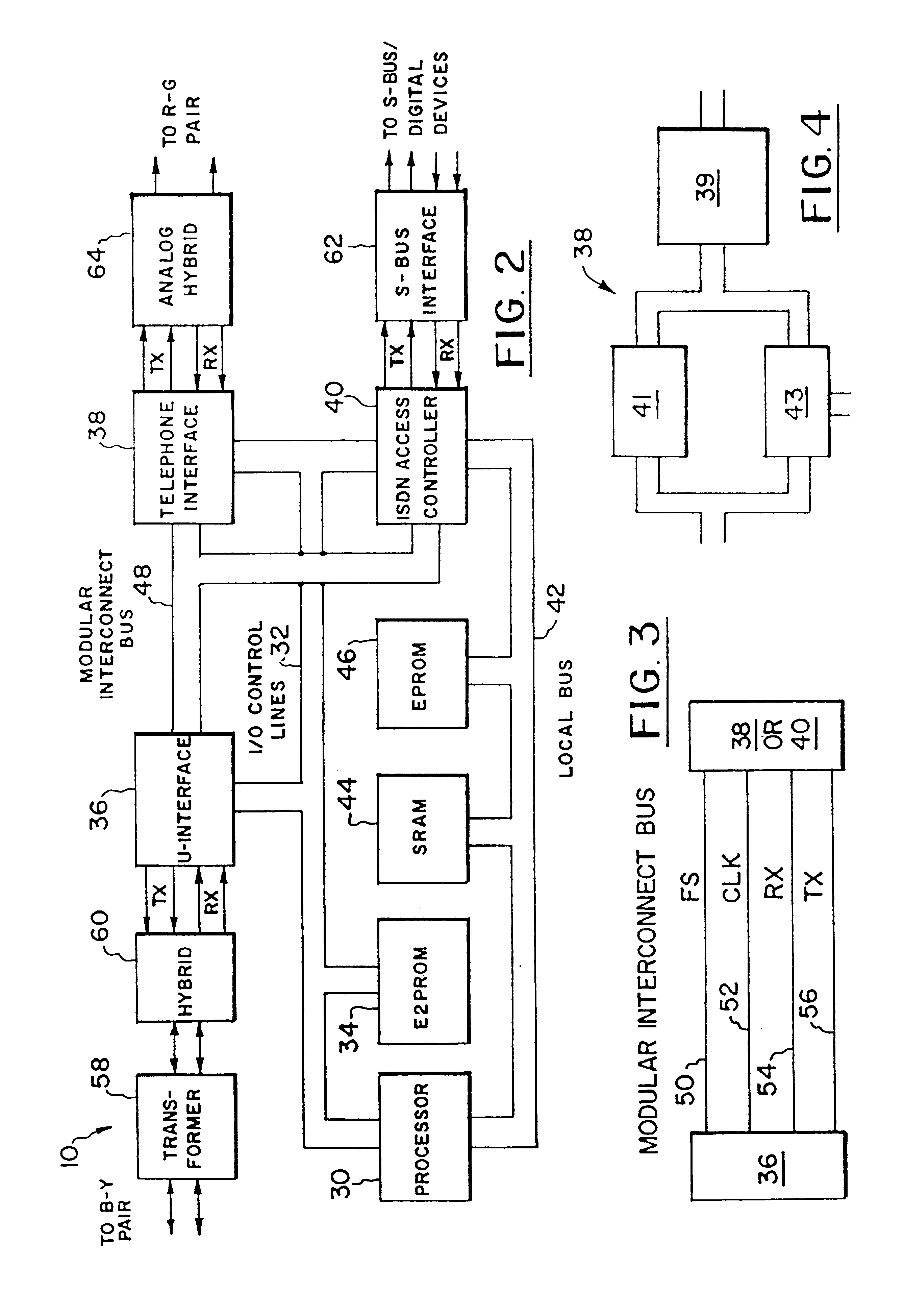
FIG. 1 illustrates an arrangement for linking both analog and digital devices to a single subscription line in an ISDN network, using pre-existing telephone wires 24, 26. This arrangement serves a number of functions (some of which will be more particularly described hereinafter) and is more fully disclosed in co-pending, earlier filed U.S. patent application Ser. No. 085,333, filed Jun. 30, 1993, now U.S. Pat. No. 5,448,635, and owned in common with this invention. To any extent necessary or appropriate to a full understanding of this invention, the co-pending application is hereby incorporated by reference into the present description.
The wiring in a subscriber premise comprises four signal wires. These wires extend to a junction box 2 that connects the customer premise to an ISDN carrier network Inside the premise, these wires terminate at modular telephone jacks 4 located in the walls of the subscriber premise. A Green-Red (G-R) pair of wires 24 is coupled to analog terminal equ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com