Refraction free curve design method for uniform lighting and its lens
A uniform lighting and design method technology, applied in the direction of lens, optics, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of inapplicability, complexity, and failure to get rid of the excessive volume of the CPC system, and achieve the effect of simple structure, cost reduction, and simplified structure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0097] The following describes in detail the method of realizing the refractive free-form surface lens shown in FIG. 1 by using the above-mentioned mathematical idea. This embodiment is applicable to various light sources with a half light emitting angle of 0°-90°. However, for economical considerations, it is more suitable for light sources with a half-lighting angle of 60°-90° and a large divergence angle.
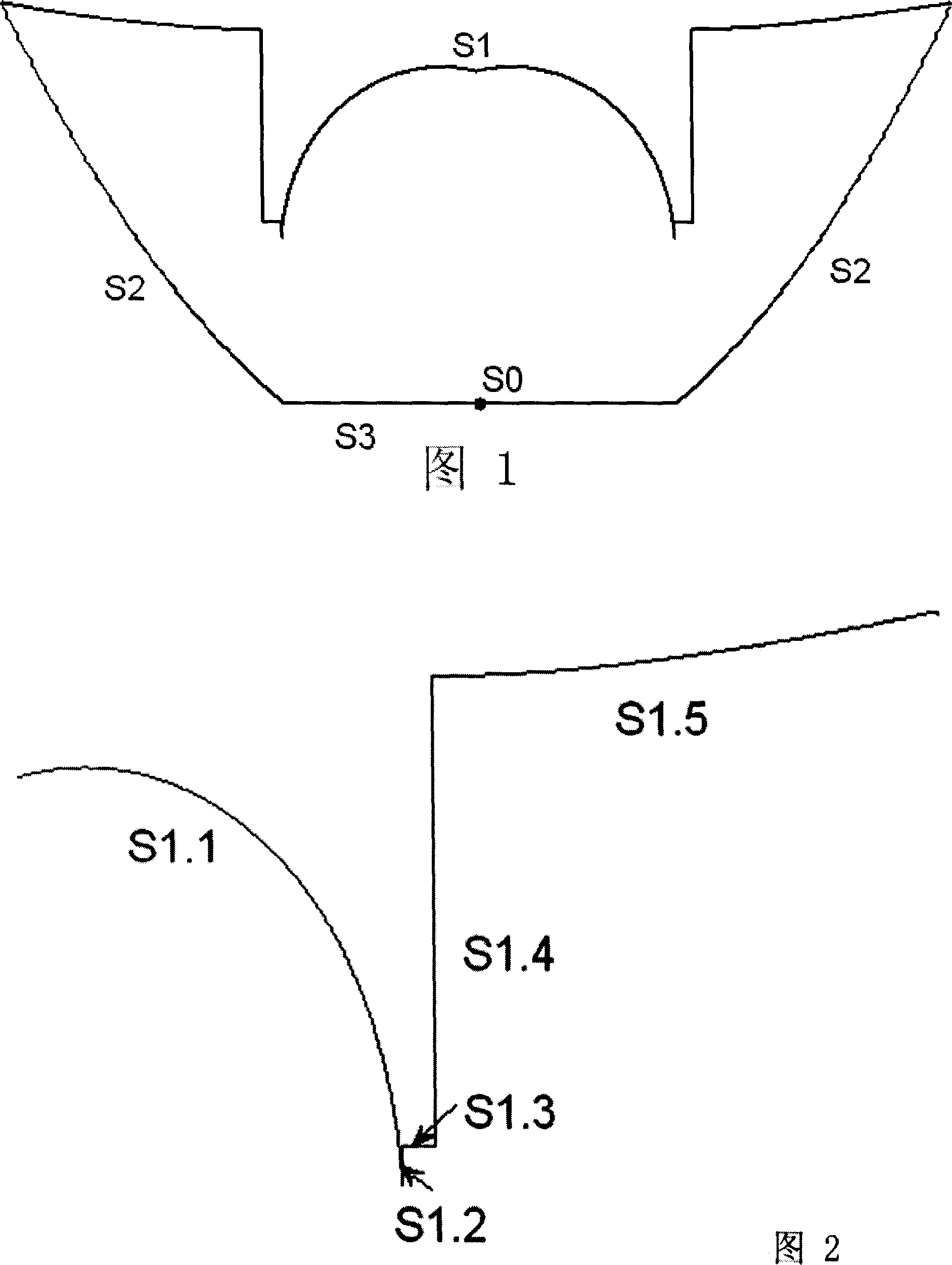
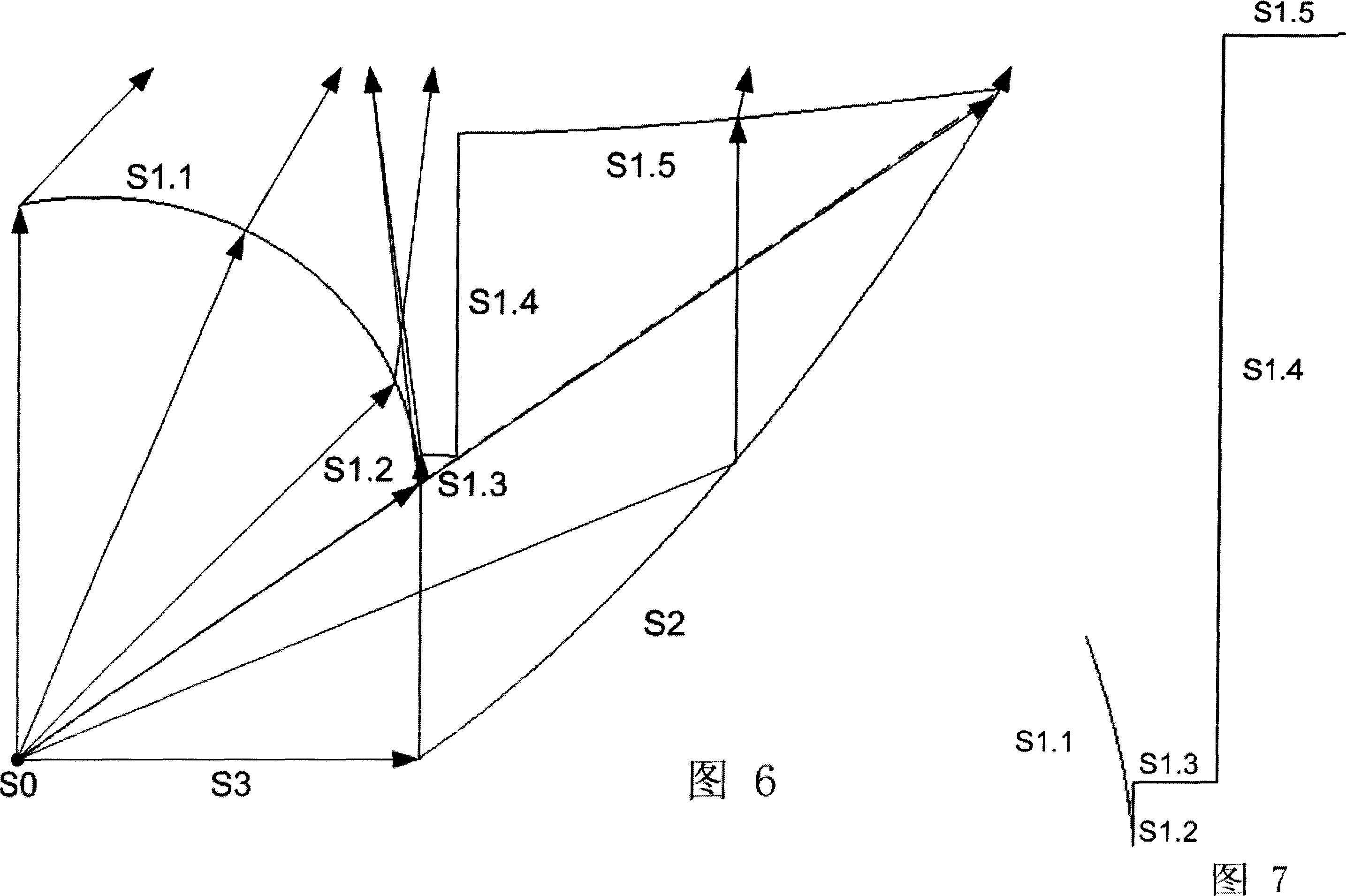
[0098] The refracting free-form surface lens for uniform illumination includes a Lambertian light source S0, a free-form surface S1 for refracting light beams, a reflective surface S2 for reflecting light within a specific divergence angle, and a base surface S3; where S1 includes a central free-form surface S1.1, free-form surfaces S1.3, S1.5, cylindrical surfaces S1.2, S1.4 perpendicular to the base surface S3.
[0099] As shown in FIG. 6 is a schematic diagram of characteristic rays of this embodiment. In order to cover the entire luminous area, the light is artific...
Embodiment 2
[0116] The design method and idea are also applicable to uniform lighting of a specific lighting area with a light source with a small divergence angle of 0-50 degrees, and a simplified structure can be used.
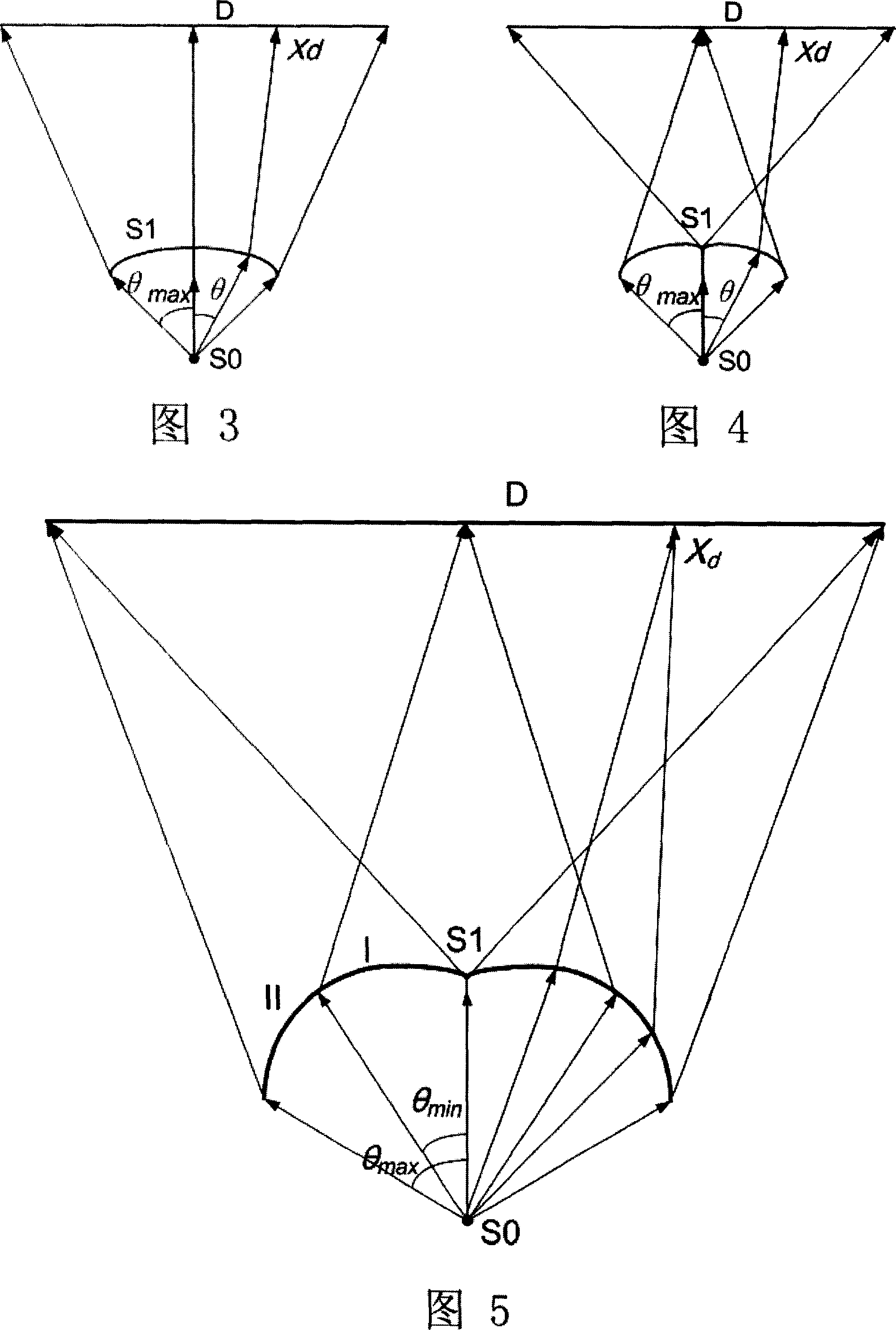
[0117] Fig. 12 shows a schematic diagram of an embodiment of a refractive free-form surface lens applied to a light source with a half light angle φ of 30°. The freeform surface shown in the figure uses the "forward lighting model" shown in Figure 3. In this and the following embodiments, S2 has no reflective function, and is only a cylindrical surface perpendicular to the base surface S3.
[0118] Fig. 13 shows a schematic diagram of another embodiment of a refractive free-form surface lens applied to a light source with a half light emission angle [phi] of 30°. The freeform surface shown in the figure uses the "reverse lighting model" shown in Figure 4.
[0119] FIG. 14 shows a schematic diagram of a third embodiment of a refractive free-form surface lens applied to...
Embodiment 3
[0122] If the refractive index of the medium can be increased from the general 1.5 to more than 1.8, this simplified structure is also applicable to certain larger angles (50-75°). Figure 16 shows the light source applied to a half-light emitting angle of 60° Schematic diagram of another embodiment of the applied refractive free-form surface lens. The freeform surface shown in the figure uses the "forward lighting model" shown in Figure 3.
[0123] Fig. 17 shows a schematic diagram showing another embodiment of a refractive free-form surface lens applied to a light source with a half light emission angle [phi] of 60°. The freeform surface shown in the figure uses the "mixed lighting model" shown in Figure 5.
[0124] This embodiment applied to a light source with a large divergence angle is mainly applicable to some occasions that have a certain requirement on the total luminous flux (20-40lm) and hope to save energy.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com