Patents
Literature
32results about "ISDN systems" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
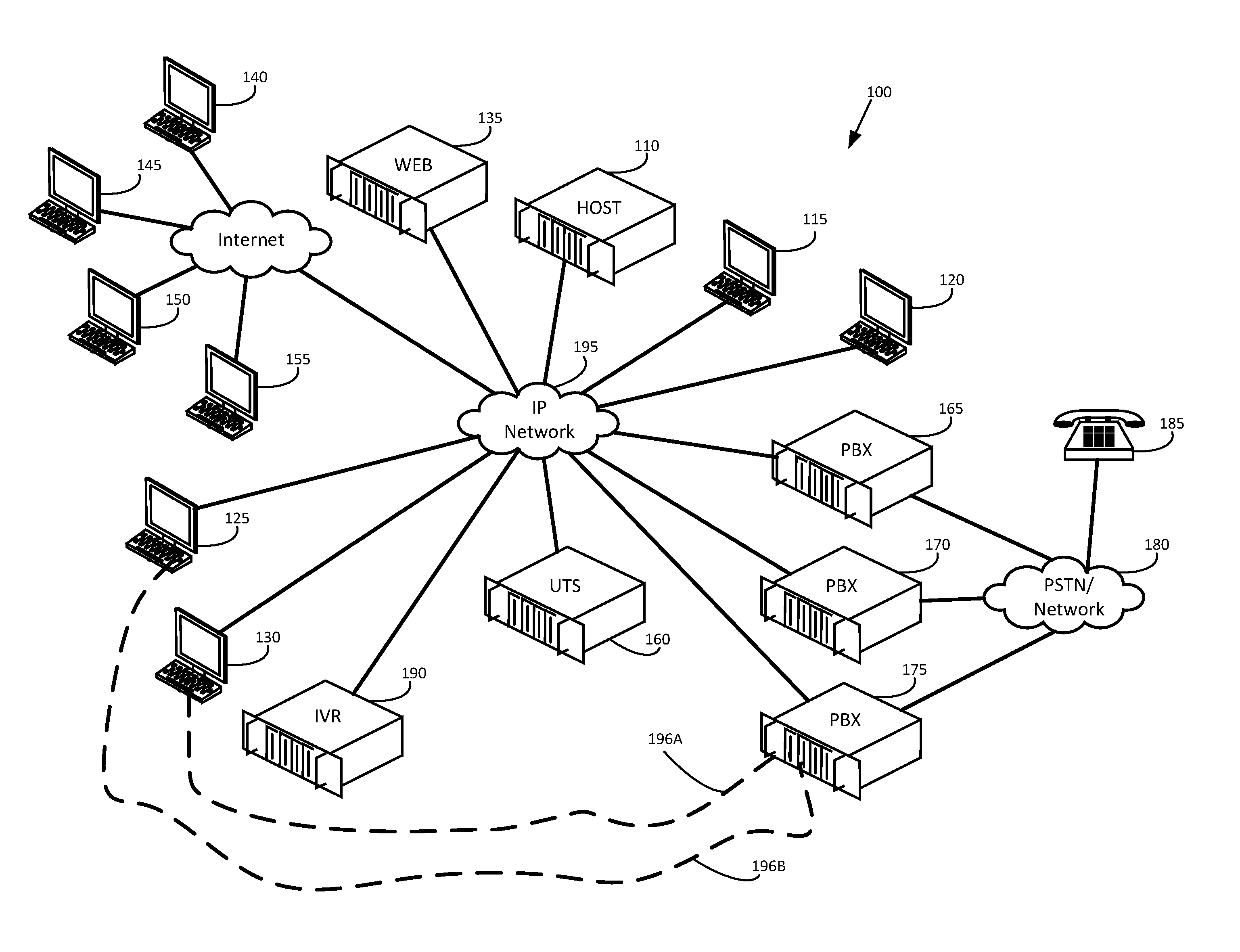
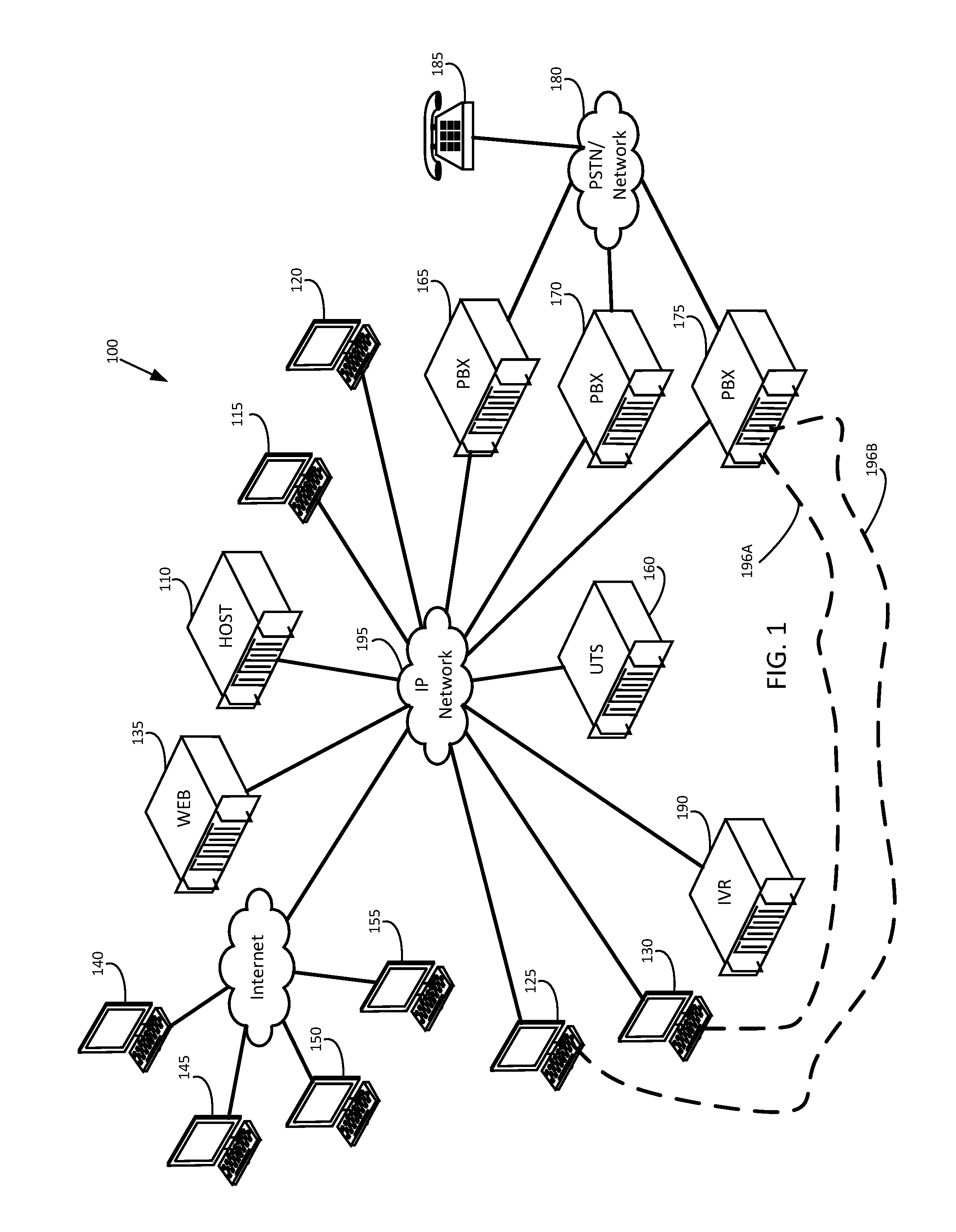
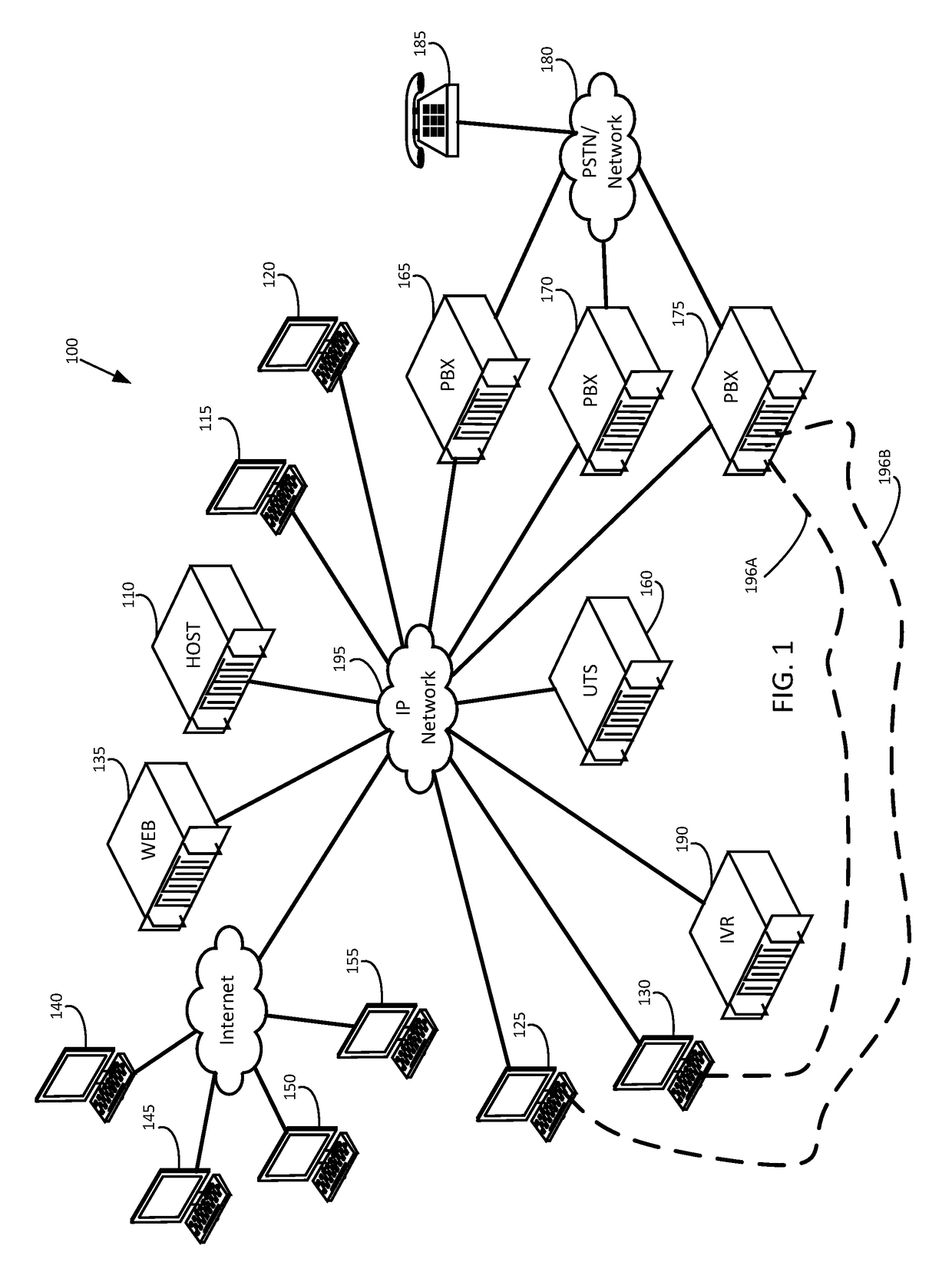
Apparatus, method and computer program product for providing self adapting transport of public switched telephone network (PSTN) circuits over a wireless network
InactiveUS20090257345A1Suppress any silenceError preventionTransmission systemsWireless mesh networkWireless sensor network
An adaptive telecommunications system for transporting communication traffic over a network comprising a means for transmitting communication traffic between a plurality of devices through a network, monitoring the communication traffic between the plurality of devices, and a adaptively changing the mode of operation either before and / or during a call, based on at least one of instantaneous network changes, connection type characteristics, and type of communication traffic. The devices attached to the network may consist of, for example, a fax machine, phone, mobile phone, public branch network exchange, a computer, or a switch. The traffic traveling across the system, voice, fax, or data, for example, may be compressed and / or restricted based on the type of traffic. The system may fully replace the existing PSTN circuits or may be used for overflow when the existing PSTN circuits are at near or full capacity.
Owner:NSGDATACOM
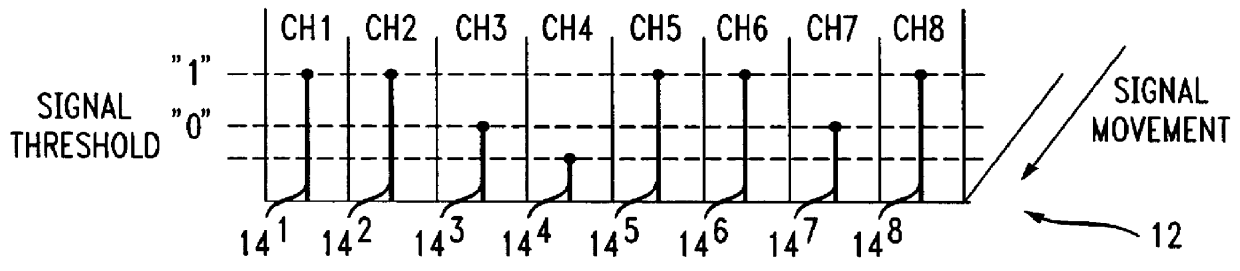
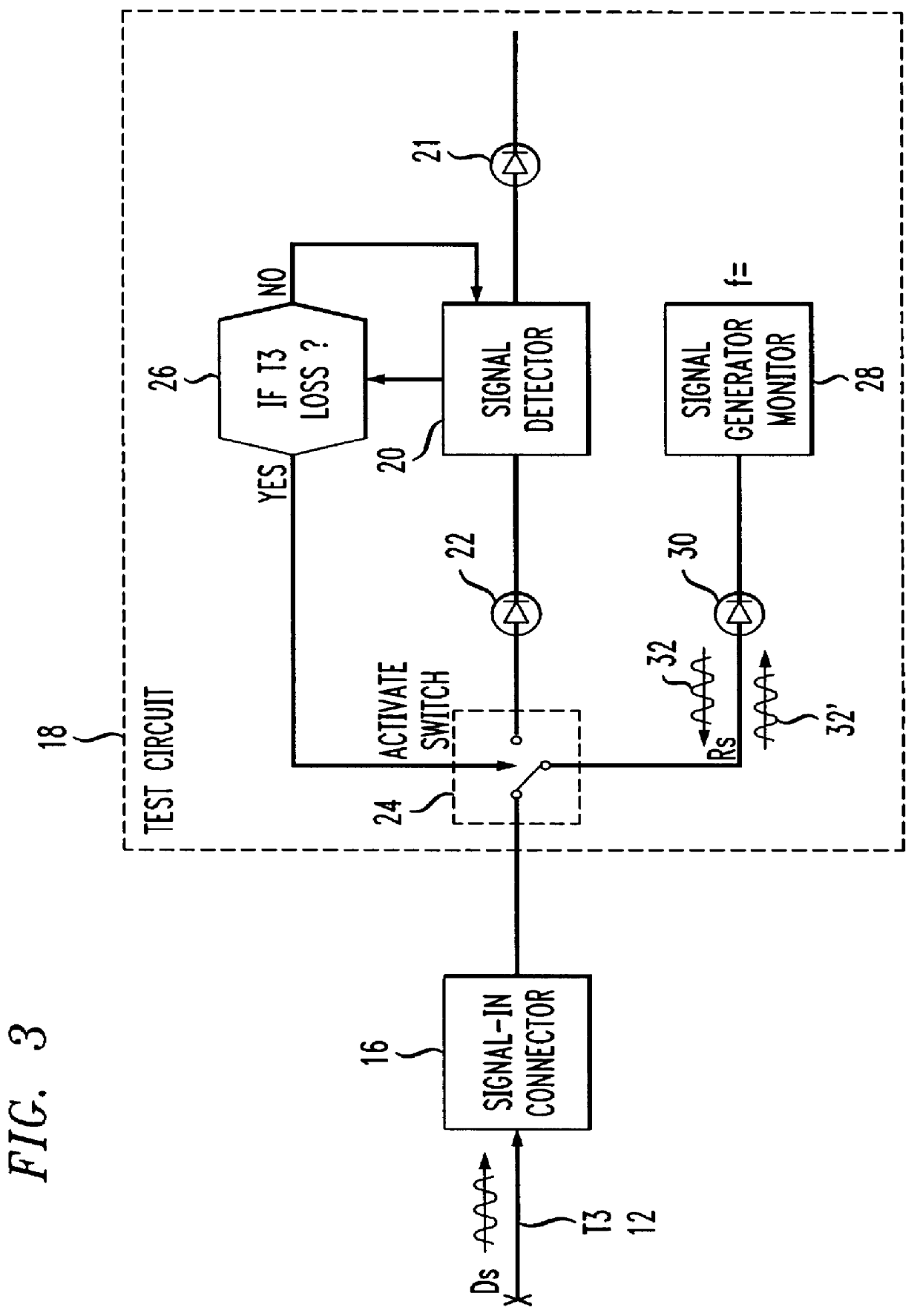
Methods and apparatus for detecting and locating cable failure in communication systems
In switching centers serving multiple local access providers, a problem arises in detecting cable failure and identifying the provider of the failed cable connected between the switching center and remote terminals. A test circuit installed in each cable port of the switching center detects failed cables; identifies the operator of the failed cable, and designates the cable end at which the failure occurs. The test circuit includes a signal detector and a signal generator and monitor connected through a switching device to the cables. A data signal Ds is transmitted on the cables. When the detector recognizes a loss of a data signal Ds exceeding a threshold a failed cable has occurred at one end of the cable or the other. The switch is activated by the signal loss to connect the signal generator and monitor to determine at which cable end the cable has failed. A reference signal Rs is injected into a cable by the signal generator and monitor. If the data signal Ds on the failed cable matches the reference signal Rs in amplitude and phase, a cable failure is indicated at the near end of the cable detector. If the data signal Ds is degraded in amplitude and shifted in phase relative to the reference signal Rs, a cable failure is indicated at the far end of the cable.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
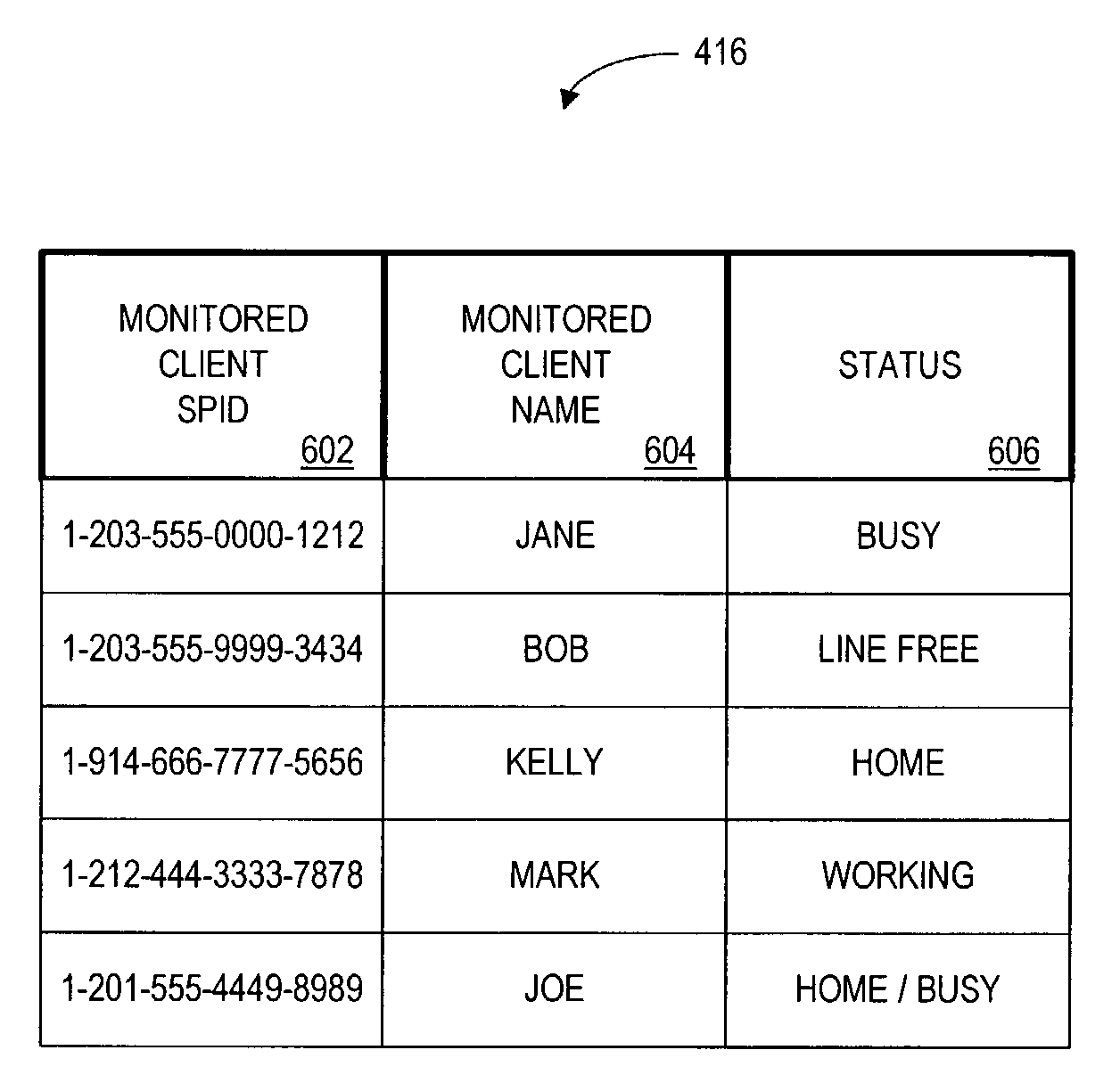
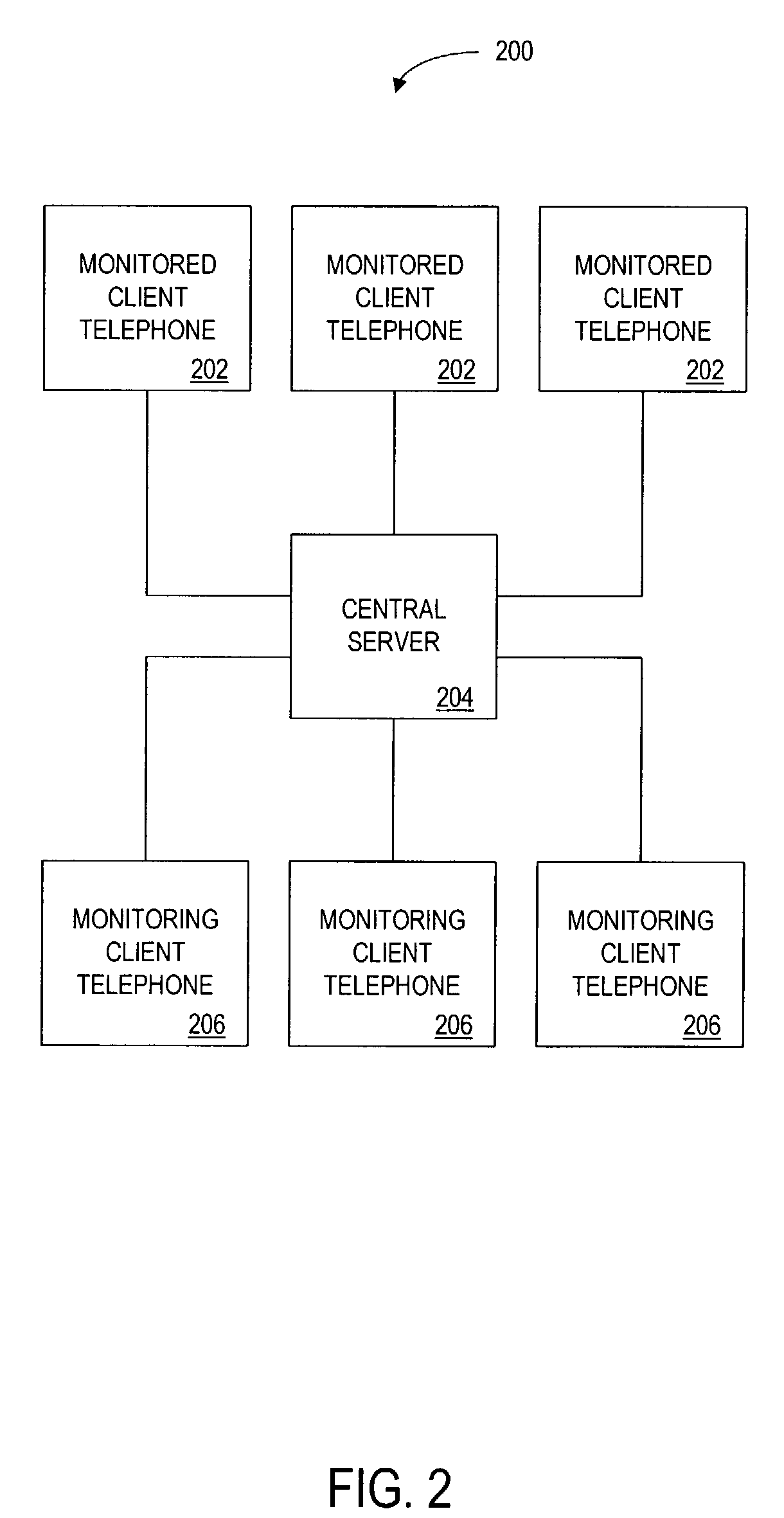
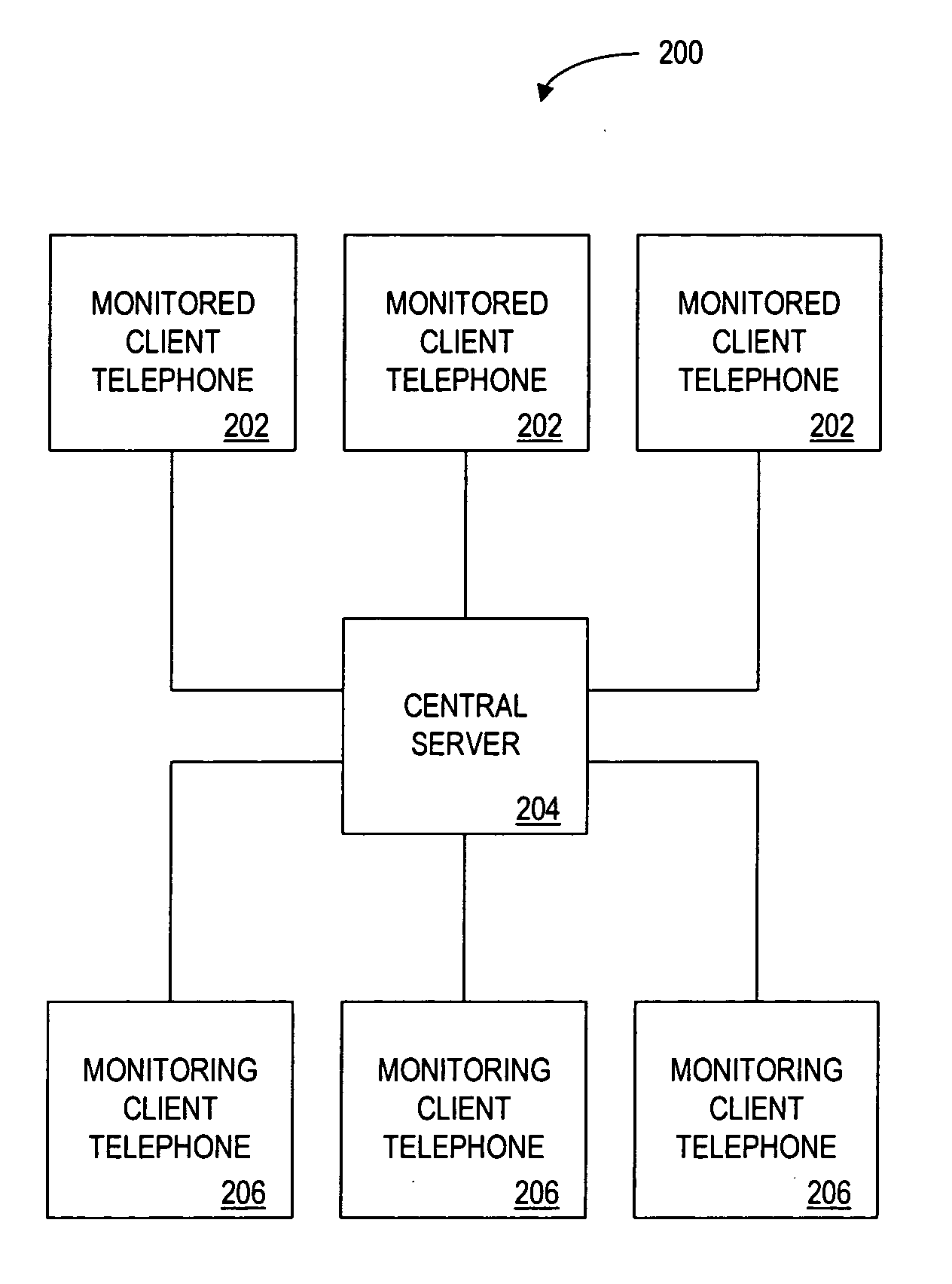
Method and apparatus for monitoring telephone status
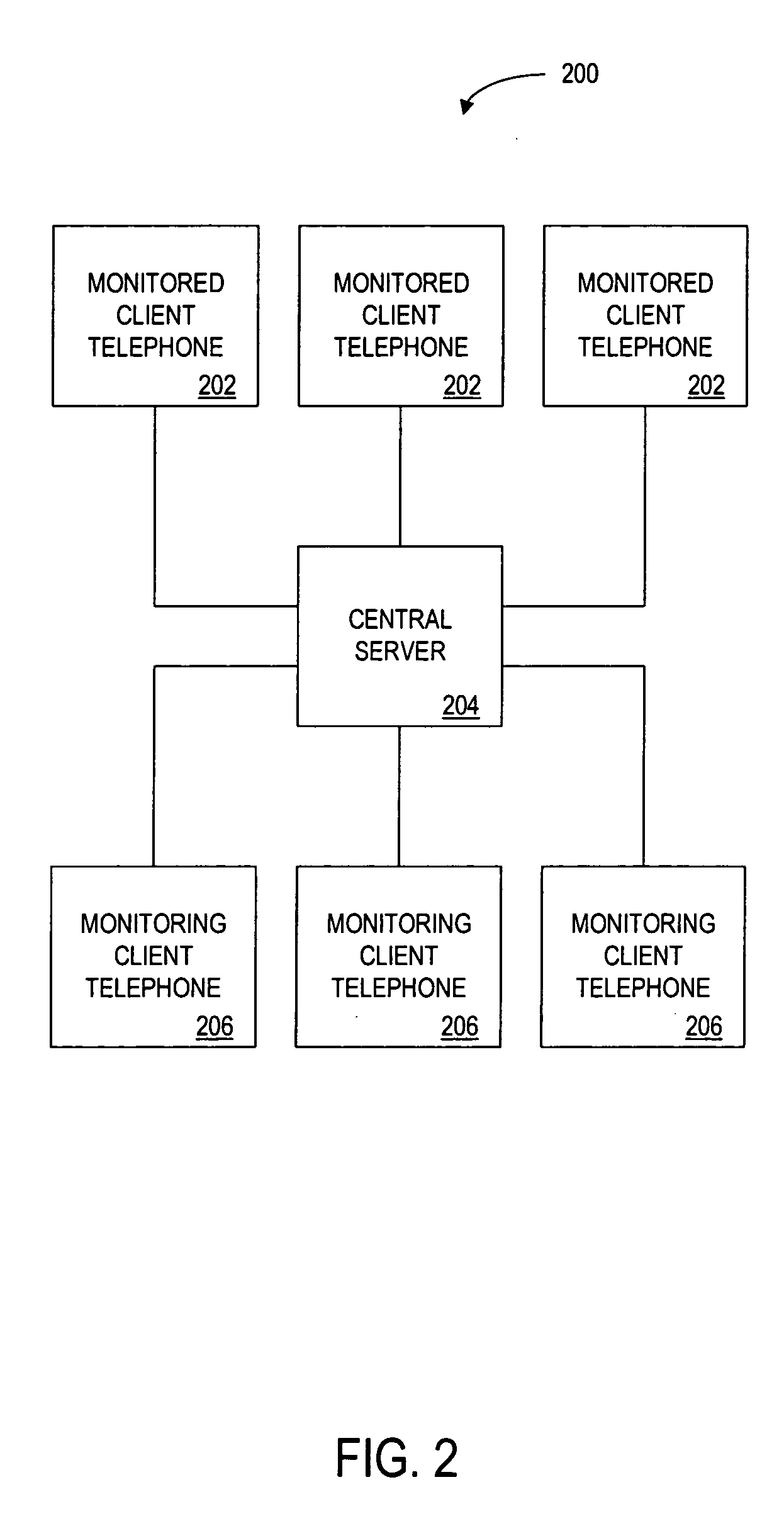
The monitor is for monitoring the status of a first client telephone, and for sending this status information via a central server to an authorized second client telephone. The central server stores a database of registered client telephones and corresponding client telephones that the client may monitor. A user of a registered client telephone monitors in real time the telephone status of registered friends, family, or co-workers that have agreed to be monitored by the user.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Method and apparatus for extending PBX features via the public network
InactiveUS7200218B1Avoid toll chargeISDN systemsSpecial service for subscribersTelecommunicationsPublic network
A system and method allow PBX features to be extended through the public network. A teleworker calls into a PBX system and is assigned a fictitious port. The fictitious port is controlled by a telework server and appears to the PBX to be a local device. PBX features are invoked by particular sequences of DTMF tones or by voice prompt, or another data input system.
Owner:UNIFY INC
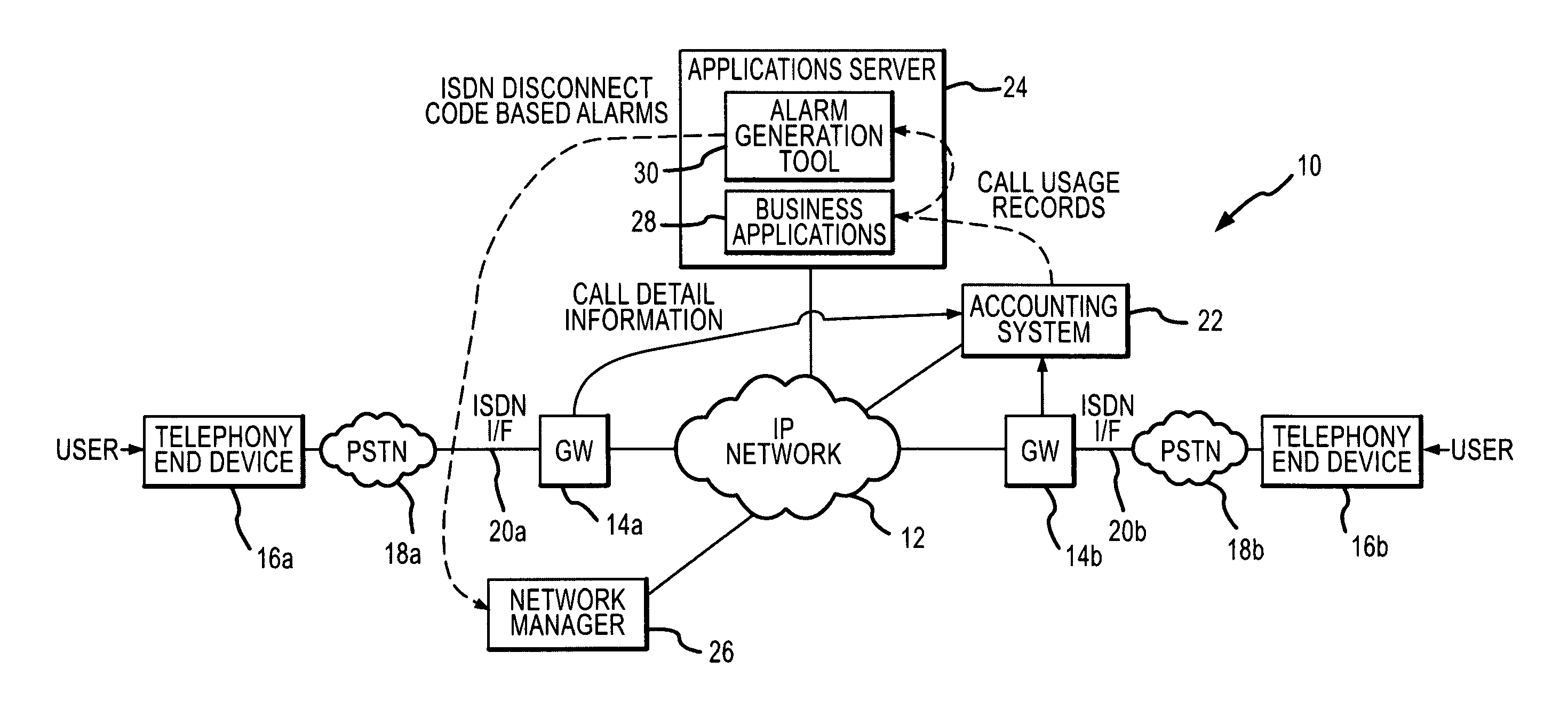
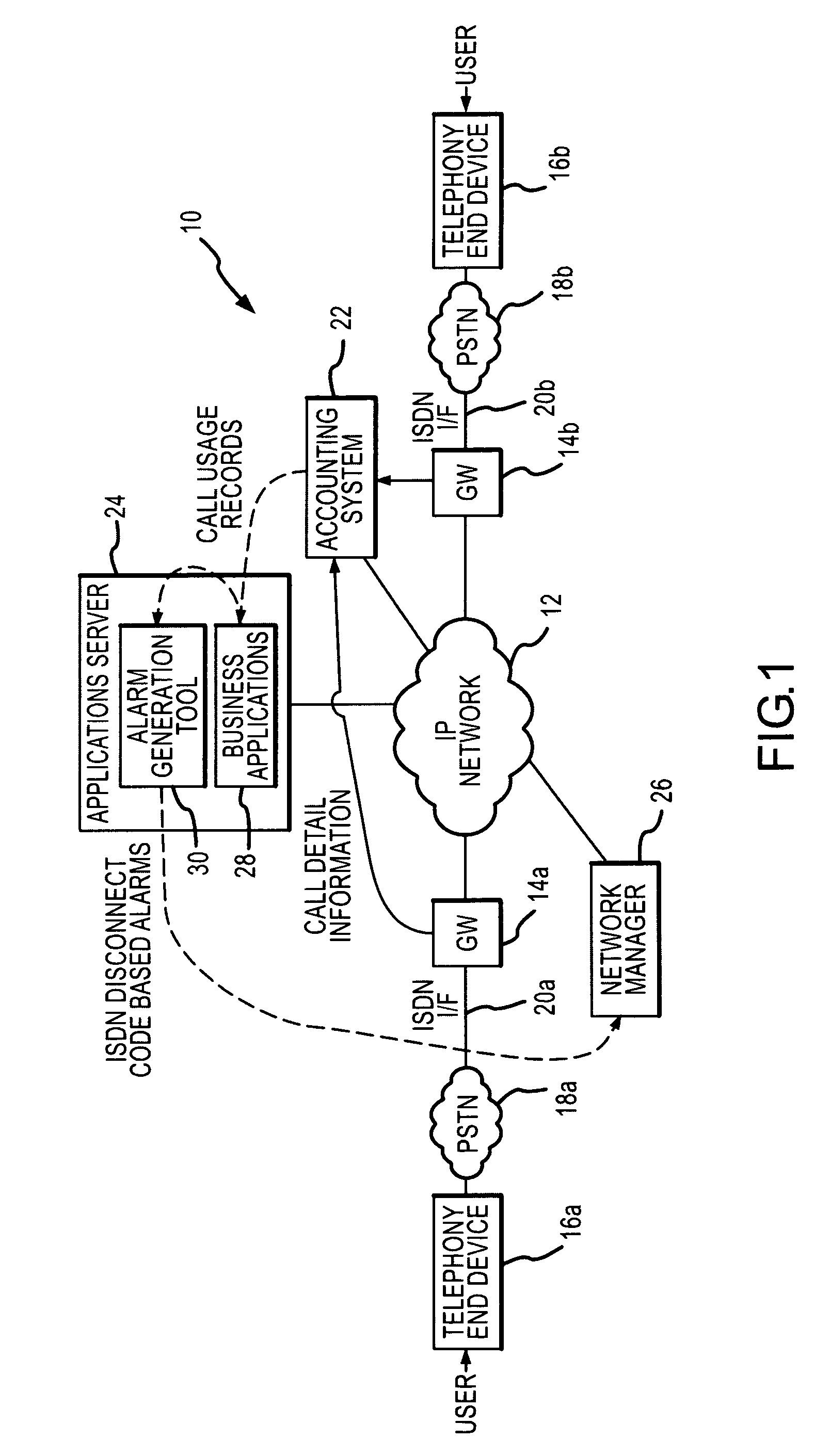
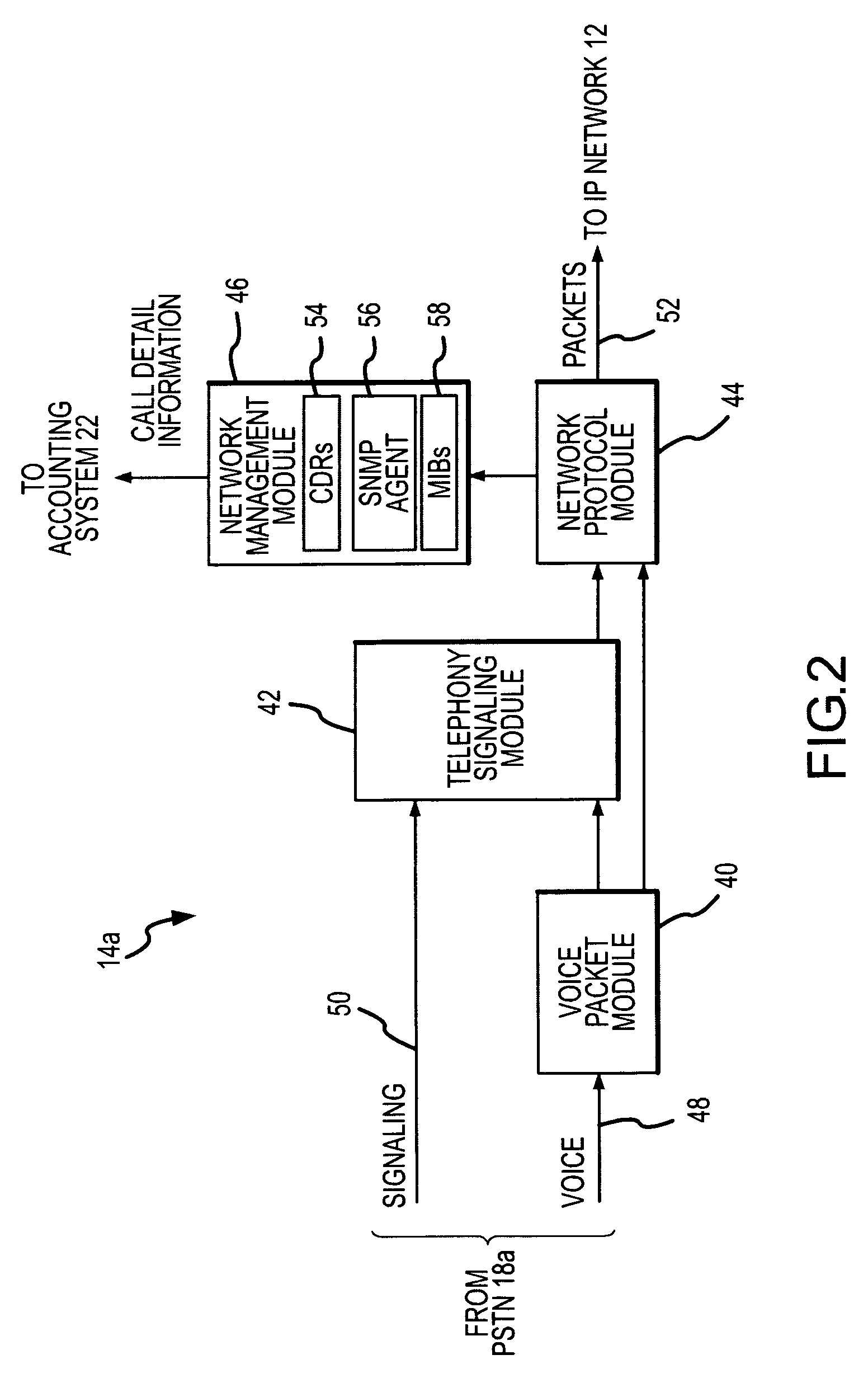
ISDN disconnect alarm generation tool for use in voice over IP (VoIP) networks
ActiveUS7051099B2Improve real-time informationAvoid serious problemsMultiplex system selection arrangementsISDN systemsTraffic capacityFailure rate
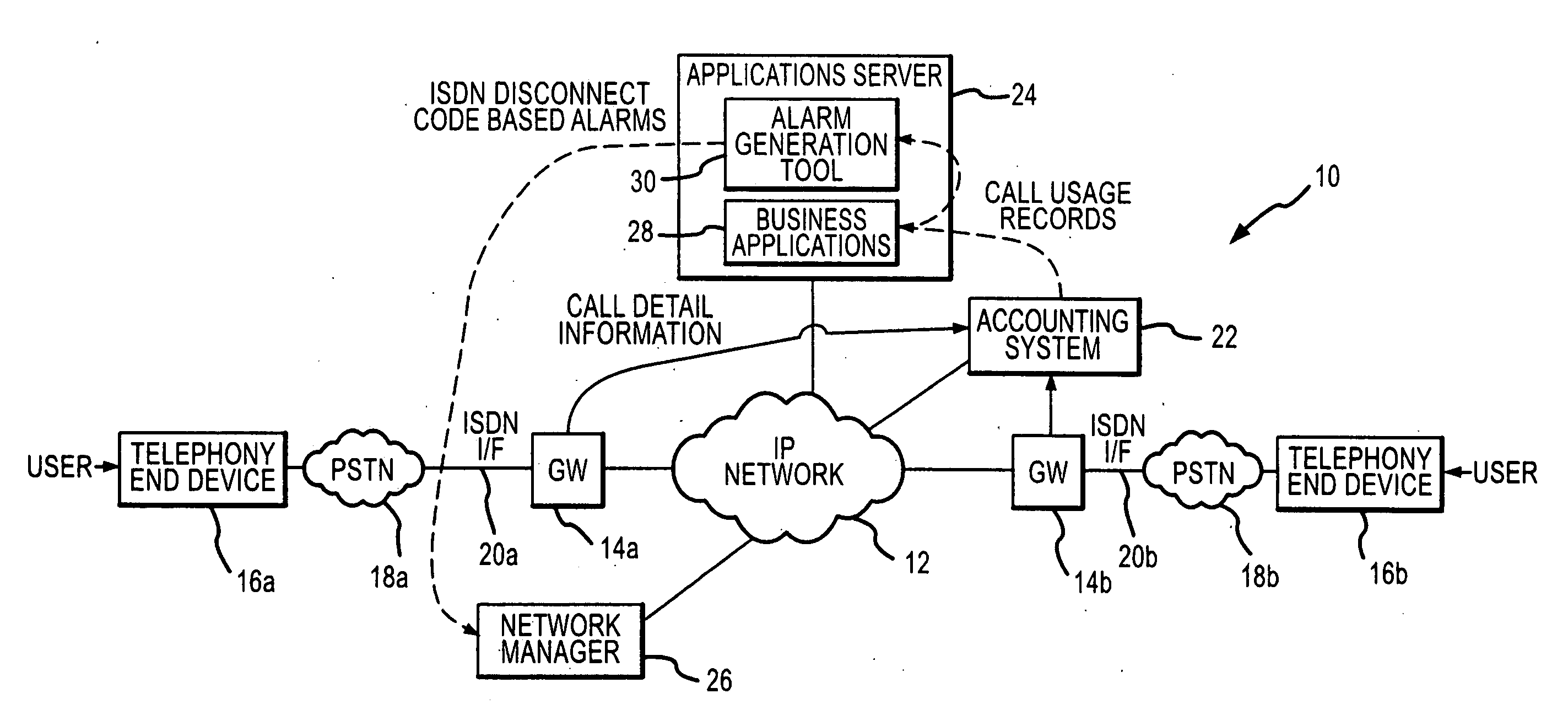
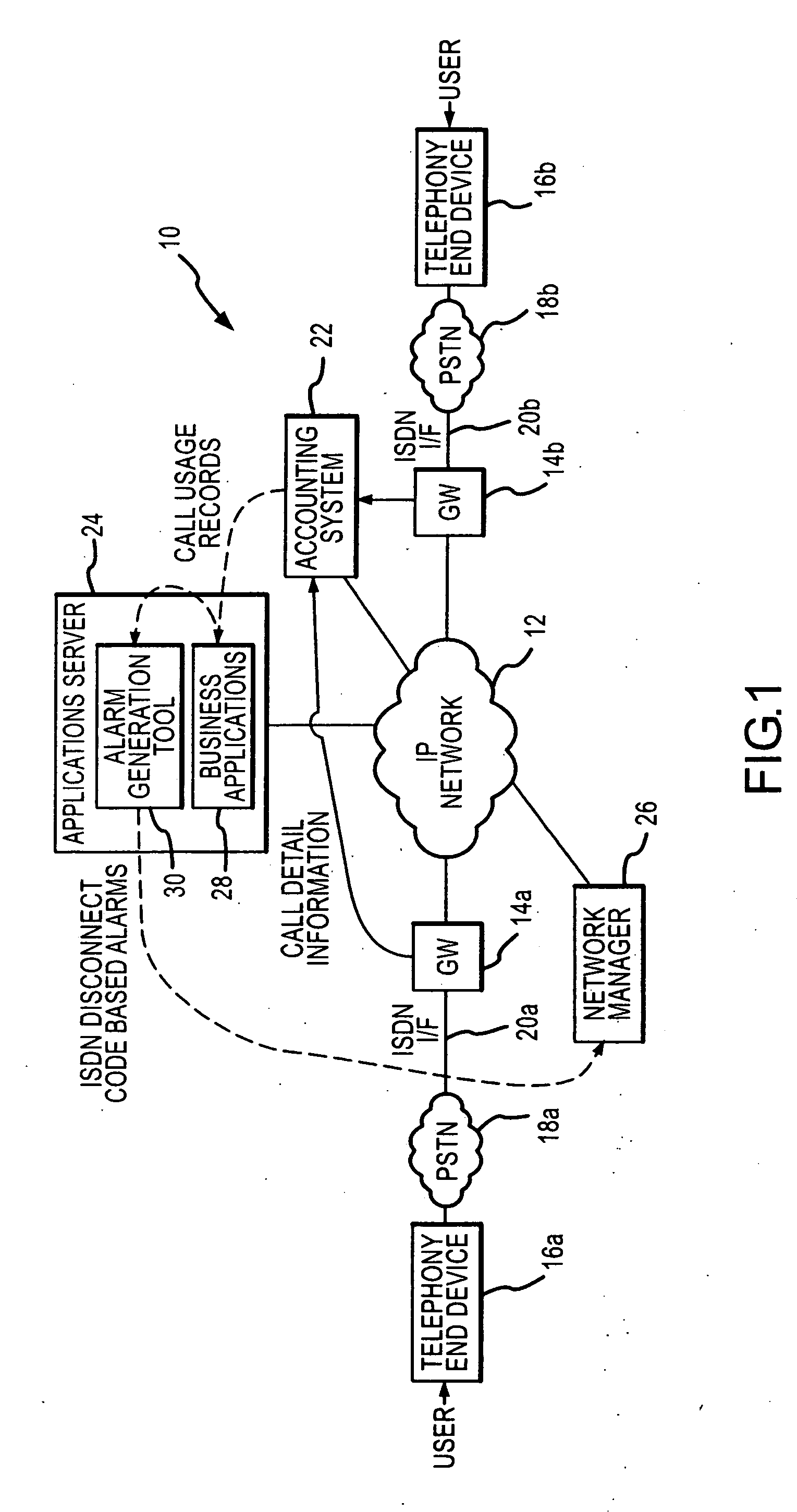
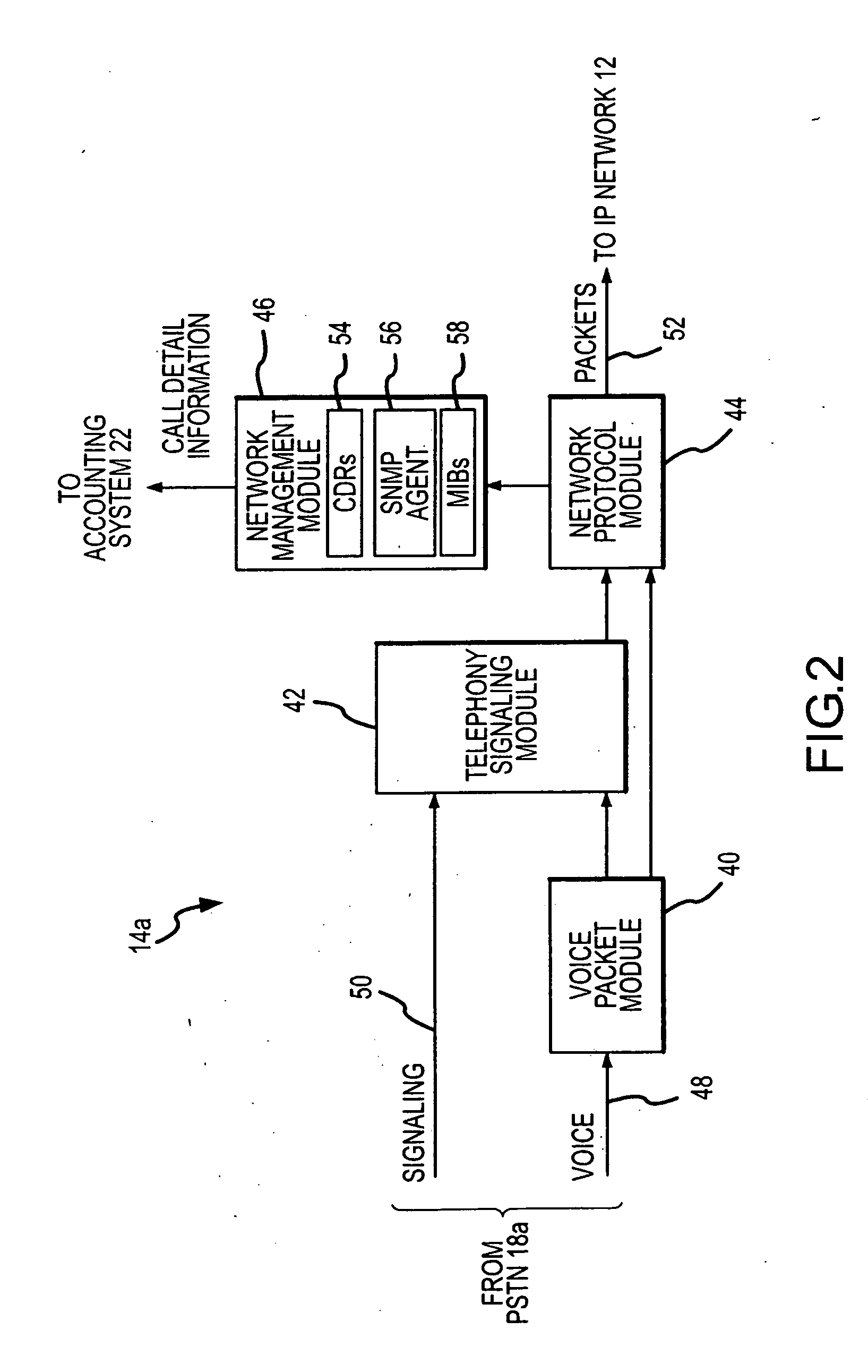
An alarm generation tool that operates within a Voice over IP (VoIP) network environment to generate alarms based on ISDN disconnect cause codes. The tool examines call-specific usage records associated with VoIP traffic to detect ISDN disconnect cause codes and determines failure rate information from failure-type disconnect cause codes among the ISDN disconnect cause codes on a per-gateway basis. The tool generates alarms when the failure rate information, such as failure rates and / or counts, exceeds defined thresholds.
Owner:LEVEL 3 COMM LLC
Location information for remote user
InactiveUS7411940B2ISDN systemsSpecial service for subscribersTelephone networkRemote Access Service
Owner:SOUND VIEW INNOVATIONS
ISDN disconnect alarm generation tool for use in Voice over IP (VoIP) networks
InactiveUS20060230143A1Improve real-time informationMultiplex system selection arrangementsISDN systemsTraffic capacityFailure rate
An alarm generation tool that operates within a Voice over IP (VoIP) network environment to generate alarms based on ISDN disconnect cause codes. The tool examines call-specific usage records associated with VoIP traffic to detect ISDN disconnect cause codes and determines failure rate information from failure-type disconnect cause codes among the ISDN disconnect cause codes on a per-gateway basis. The tool generates alarms when the failure rate information, such as failure rates and / or counts, exceeds defined thresholds.
Owner:LEVEL 3 COMM LLC +1
System and method for identifying and treating calls
ActiveUS7916846B1ISDN systemsAutomatic call-answering/message-recording/conversation-recordingTelephonyUser information
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
Broadcast/multicast system and protocol for circuit-switched networks
ActiveUS6940857B2Save network resourcesImprove efficiencySpecial service provision for substationMultiplex system selection arrangementsBroadcastingCircuit switching
A system and method directed to providing a broadcast / multicast in a circuit-switched network. An exemplary method includes receiving at a first switch a call directed to a called number; determining whether the first switch has an active connection to the called number; if the first switch has an active connection to the called number, merging the call with the active connection; and if the first switch does not have an active connection to the called number, routing the call to a next switch. The process is repeated as necessary until a next switch with an active connection is identified and / or the switch serving the called number is reached. The present invention conserves network resources and increases network efficiency, in part, by not carrying a call any further than is necessary for the caller to participate in a broadcast / multicast.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
Ring network implemented by telephony switches and links
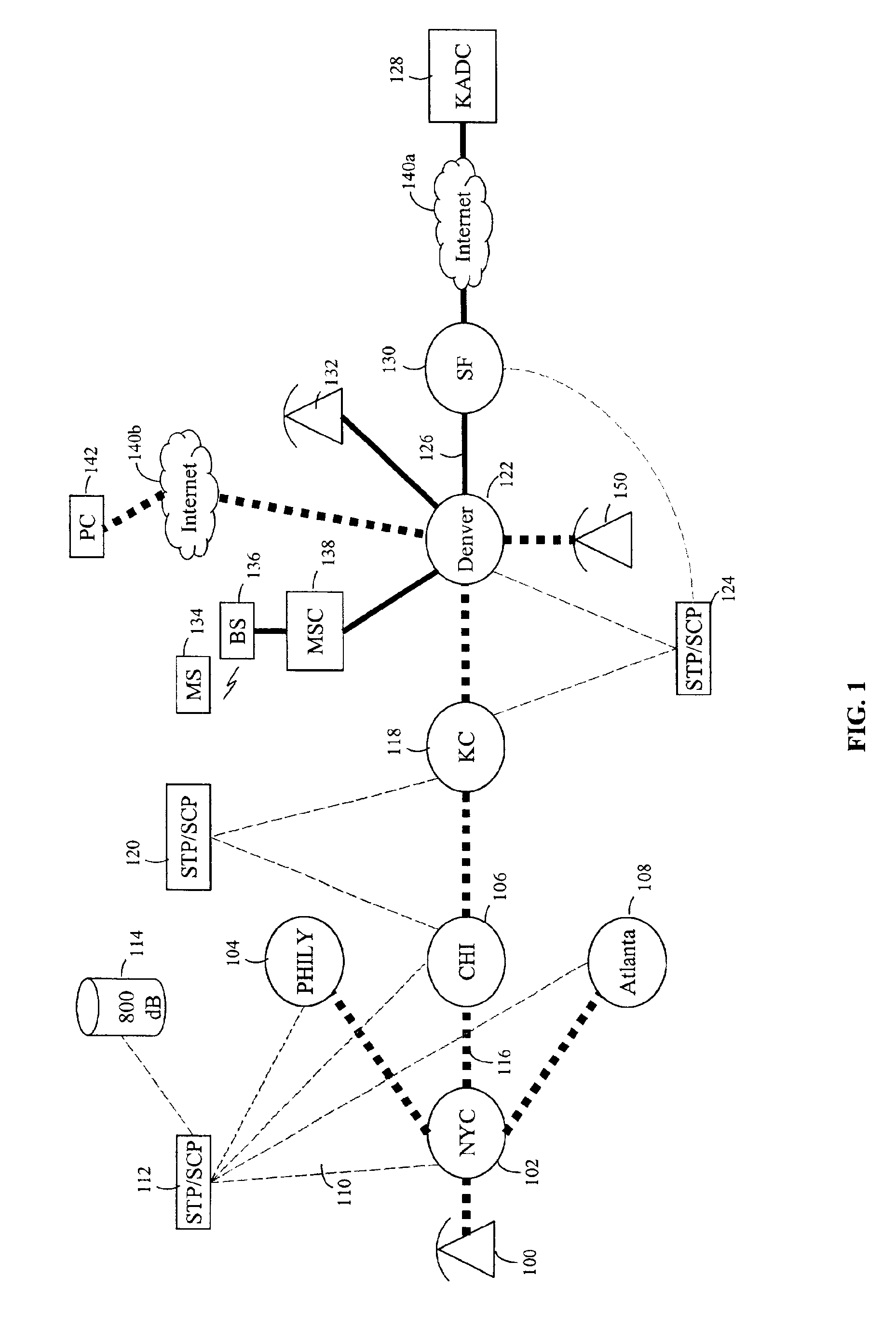
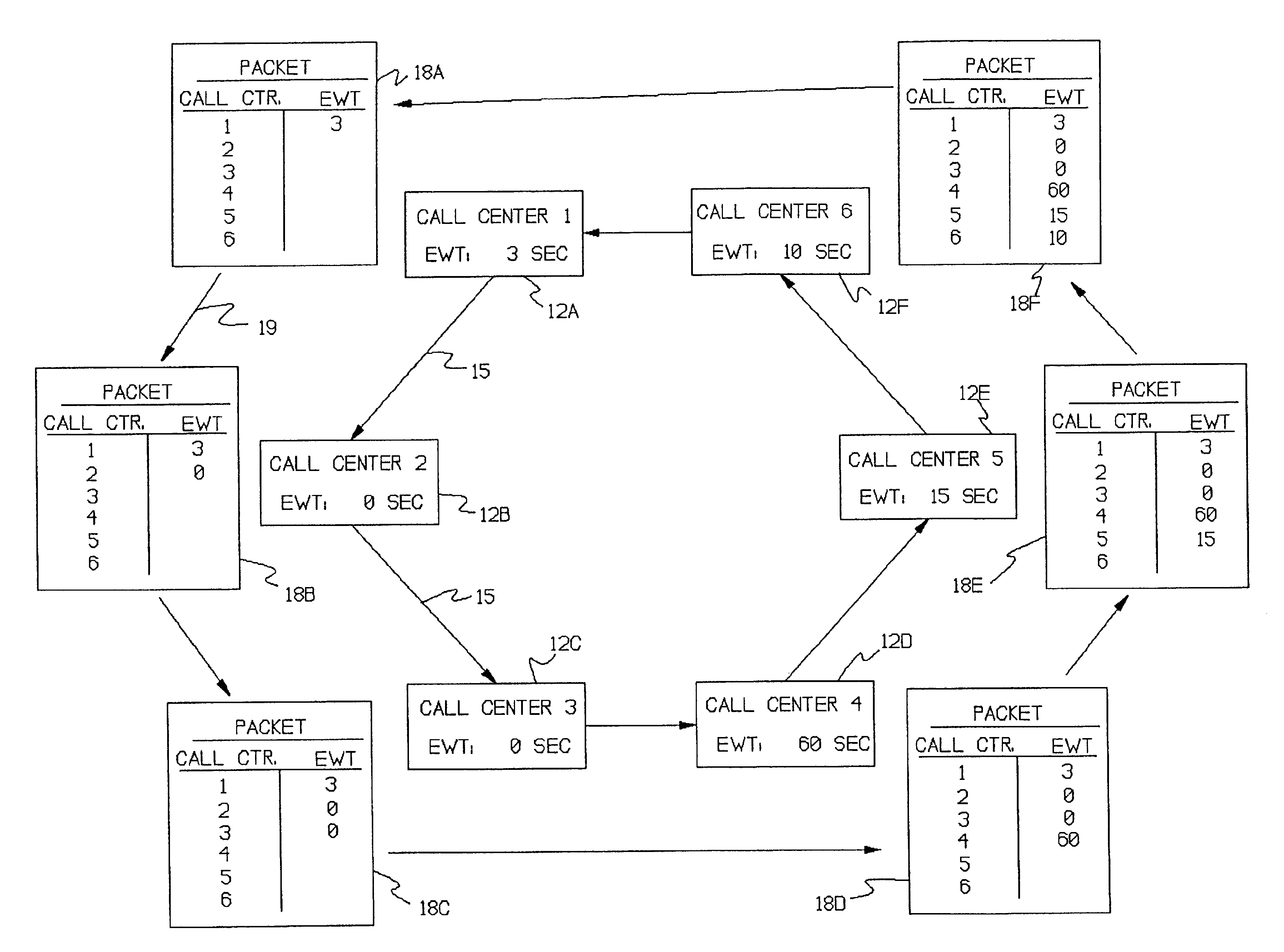
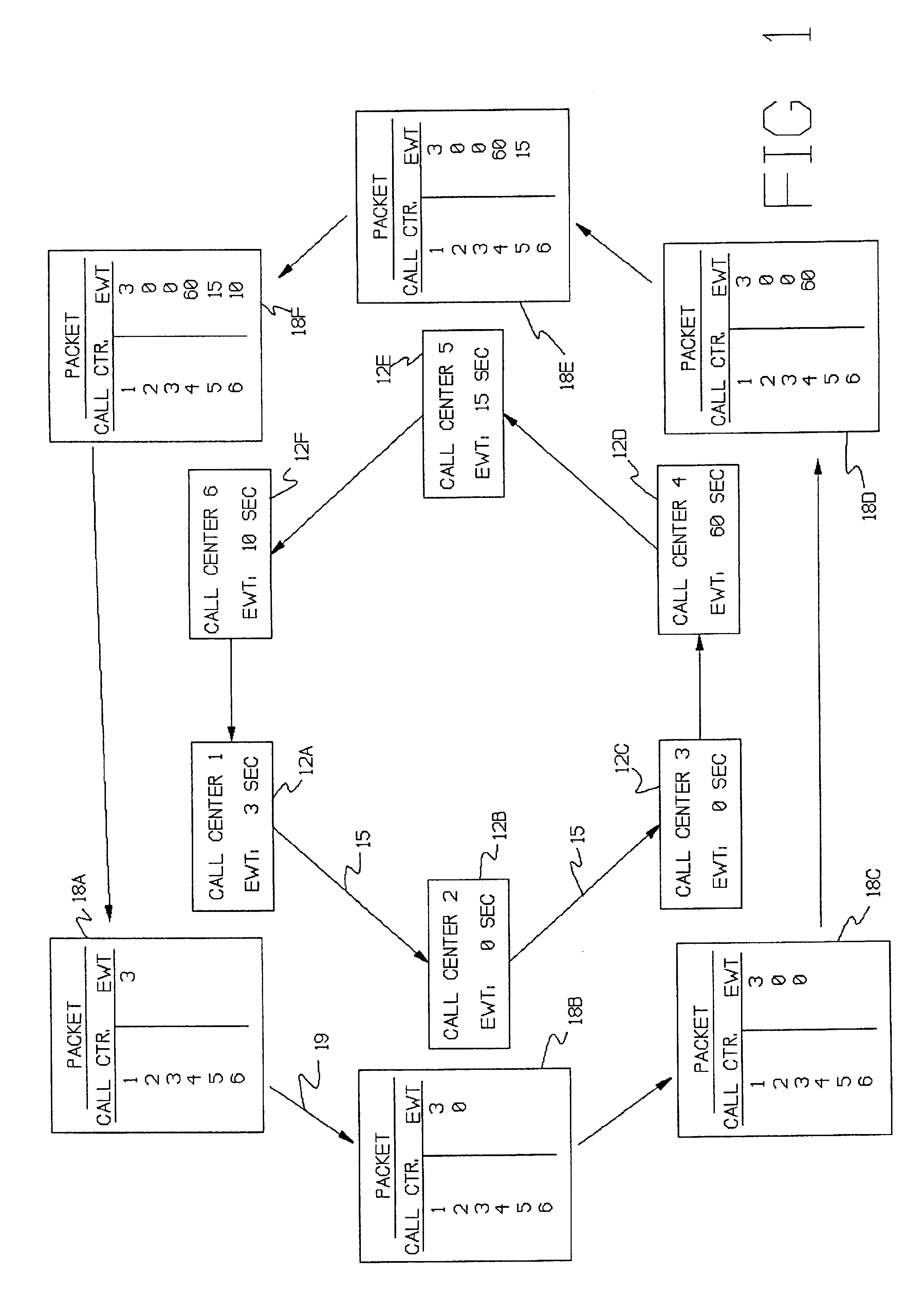
InactiveUS6839419B1Save the processSimple methodISDN systemsSpecial service for subscribersRing networkNetwork pattern
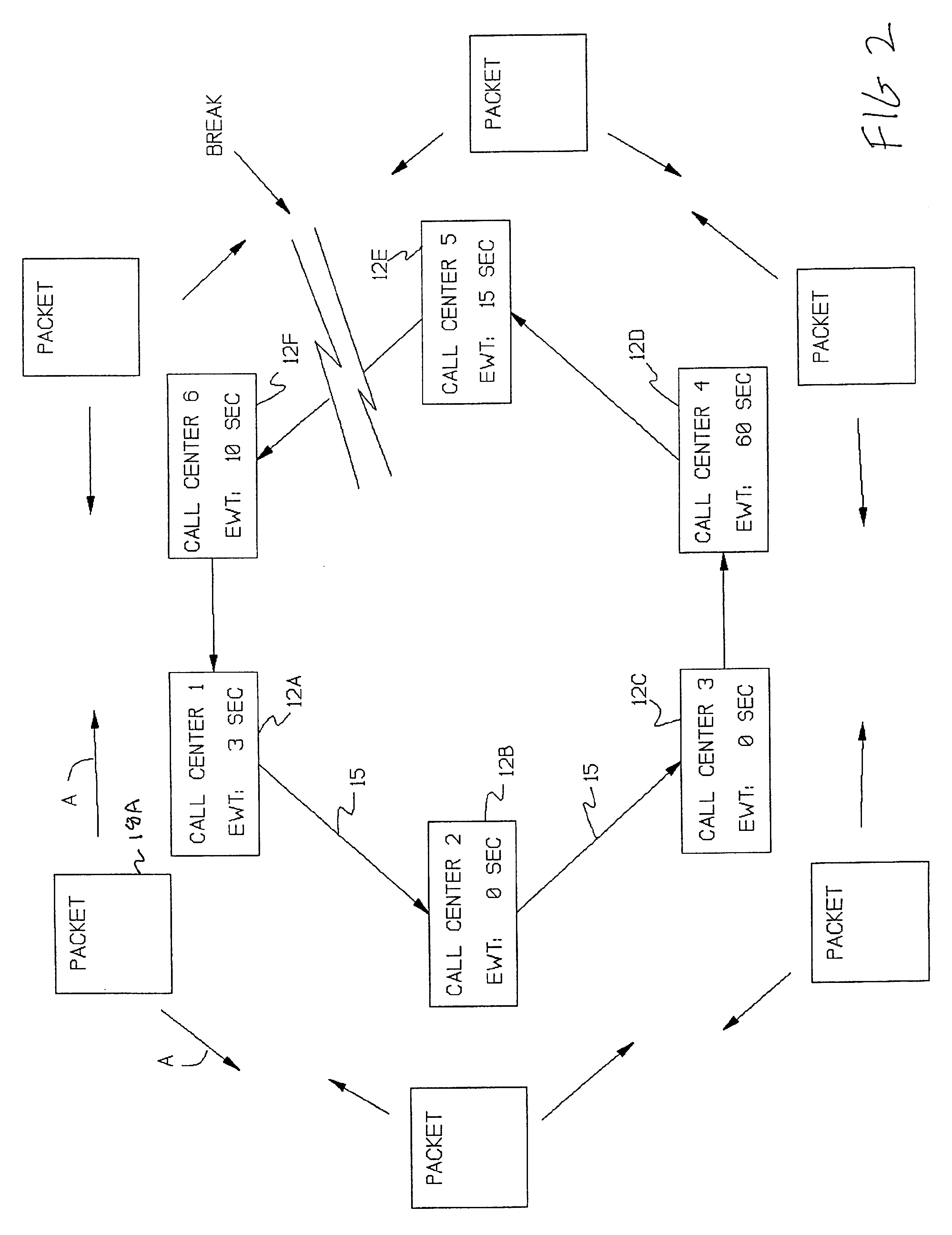
A system for using an under-utilized data channel for carrying additional data, in a network mode. One such channel is the D-channel in the ISDN system. In one implementation, a group of telephone call centers share data, using the D-channel, about the lengths of time incoming callers must wait before being answered. Using the shared data, the call centers collectively route incoming calls to call centers having smaller waiting times.
Owner:AVAYA INC
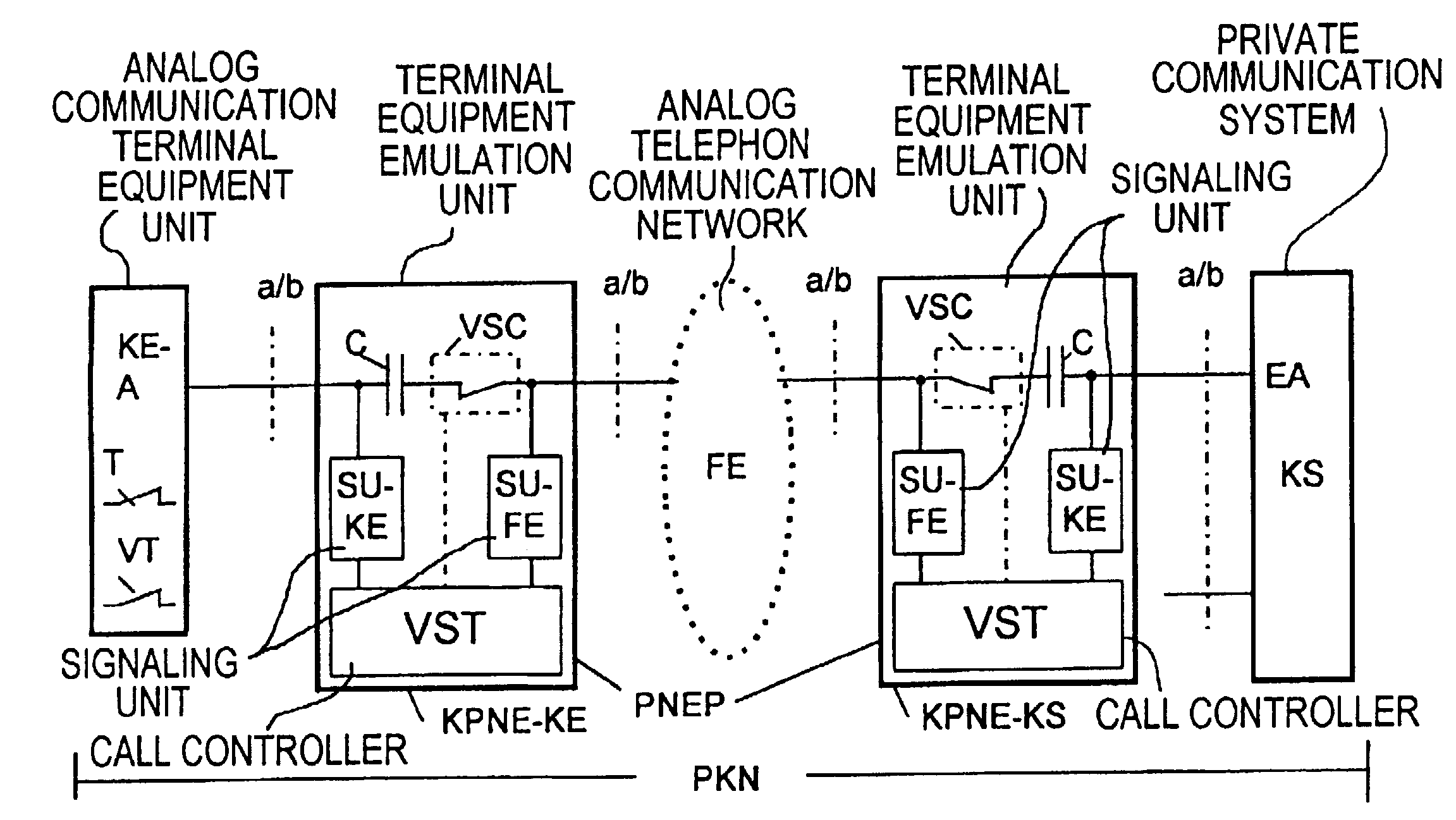
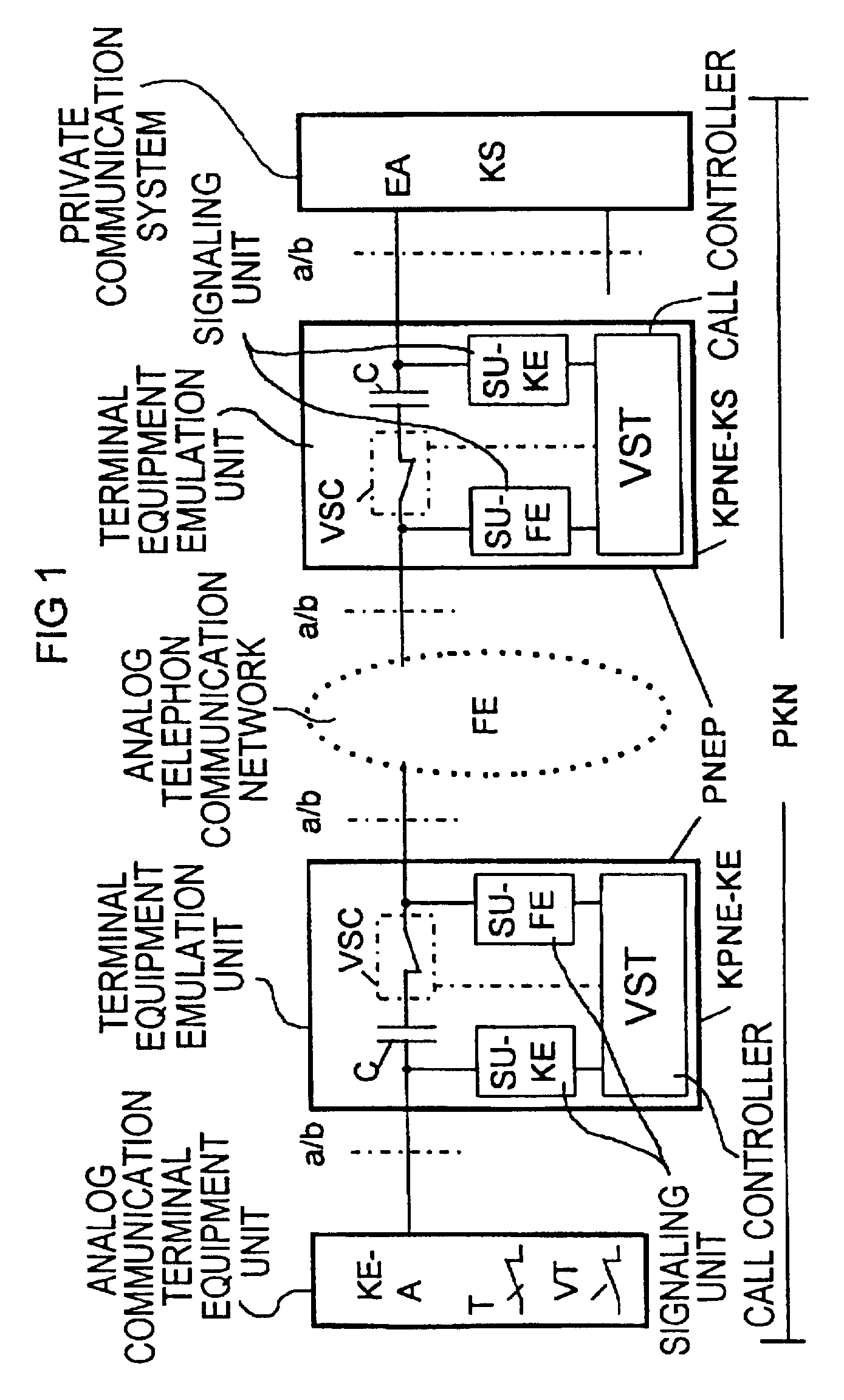
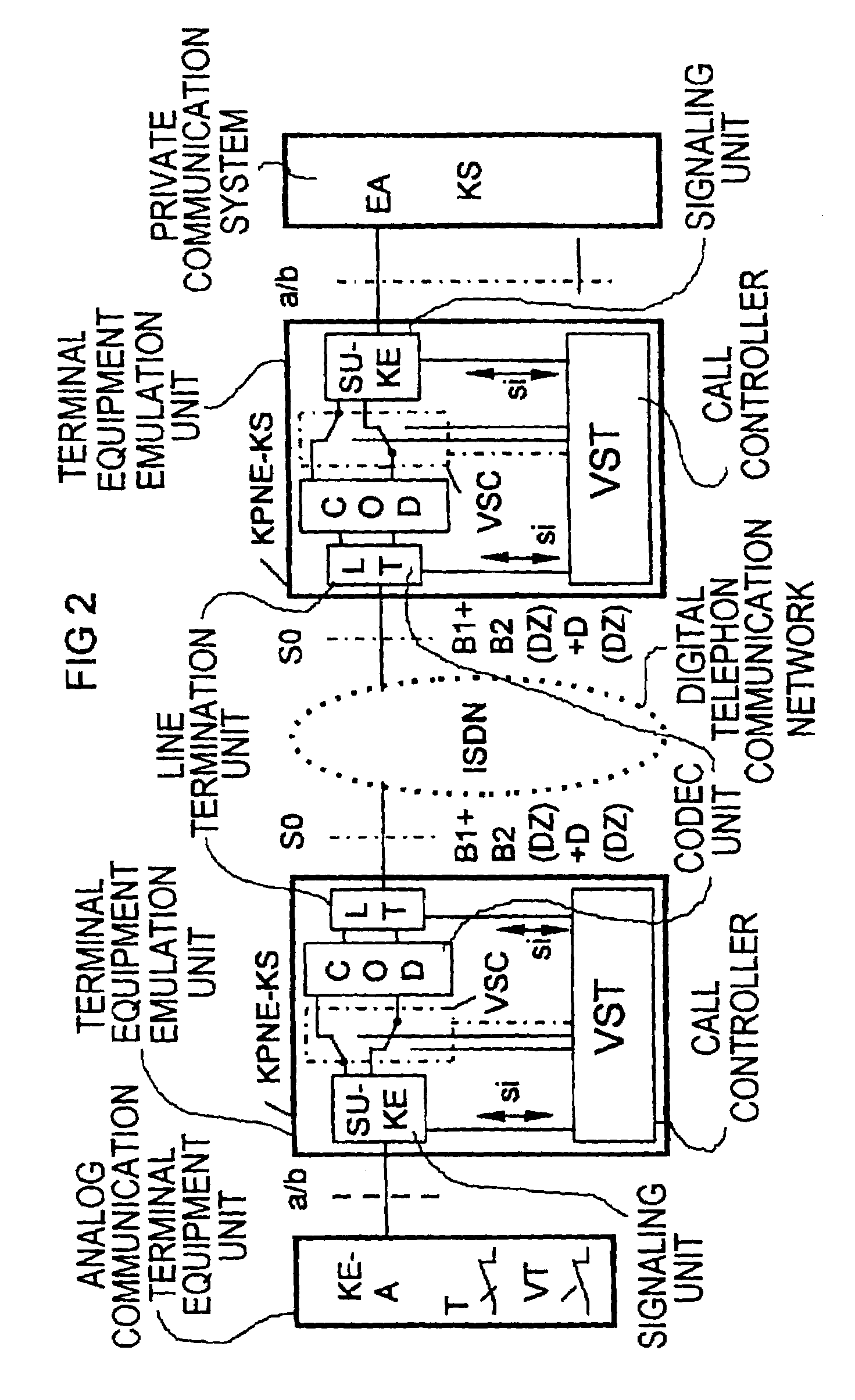
Method for signaling a connection set-up emanating from a calling terminal via a communications network to a called terminal
InactiveUS20060159247A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsISDN systemsTelecommunicationsAuthorization
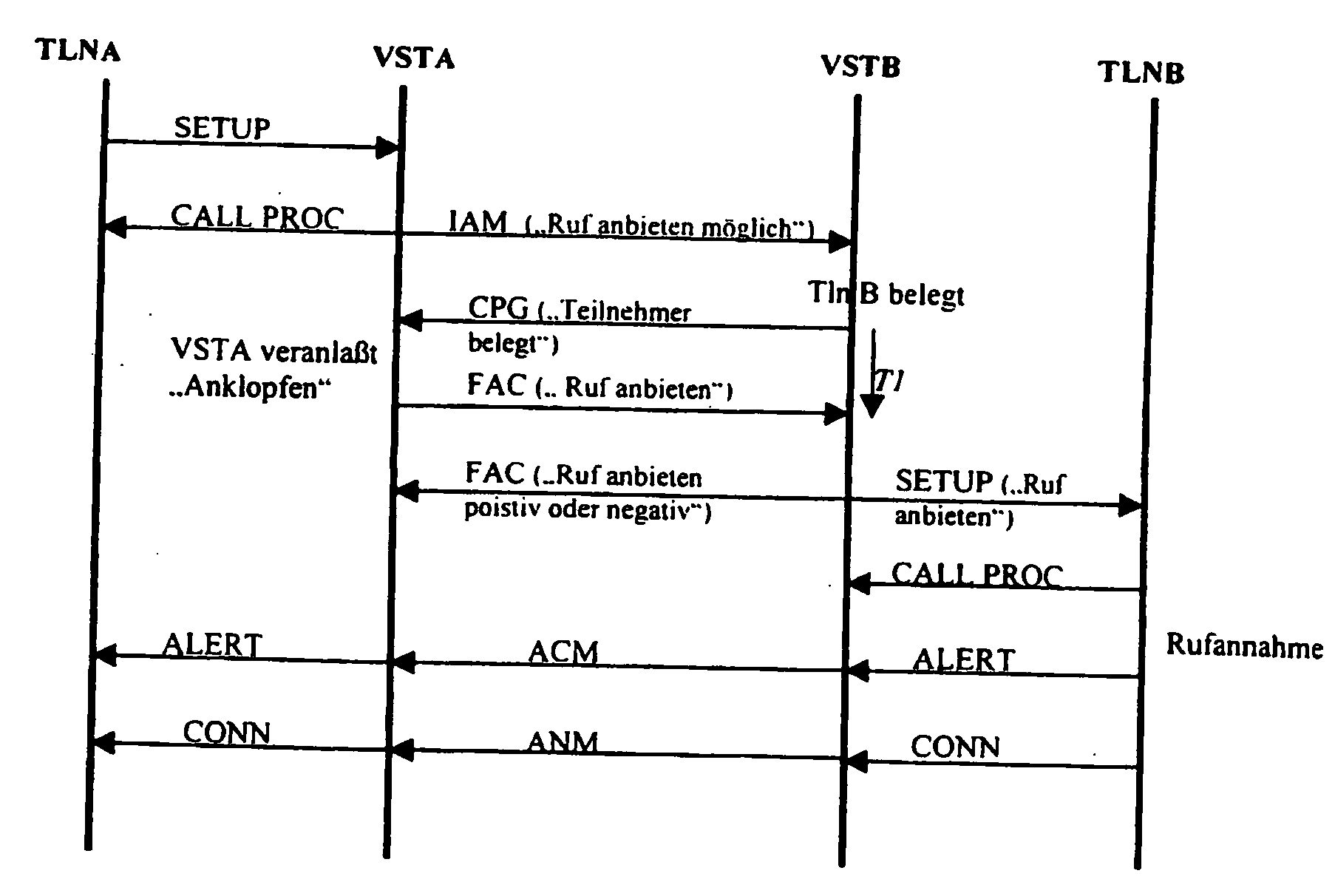
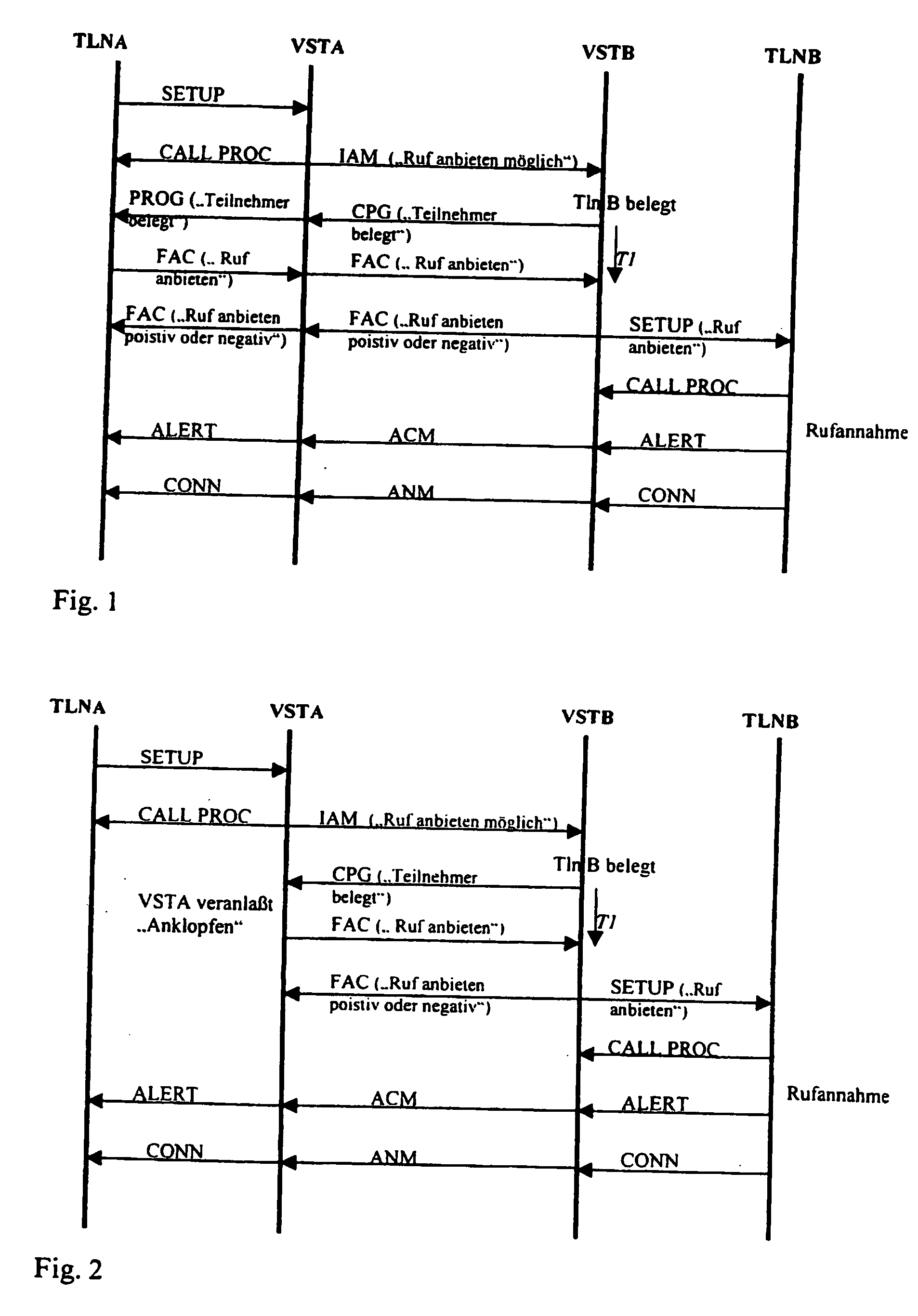
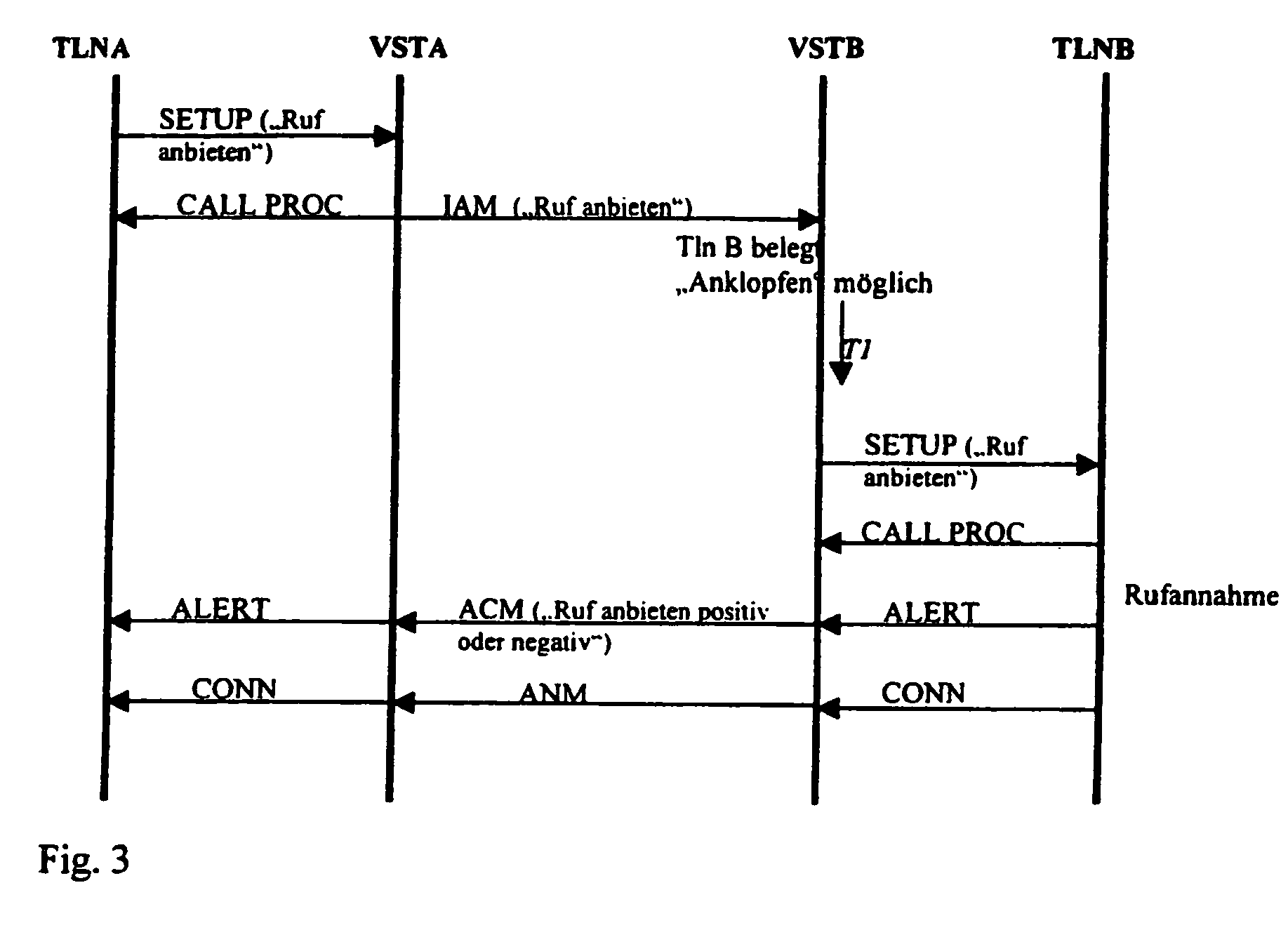
A method for signaling connection setup emanating from a calling terminal (TLNA) via a communications network to a called terminal (TLNB), where at least one access connection routed to the called terminal is busy, characterized in that, if there is no authorization for such singaling for the relevant called terminal (TLNB), signaling which indicates said connection setup is prompted for the called terminal (TLNB) in the case of the calling terminal (TLNA) or is initiated by the originating exchange (VSTA) in the communications network, in that this originating exchange (VSTA) stores appropriate signaling authorization for the relevant calling terminal (TLNA), and in that the calling terminal (TLNA) or the originating exchange (VSTA) has received a message indicating the busy condition of the at least one access connection routed to the called terminal (TLNB).
Owner:SIEMENS AG
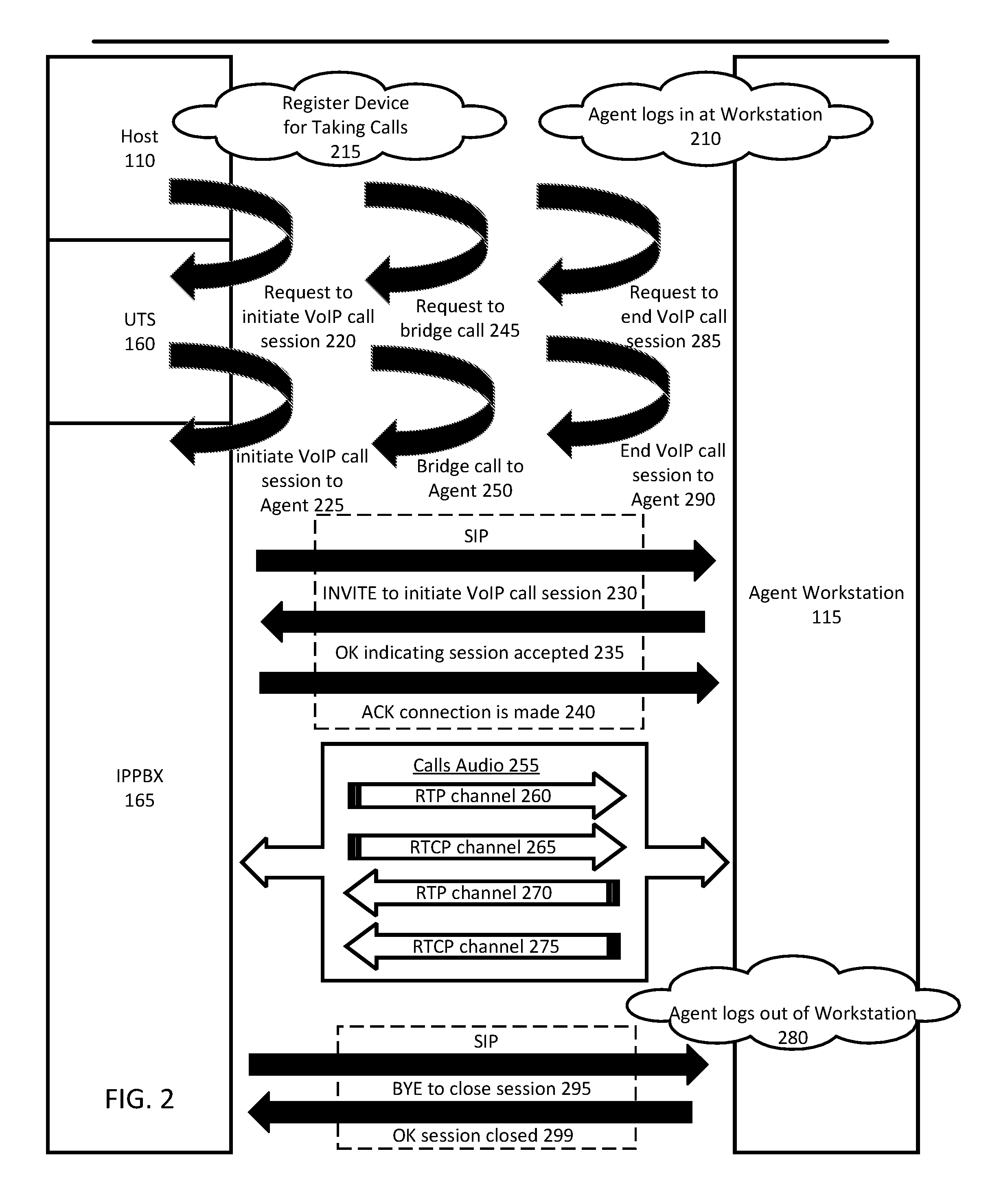
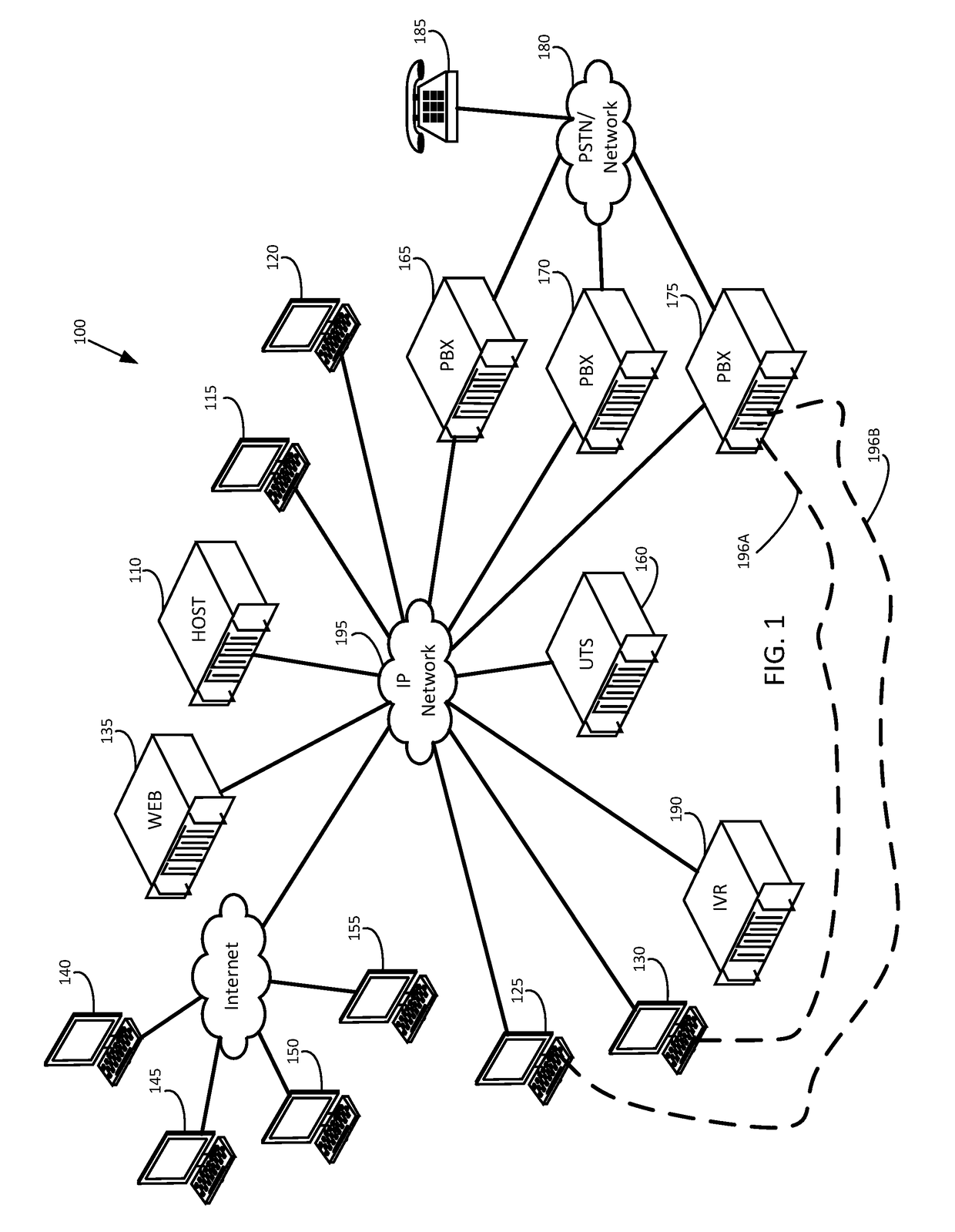
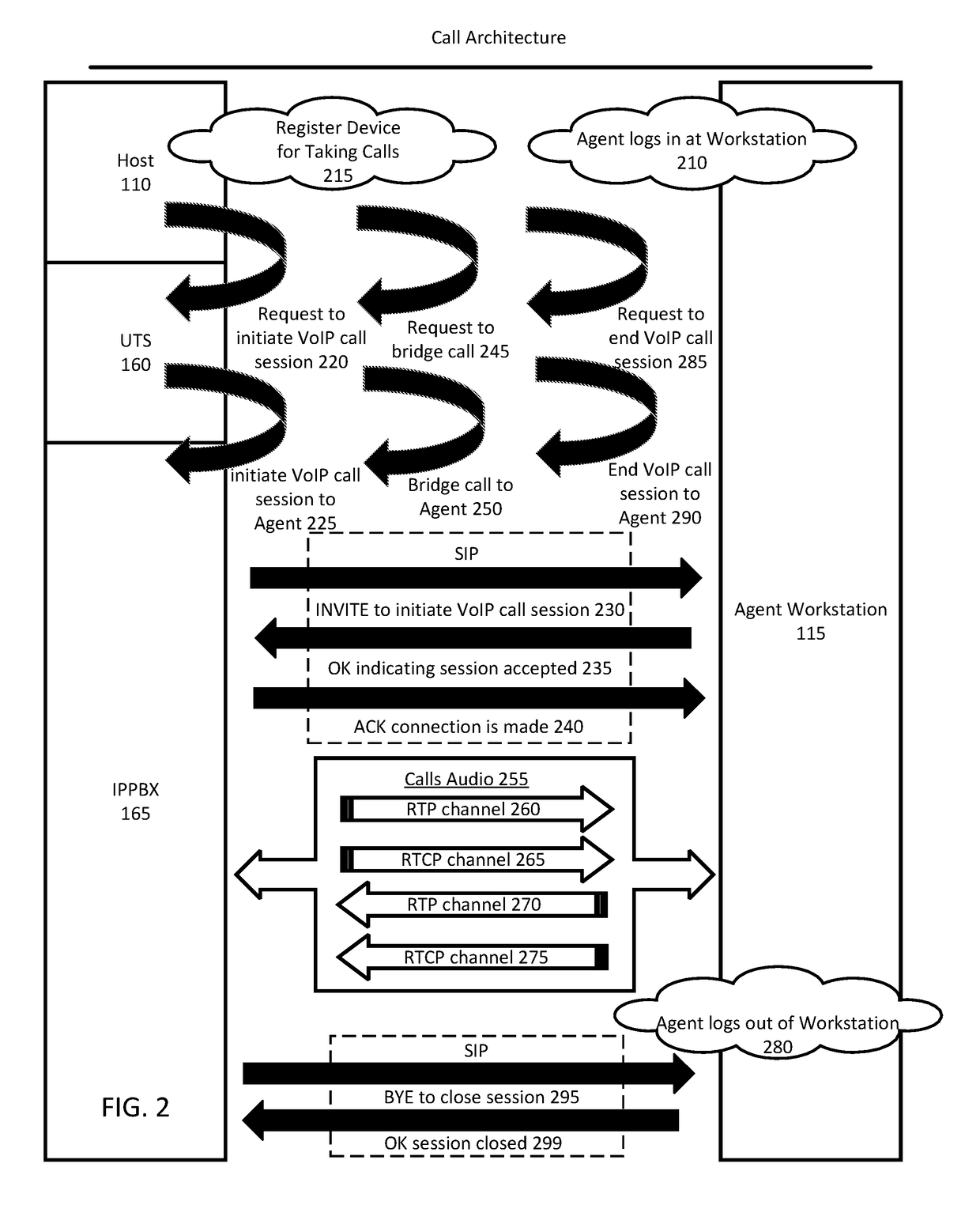
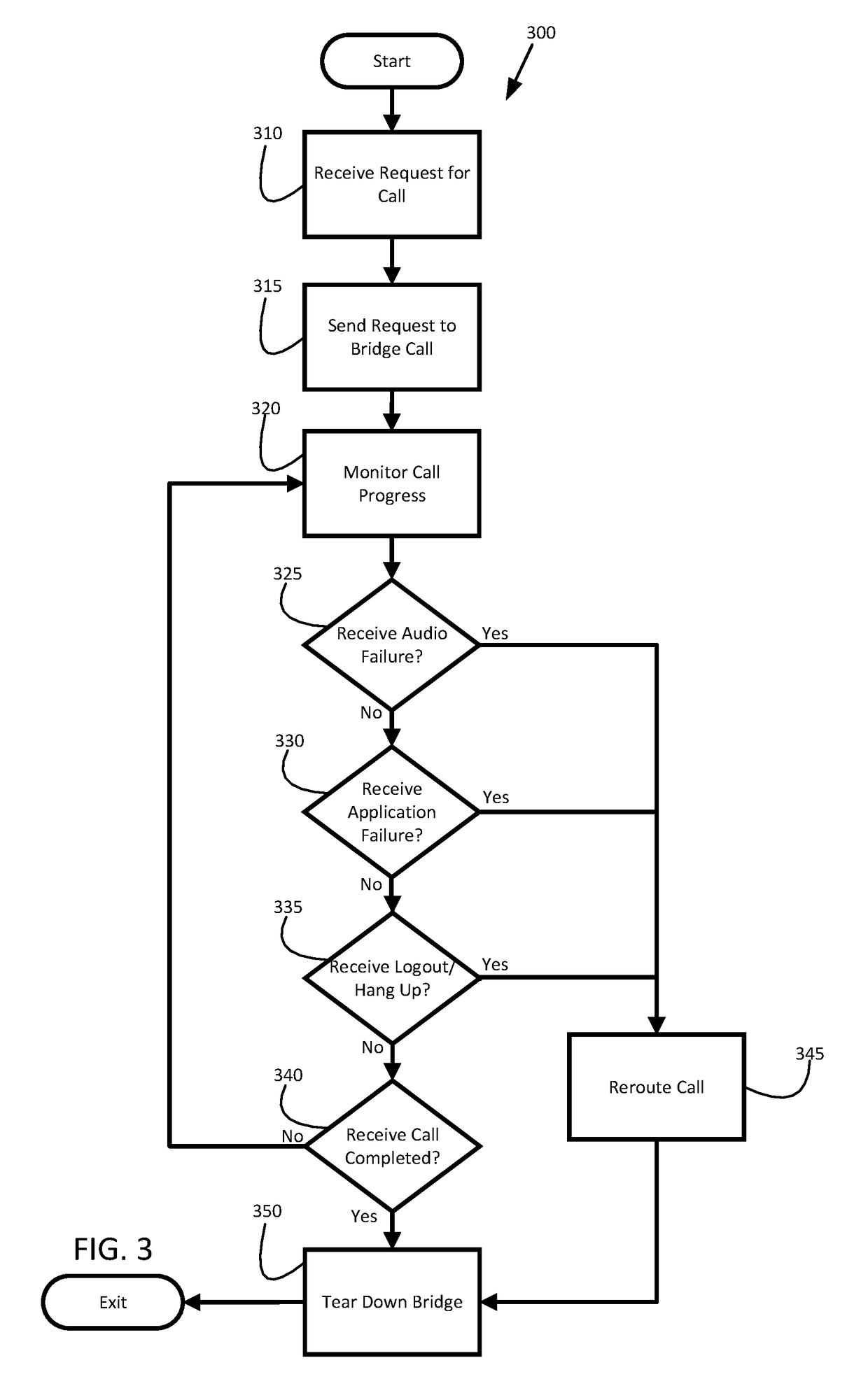
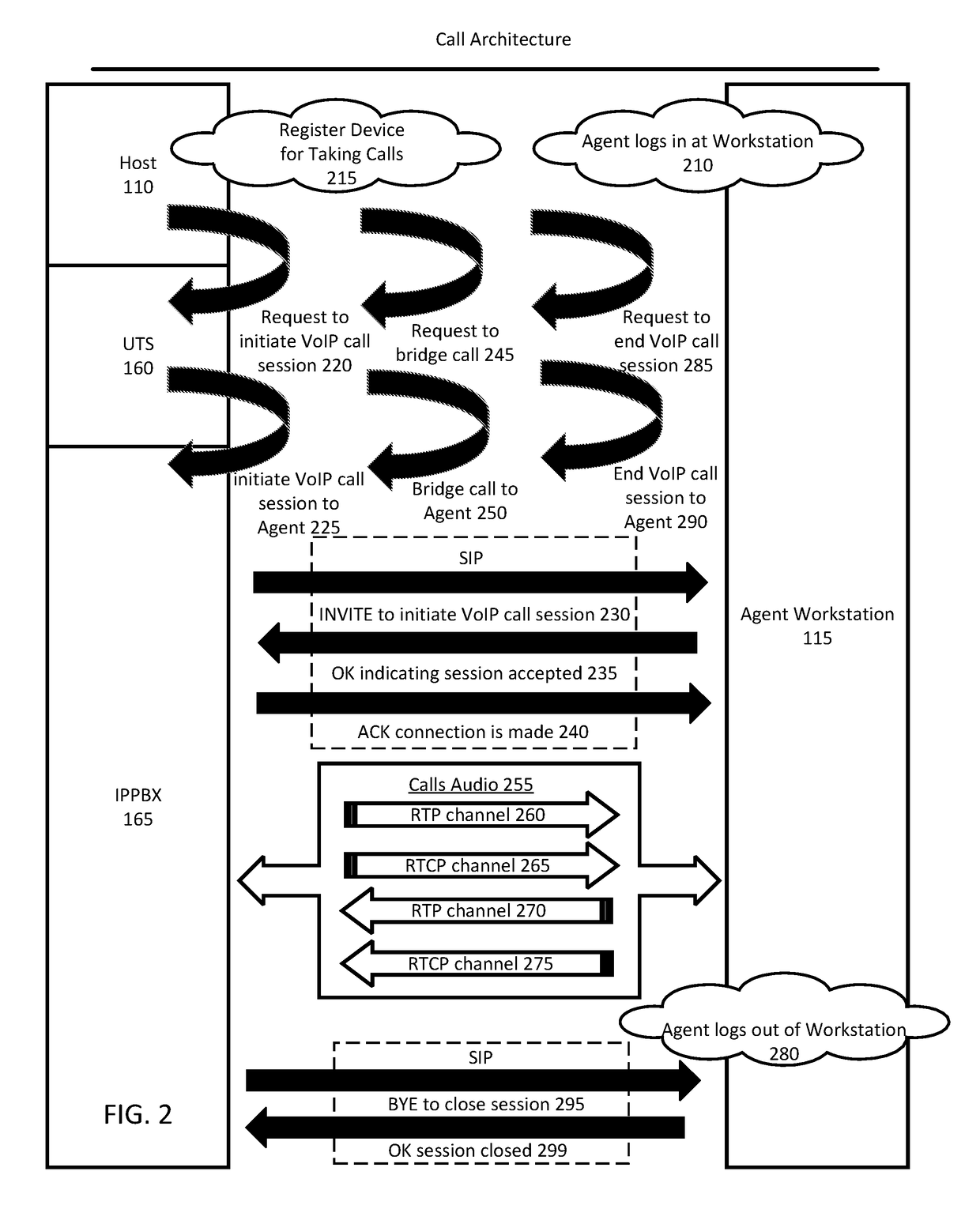
Handling audio path failure and poor quality of service for voice calls in a contact center
ActiveUS9456076B1Poor serviceISDN systemsSpecial service for subscribersQuality of serviceComputer hardware
Various embodiments of the invention provide methods, systems, and computer program products for handling an audio path failure and / or non-conformant QoS for a call between a contact center agent and remote party. Specifically, an audio path is established to a first telephony device being used by the agent and a call is bridged onto the audio path so that audio can be streamed back-and-forth between the first telephony device and a second telephony device being used by the party. Accordingly, various embodiments of the invention involve monitoring the audio path to detect an audio path failure and / or non-conformant QoS for the audio and bridging the call onto a second audio path when a failure or non-conformant QoS is detected so that the call is not disconnected from the second telephony device and a third device (e.g., IVR) can stream audio over the second audio path to the second telephony device.
Owner:NOBLE SYSTEMS CORPORATION
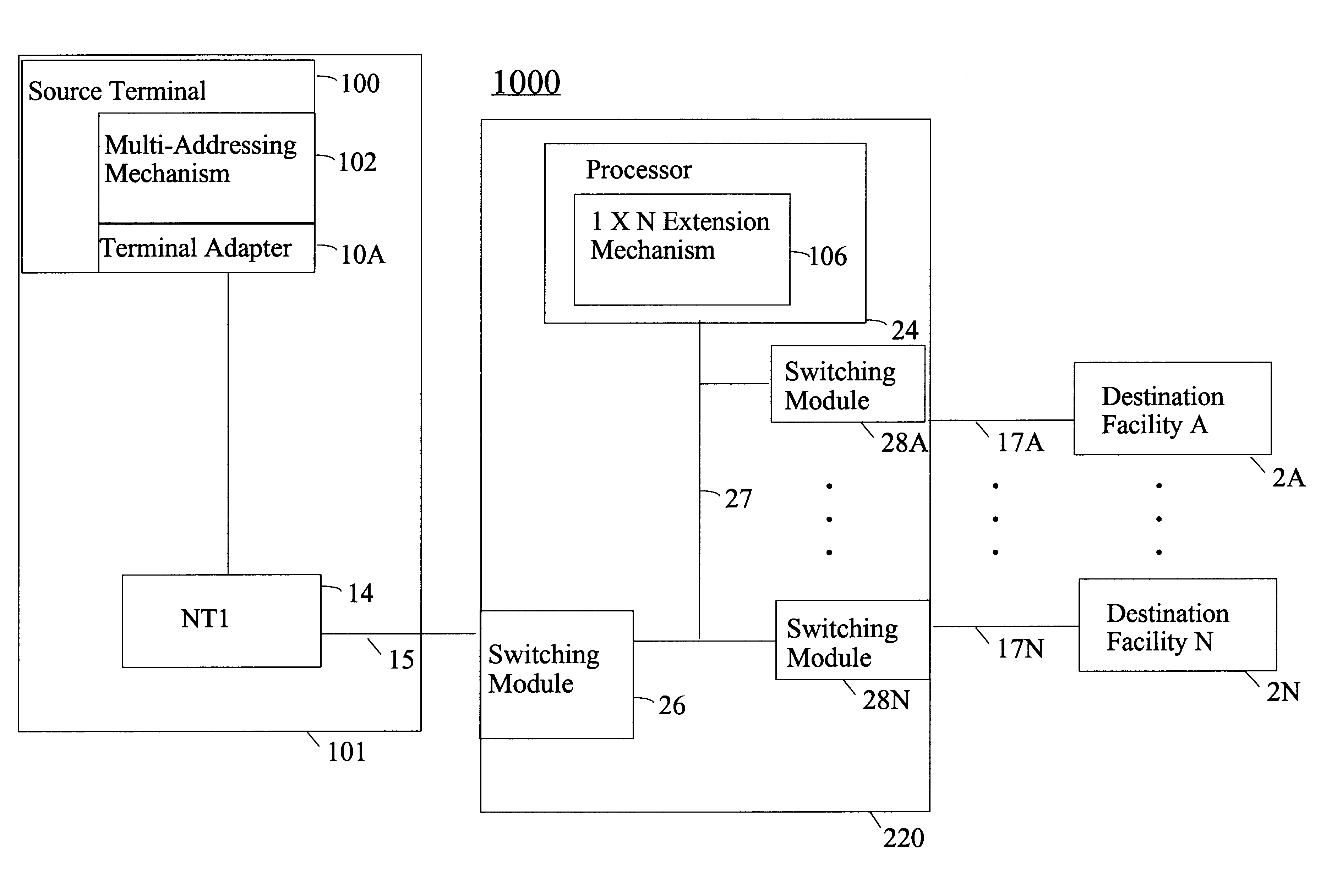
Method and apparatus for sending a 1xN communication message
InactiveUS6304579B1ISDN systemsSpecial service for subscribersTelecommunications linkCommunication link
A method and apparatus in a computer network system form a setup message at a source terminal. The setup message includes a 1xN extension message that identifies N different destination facilities, as identified by an operator, to which a data message is to be sent. The source terminal relays the setup message to a 1xN switch, where the 1xN switch invokes a 1xN extension mechanism that coordinates the establishment of communication links with the N different destination facilities identified in the setup message. For the destination facilities that have at least one communication link available thereto, the 1xN extension mechanism sends the data message to the available destination facilities at the same time.
Owner:RICOH KK
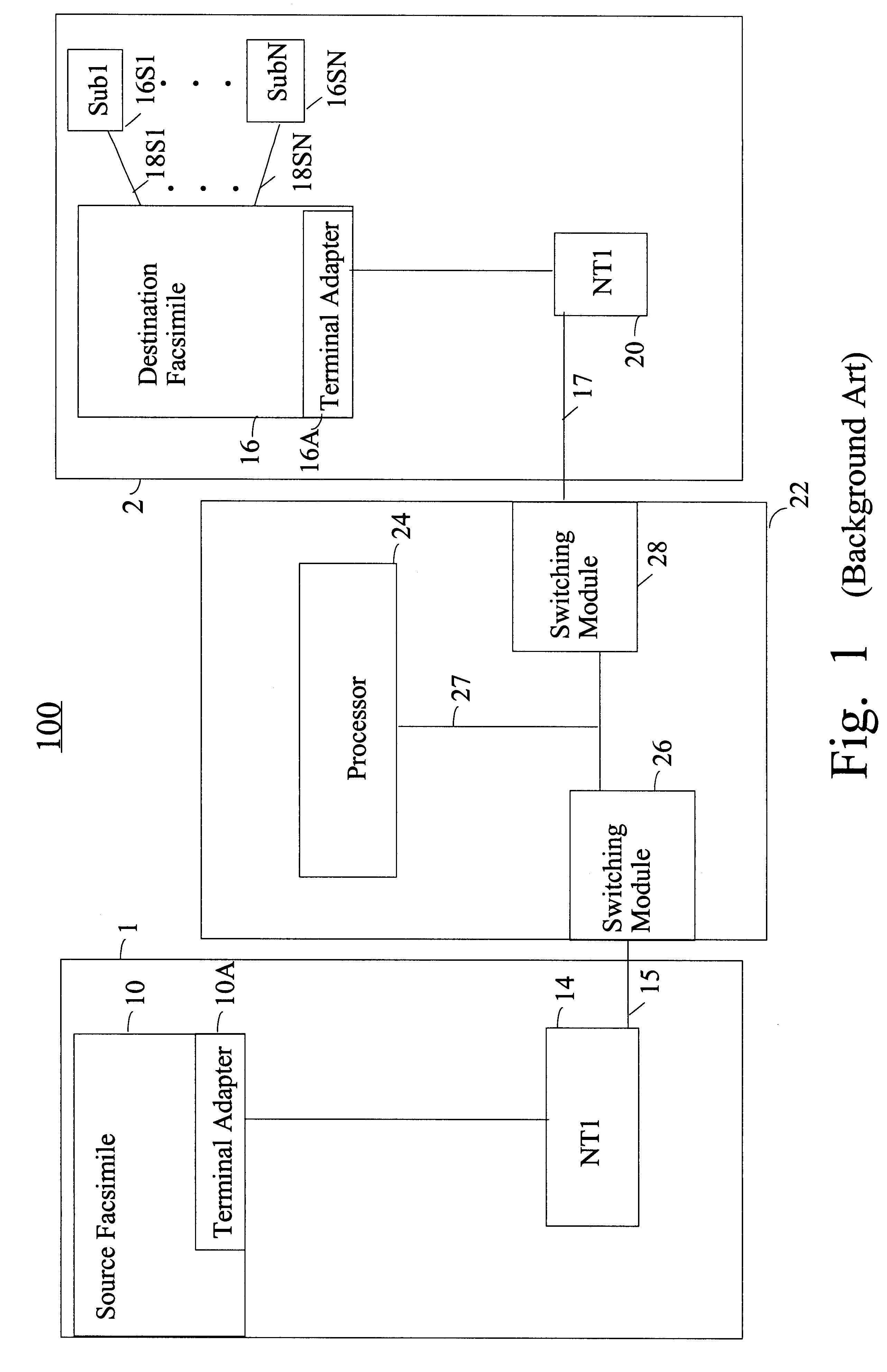
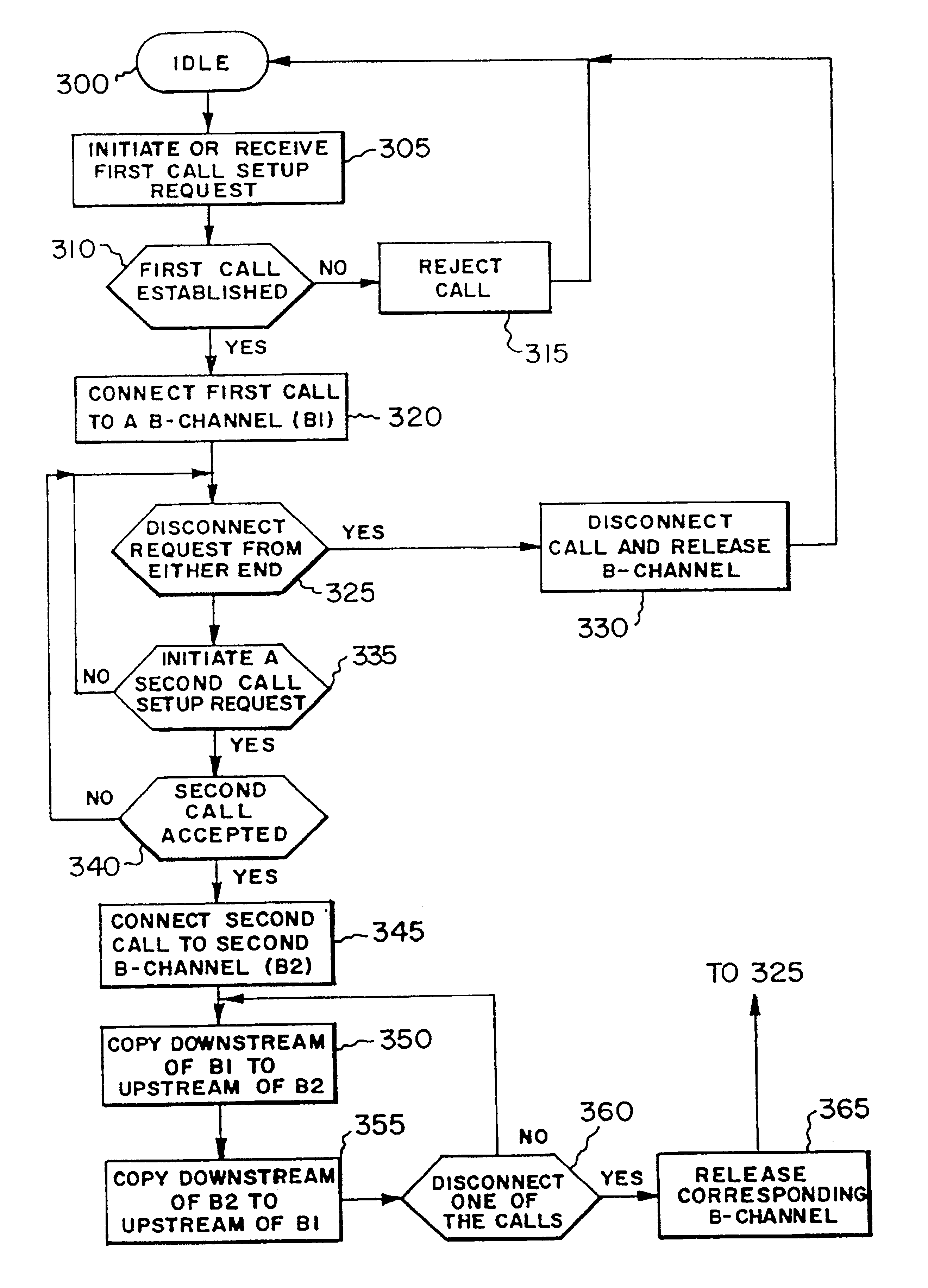
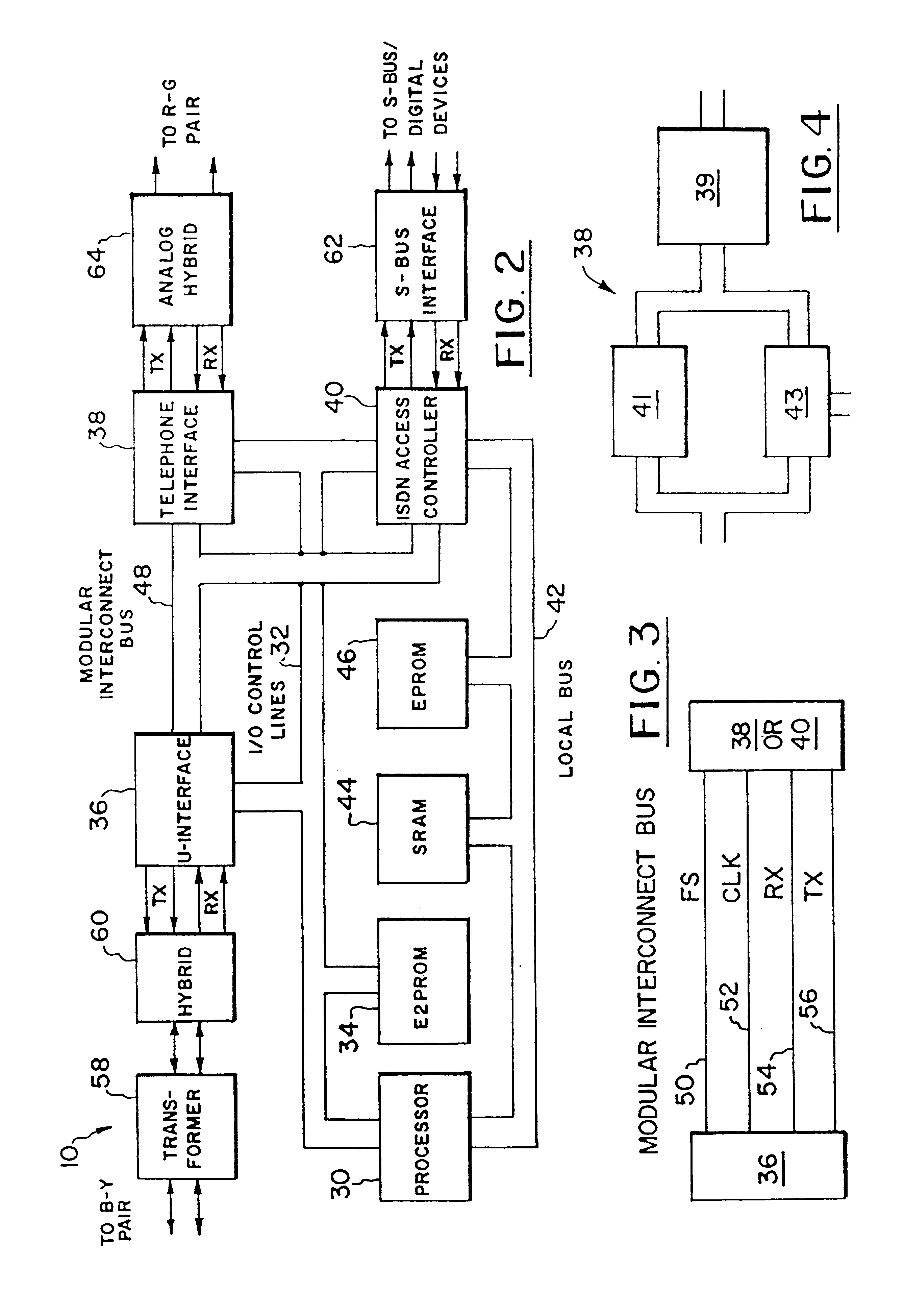
Methods for performing intelligent network services with an ISDN network terminator located at a subscriber's premise
InactiveUSRE38596E1Eliminate interventionEliminate needCordless telephonesSpecial service provision for substationIntelligent NetworkSmart network
Disclosed are call processing methods which are performed by a network terminator located at a subscriber's premise. The network terminator is coupled to a digital network and a communication device at the subscriber's premise and can perform call waiting, caller identification, call conferencing without intervention from a telco's switching system that requires an additional charge to the subscriber for these services. In addition, the network terminator can perform a method which allows two digital communication devices coupled to one S-bus to share a communication session. In another embodiment, up to a six way conference call can be established with an analog telephone coupled to an ISDN network via the network terminator of the present invention.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
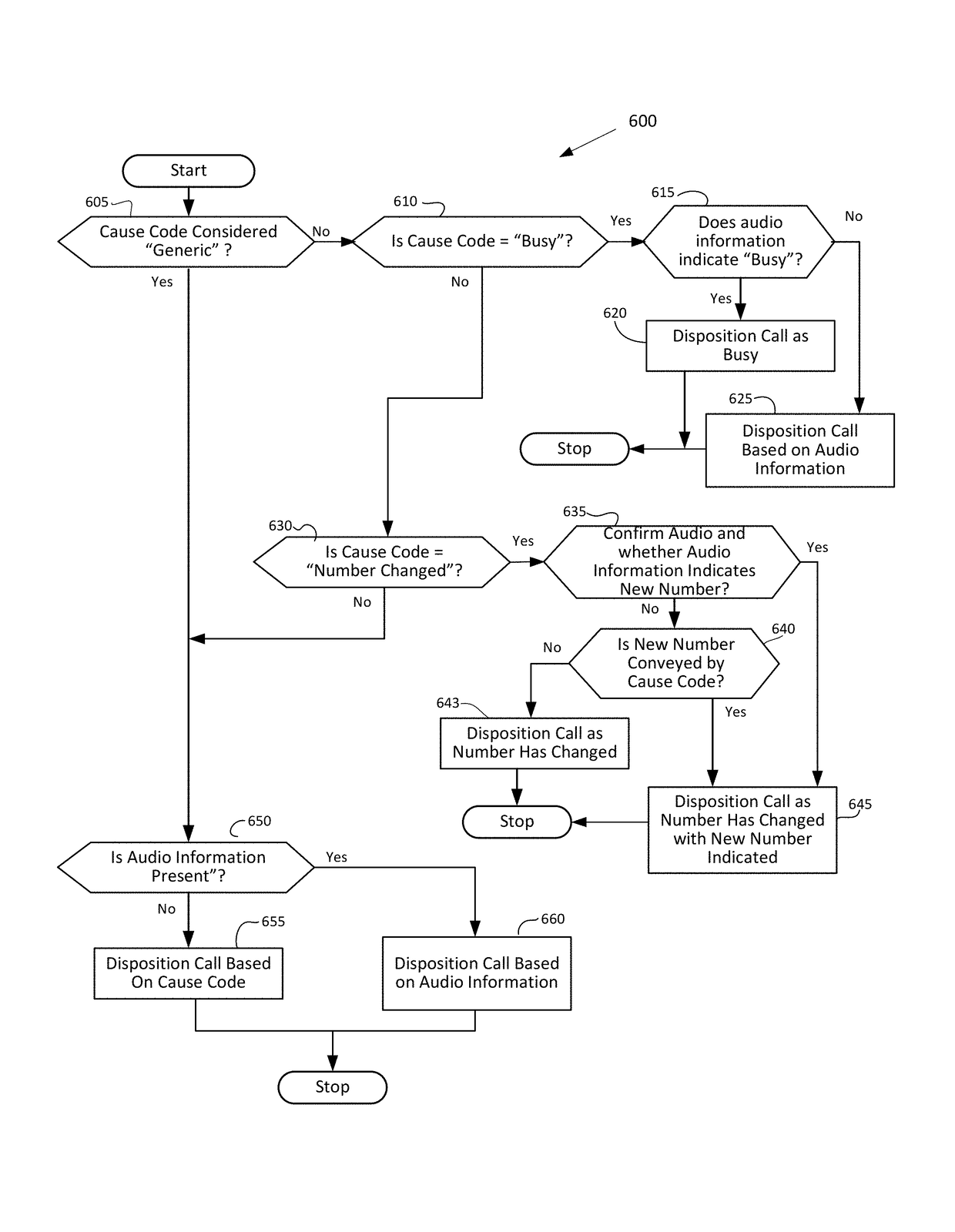
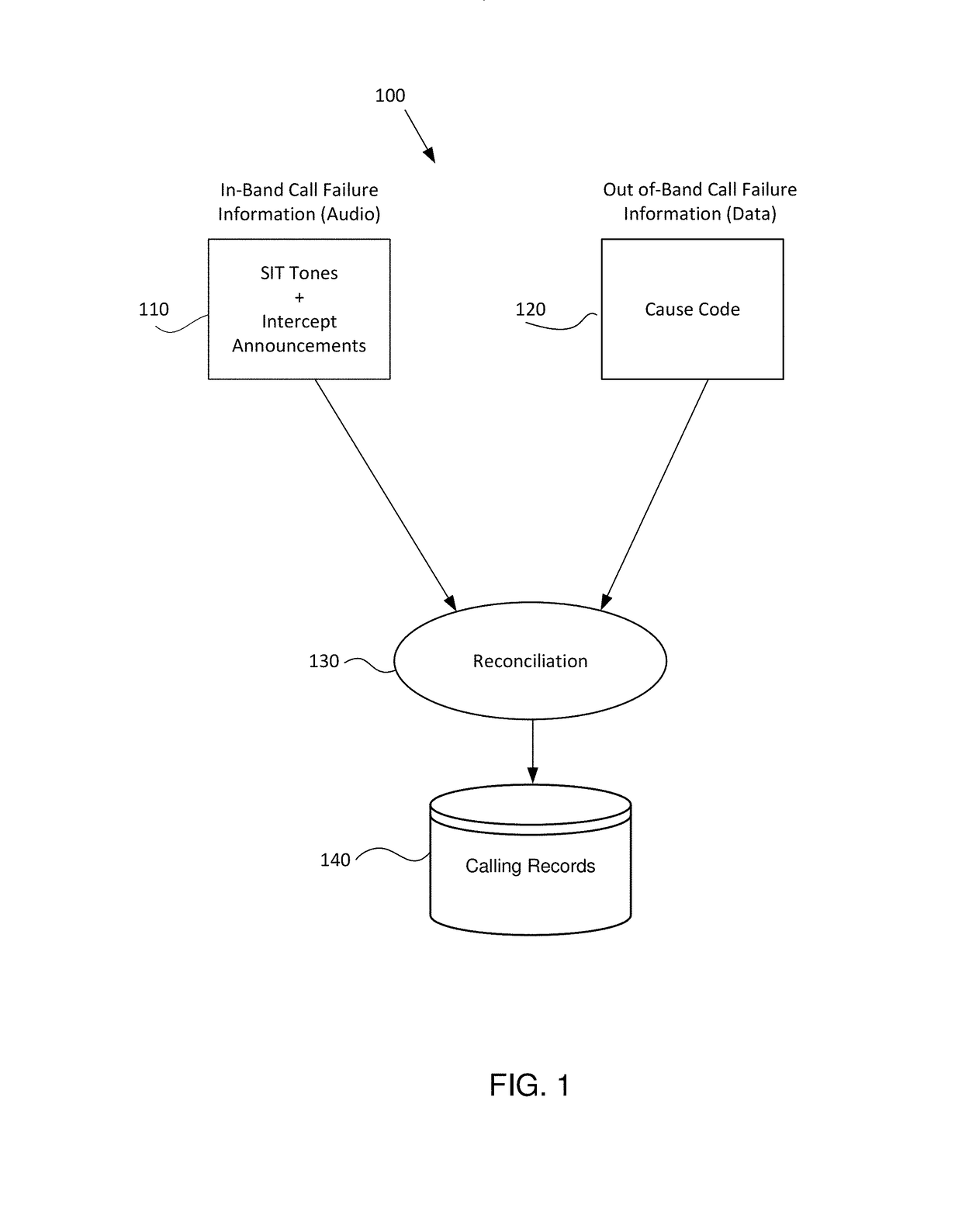
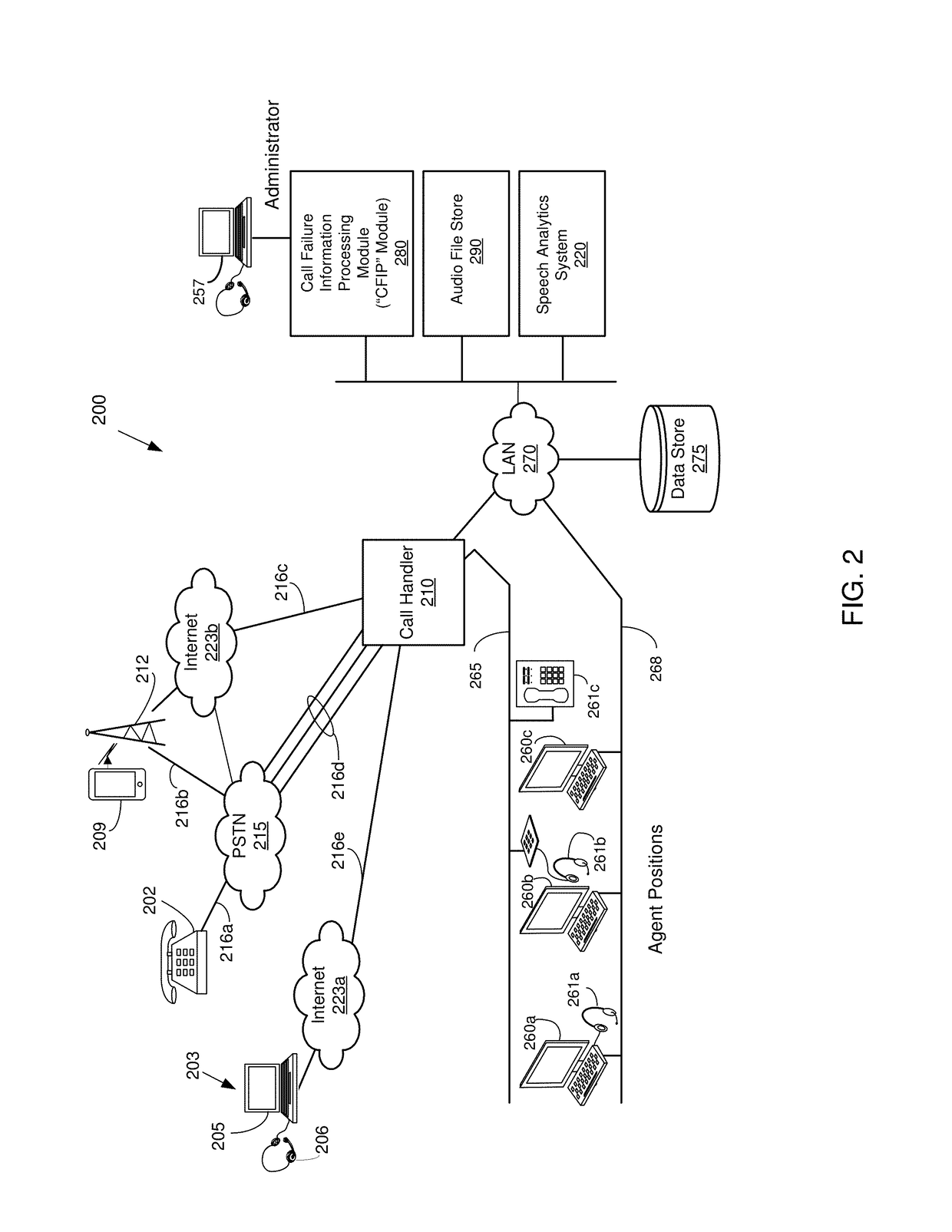
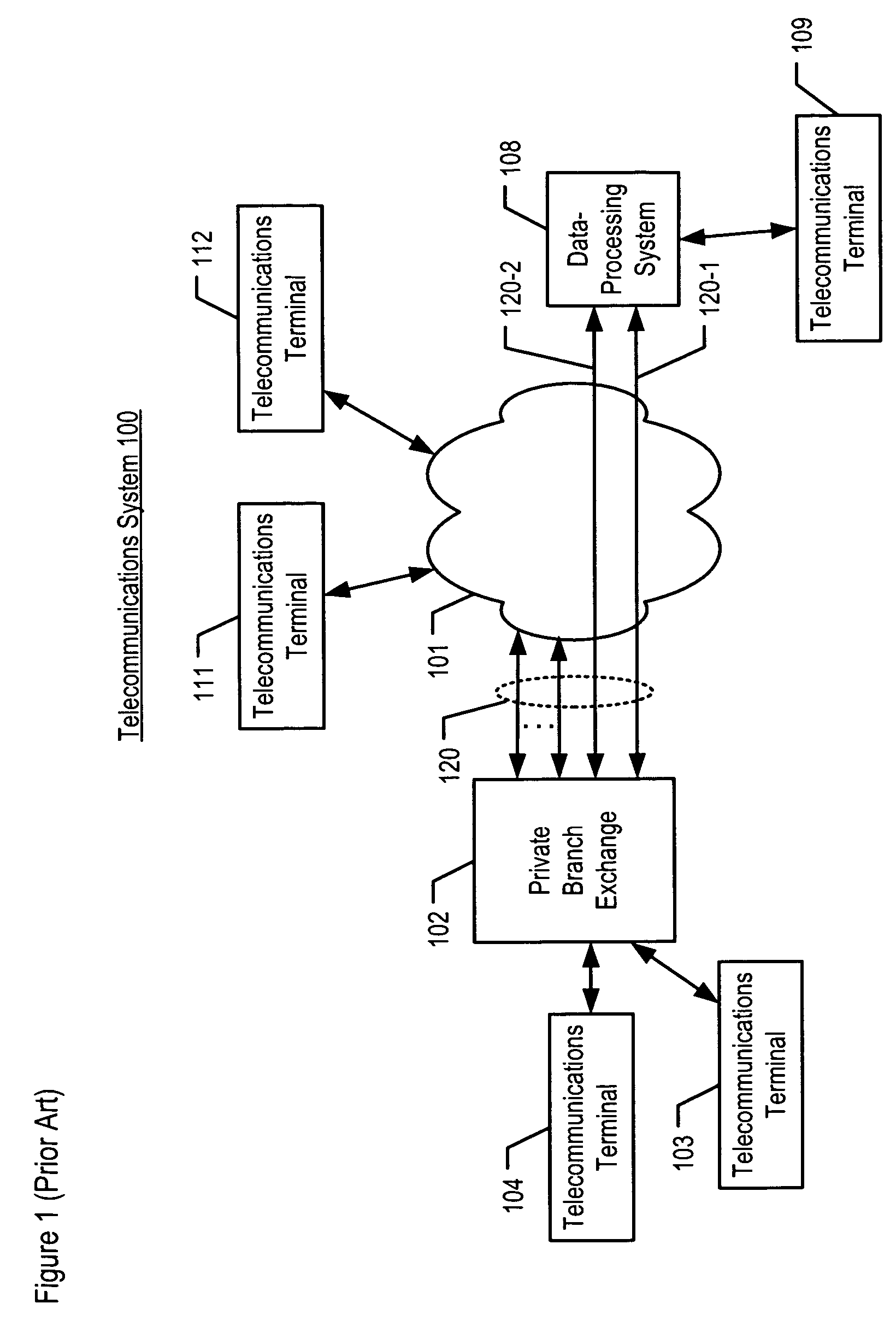
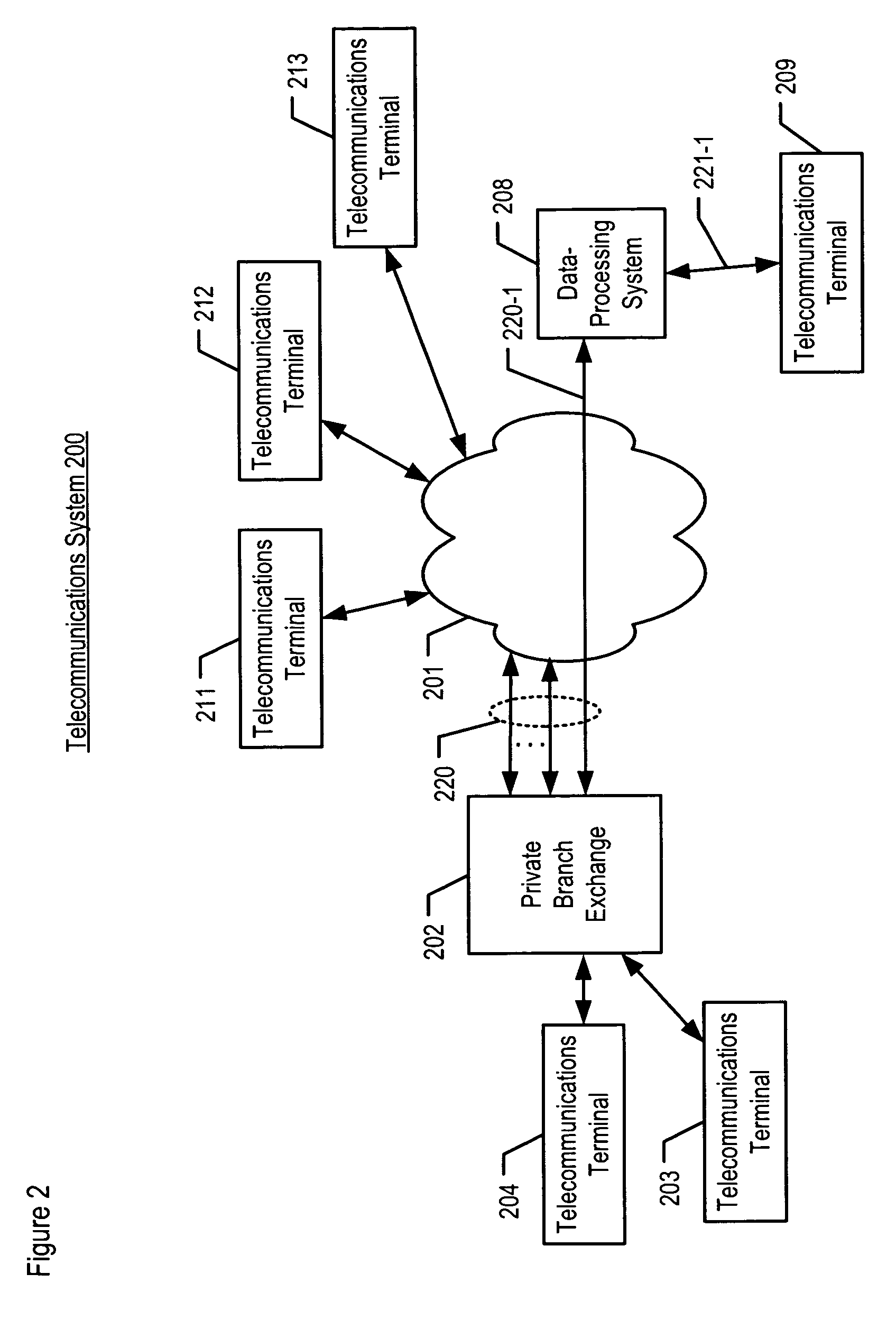
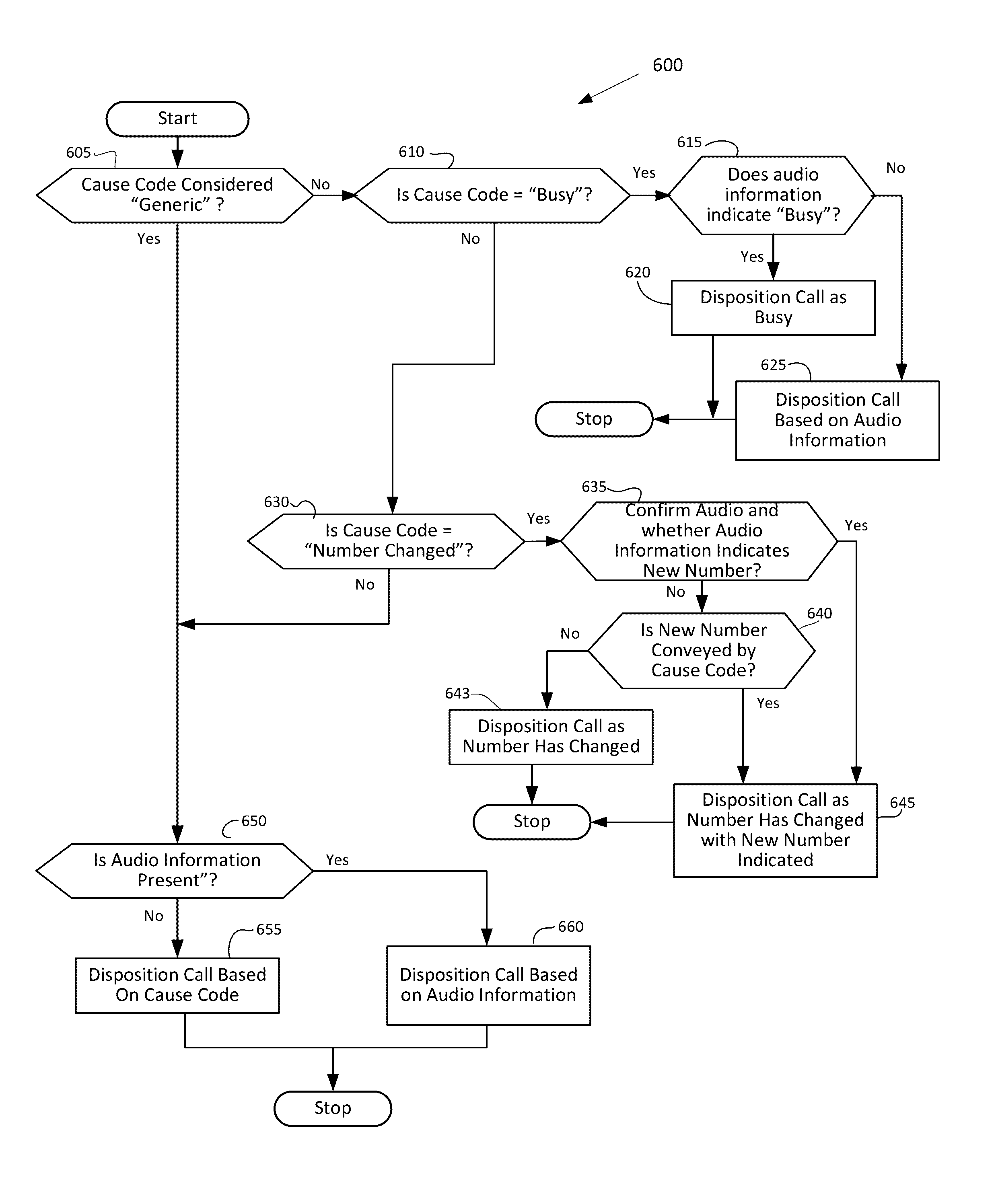
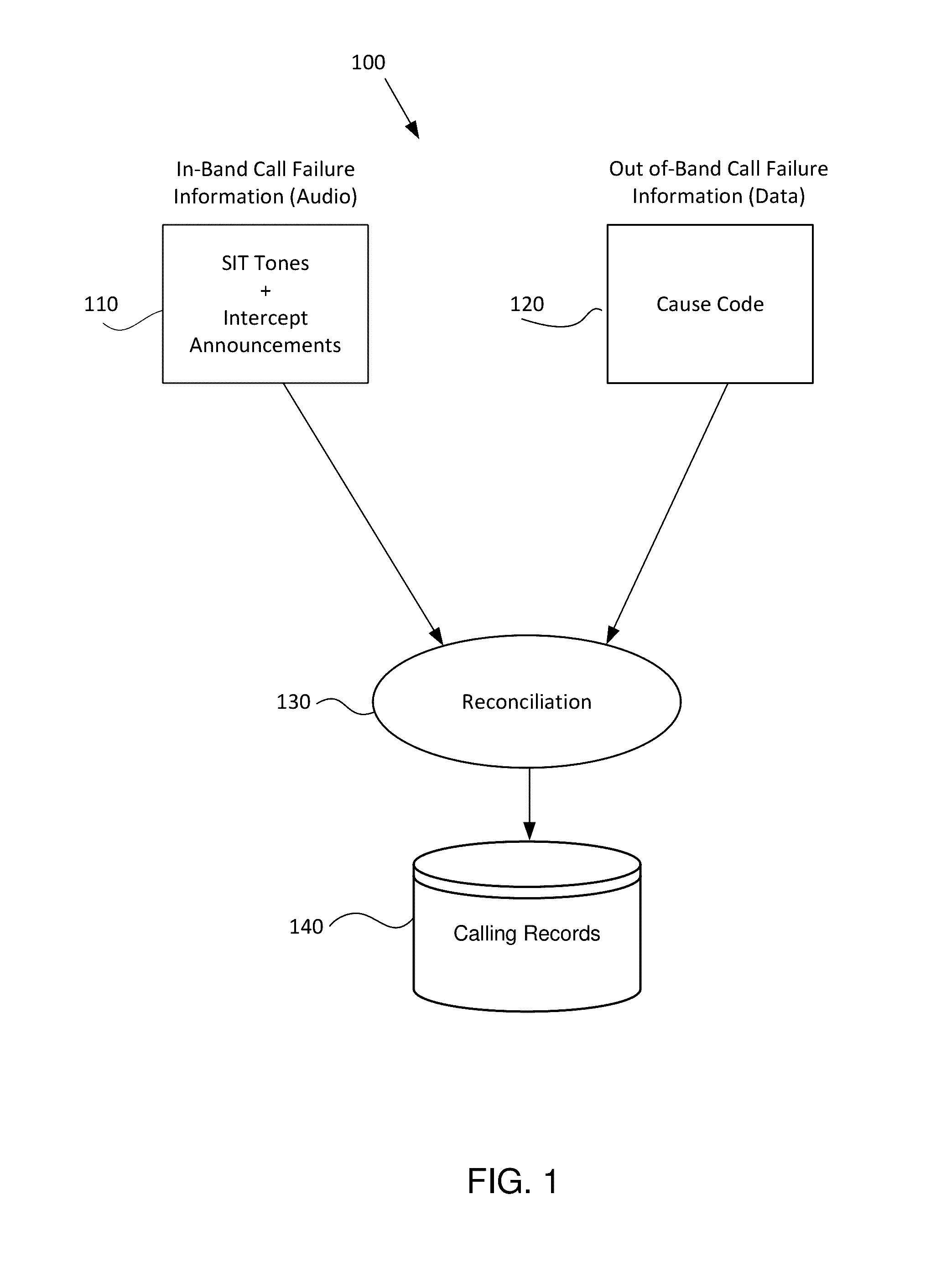
Accurate dispositioning of a telephone call by reconciling cause codes with in-band audio information
ActiveUS9787839B1Avoiding unnecessary reattemptsThe result is accurateInterconnection arrangementsISDN systemsSignal elementSpeech sound
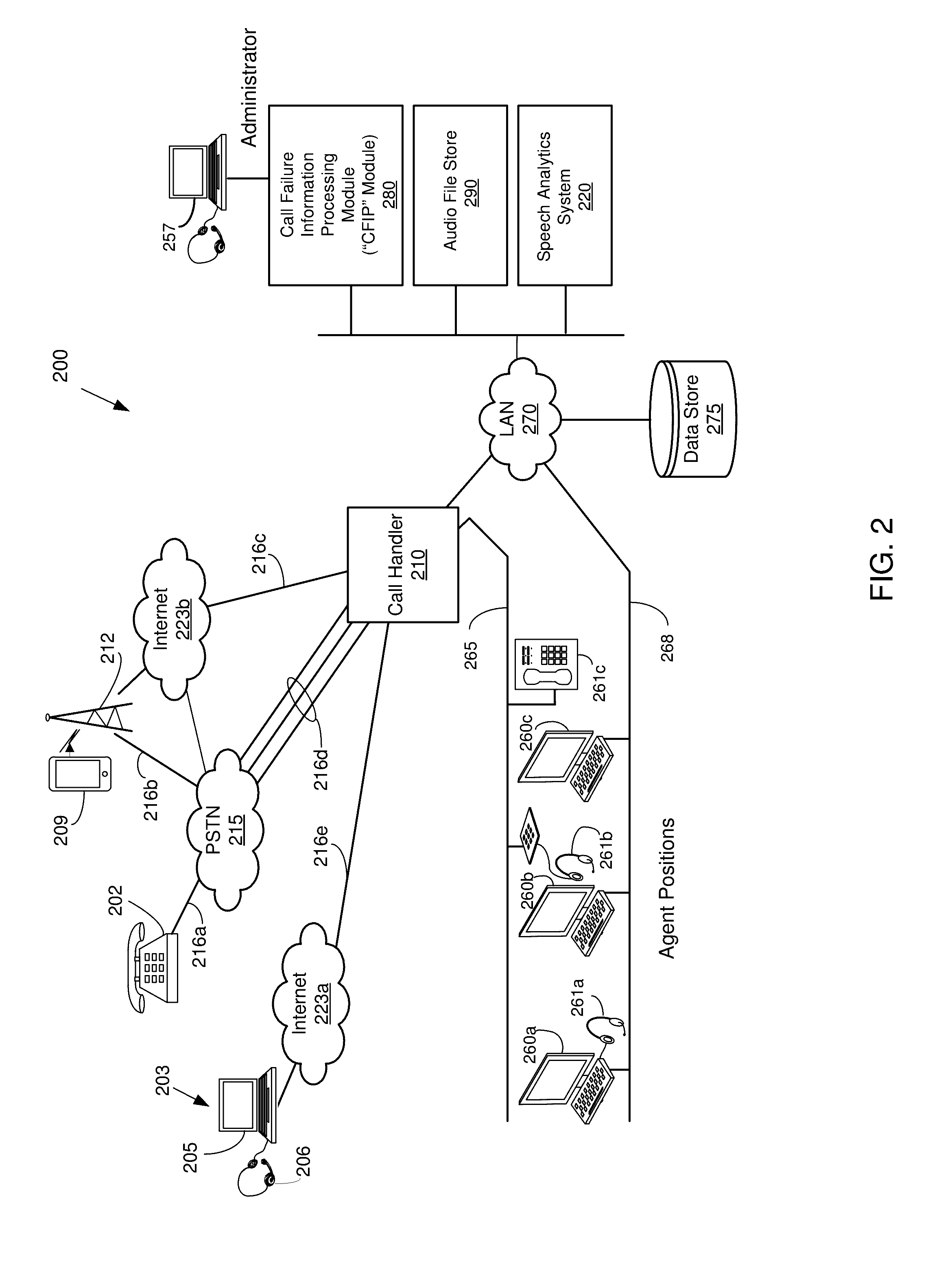
A telephone call to a remote party may encounter a number of abnormal conditions, which prevents the call from being offered to the remote party's interface. These conditions may be indicated to the calling party using call progress information conveyed as out-of-band information, in the form of signaling elements and / or as in-band information, in the form of audio information. The audio information may include a special information tone and / or an intercept announcement. The call handler originating the outbound call may provide the audio information to a speech analytics component that analyzes the audio information. The analyzed audio information may be reconciled with the out-of-band information. Various rules can be applied to ascertain how to disposition the call in instances where the in-band and out-of-information are inconsistent. Once reconciled, accurate call disposition information can be recorded in the call record for that call.
Owner:NOBLE SYSTEMS CORPORATION
Implementation of additional functions for user connections having individually configured performance criteria
InactiveUS7127052B1Avoid unnecessary useAvoid disadvantagesMultiplex system selection arrangementsISDN systemsVirtual userComputer science
At least one part of at least two user connections (TA1 . . . 6) having configured performance criteria and being allocated to at least two network devices (LE1 . . . 3) is assigned to at least one group (NWHG), to which group-specific performance criteria and / or characteristics (PDN, HUNT) can be allocated. The group (NWHG) is controlled by one of the network devices (LE1), whereby the user connections (TA1, 3, 4, 6) which have not been physically allocated to this network device (LE1) are allocated to said device as virtual user connections.
Owner:NOKIA SIEMENS NETWORKS GMBH & CO KG
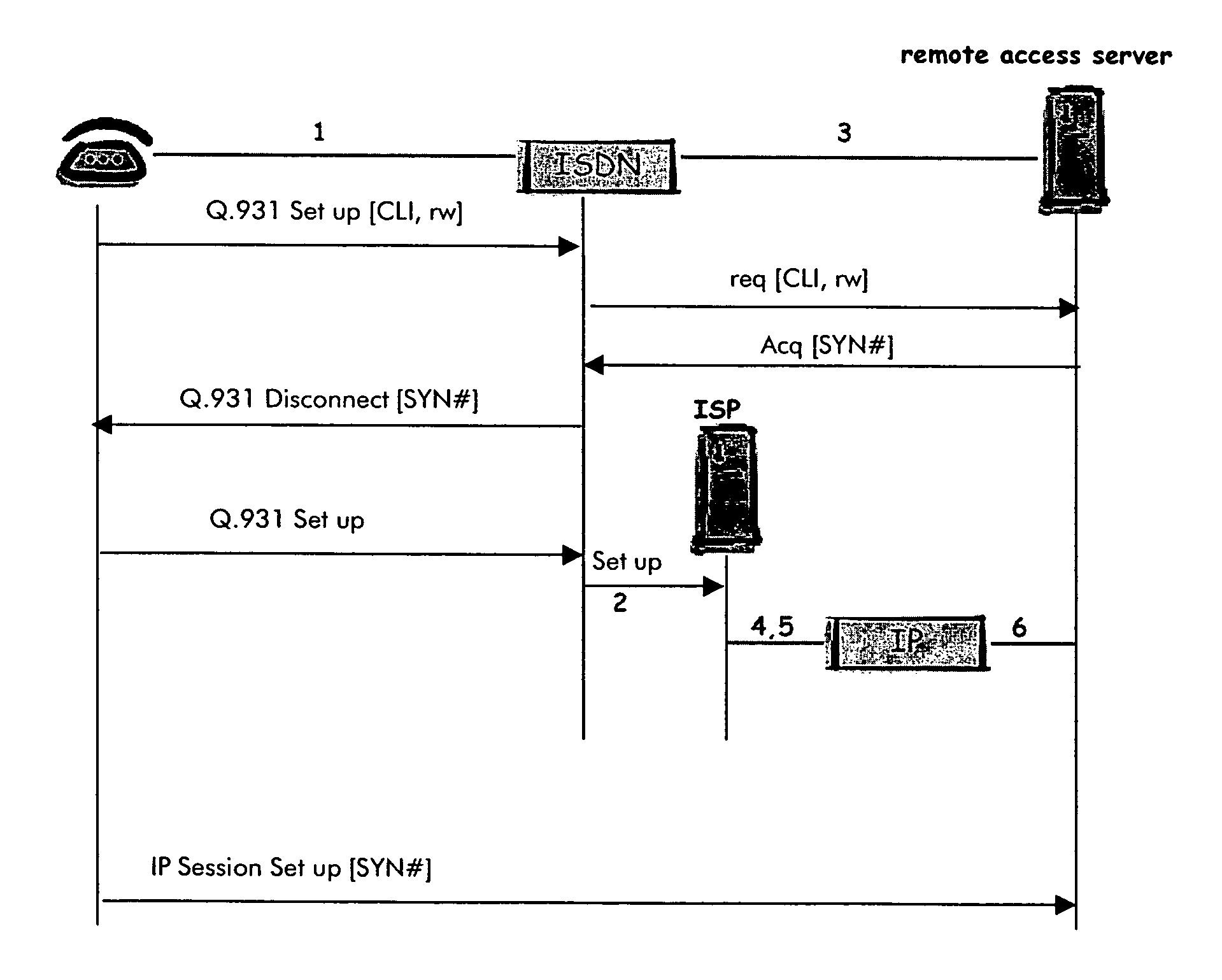
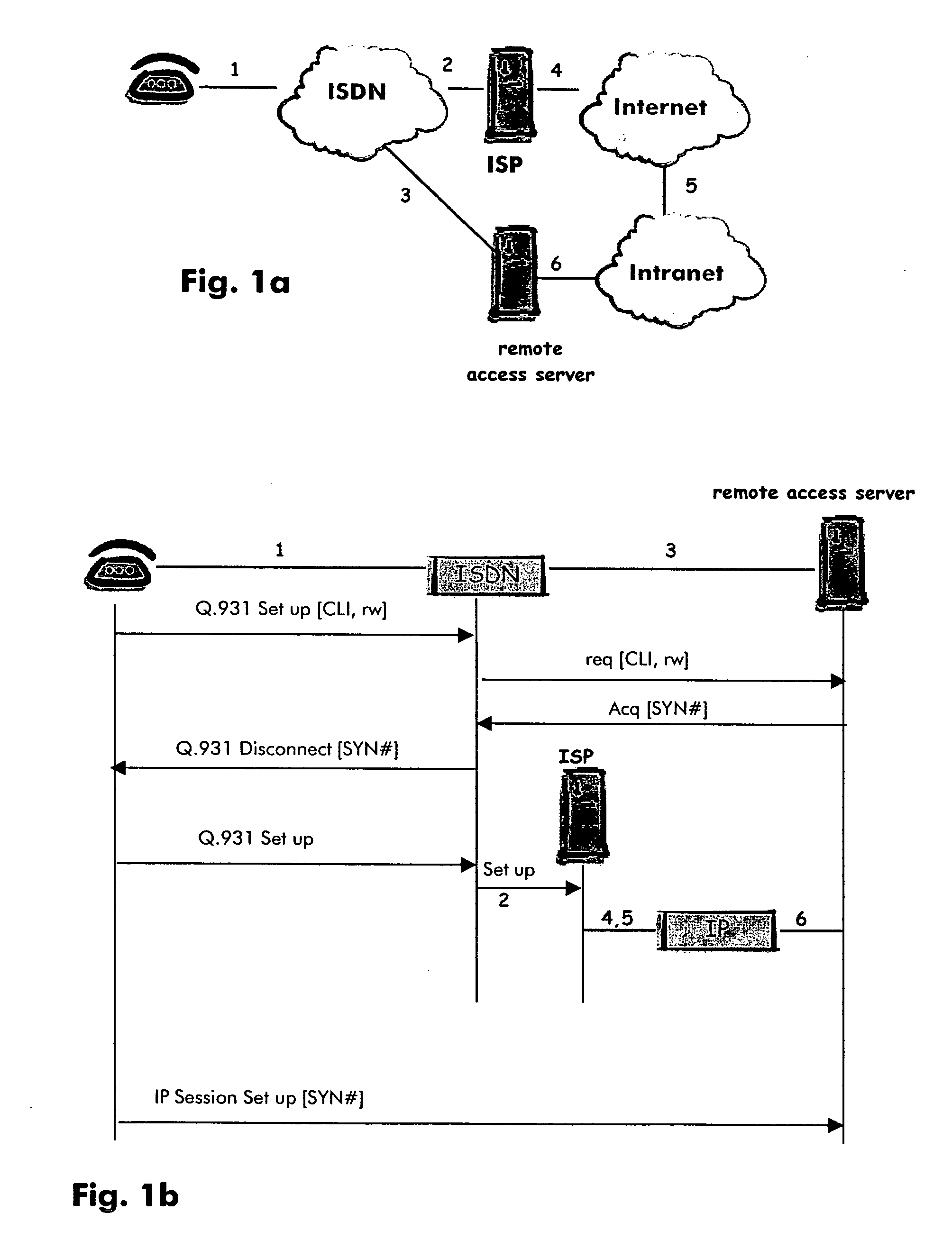
Location information for remote user
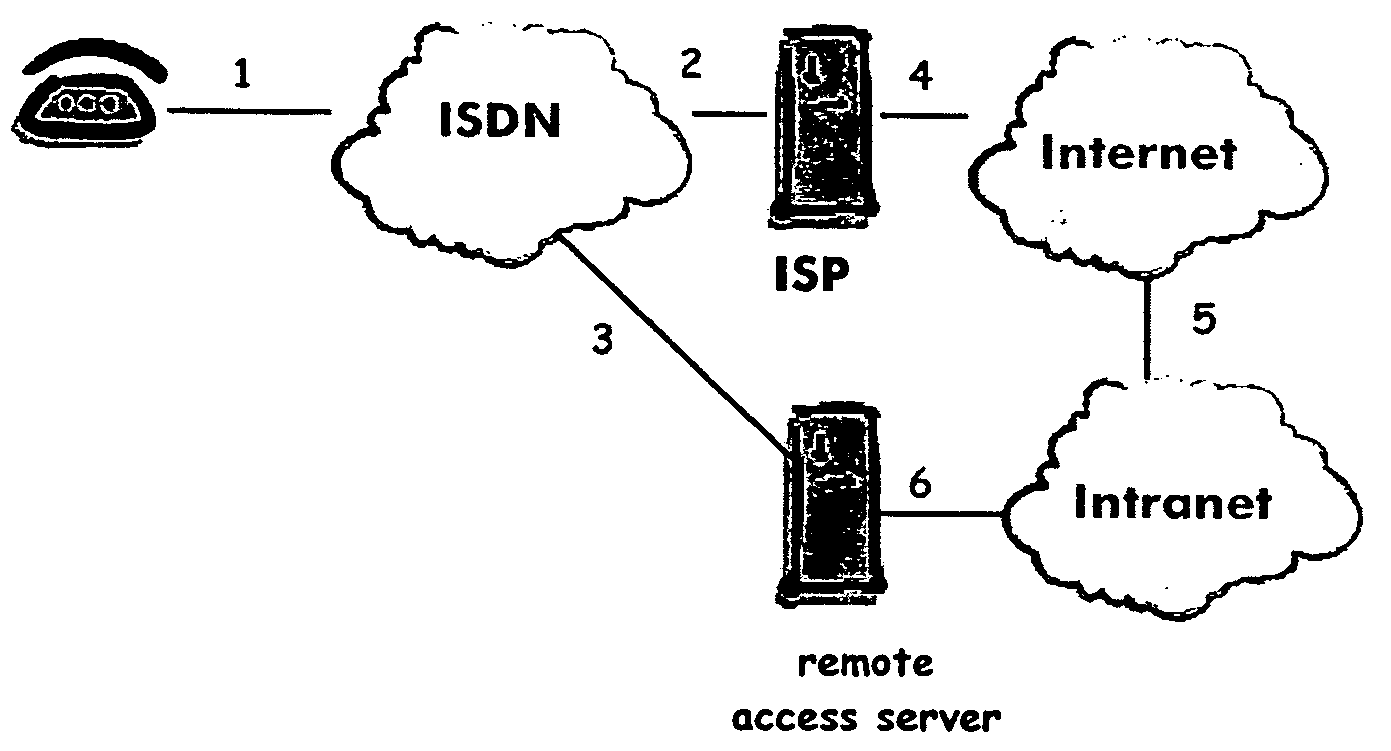
InactiveUS20050094627A1ISDN systemsSpecial service for subscribersTelephone networkInternet Protocol
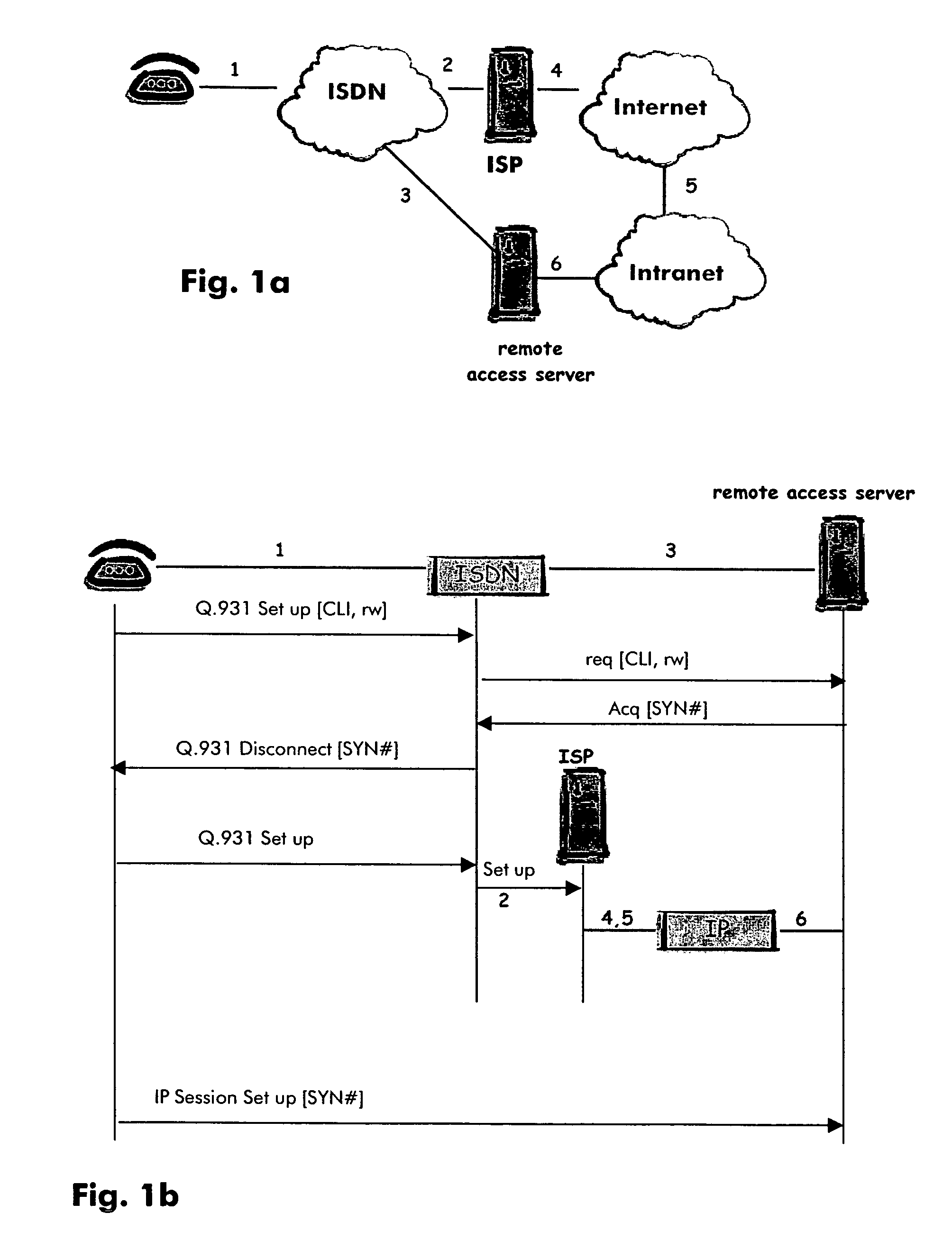
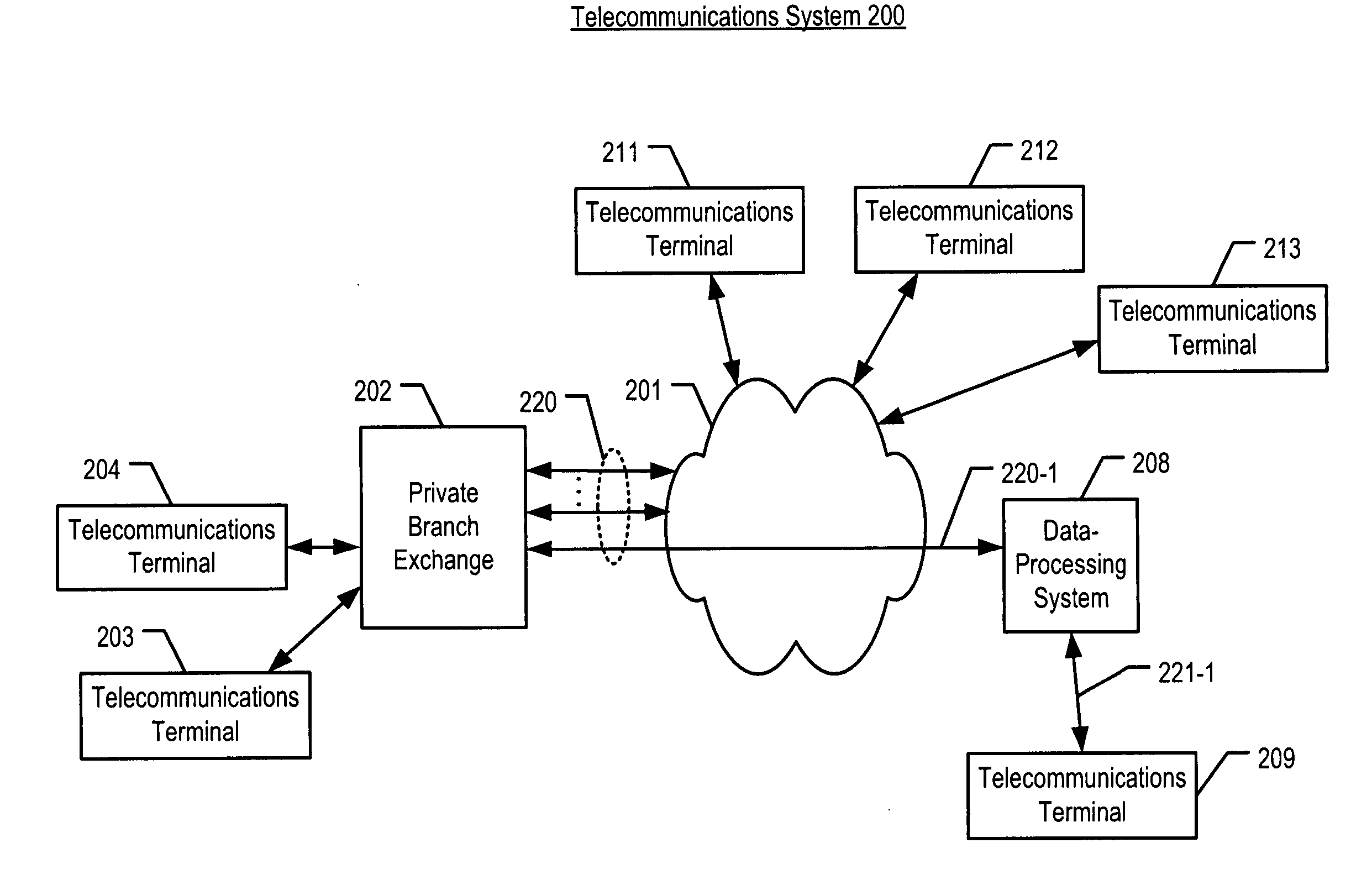
A remote user will set up a telecommunication from some remote terminal to some remote access server through a telephone network. Such telephone network will provide calling line identity information of said remote terminal to said remote access server while this first telecommunications being identified by said remote access server as being performed by a remote worker. The remote access server will then acknowledge said telecommunications by rejecting it with some tag. The remote access server will also register the received calling line identity information to which it will associate said forwarded tag. After a complete disconnection of the telecommunications, the remote terminal will initiate an Internet protocol session to said remote access server using the received tag. The remote access server will then be able to identify said remote terminal while the identification procedure be based on the use of the registered calling line identity affected to said tag.
Owner:SOUND VIEW INNOVATIONS
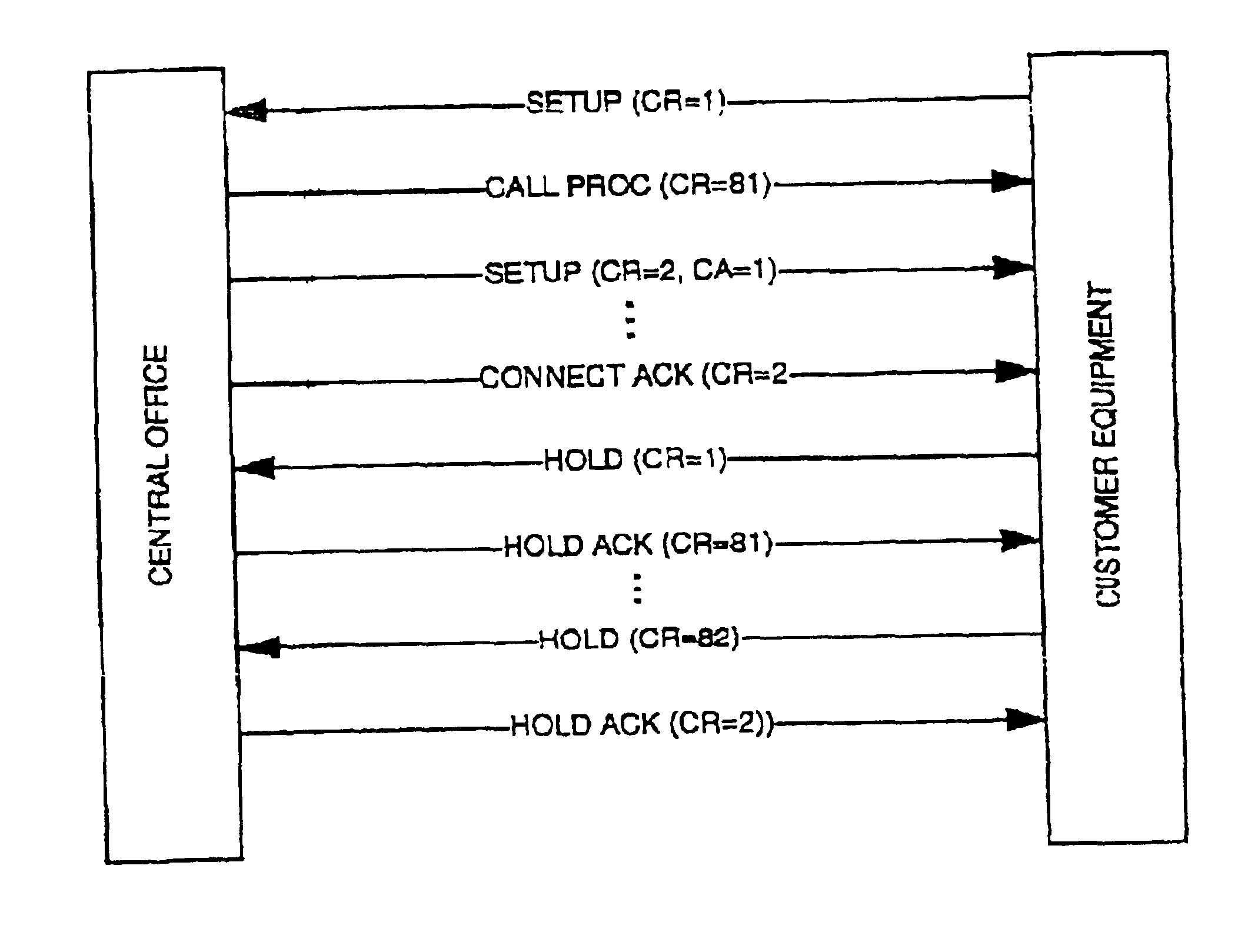
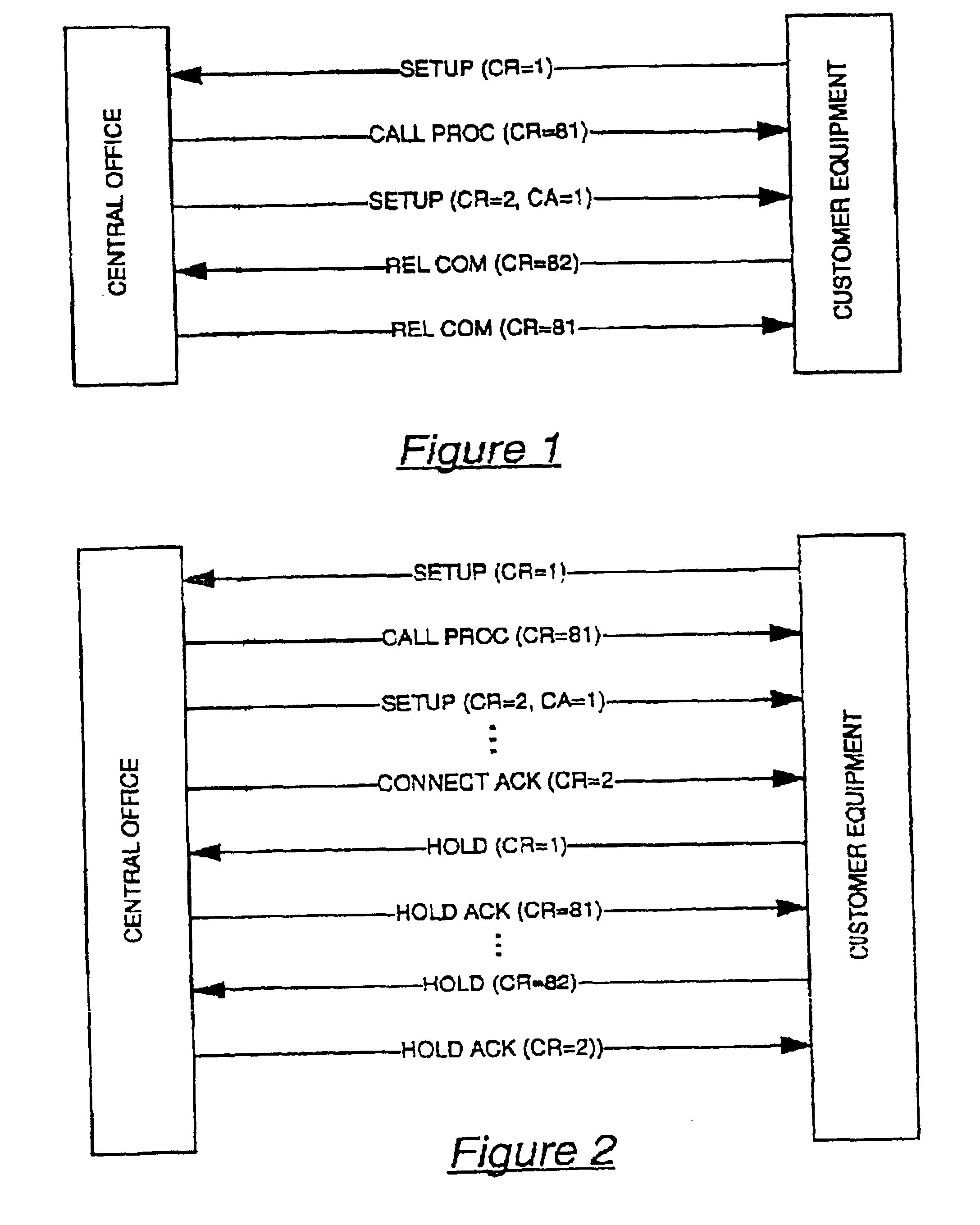
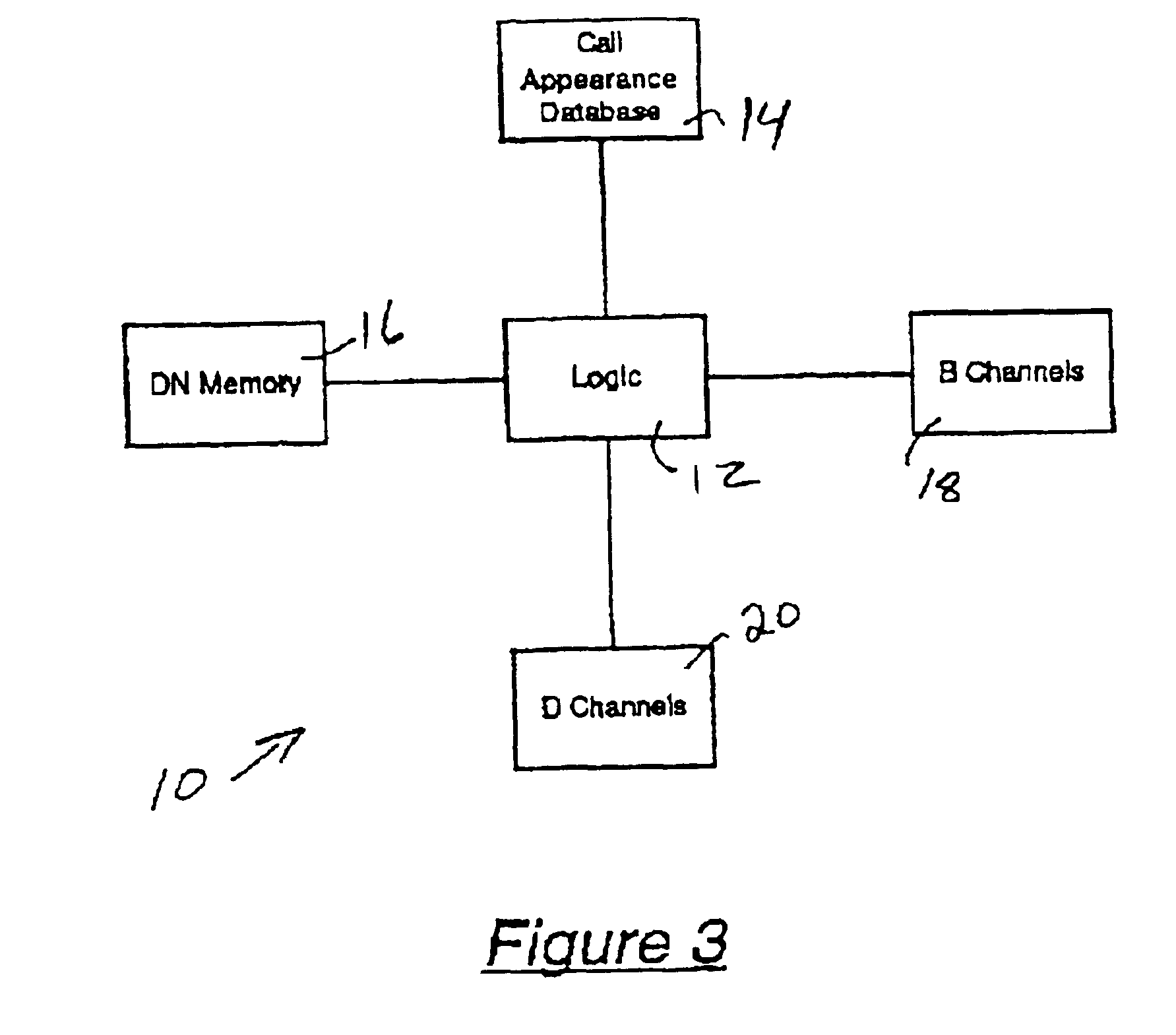
PBX switch incorporating methods and apparatus for automatically detecting call appearance values for each primary directory number on a basic rate interface
InactiveUS6912273B2OptimizationAccurate configurationInterconnection arrangementsError preventionAuto-configurationDirectory number
Owner:UNIFY GMBH & CO KG
Handling audio path failure and poor quality of service for voice calls in a contact center
Various embodiments of the invention provide methods, systems, and computer program products for handling an audio path failure and / or non-conformant QoS for a call between a contact center agent and remote party. Specifically, an audio path is established to a first telephony device being used by the agent and a call is bridged onto the audio path so that audio can be streamed back-and-forth between the first telephony device and a second telephony device being used by the party. Accordingly, various embodiments of the invention involve monitoring the audio path to detect an audio path failure and / or non-conformant QoS for the audio and bridging the call onto a second audio path when a failure or non-conformant QoS is detected so that the call is not disconnected from the second telephony device and a third device (e.g., IVR) can stream audio over the second audio path to the second telephony device.
Owner:ALVARIA CAYMAN (CX)
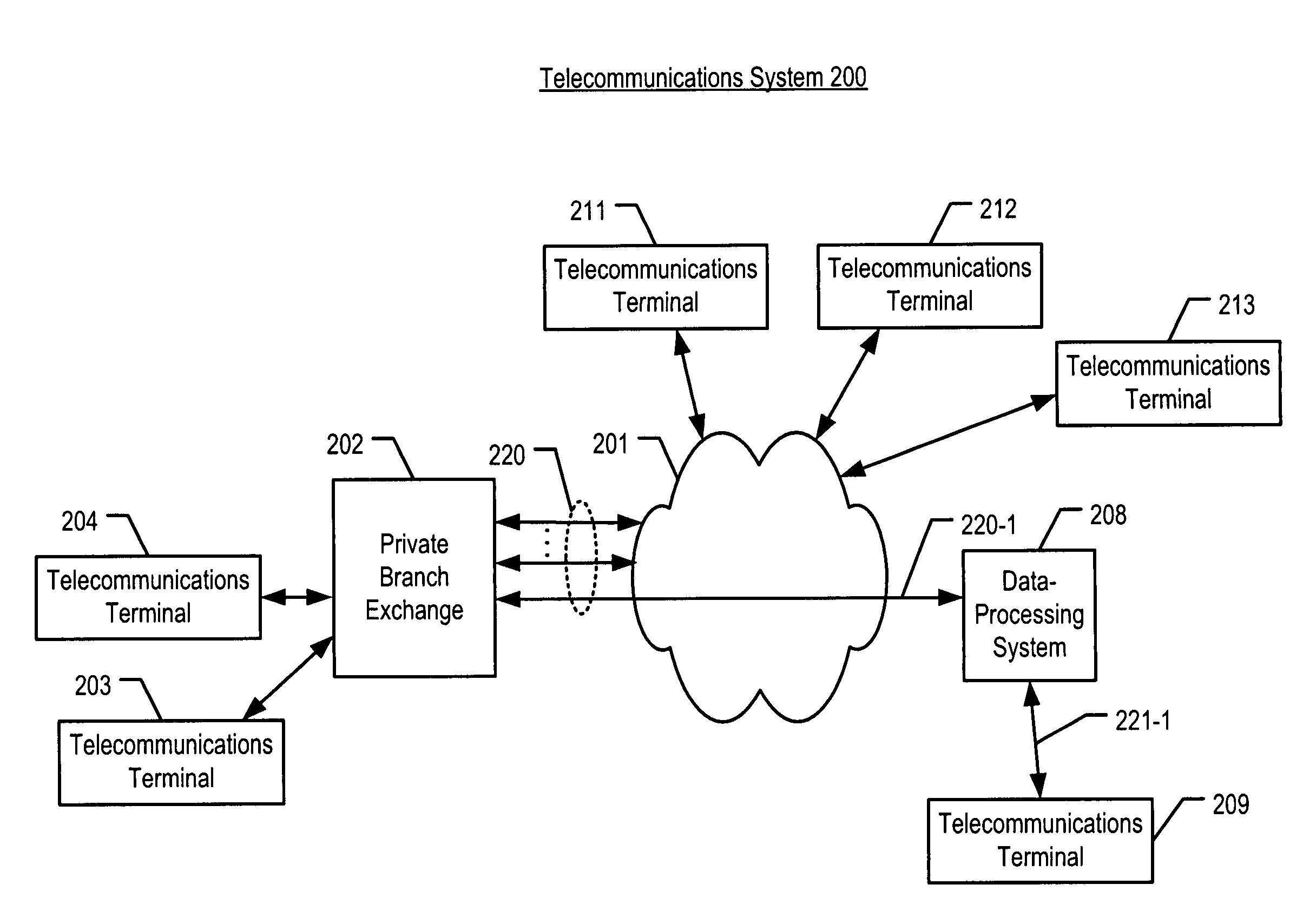
Managing held telephone calls at the call-forwarding system
ActiveUS9160861B2Low costGood choiceISDN systemsSpecial service for subscribersData processing systemCall forwarding
A method and an apparatus are disclosed that manage the held calls for an off-premises terminal at the system that extends calls to the terminal, such as a private branch exchange or other type of data-processing system, instead of at the system that is receiving the extended calls, such as a mobile switching center at which a cell phone is registered. The disclosed technique is based on the observation that the extending system knows of an incoming call to an off-premises terminal before the receiving system. As a result, the extending system can advantageously select the calls that it holds versus the calls that it sends to the receiving system. The extending system can control the routing costs and provide a consistent look-and-feel of call control to the off-premises terminal user.
Owner:AVAYA INC
Accurate dispositioning of a telephone call by reconciliating cause codes with in-band audio information
ActiveUS9538009B1The result is accurateAvoiding unnecessary reattemptsInterconnection arrangementsISDN systemsSpeech analyticsSpeech sound
A telephone call to a remote party may encounter a number of abnormal conditions, which prevents the call from being offered to the remote party's interface. These conditions may be indicated to the calling party using call progress information conveyed as out-of-band information, in the form of signaling elements and / or as in-band information, in the form of audio information. The audio information may include a special information tone and / or an intercept announcement. The call handler originating the outbound call may provide the audio information to a speech analytics component that analyzes the audio information. The analyzed audio information may be reconciled with the out-of-band information. Various rules can be applied to ascertain how to disposition the call in instances where the in-band and out-of-information are inconsistent. Once reconciled, accurate call disposition information can be recorded in the call record for that call.
Owner:NOBLE SYSTEMS CORPORATION
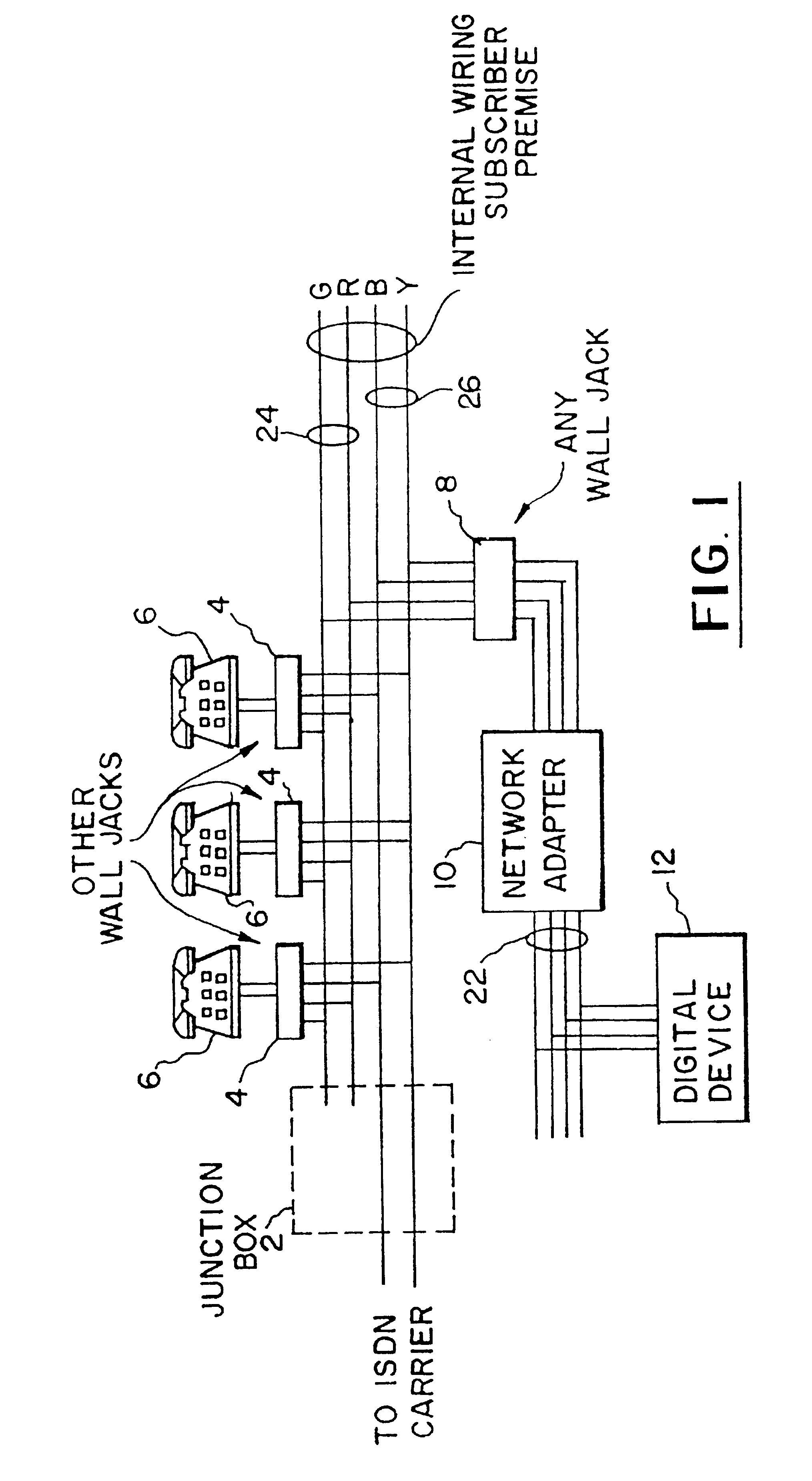
Wiring equipment and microswitch terminals
ActiveCN105592243BReduce wiring costsReduce complexityInterconnection arrangementsMultiplex communicationNetworking cablesTelephony
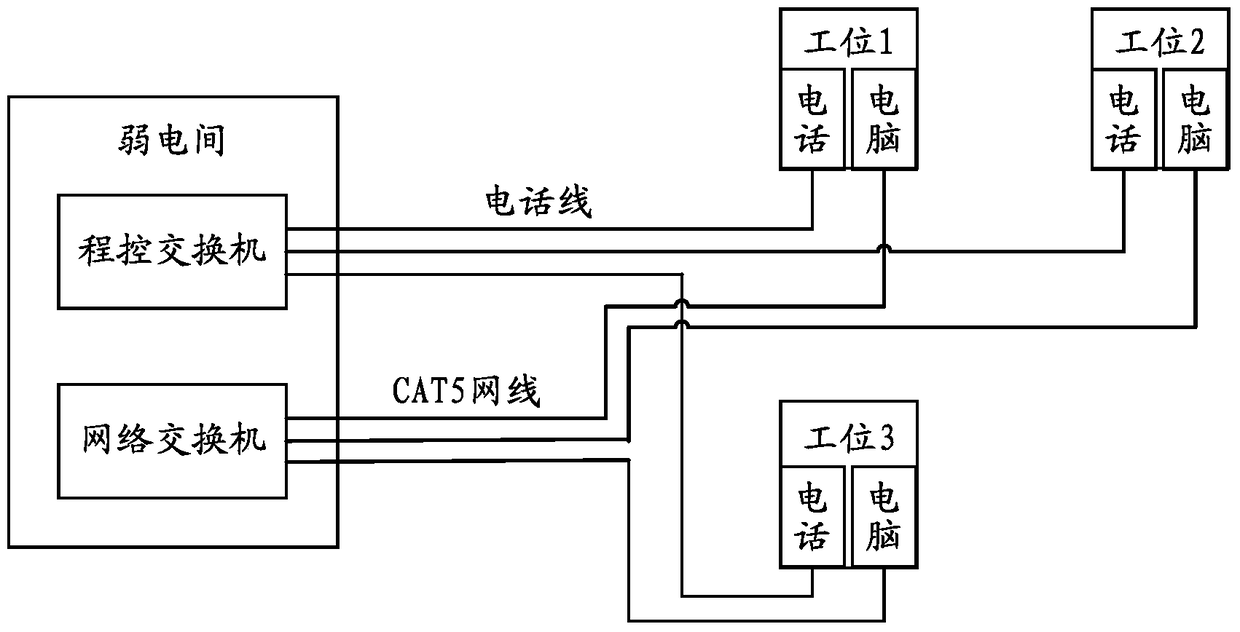
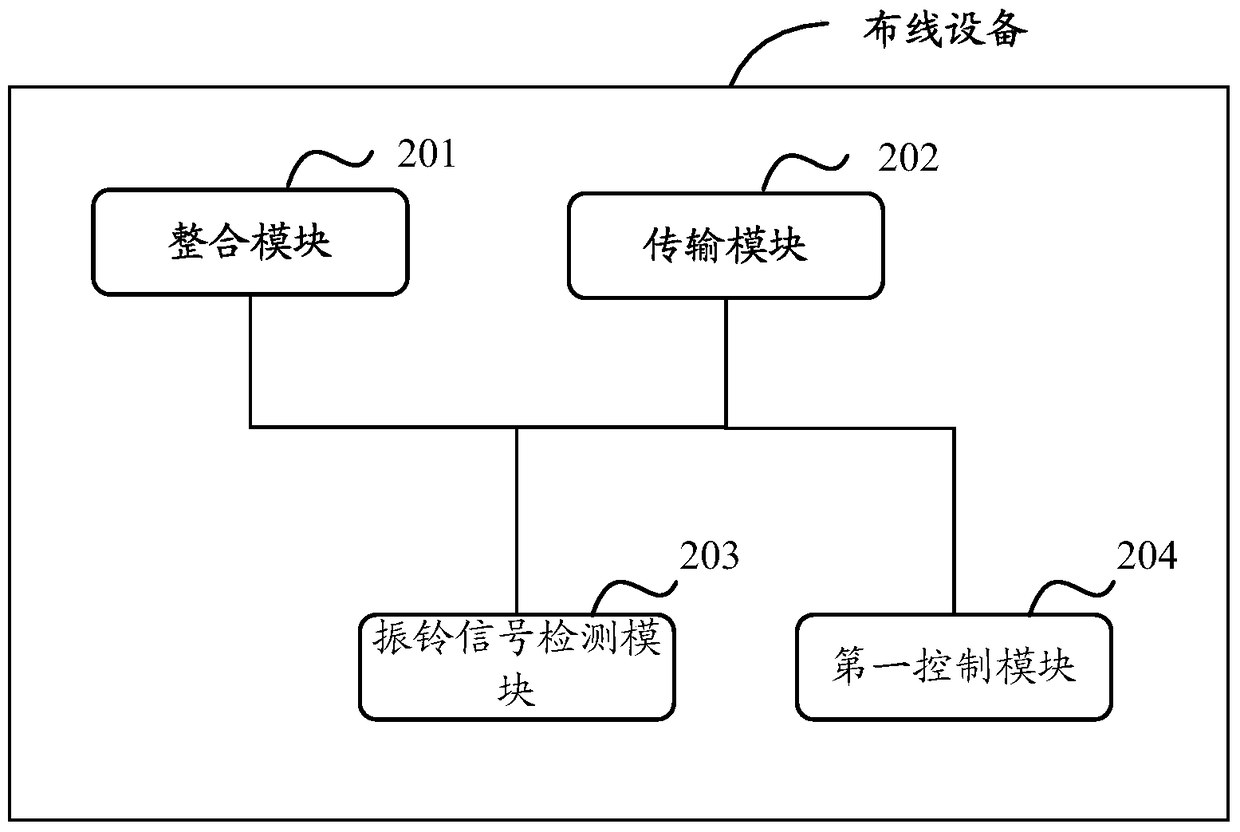
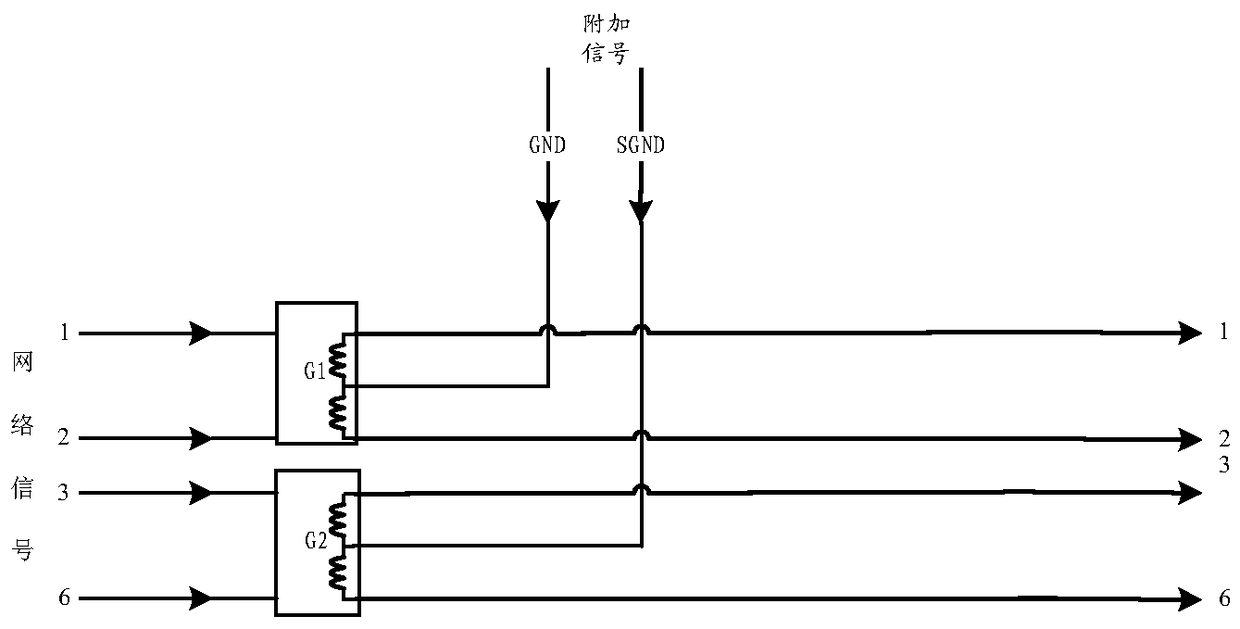
The invention discloses wiring equipment and a micro-exchange terminal. According to the technical scheme of the invention, an additional signal (such as a current signal and / or a telephone signal) is integrated with a network signal transmitted by a network wire to form an integration signal. The integration signal is transmitted by the network wire, and then a receiving terminal can receive the integration signal by the network wire. Meanwhile, according to the integration signal, a corresponding network signal and a corresponding additional signal, (such as a power supply signal and a network signal, or a telephone signal and a network signal, or a power supply signal, a telephone signal and a network signal), can be obtained. Therefore, the problem in the prior art that the existing wiring method is excessive in wired circuits, large in difficulty and high in cost can be solved. Meanwhile, the network wiring complexity is greatly reduced, and the network wiring cost is lowered.
Owner:RUIJIE NETWORKS CO LTD
Call over flow address pointer method and apparatus
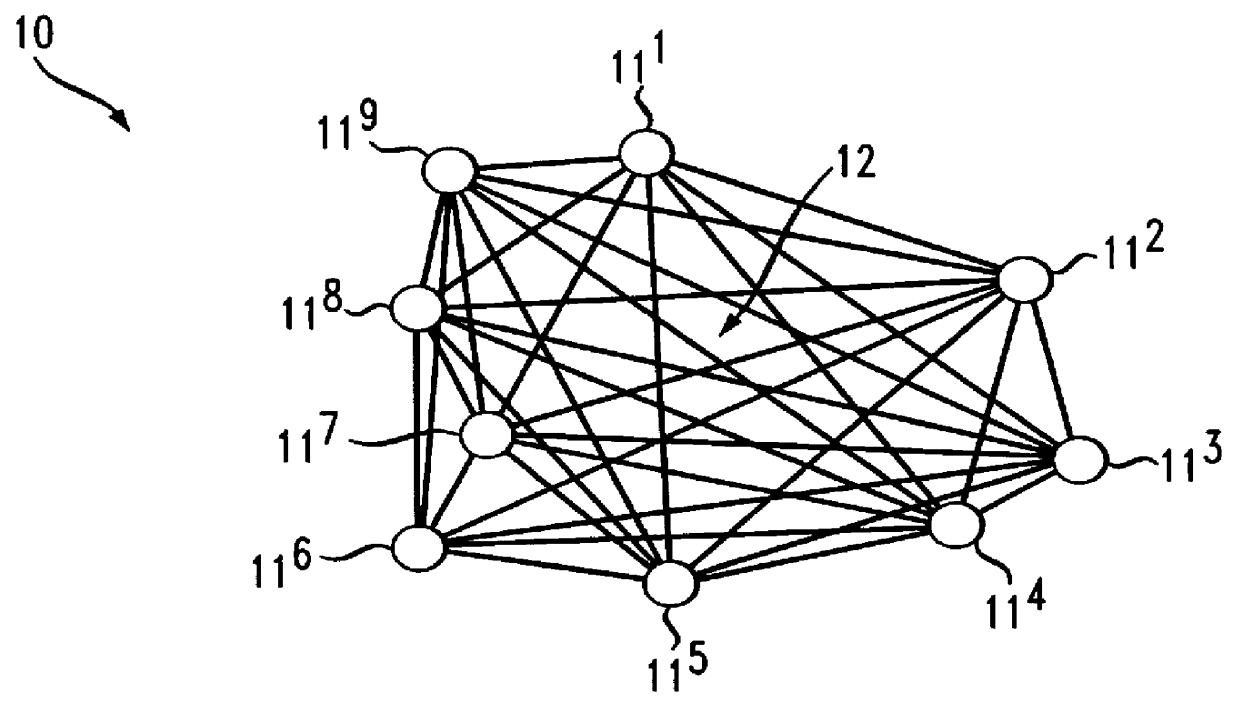
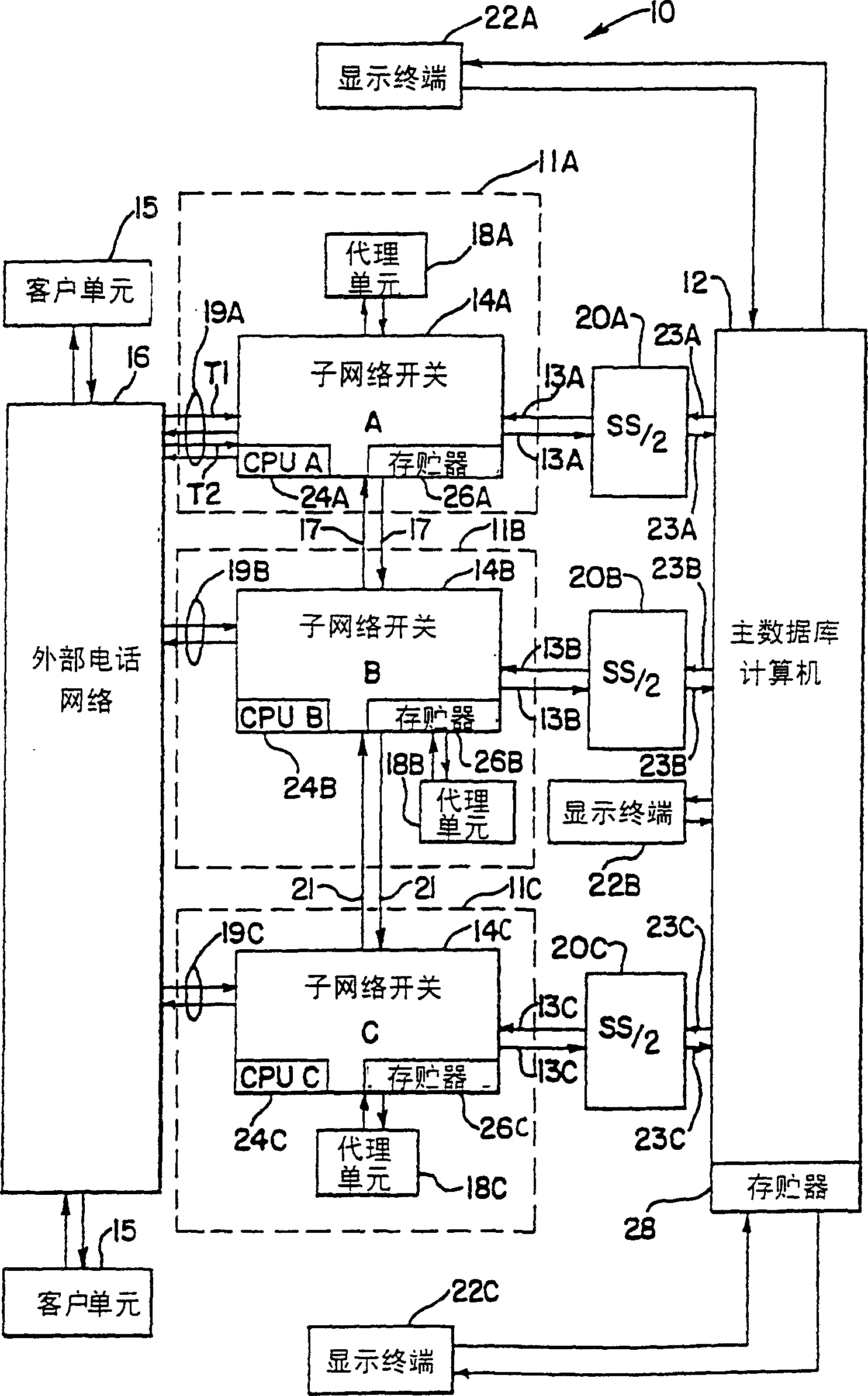
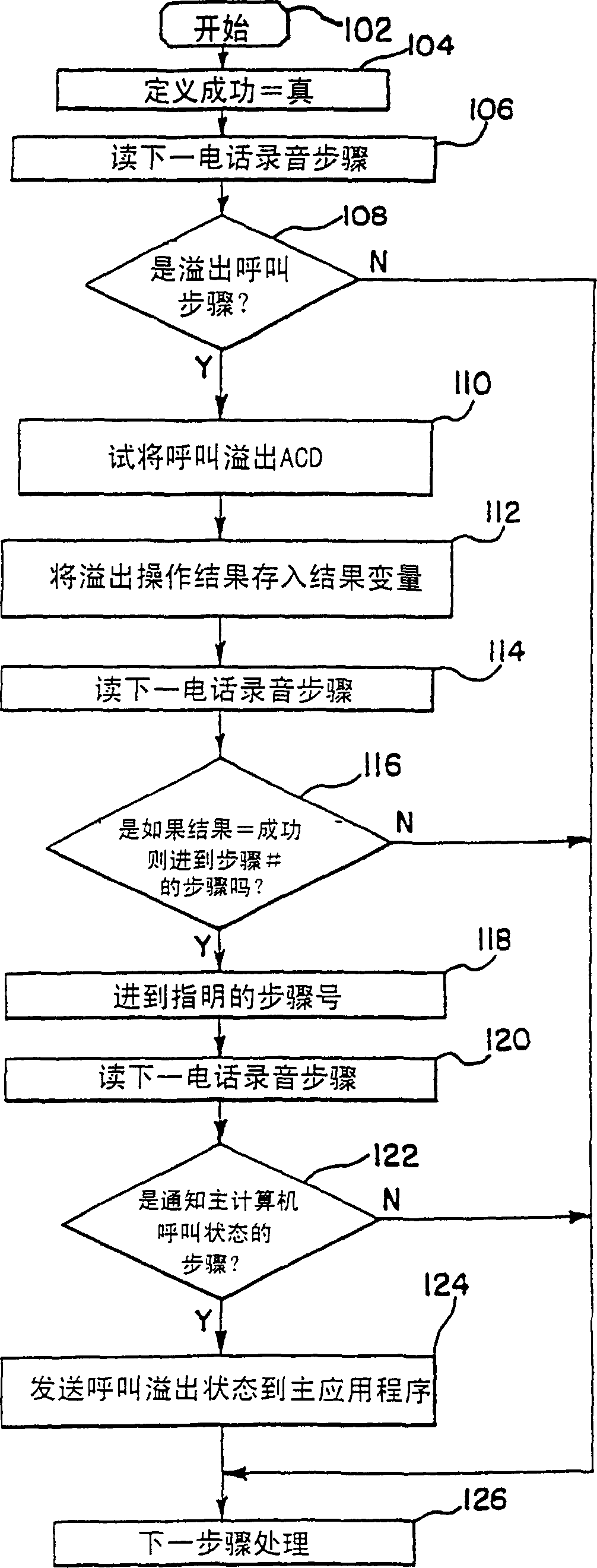
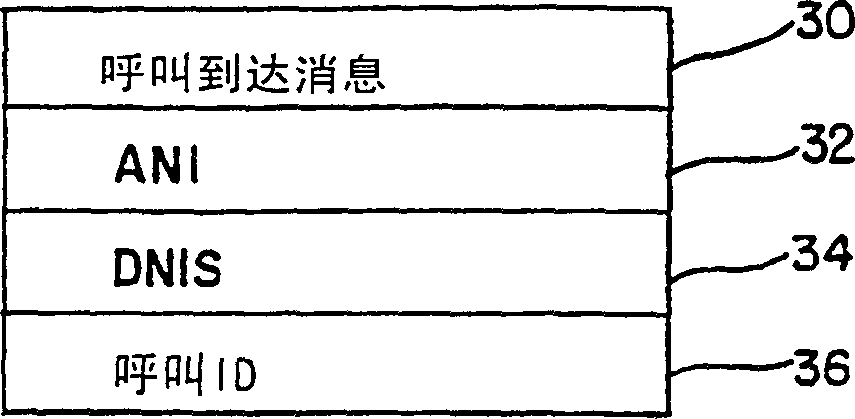
A method and appartus are provided for identifying a call record by a source automatic call distributor (11A) to a host computer (12) of a telephone call received from a public switched telephone network (PSTN) (16) and overflowed from the source automatic call distributor (11A) to a destination automatic call distributor (11B, 11C) in a call distribution system (10) using telescripted call control. The call record is stored under a call identifier of the source automatic call distributor (11A) in a memory (28) of the host computer (12).
Owner:ROCKWELL SEMICON SYST INC
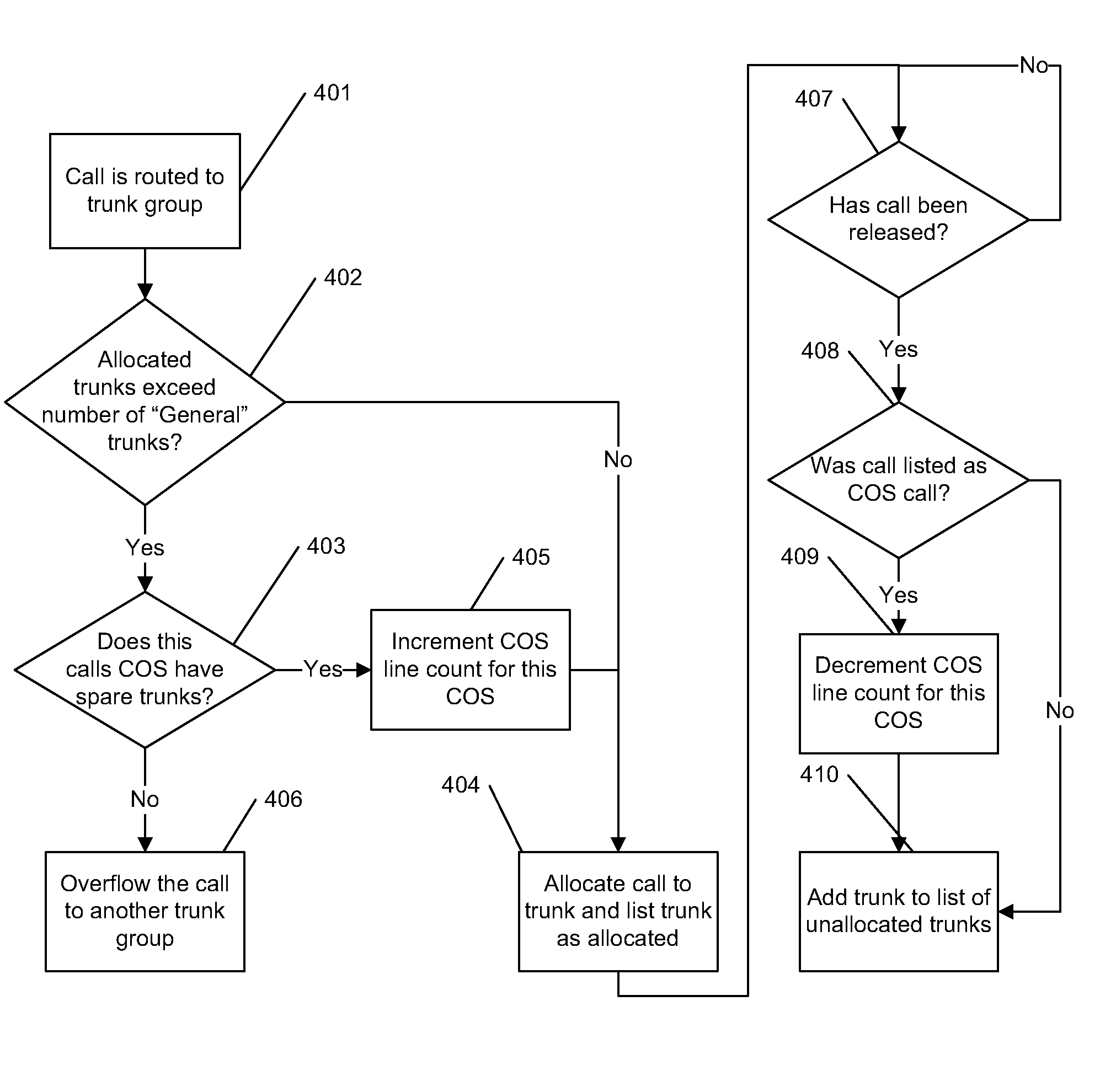
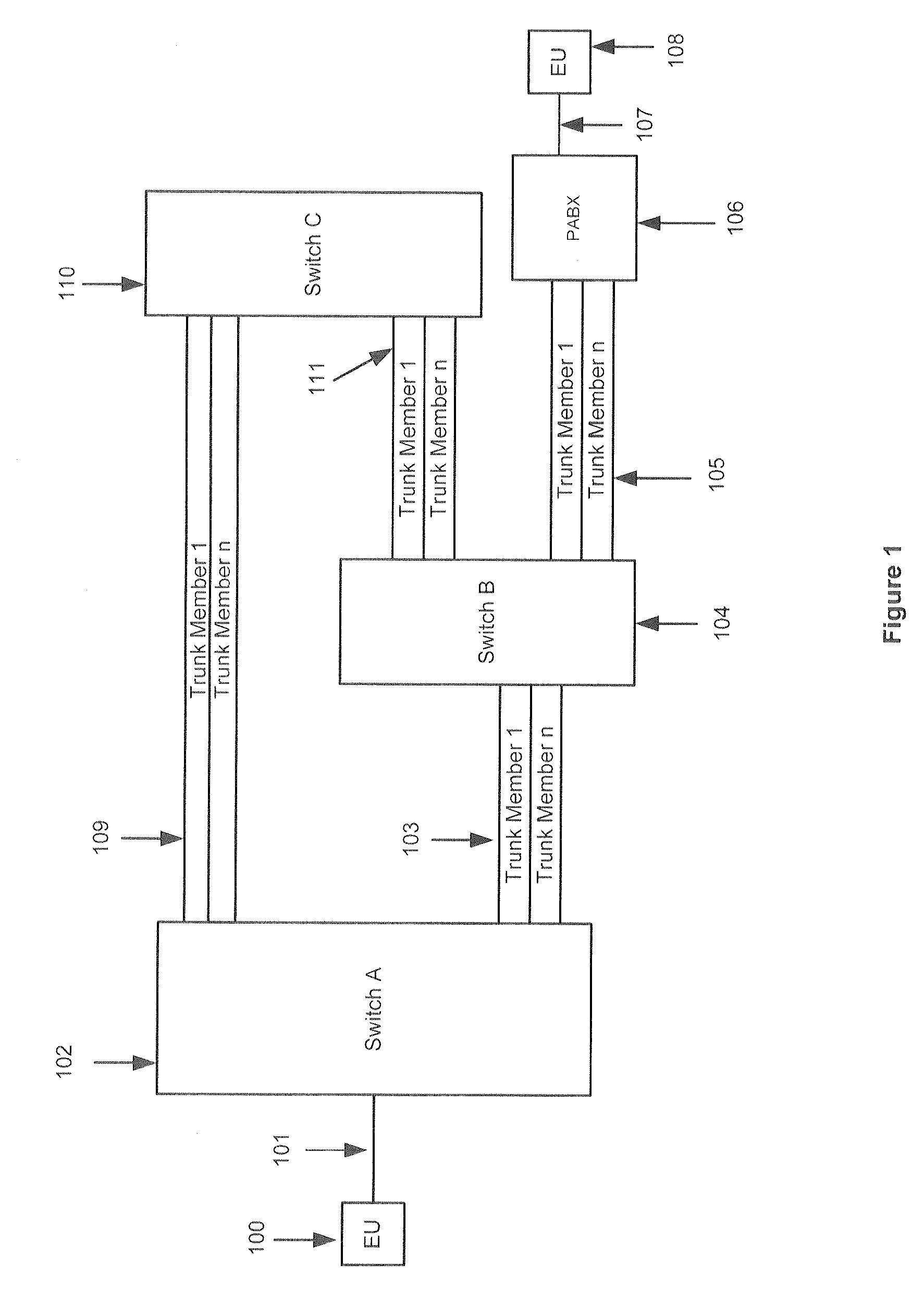
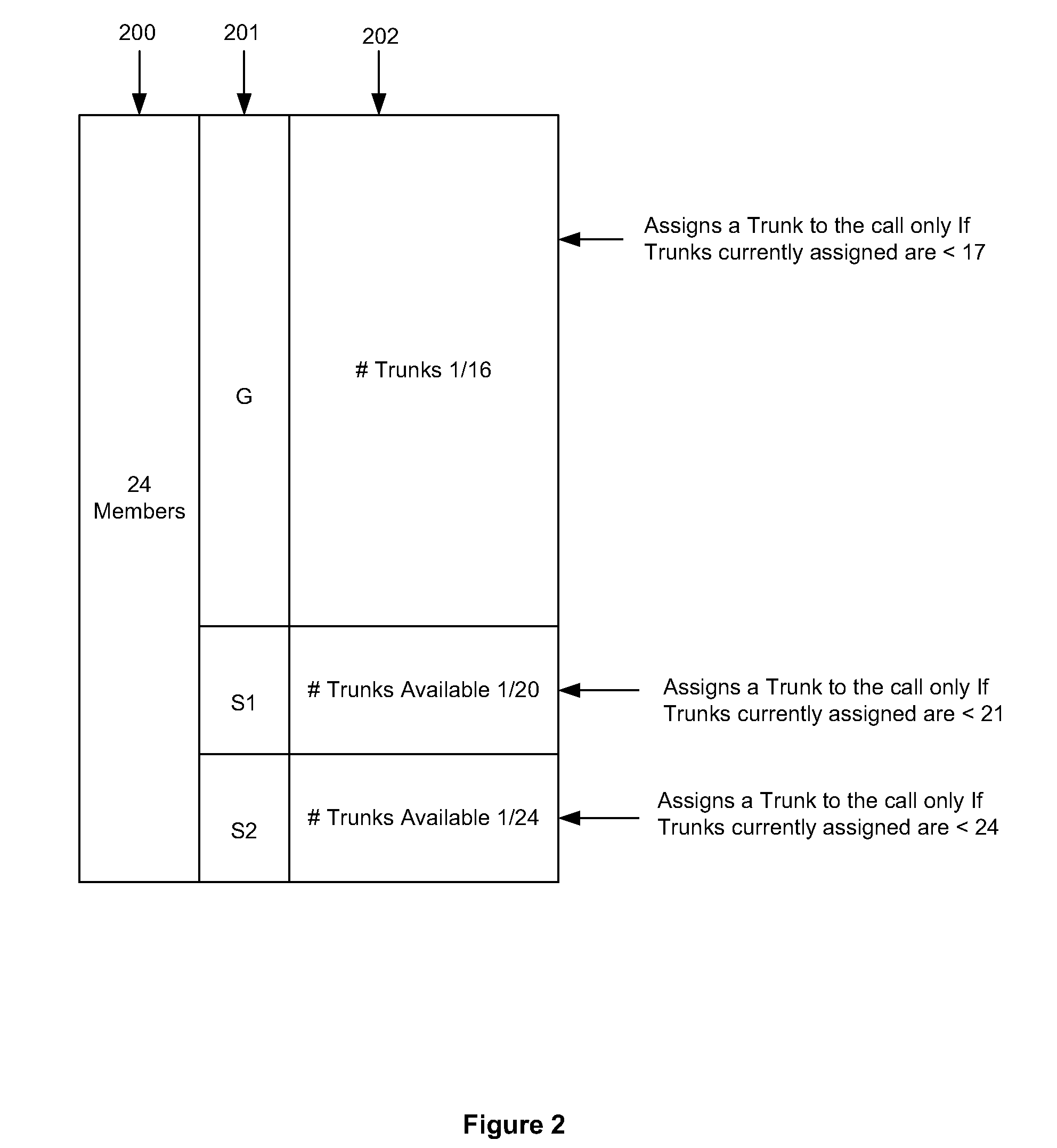
Trunk sparing
A method is provided for reserving trunks on a trunk group for designated class of service calls. The trunks available for a denominated class of service is specified, and the trunks remaining are enumerated and designated as of no class and available for all calls. When the no class trunks are in use and a new call is a denominated class of service, it is allocated to a trunk and the trunks available is reduced accordingly. If the no class trunks are in use and a new call is not of a denominated class of service, the new call is allocated to a further trunk group. When a call is released and the number available is reduced below a specified number, the number of available trunks increases. If the number of trunks available is not reduced below a specified number, the released trunk is made available for all calls.
Owner:SPRINT CORPORATION
Method and apparatus for monitoring telephone status
The monitor is for monitoring the status of a first client telephone, and for sending this status information via a central server to an authorized second client telephone. The central server stores a database of registered client telephones and corresponding client telephones that the client may monitor. A user of a registered client telephone monitors in real time the telephone status of registered friends, family, or co-workers that have agreed to be monitored by the user.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Managing held telephone calls at the call-forwarding system
ActiveUS20070041559A1Low costGood choiceISDN systemsSpecial service for subscribersData processing systemSystems management
A method and an apparatus are disclosed that manage the held calls for an off-premises terminal at the system that extends calls to the terminal, such as a private branch exchange or other type of data-processing system, instead of at the system that is receiving the extended calls, such as a mobile switching center at which a cell phone is registered. The disclosed technique is based on the observation that the extending system knows of an incoming call to an off-premises terminal before the receiving system. As a result, the extending system can advantageously select the calls that it holds versus the calls that it sends to the receiving system. The extending system can control the routing costs and provide a consistent look-and-feel of call control to the off-premises terminal user.
Owner:AVAYA INC
ISDN alarm notification system
InactiveUS7151750B2Special service provision for substationError preventionTelecommunicationsComputer terminal
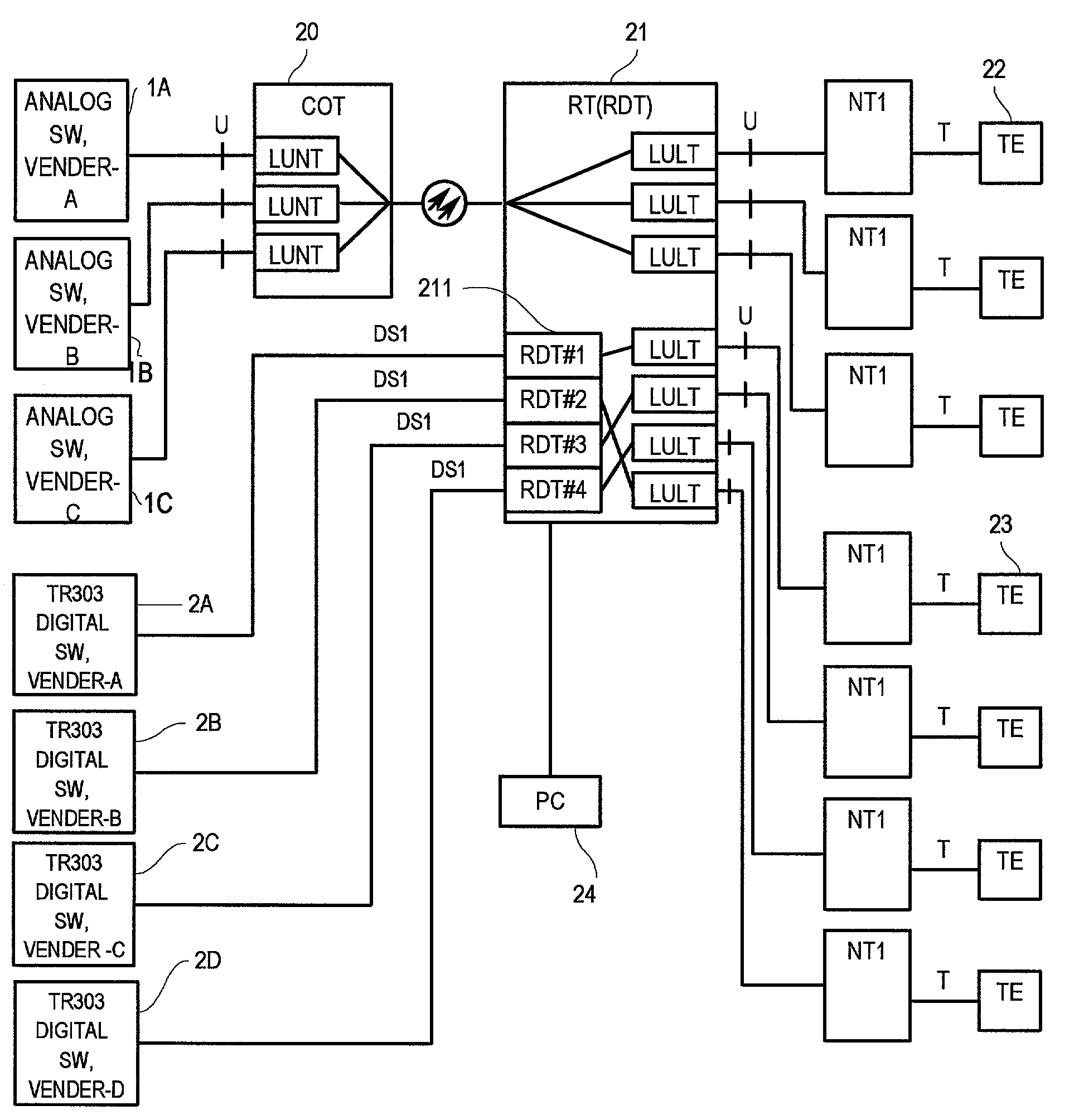
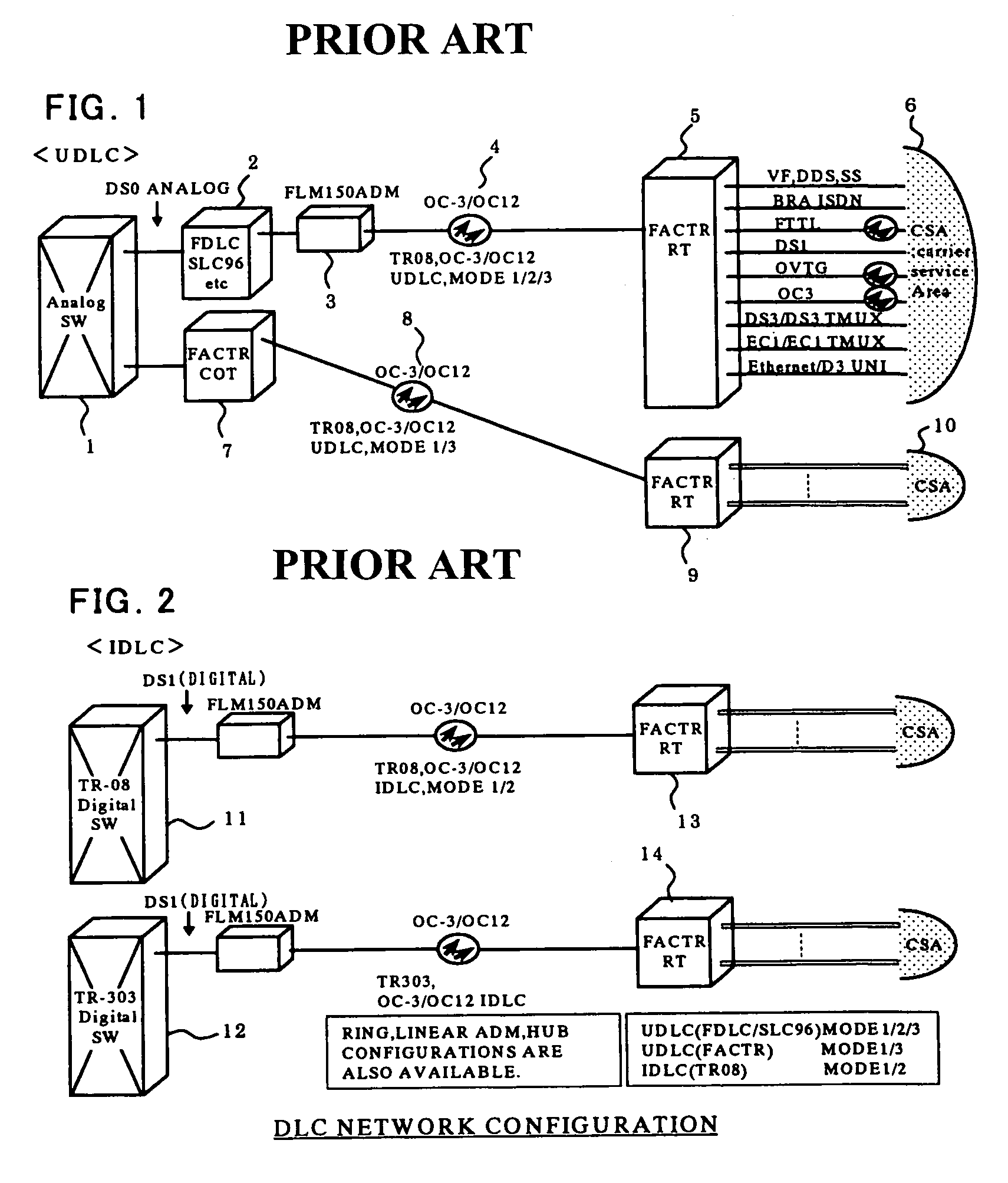
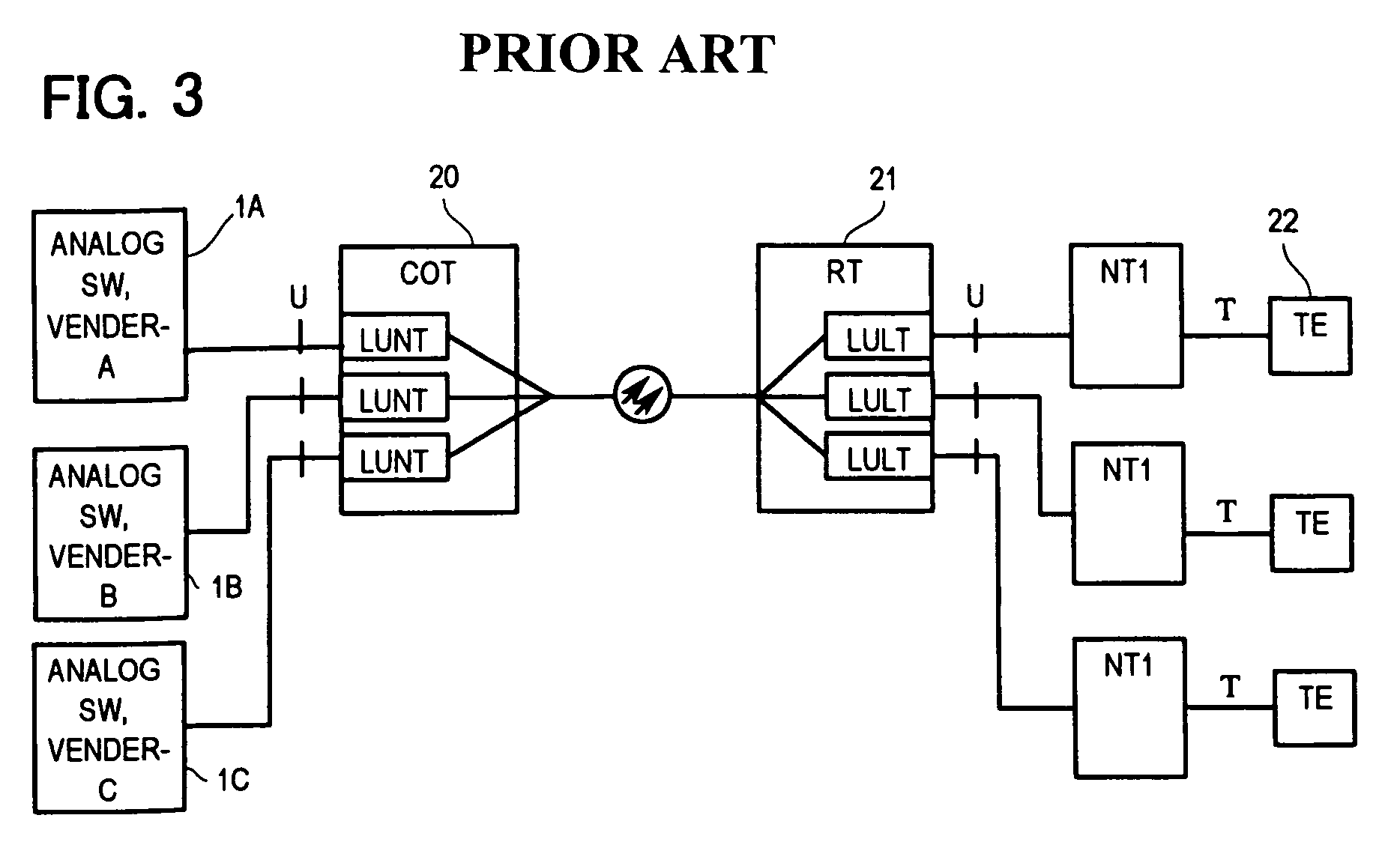
An ISDN alarm notification (fault locating) system in subscriber transmission equipment is connected to switching equipment conforming to TR-303 standard, in particular. The system includes a controller for setting switch options in subscriber transmission equipment externally, in addition to a digital switch and subscriber transmission equipment. The subscriber transmission equipment is provided with a switching equipment interface unit, a control path unit, and an ISDN subscriber interface unit. The controller sets the switch options provided in the switching equipment interface unit, the control path unit, and the ISDN subscriber interface unit. Thereby each switch option performs identical function, corresponding to each digital switch connected to the subscriber transmission equipment. Thus an ISDN alarm can be notified accurately to any TR-303 digital switch even network terminals NT1 of different types are connected to ISDN subscribers, and the compatibility with conventional services (TR-008 POTS / ISDN, TR-303 POTS / ISD N) is maintained.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Handling audio path failure and poor quality of service for voice calls in a contact center
Various embodiments of the invention provide methods, systems, and computer program products for handling an audio path failure and / or non-conformant QoS for a call between a contact center agent and remote party. Specifically, an audio path is established to a first telephony device being used by the agent and a call is bridged onto the audio path so that audio can be streamed back-and-forth between the first telephony device and a second telephony device being used by the party. Accordingly, various embodiments of the invention involve monitoring the audio path to detect an audio path failure and / or non-conformant QoS for the audio and bridging the call onto a second audio path when a failure or non-conformant QoS is detected so that the call is not disconnected from the second telephony device and a third device (e.g., IVR) can stream audio over the second audio path to the second telephony device.
Owner:NOBLE SYSTEMS CORPORATION
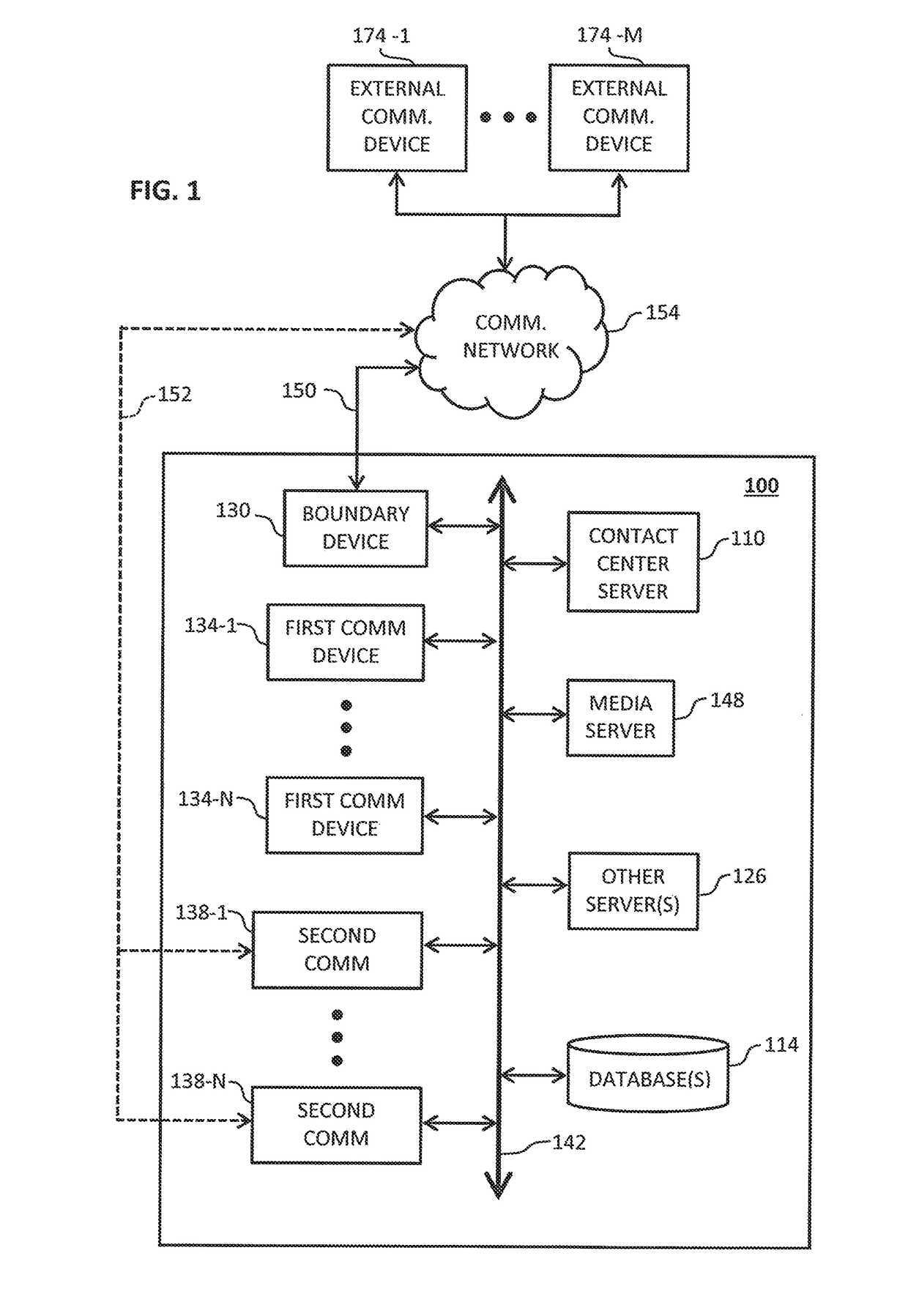
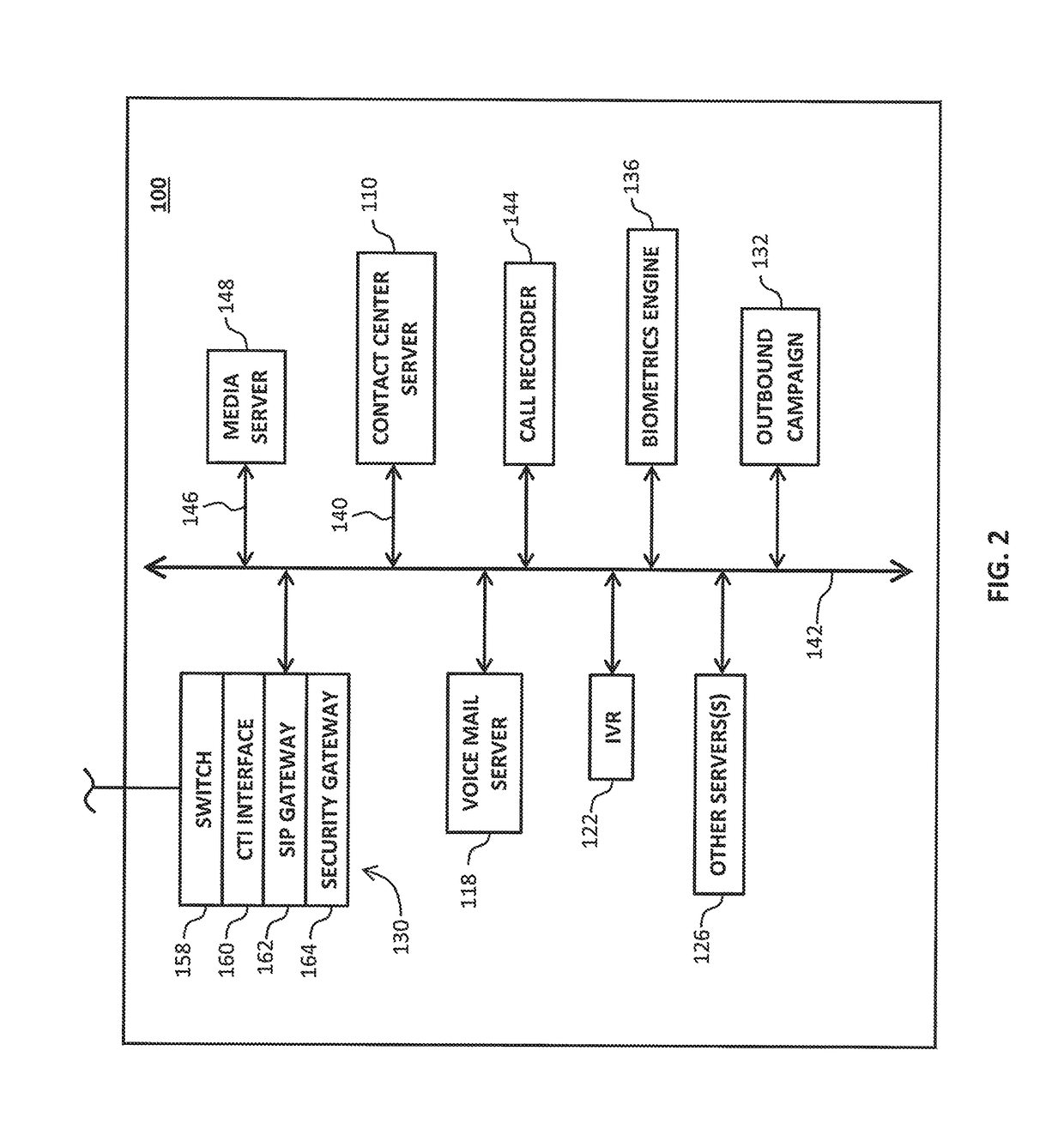
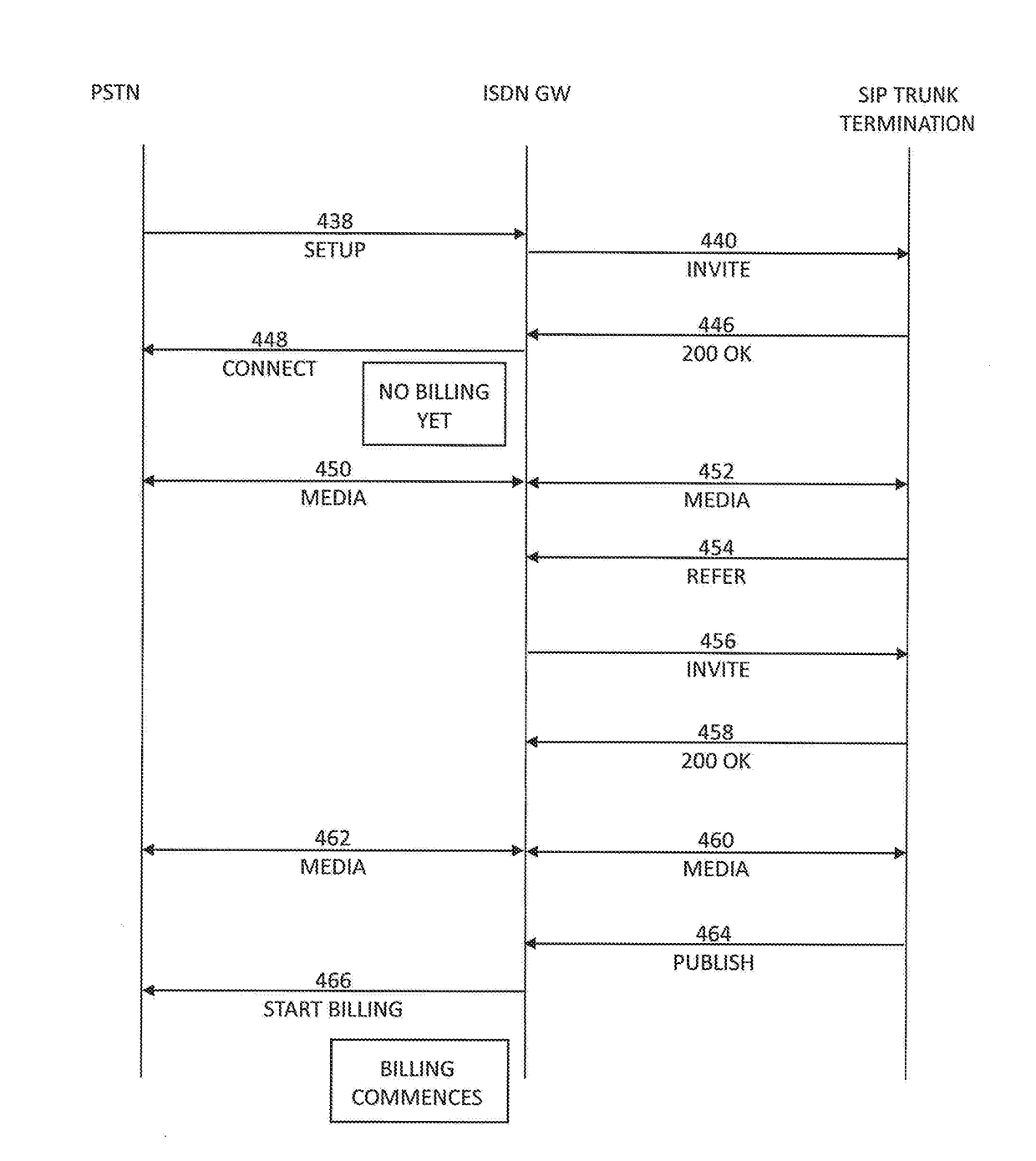
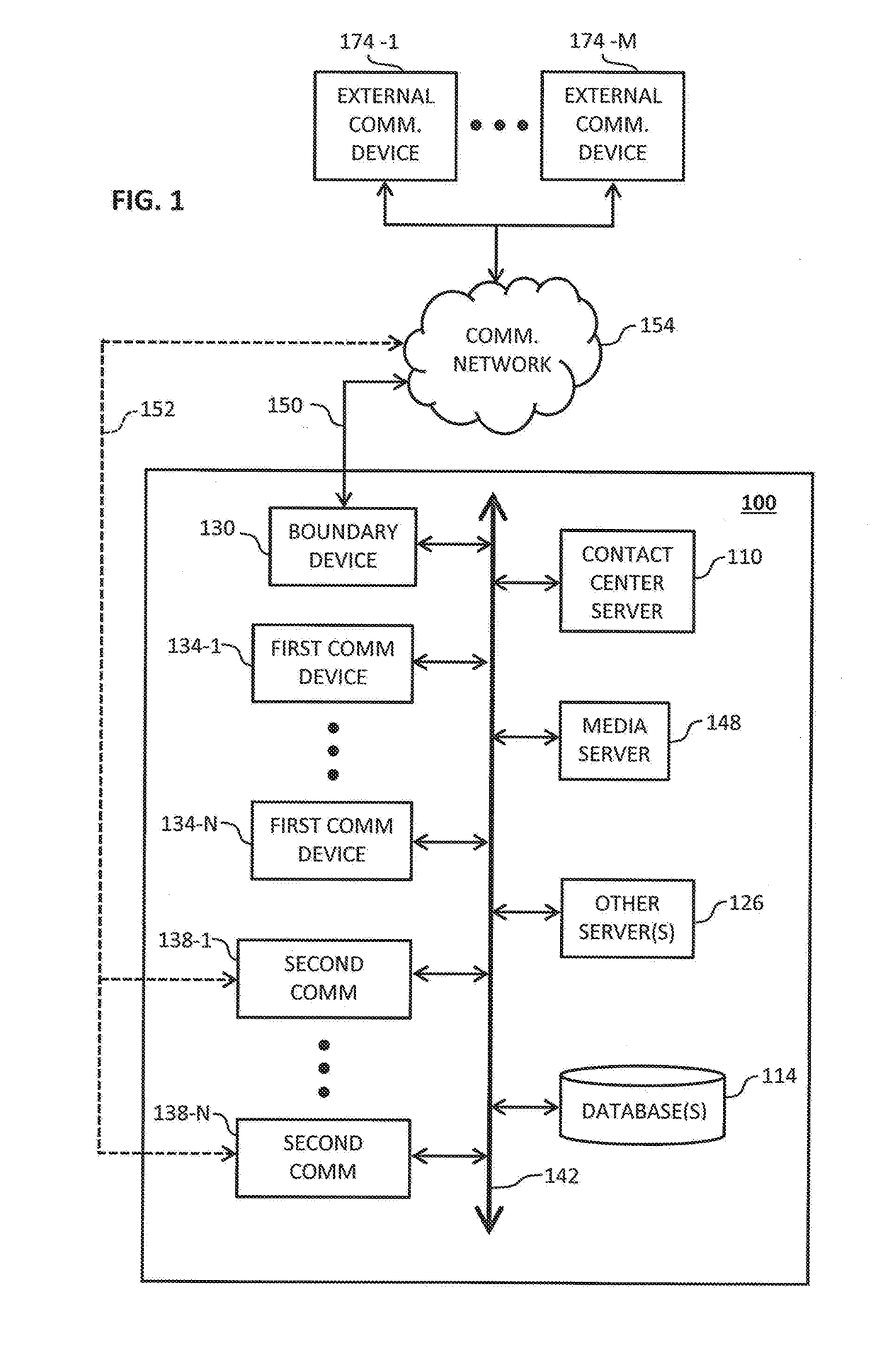
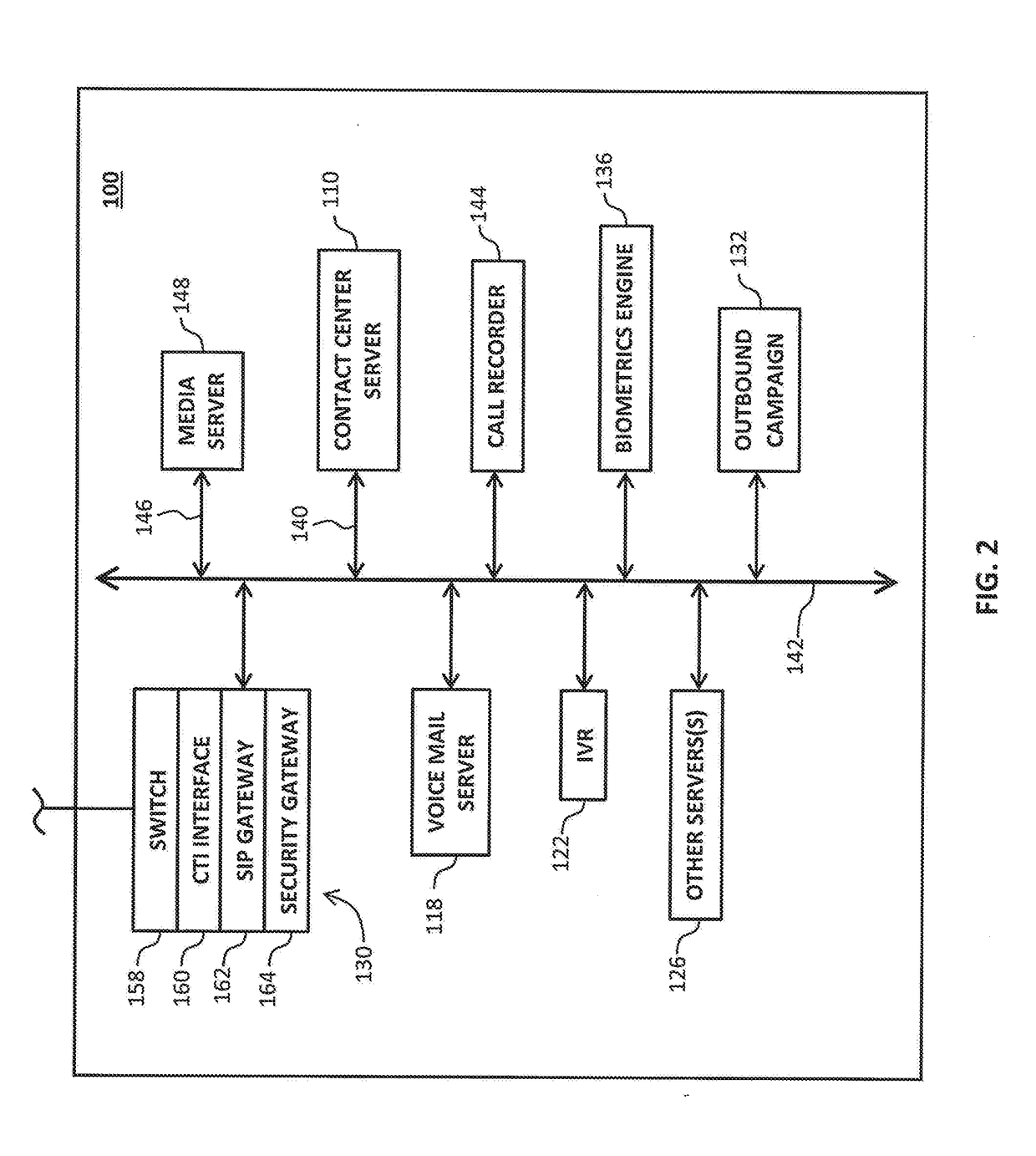
System and method for tracking call billing
Owner:AVAYA INC
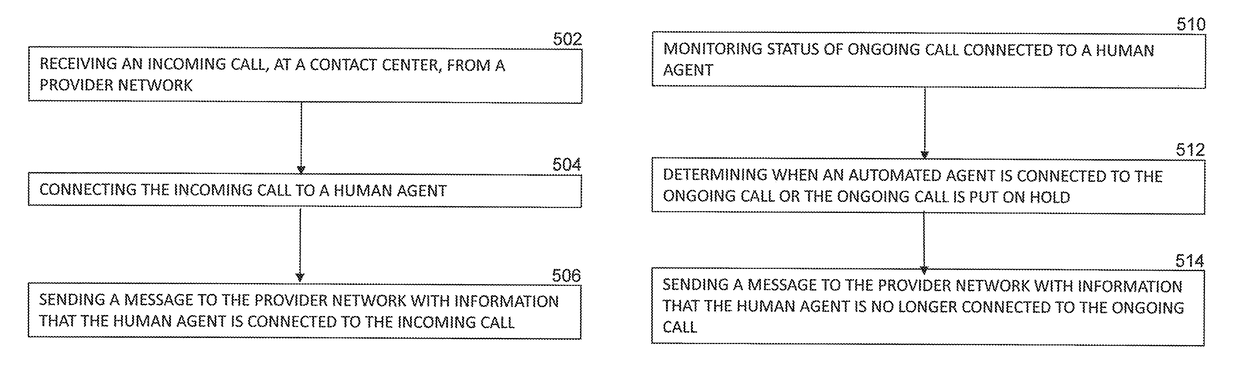
System and method for tracking call billing
Tracking a status of an ongoing call includes monitoring, by a computer of a contact center, the ongoing call that is connected with a human agent and that originated from a provider network and determining when an automated agent instead of the human agent is connected with the ongoing call. The computer of the contact center can then send a first message to the provider network, wherein the first message comprises first data indicative that the automated agent instead of the human agent is connected with the ongoing call.
Owner:AVAYA INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com