Short message value-added service processing method and system
A technology of value-added services and processing methods, applied in the direction of messages/mailboxes/notifications, subscriber special services, electrical components, etc., can solve problems such as increasing the difficulty of system transformation and reducing investment benefits, so as to save investment costs and ensure investment Benefits, impact prevention effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
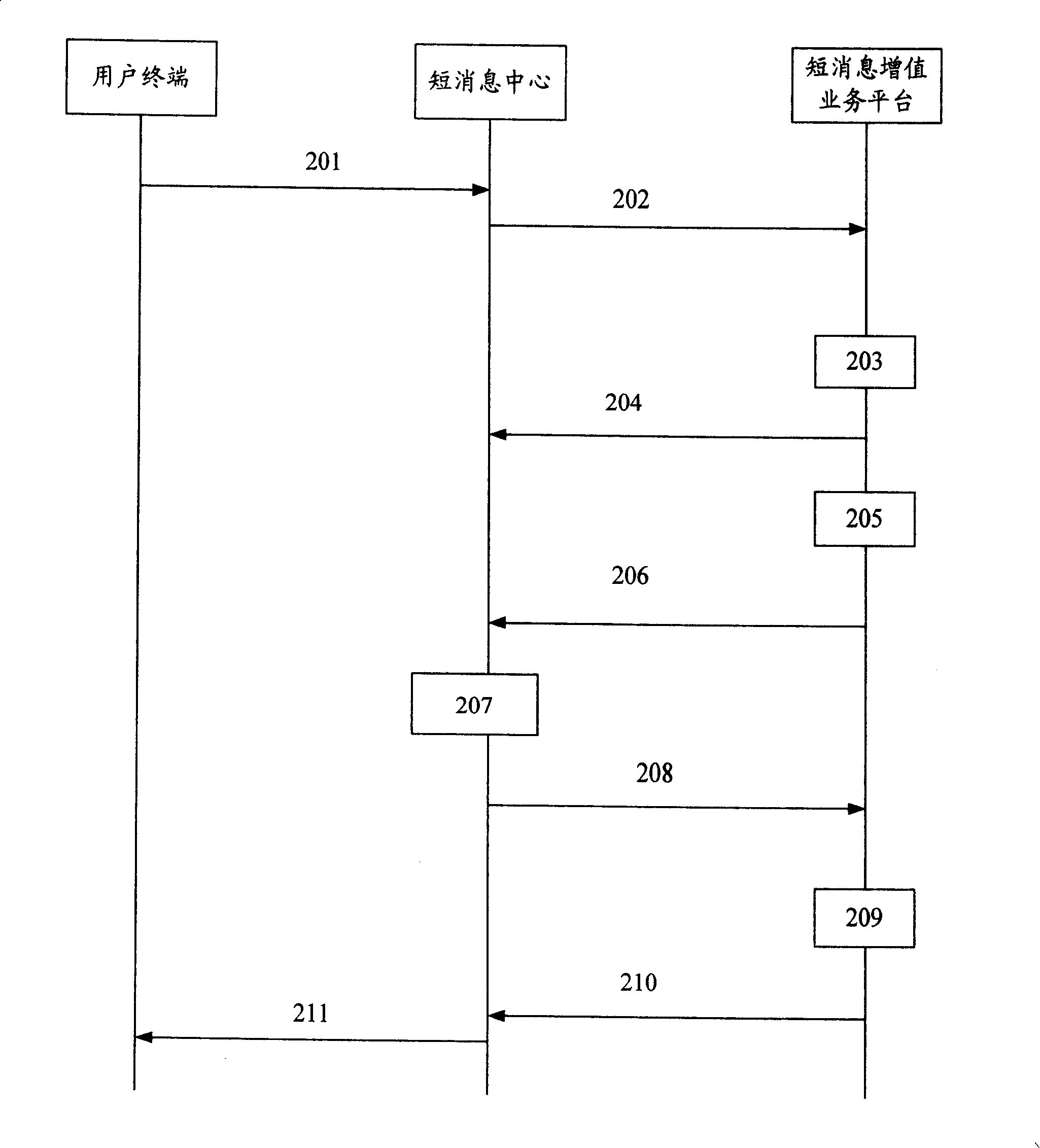
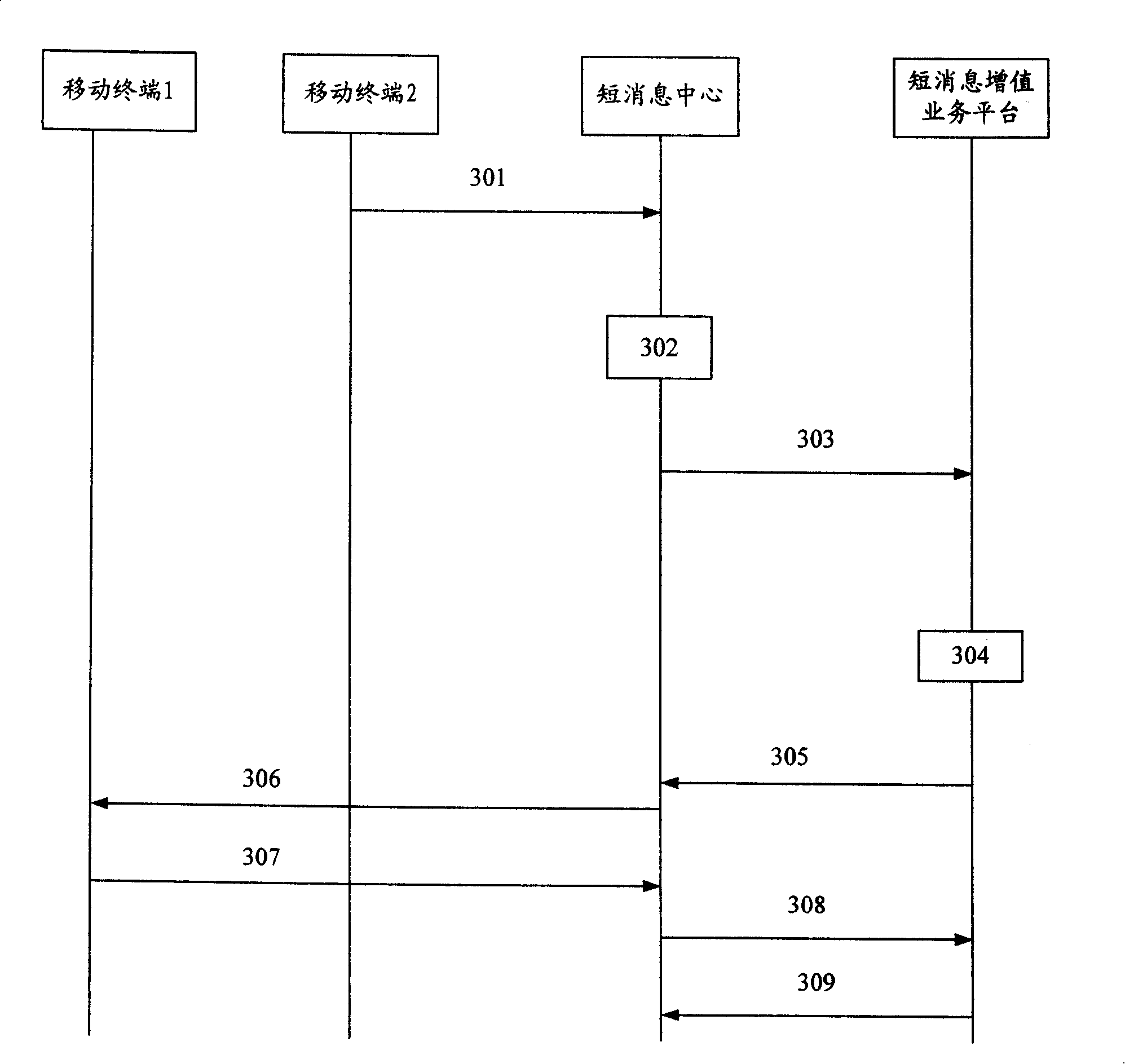
[0044] The method and system of the present invention are applicable to GSM / GPRS / WCDMA / TDCDMA networks.
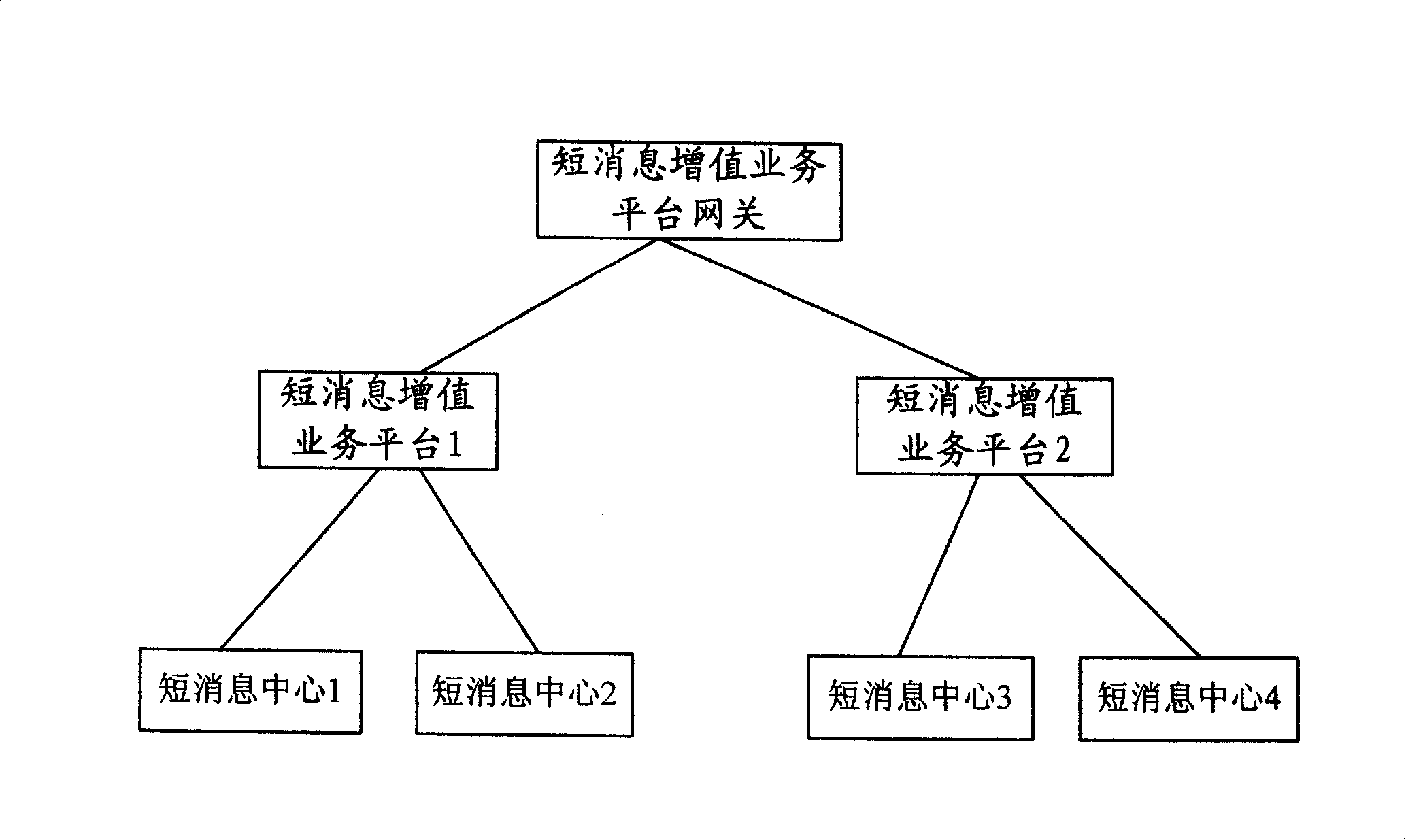
[0045] The short message value-added service processing system of the present invention includes SMVP (short message value-added service platform) and VPGW (short message value-added service platform gateway), and the extended SMPP protocol is used for communication between them.
[0046] Among them, the main function of SMVP is to store the subscription information of value-added services for users in this service area (if you want to open the whole network service, you also need to store the subscription identifier of the called service of the entire network user), and synchronize the subscription identifier of the user to the SMSC to which the user belongs. And responsible for the processing priority of various value-added services and the specific realization of value-added services. The subscription information is used to record the detailed subscription records of th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com