IPv6 route list checking and repeating method
An IP routing and table lookup technology, applied in special data processing applications, instruments, electrical digital data processing, etc., can solve problems such as high cost, affecting forwarding performance, and increasing the number of accesses to RAM, improving utilization and saving Memory, the effect of reducing the burden
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
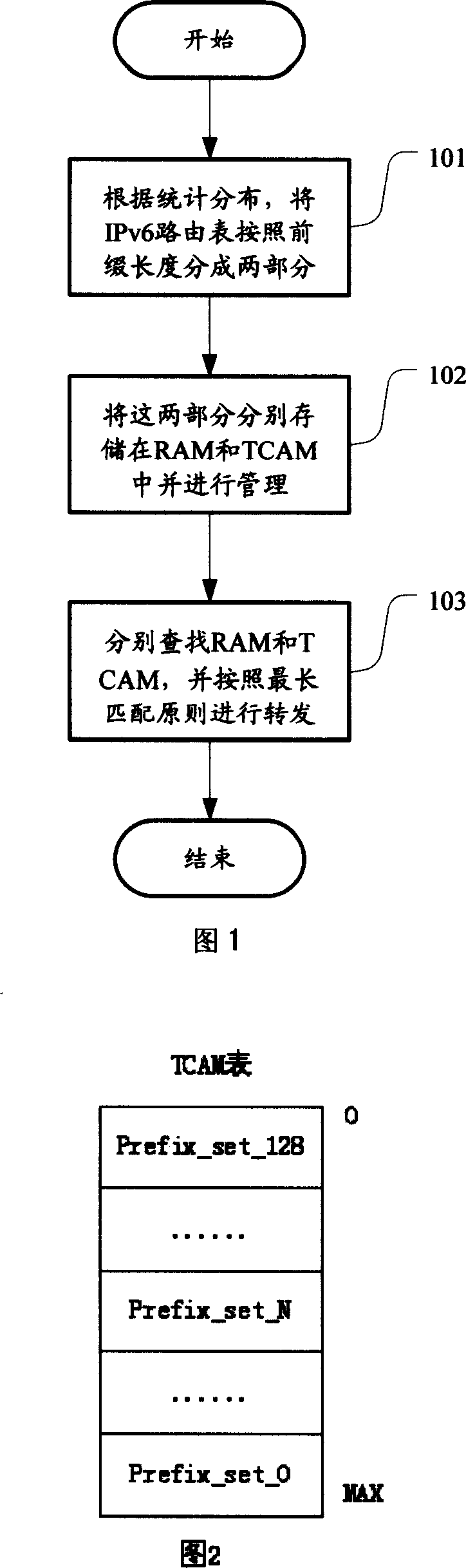
[0032] Below in conjunction with accompanying drawing and specific embodiment the present invention is described in further detail:
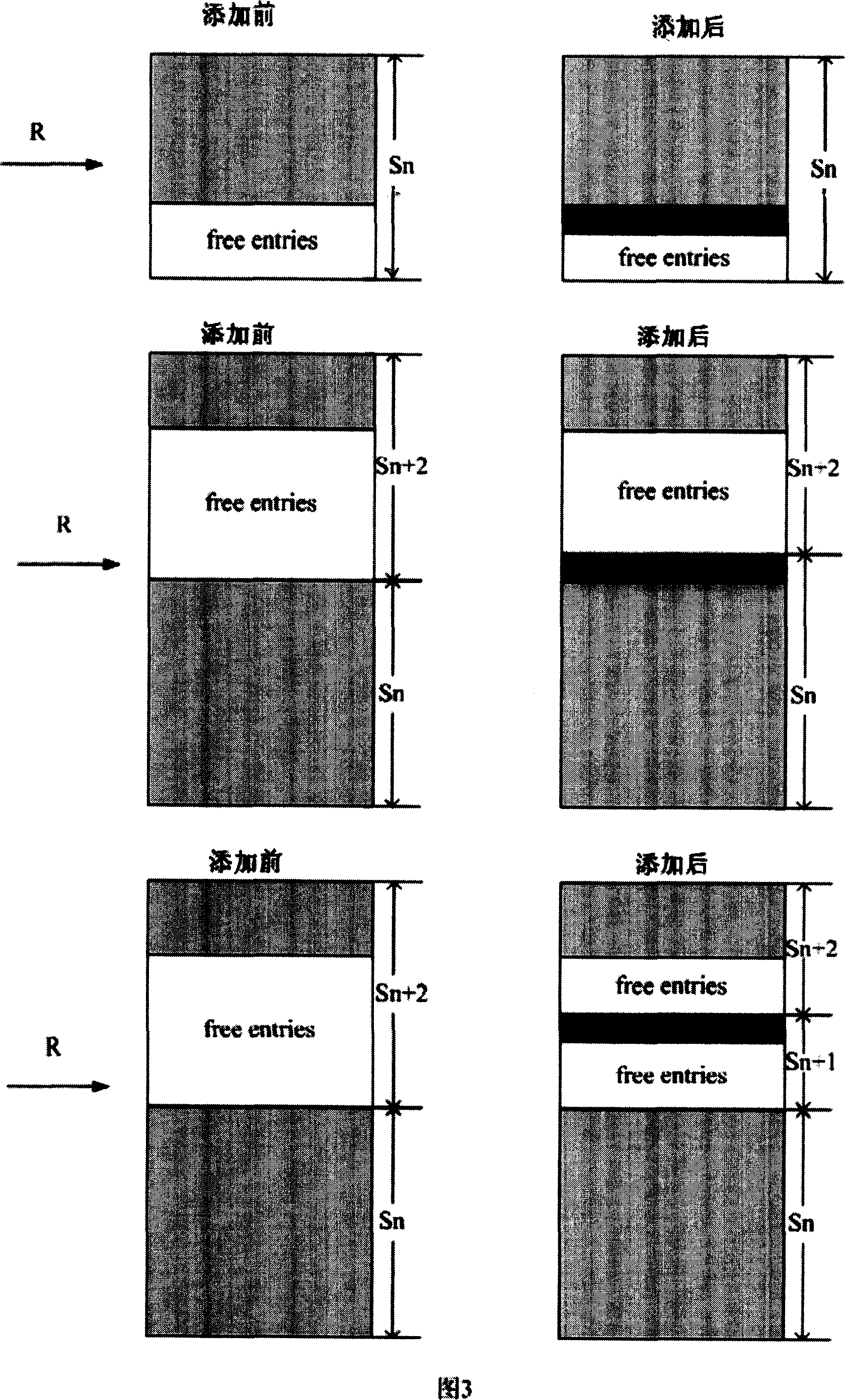
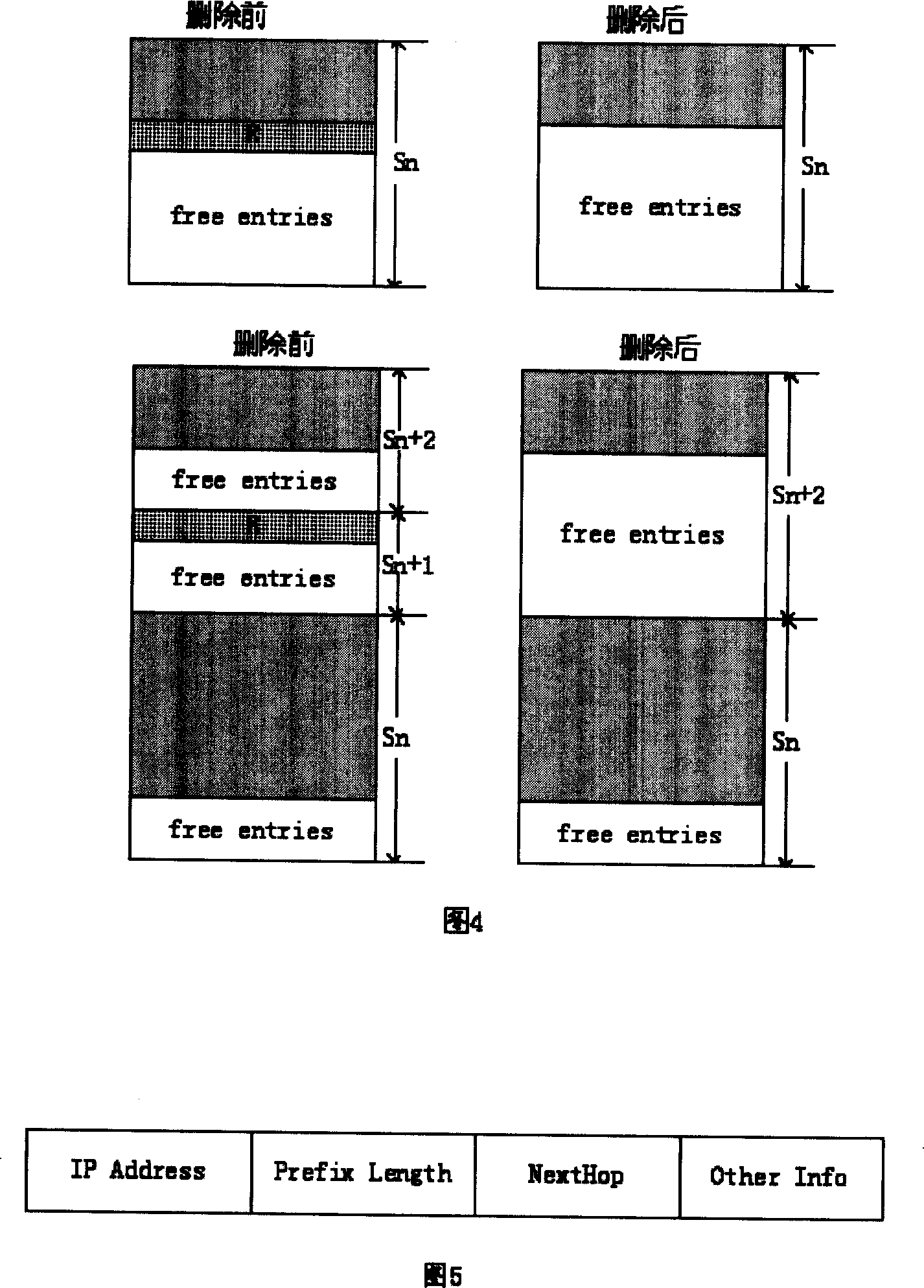
[0033] According to the statistical distribution, most of the prefix lengths in the network are concentrated in a certain interval, and currently up to 70% of IPv6 routes have a prefix length of 48. Accordingly, the present invention divides IPv6 routes into two major parts, the routes whose prefix lengths belong to the interval [a, b] and other routes (the values of a and b depend on the distribution of actual network addresses, ensuring that most of the routes fall within In the interval [a, b], at present, a=40, b=48 can be taken). For the former, M-Trie with a preprocessing engine is used. For the latter, TCAM is used for realization.
[0034] 1) M-Trie table with preprocessing engine
[0035] Routes whose prefix lengths are distributed in [a, b] are implemented using M-Trie with a preprocessing engine.
[0036] Specific steps are as f...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com