Non-equal multi-user high order modulation approach
A high-order modulation and multi-user technology, applied in the field of communication, can solve the problems of limiting performance, multiple access interference of users with good channels, and reducing the performance of users with good channels, so as to achieve the effect of enhancing throughput efficiency and improving performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
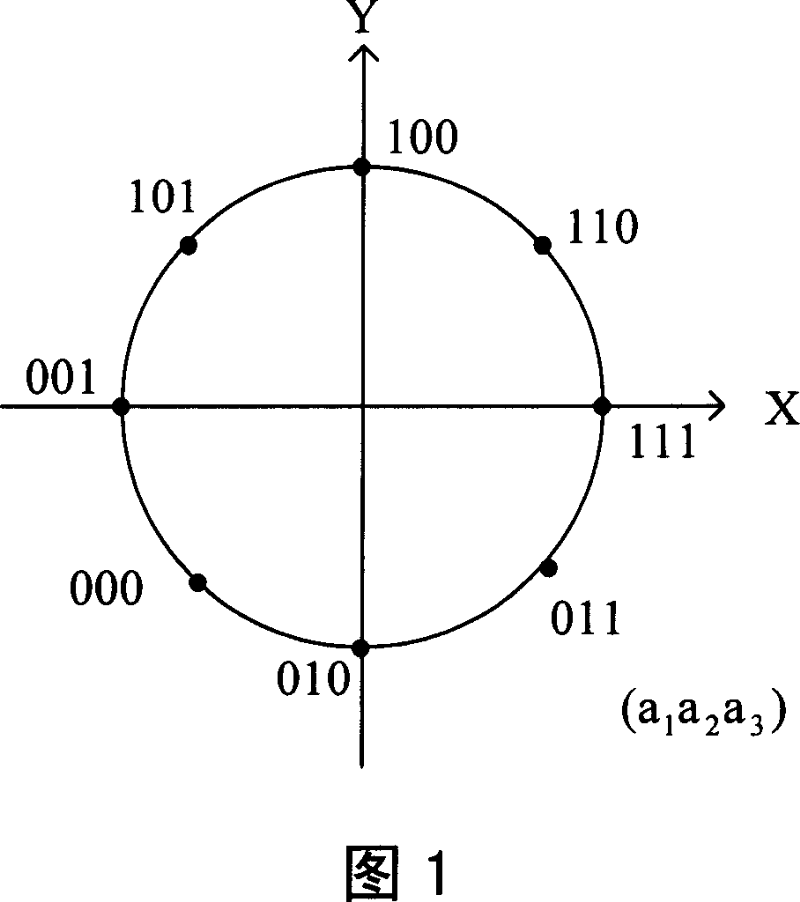
[0060] Suppose there are two users A and B, user A is at the edge of the cell, its SINR is low, and user B is close to the base station, its SINR is high. The base station defines user A as a weak user and user B as a strong user according to the SINR of each user. Assume that the binary data block of user A after channel coding and interleaving is {a i}, i ∈ [0, N-1]. The binary data block of user B after channel coding and interleaving is {b i}, i ∈ [0, N-1]. Wherein, N is the block length, N=0 (mod 3). The multi-user bit data stream after matching multiplexing is {c i}, i ∈ [0, 2N-1]. When Gray-mapped 8PSK is used, the following multiplexing methods can be used:
[0061] c 3k =a k c 3k+2 =b k k ∈ [ 0 , 2 N 3 - 1 ]
[0062] c 3i+1 =a i+2N / 3 c 3i+N+1 =b i+2N / 3 i ...
Embodiment 2
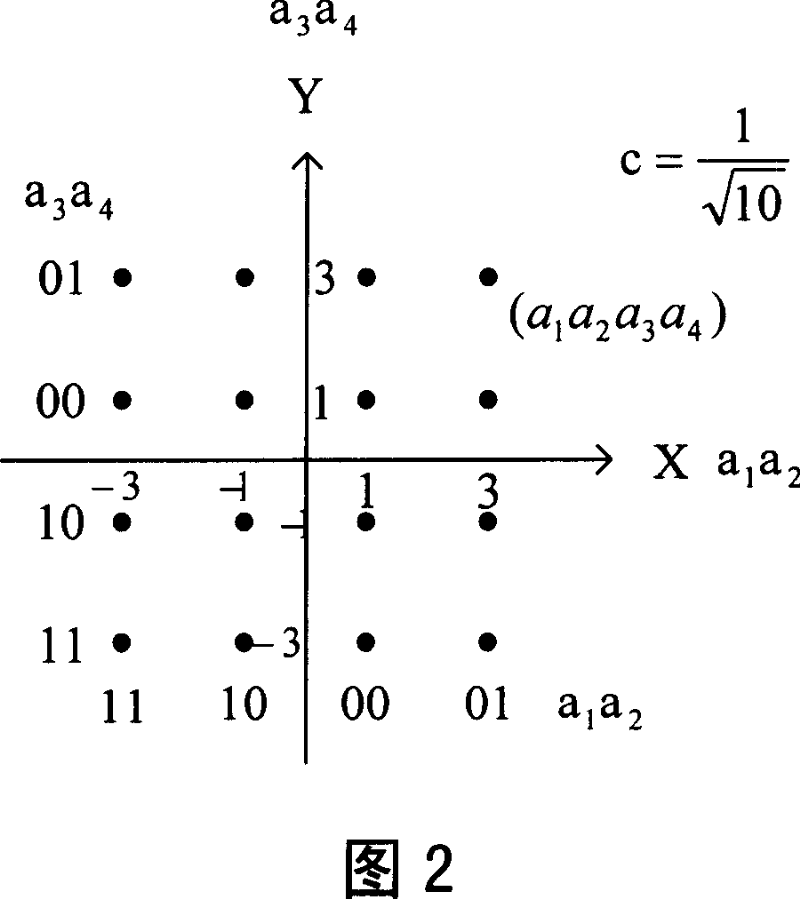
[0065] Suppose there are two users A and B, user A is at the edge of the cell, its SINR is low, and user B is close to the base station, its SINR is high. The base station defines user A as a weak user and user B as a strong user according to the SINR of each user. Assume that the binary data block of user A after channel coding and interleaving is {a i}, i ∈ [0, N-1]. The binary data block of user B after channel coding and interleaving is {b i}, i ∈ [0, N-1]. Wherein, N is the block length, N=0 (mod 2). The multi-user bit data stream after matching multiplexing is {c i}, i ∈ [0, 2N-1]. When Gray-mapped 16QAM is used, the following multiplexing method can be used:
[0066] c 4k =a k c 4k+2 =a k+N / 2 c 4k+1 =b k c 4k+3 =b k+N / 2 k ∈ [ 0 , N 2 - 1 ]
[0067] then to {c i} Each group of four bits is mapped to the constellation d...
Embodiment 3
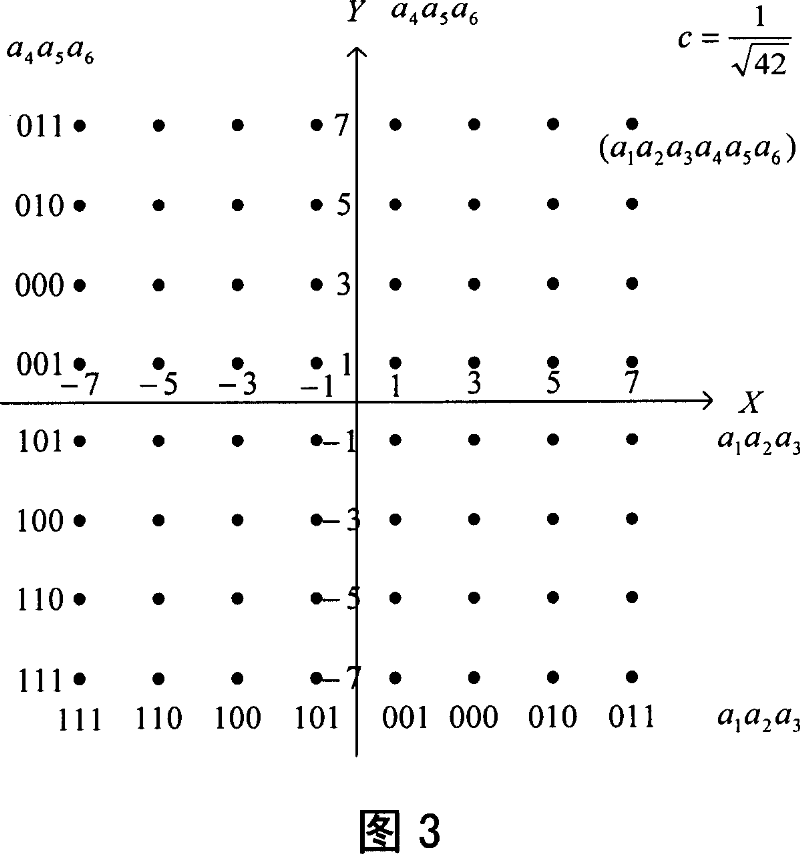
[0069] Assume that there are three users A, B and C, and their SINRs increase sequentially. According to the SINR of each user, the base station defines user A as a weak user, user C as a strong user, and user B in the middle. Assume that the binary data blocks of users A, B, and C after channel coding and interleaving are respectively {a i}, {b i}, {c i}, i ∈ [0, N-1]. Wherein, N is the block length, N=0 (mod2). The multi-user bit data stream after matching multiplexing is {d i}, i ∈ [0, 3N-1]. When Gray-mapped 64QAM is used, the following multiplexing method can be used:
[0070] d k =a k d k+3 =a k+N / 2 d k+4 =b k
[0071] d k+1 =b k+N / 2 d k+2 = c k d k+5 = c k+N / 2 k ∈ [ 0 , N 2 - 1 ]
[0072] then to {d i} Each group of six bits is mapped to the constellation diagram of 64QAM for transmission.
[007...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com