Radar device
A technology of radar devices and optical circuits, applied in measuring devices, re-radiation of electromagnetic waves, utilization of re-radiation, etc., can solve the problem of reduced observation accuracy, difficulty in detecting low-brightness reflected light, and inability to correctly observe high-brightness reflected light, etc. problem to ensure responsiveness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0037]Hereinafter, a radar device as an embodiment of the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings.
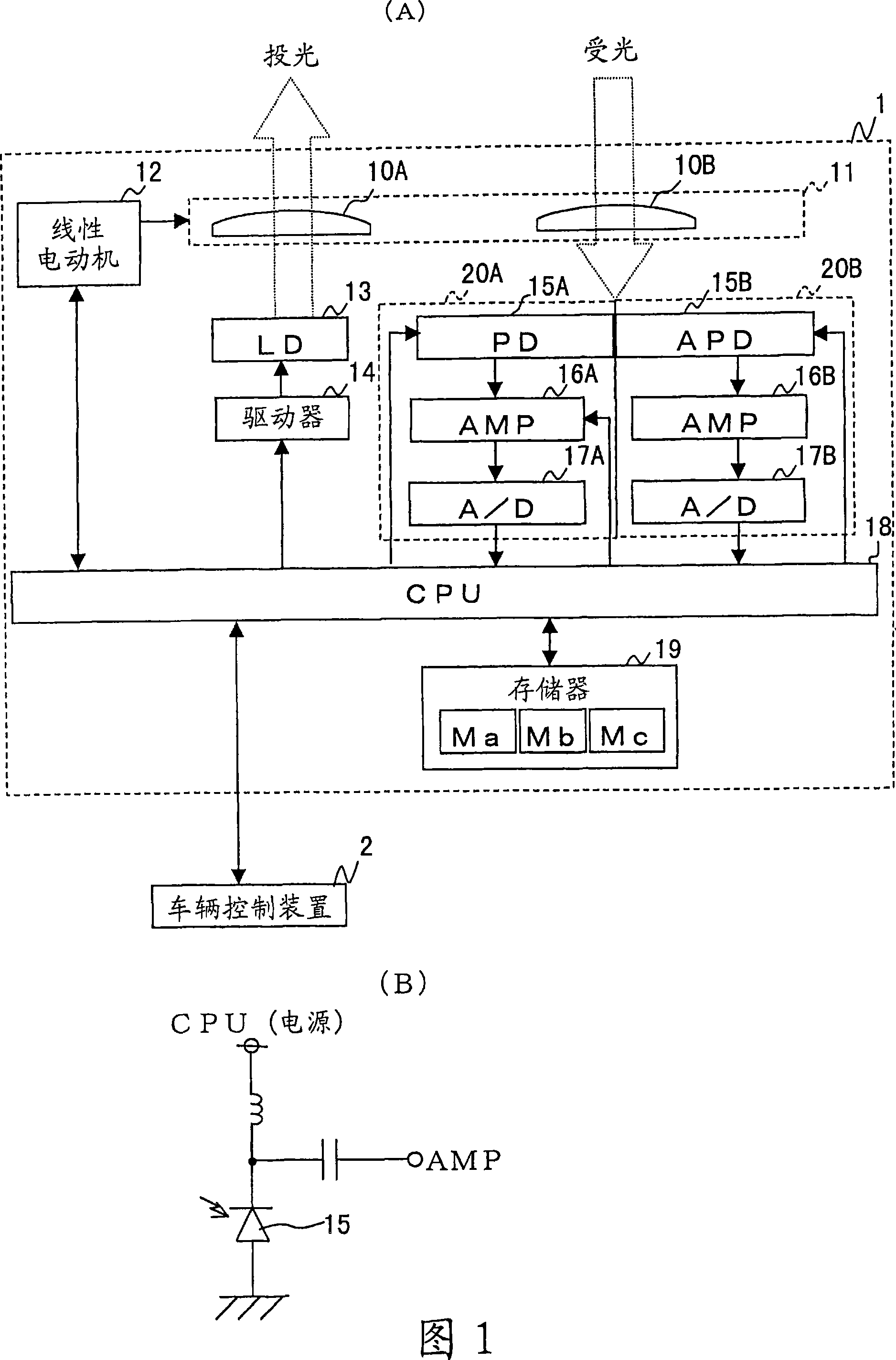
[0038] FIG. 1(A) is a block diagram showing the configuration of a radar device. The radar device 1 includes a lens unit 11 , a linear motor 12 , a laser diode (LD) 13 , a driver 14 , light receiving circuits 20A and 20B, a CPU 18 , and a memory 19 .
[0039] In the lens unit 11 , the light-projecting lens 10A and the light-receiving lens 10B are arranged on the same frame so that their respective optical axes are parallel. LD 13 is provided at the focal position of lens 10A, and PD 15A and APD 15B are provided at the focal position of lens 10B. The linear motor 12 is connected to the CPU 18, and the swing angle of the lens unit 11 is set according to the control of the CPU 18, so that the lens unit 11 (relative to the traveling direction of the vehicle) swings left and right.
[0040] LD 13 is connected to CPU 18 via driver 14 . The driver 14 sets...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com