Temperature-fixing dehumidifying air conditioner and control method thereof
A control method, air conditioner technology, applied in air conditioning system, heating method, space heating and ventilation, etc., can solve the problem that the room temperature and humidity cannot be controlled separately, the difference between the set temperature and the indoor temperature is not considered, and there is no optimization Problems such as the operation mode of outdoor fans and compressors, to achieve the effect of simple structure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
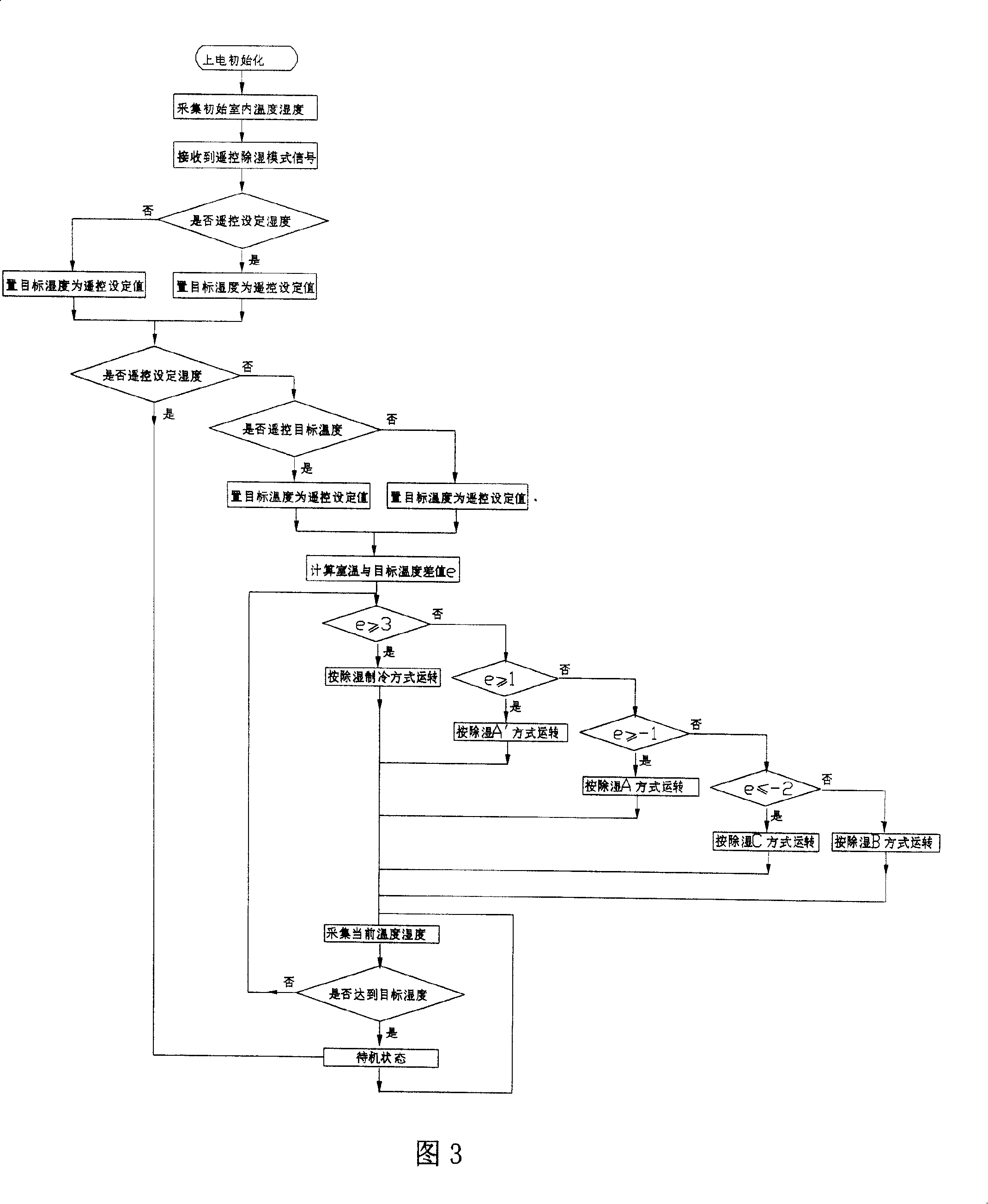
Examples
Embodiment Construction
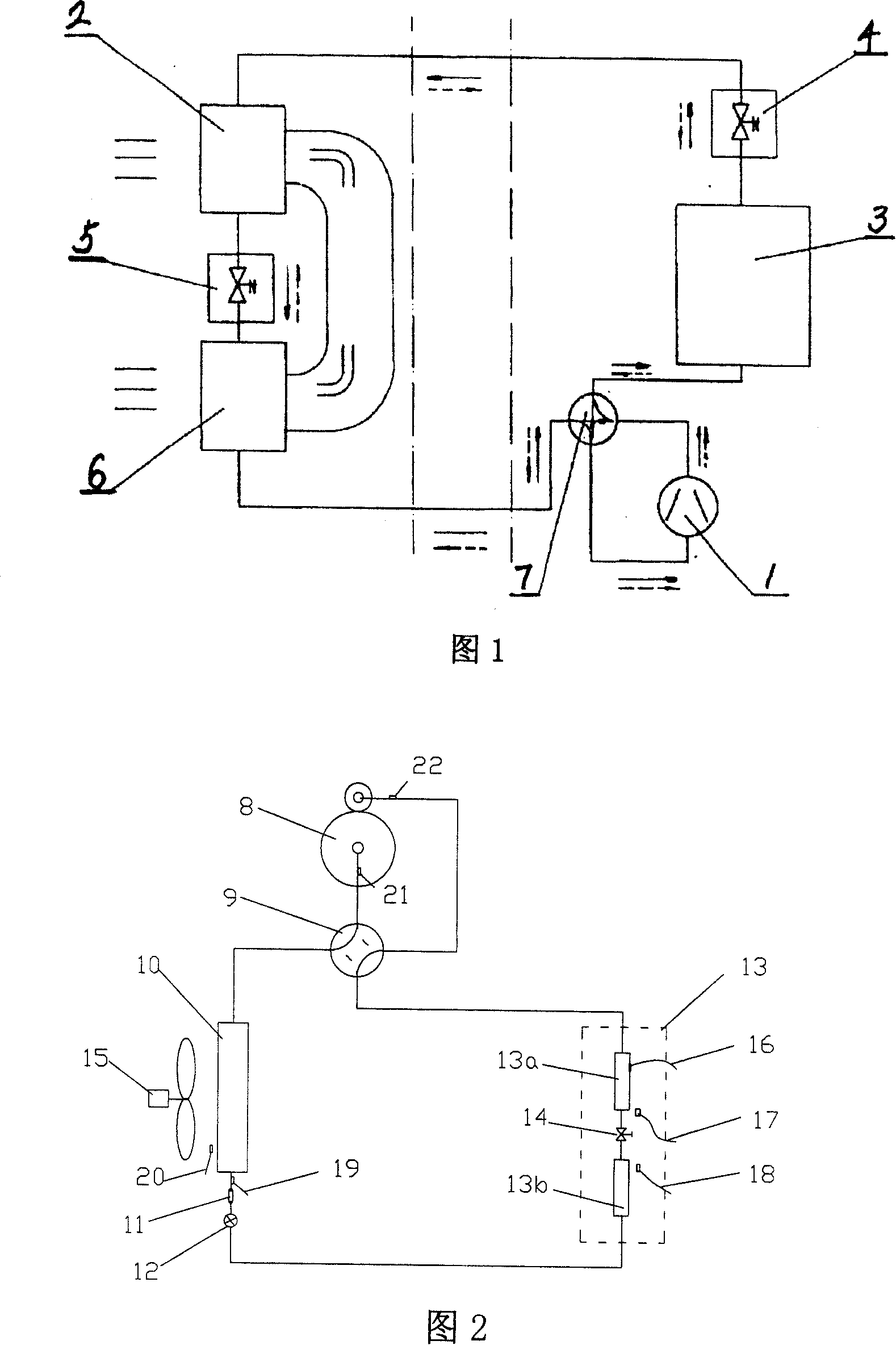
[0054] As shown in Figure 2, the air conditioner system includes a compressor 8, an electromagnetic four-way reversing valve 9, an outdoor heat exchanger 10, a filter 11, a throttling electronic expansion valve 12, an indoor heat exchanger 13, and the indoor The heat exchanger 13 is divided into two sections before and after the indoor heat exchanger dehumidification section 13a and the indoor heat exchanger heating section 13b, and a dehumidification solenoid valve is arranged between the indoor heat exchanger dehumidification section 13a and the indoor heat exchanger heating section 13b 14.
[0055] In order to achieve the purpose of intelligent control, several temperature and humidity sensors are set in the air conditioner system, which are respectively indoor coil temperature sensor 16, indoor temperature sensor 17, indoor humidity sensor 18, outdoor defrosting temperature sensor 19, indoor Outer ring temperature sensor 20 , compressor discharge temperature sensor 21 , co...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com