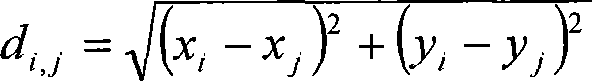Multicast randomizing routing method based on virtual Stener tree
A Steiner tree and randomization technology, applied in branch offices providing special services, data exchange details, transmission systems, etc., and can solve problems such as failure of routing process, network paralysis, and algorithm infinite loop.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
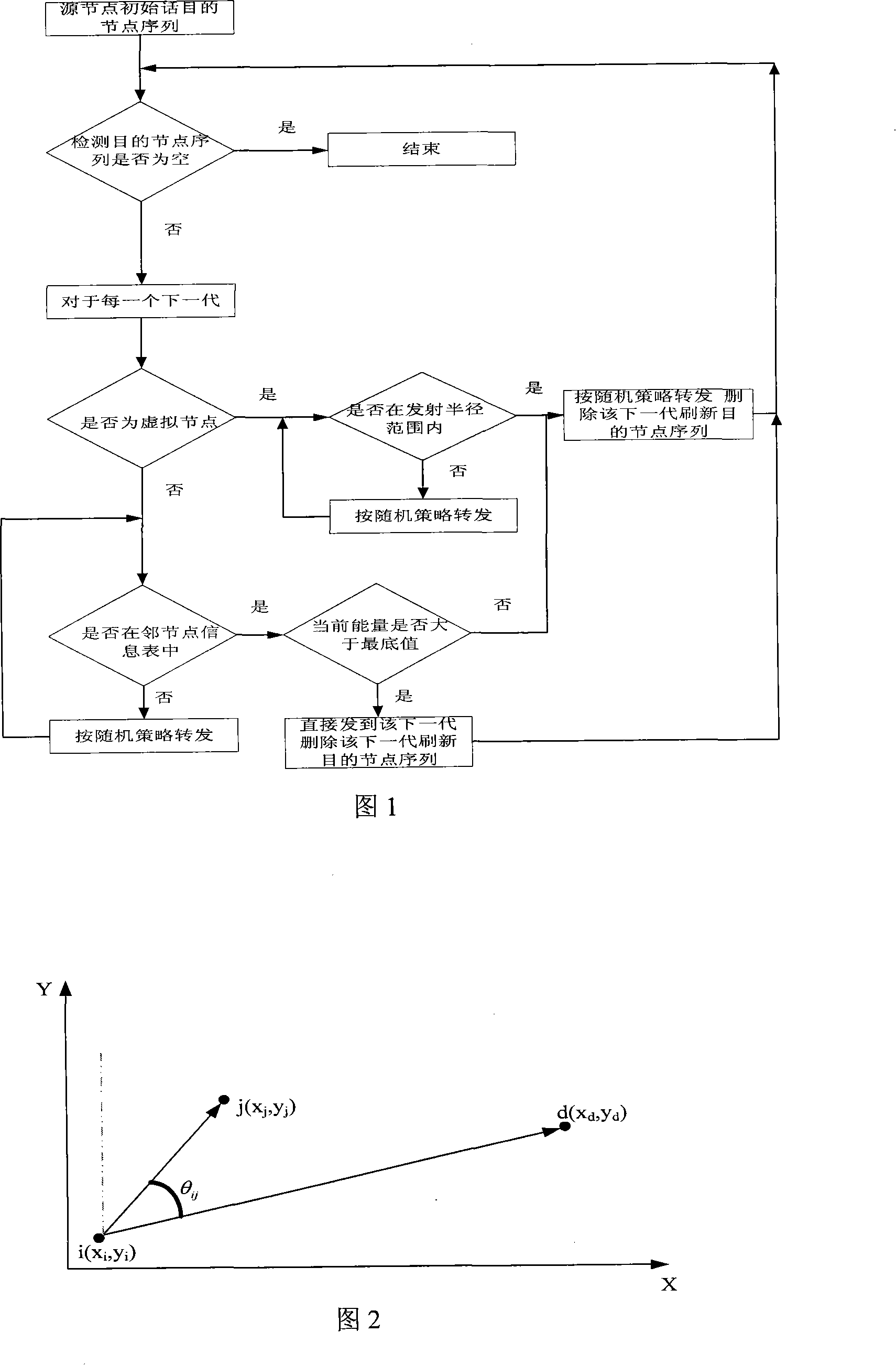
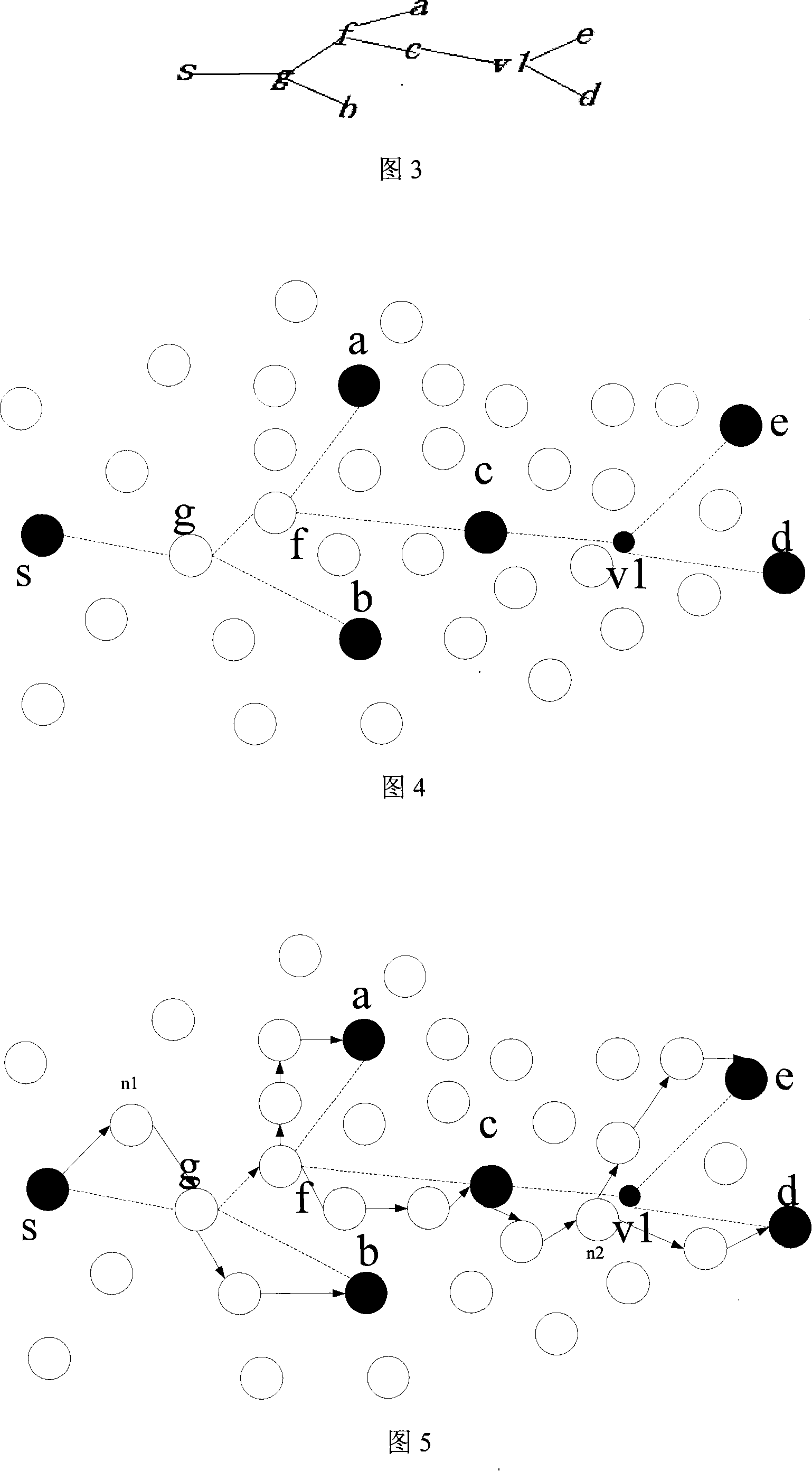
[0041] Below we use a specific example to illustrate the process of multicast routing.
[0042] 1. In the figure, s creates a virtual Steiner tree, and the destination node sequence is shown in Figure 3.
[0043] 2. First, s detects that the next generation g is not in its neighbor node information table, then s forwards the data packet to a node in the neighbor node information table according to a random strategy, for example, n1 in the figure. As time goes by and the network topology changes, the probability of each node in the neighbor node information table changes dynamically, that is, the selection of the next hop of s is not unique.
[0044] 3. Assume that after n1 node receives the data packet, it extracts the sequence information of the destination node from it, and then compares g with the information in its neighbor node information table. If it finds that g is in it, it forwards it directly to g, and then transfers g from Deleted from the destination node sequenc...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com