Method to improve cancerous lesion detection sensitivity in a dedicated dual-head scintimammography system
a dual-head scintimammography and sensitivity technology, applied in the field of dual-head scintimammography, can solve the problems of poor imaging sensitivity of lesions located in the medial aspect of the breast, poor performance, poor spatial resolution during imaging, etc., and achieve the effect of improving the contrast between background and lesion areas
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
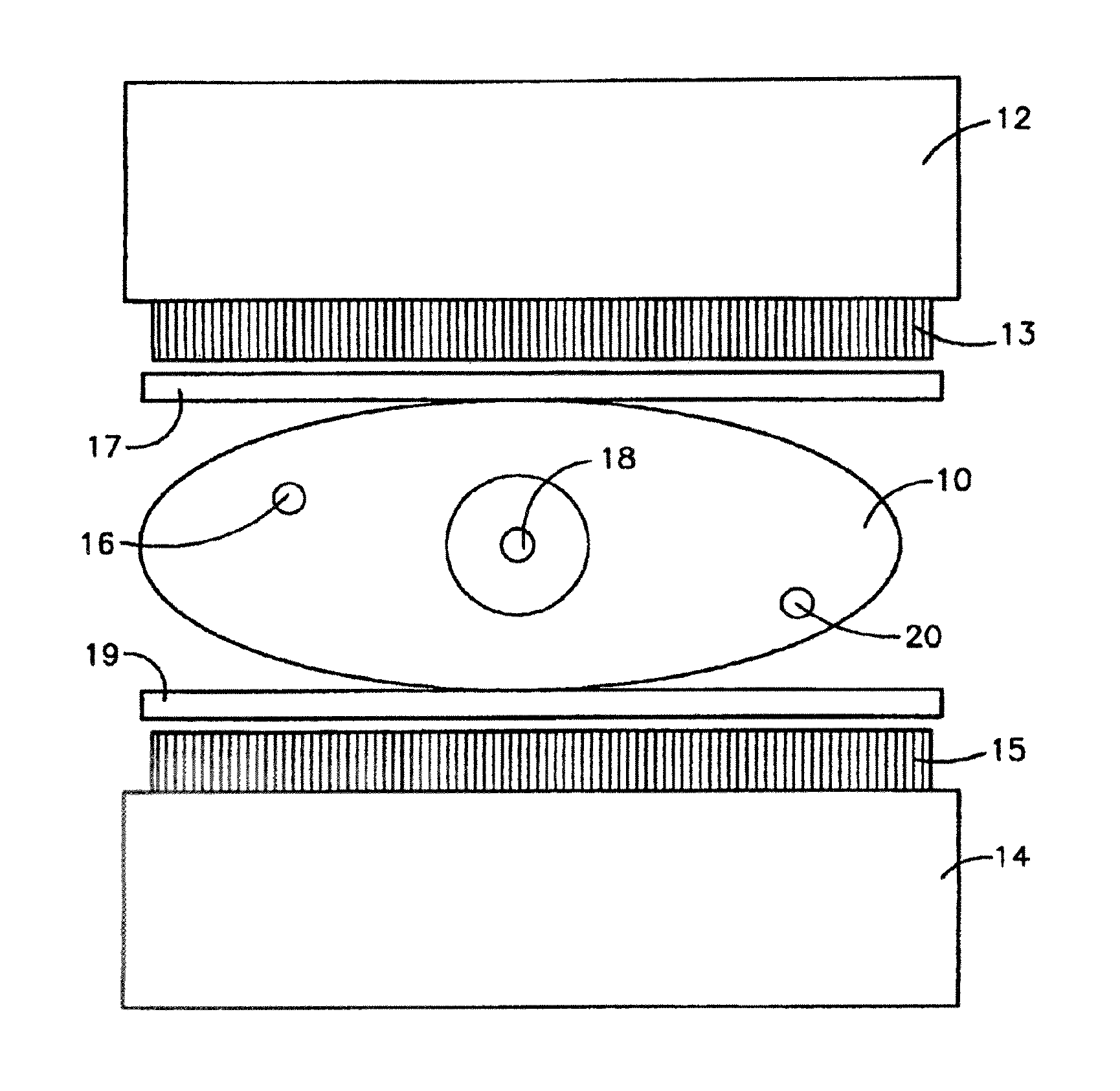
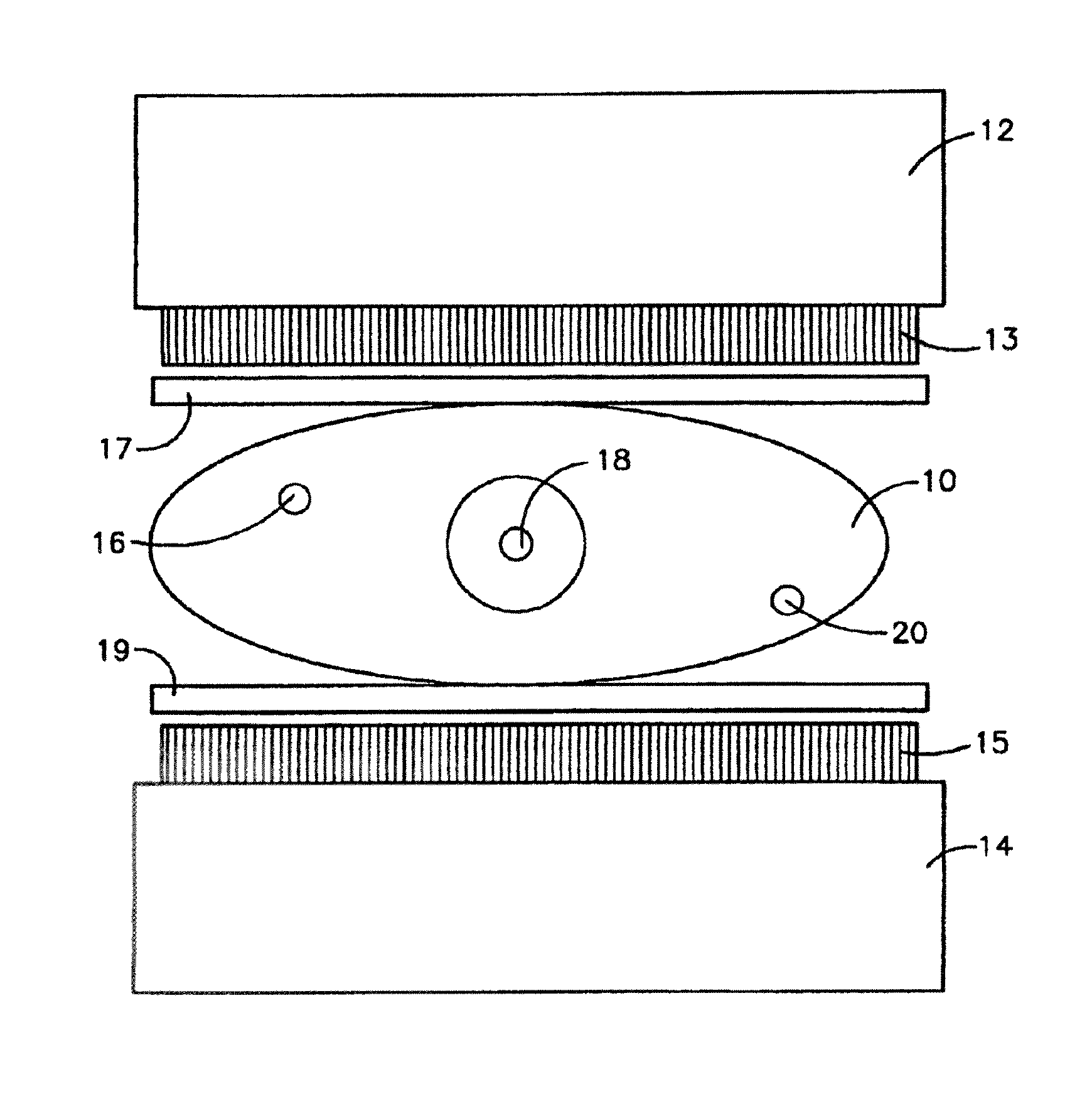
[0011]So called mini gamma or small field of view (FOV) cameras and their methods for use are well known in the art (see for example U.S. Pat. No. 6,271,525 to Majewski et al. whose description is incorporated herein by reference in its entirety) and commercially available from at least two sources: Dilon Technologies, 12050 Jefferson Ave., New Port News, Va. 23606; and Gamma Medica™, Inc., 19355 Business Center Drive, Suite 8, Northridge, Calif. 91324. Such cameras have been routinely applied to the examination of breasts for the presence of lesions by a process that involves injection of the patient with a radiopharmaceutical and examination of the breast with the mini gamma camera to detect differences in the uptake of the radiopharmaceutical between normal tissue and areas containing lesions.
[0012]In the 2002 paper by Kieper et al. described above, it was proposed to enhance lesion detection and localization through the use of a pair of opposed mini gamma cameras compressing the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com