Dominant SCAR molecule mark for wild cabbage type cole self-incompatibility and uses thereof
A Brassica napus and molecular marker technology, applied in DNA/RNA fragments, recombinant DNA technology, microbial measurement/testing, etc., can solve problems such as self-incompatibility, reduce breeding workload, and shorten breeding years Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
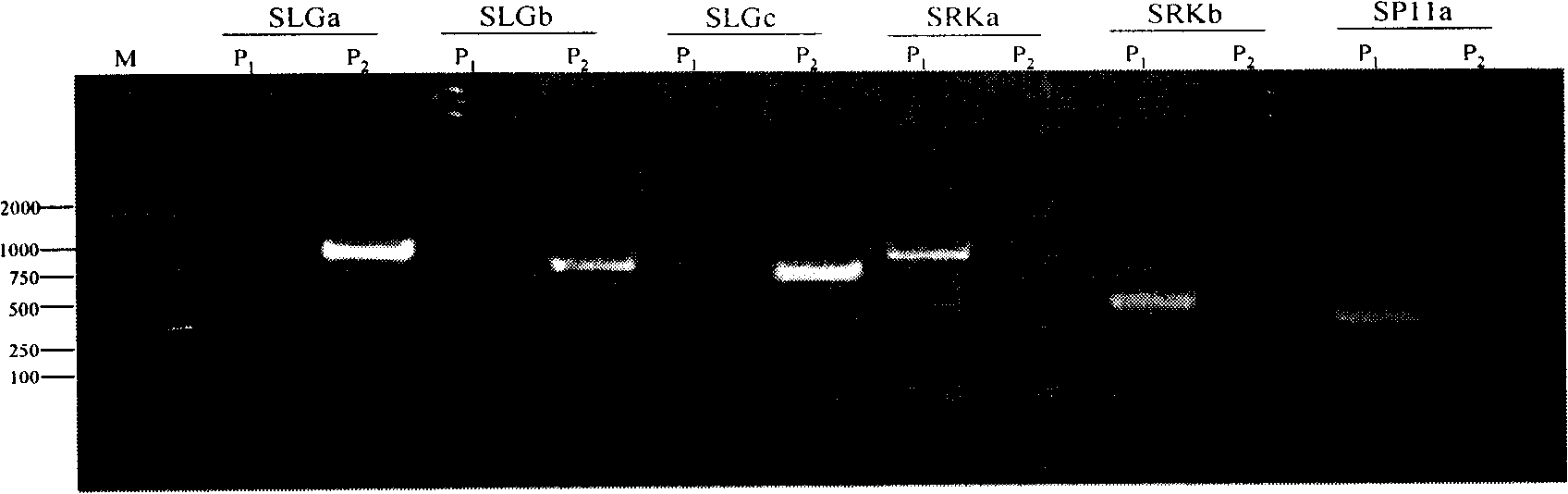
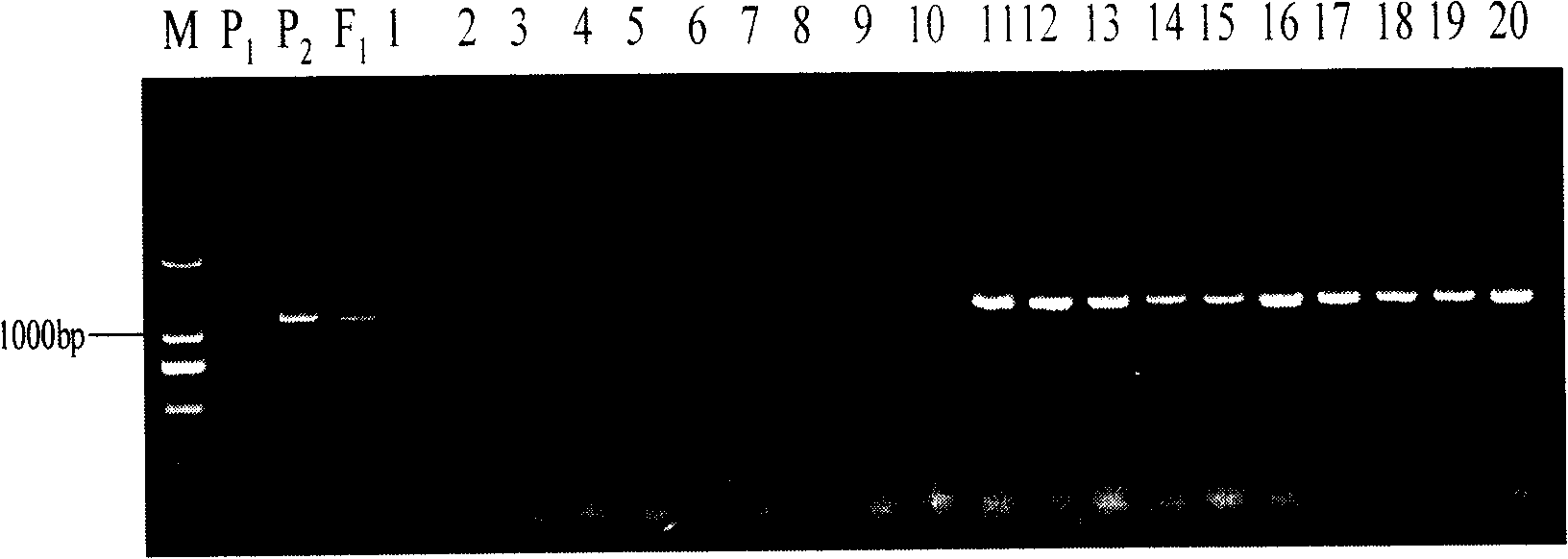
[0044] Through screening, the applicant obtained a batch of artificially created dominant SCAR molecular markers of self-incompatibility S sites in Brassica napus, including self-incompatibility line S-site dominant markers and self-incompatibility restorer lines S-site dominant markers, wherein the self-incompatible line S-site dominant markers are respectively named SRKa, SRKb and SP11a, and their nucleotide sequences are shown in the sequence table SEQ ID NO: 1, 2, 6 ; The dominant markers at the S site of the self-incompatibility restorer line are named SLGa, SLGb and SLGc respectively, and their nucleotide sequences are shown in SEQ ID NO: 3, 4, 5 in the sequence table.
[0045] A method for screening Brassica napus self-incompatibility S site dominant SCAR molecular markers, the steps are as follows:
[0046] 1) The self-incompatibility line S-1300 of Brassica napus was used as the female parent, and the self-incompatibility restorer line Defendor of Brassica napus from ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com