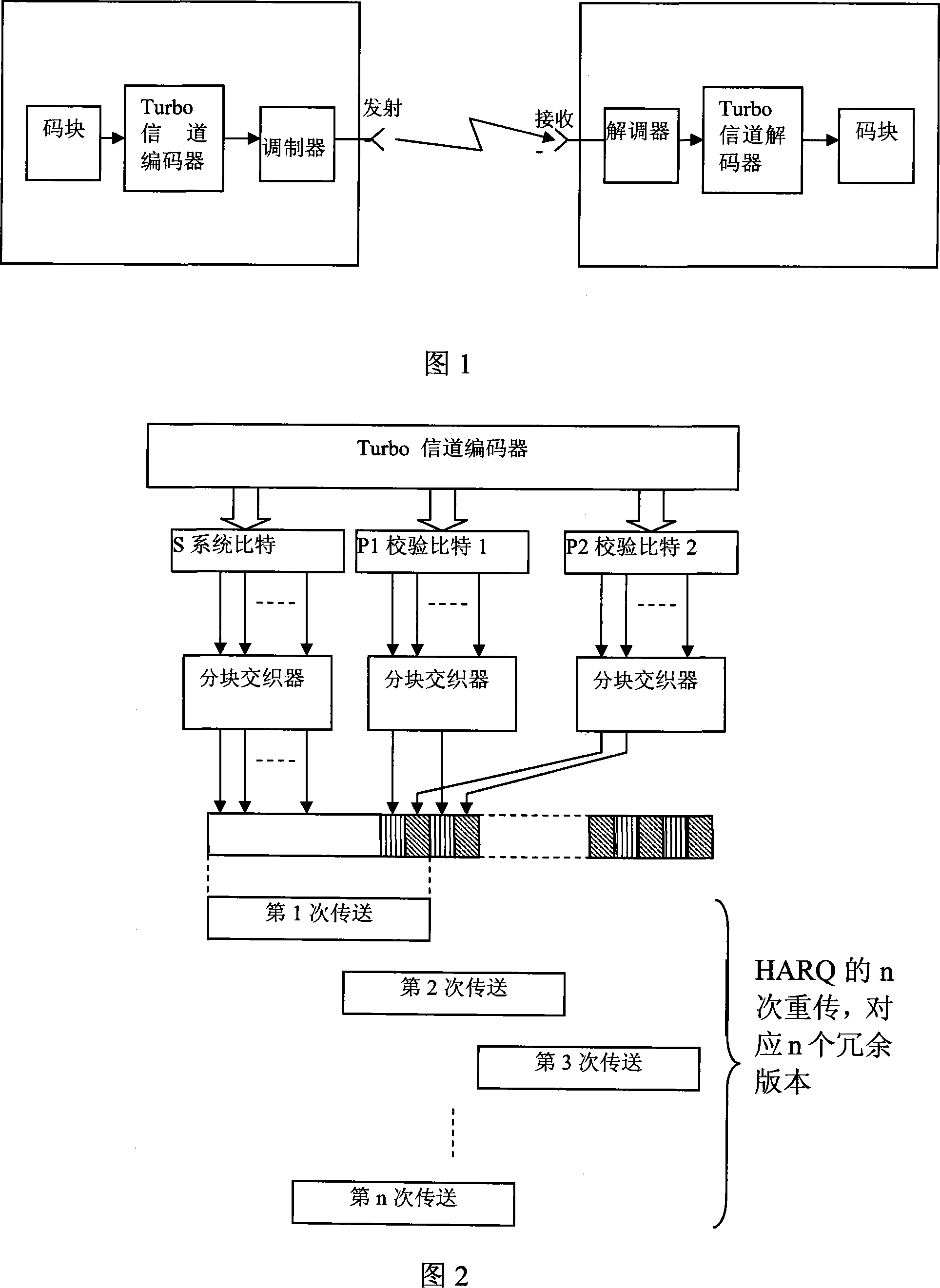
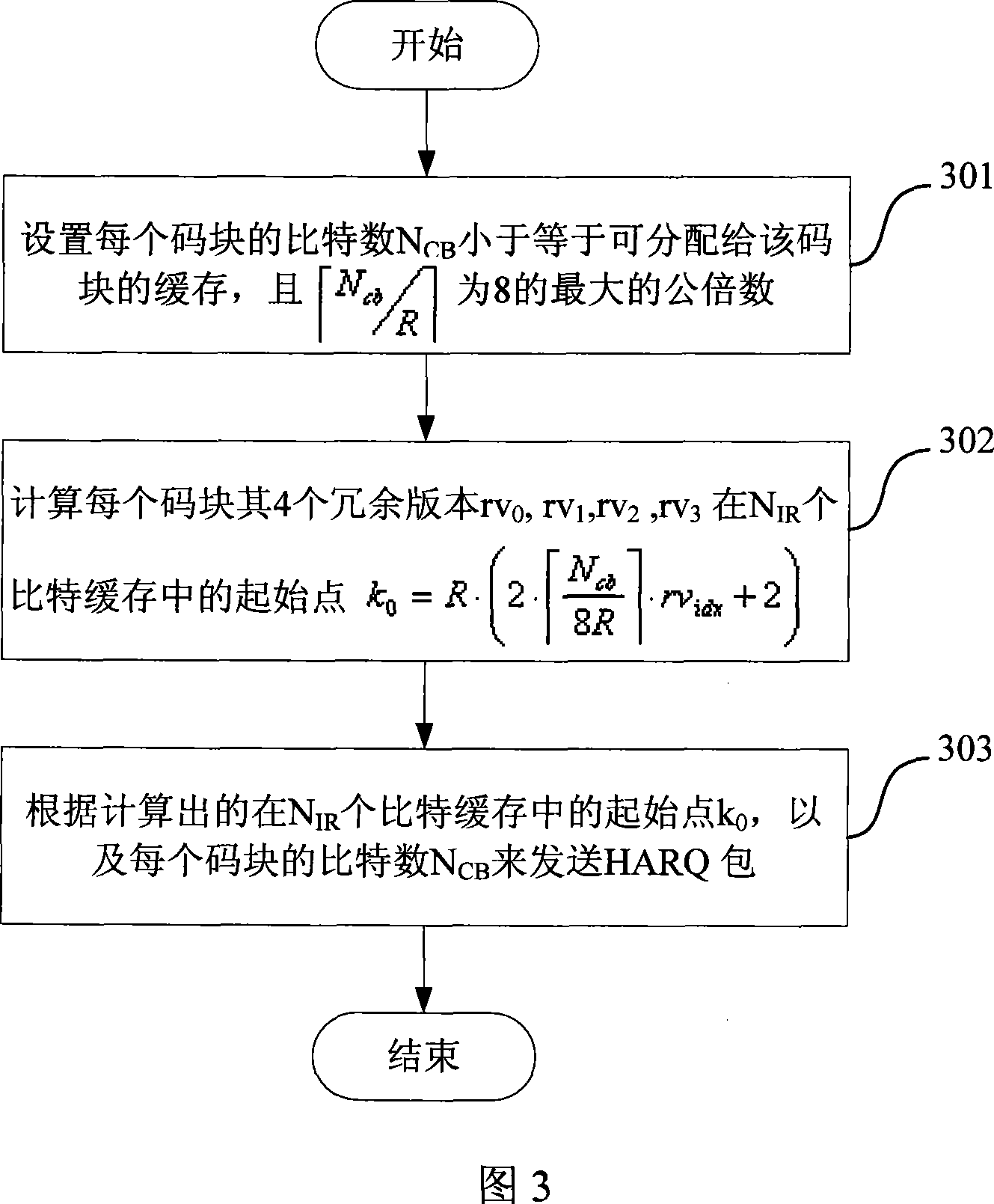
A buffering setting method of phase rate matching
A rate matching, staged technology, applied in the direction of error prevention/detection using the return channel, which can solve problems such as retransmission performance degradation, and achieve the effect of improved performance and uniform location distribution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
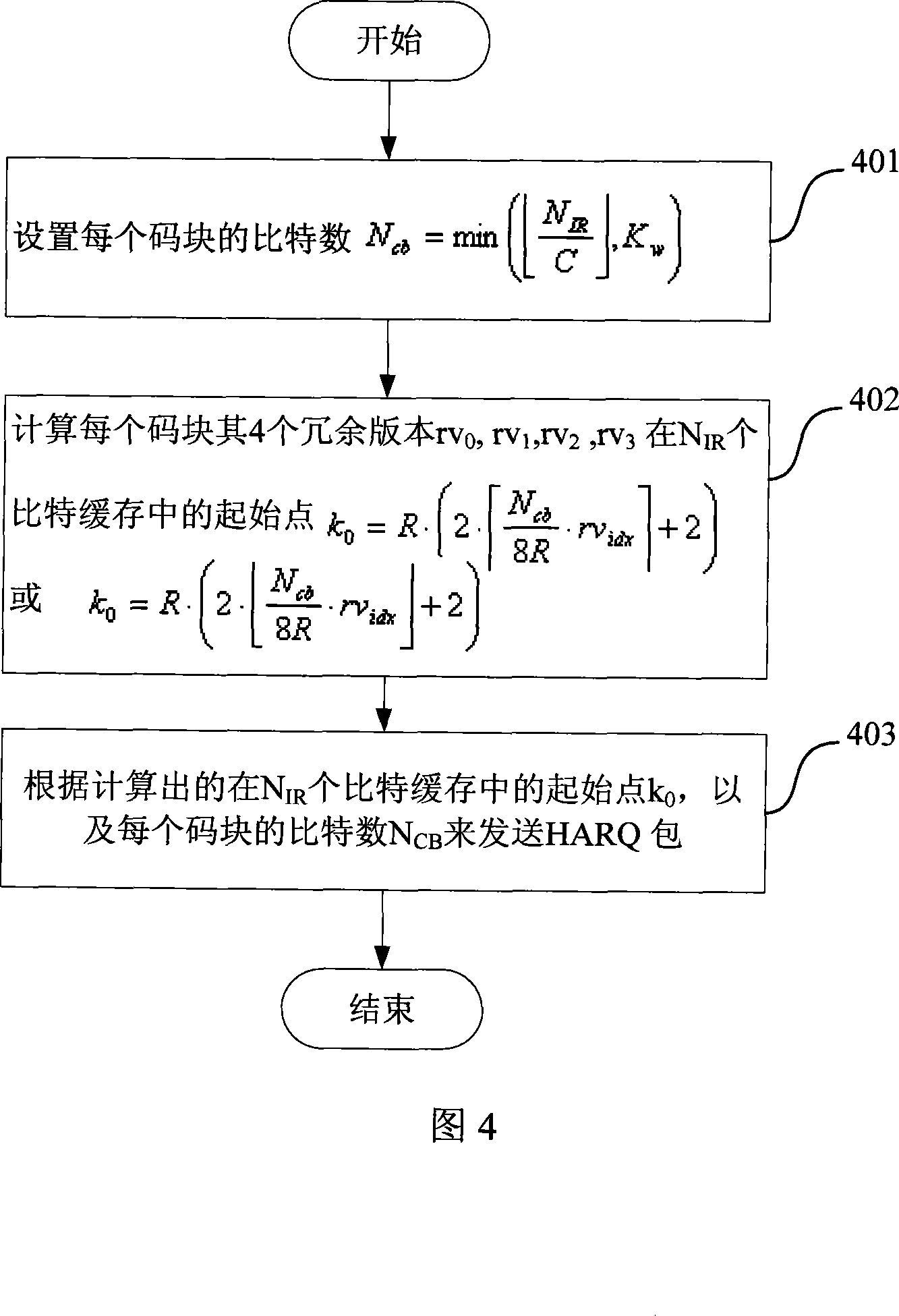
[0046] As shown in FIG. 3 , the first embodiment of the present invention makes the position distribution of RV as uniform as possible by selecting the size of bits of each code block of a suitable HARQ packet, including the following steps:
[0047] Step 301, the sender selects the number of bits N of each code block in the cache cb , set N cb is less than or equal to the buffer that can be allocated to the code block, and is the greatest common multiple of 8; where R is the number of buffer lines specified by the sending end of the digital communication system;
[0048] Among them, you can set or where N IR is the total number of cached bits, C is the number of code blocks, K w is the number of bits after channel coding;
[0049] Step 302, the sender calculates the 4 redundancy versions rv of each code block 0 , rv 1 , rv 2 , rv 3 , at N IR starting point in the bit buffer where rv idx The value is 4 redundant version numbers 0, 1, 2, 3:
[0050] Step 303, ...
Embodiment 2
[0054] As shown in FIG. 4, the second embodiment of the present invention makes the position distribution of the RV as uniform as possible by setting a suitable HARQ starting point, including the following steps:
[0055] Step 401, the sender sets the number of bits of each code block in the cache where N IR is the total number of cached bits, C is the number of code blocks, K w is the number of bits after channel coding;
[0056] Step 402, the sender calculates the 4 redundancy versions rv of each code block 0 , rv 1 , rv 2 , rv 3 , at N IR starting point in the bit buffer or, where rv idx The value is 4 redundant version numbers 0, 1, 2, 3, and R is the number of buffer lines specified by the sending end of the digital communication system;
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com