Full-wave nonzero dispersion flat single-mode optical fiber
A non-zero dispersion, single-mode optical fiber technology, applied in cladding optical fiber, optical waveguide and light guide, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
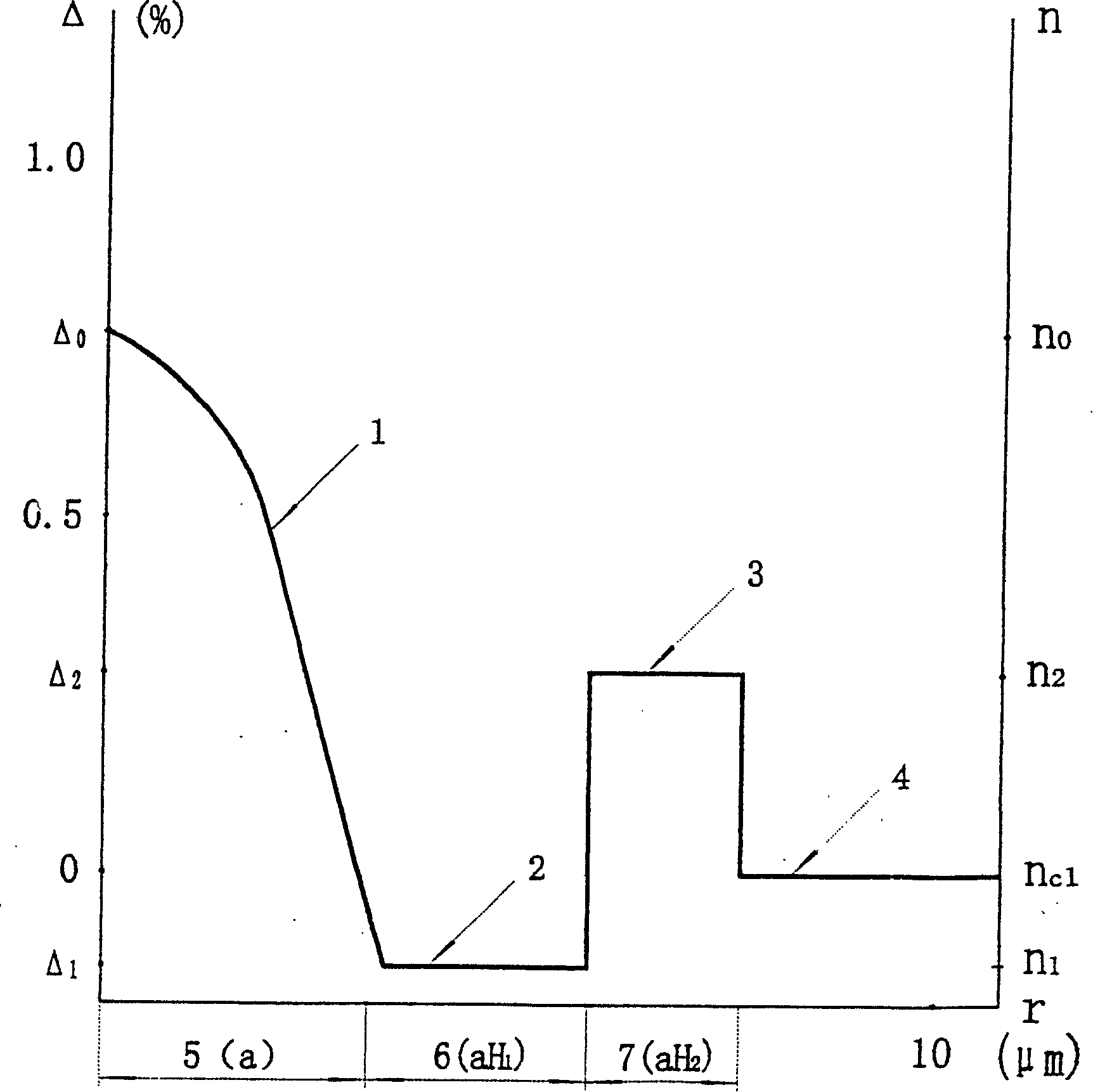
[0032] figure 1 Among them, 1, 2, 3, and 4 represent the central circular layer, the first ring layer, the second ring layer, and the outer cladding of the optical fiber, respectively, and 5, 6, 7 and 8 represent the core center of the fiber. Circular stratification radius a, first annular stratification width H 1 And the second annular layer width H 2 , N 0 Represents the maximum refractive index of the central circular layer of the core, n 1 And n 2 Respectively represent the uniform refractive index of the first annular layer and the second annular layer, n c1 Represents the uniform refractive index of the outer cladding layer. The refractive indices of the first annular layer, the second annular layer and the outer cladding layer are all substantially uniform. The first annular layer Δ 1 2 >0.
[0033] Table 1 shows the main structural parameters of a preferred embodiment of the invented full-wave non-zero dispersion flattened single-mode fiber.
[0034] Table 1
[0035] ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com