Encoding, decoding and compression of audio-type data using reference coefficients located within a band of coefficients
a reference coefficient and audio-type data technology, applied in the field of encoding, decoding and compression of audio-type data using reference coefficients located, can solve the problems of significant loss of bits, inaccurate estimation, and significant sacrifice in the precision of quantizing coefficient values, and achieve accurate estimation of masking levels and highly efficient use of available bits
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
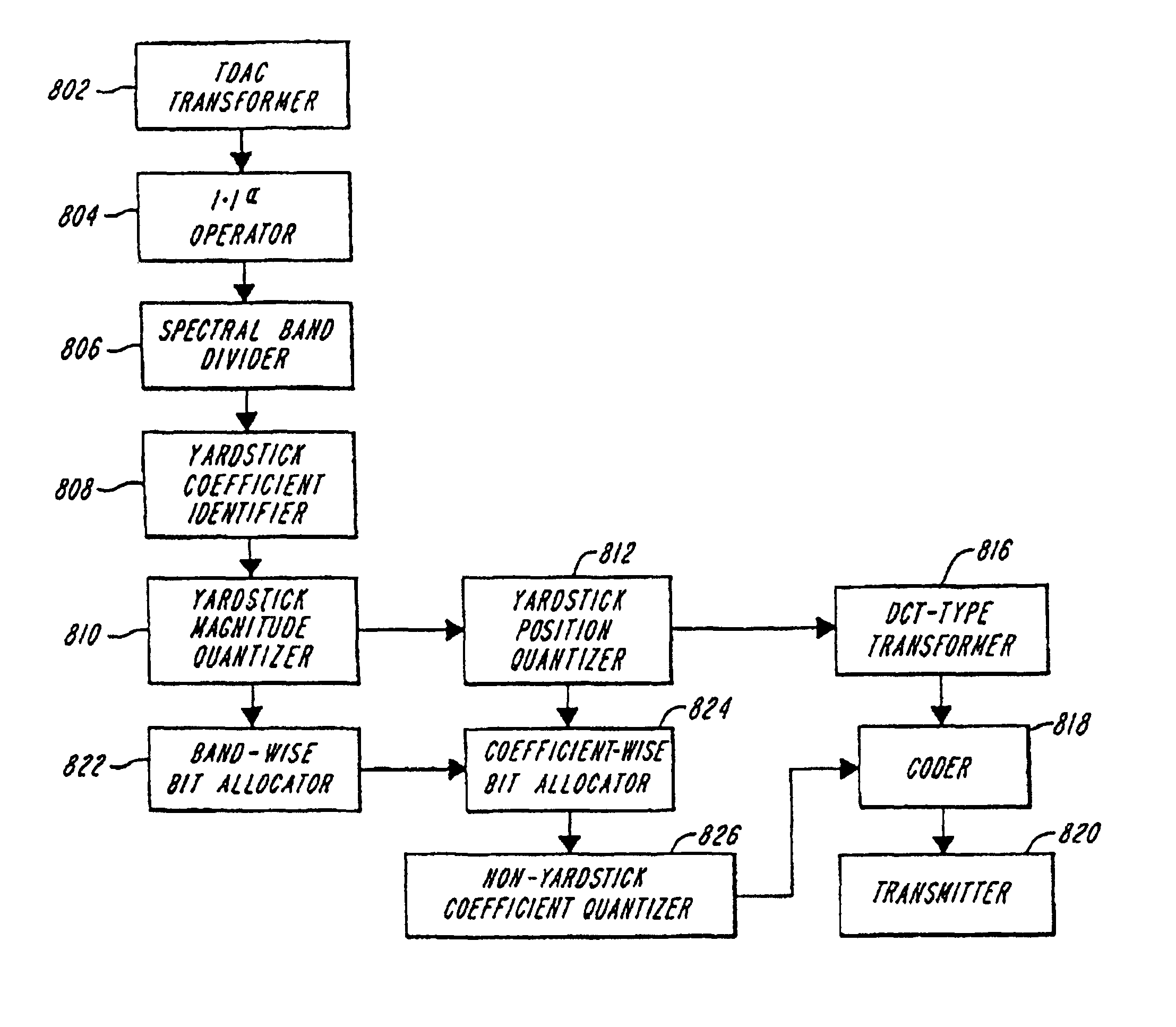
[0051]A first preferred embodiment of the invention is a method of allocating bits to individual coefficients, for the encoding of the magnitude (i.e. the absolute value of the amplitude) of these coefficients. According to the method of the invention, an audio signal x(t) is obtained as in FIG. 4a at 99, and sampled at a suitable rate, such as 48 kHz as at 102, resulting in x(n). The sampled signal is windowed and transformed, as at 104 and 106, according to a known, suitable technique, such as TDAC or DCT, using an appropriate window of a typical size, e.g. 512 or 1024 samples. It will be understood that other transformation and windowing techniques are within the scope of the present invention. If no transformation is performed, the invention is applied to sampled signal elements rather than coefficient signal elements. In fact, the invention is beneficially applied to non-transformed, sampled audio-type signals. Transformation is not necessary, but merely exploits certain struct...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com