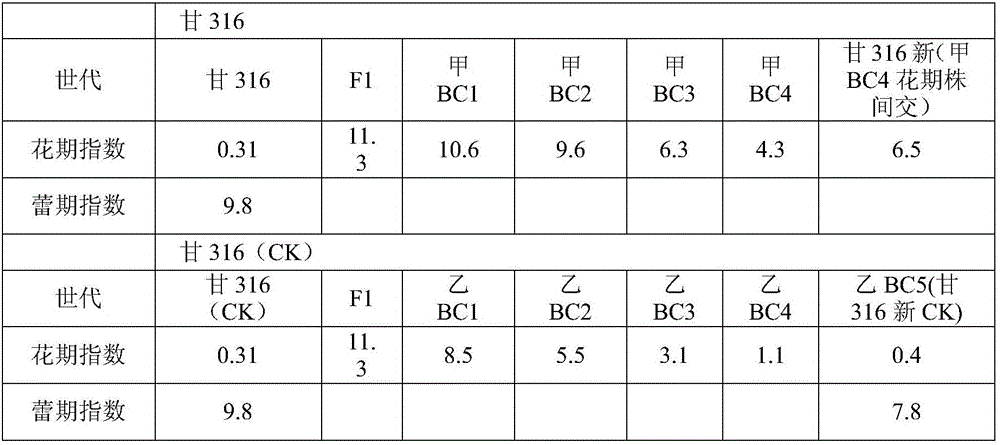
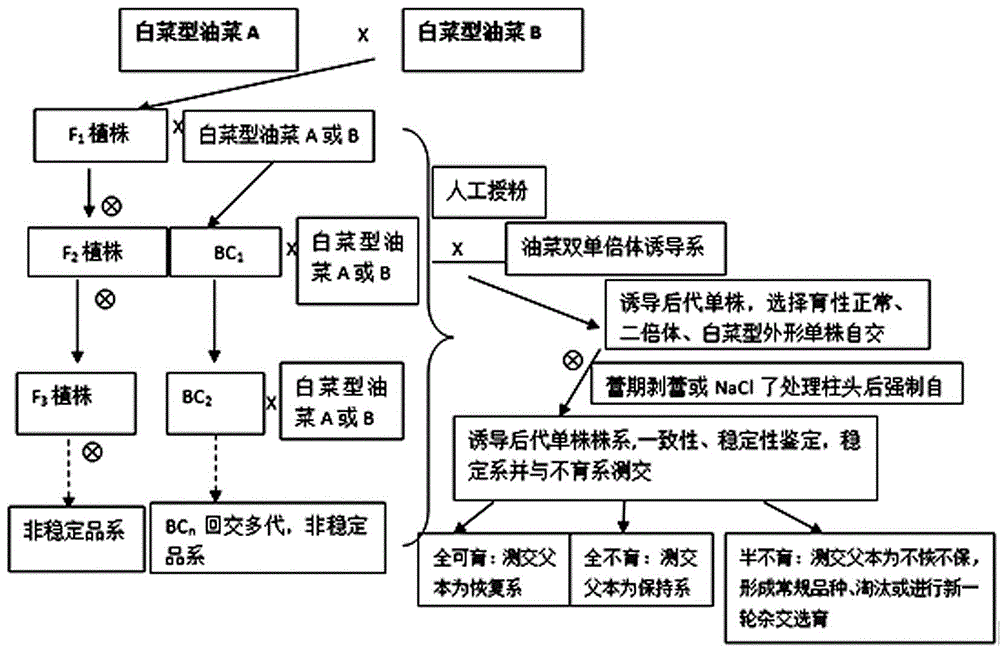
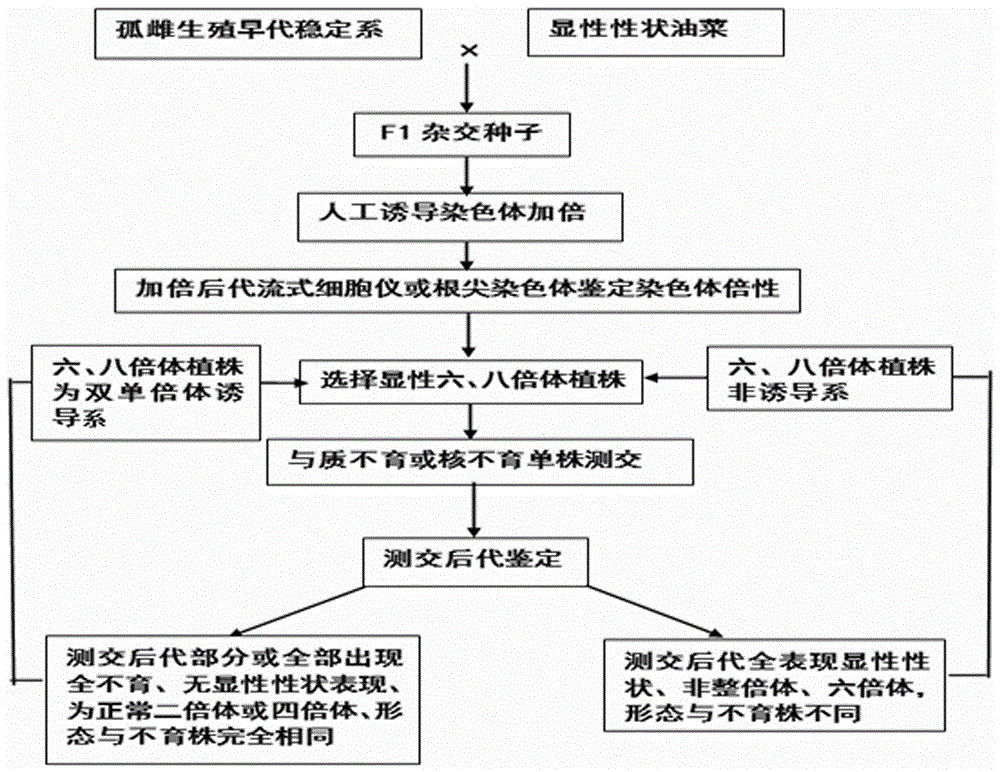
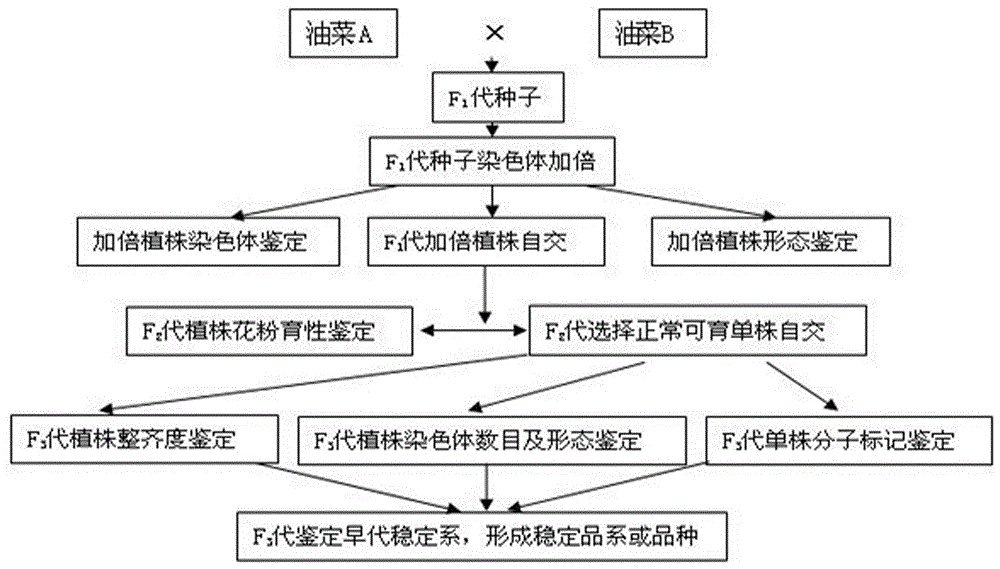
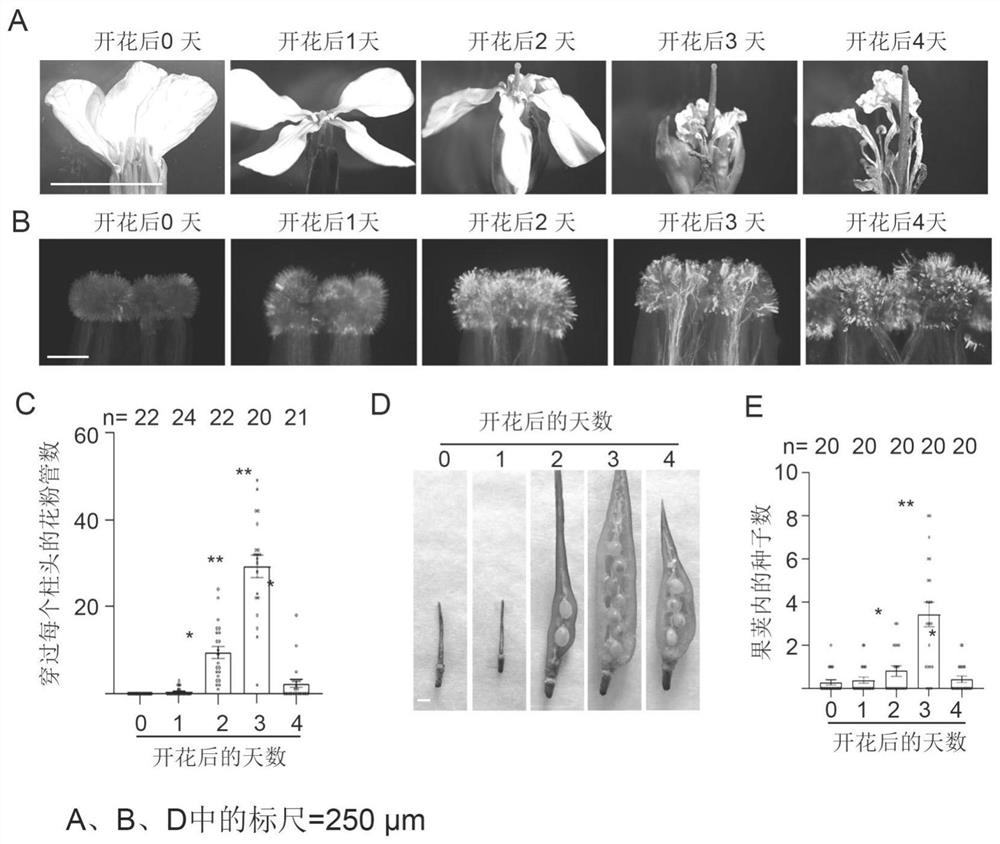
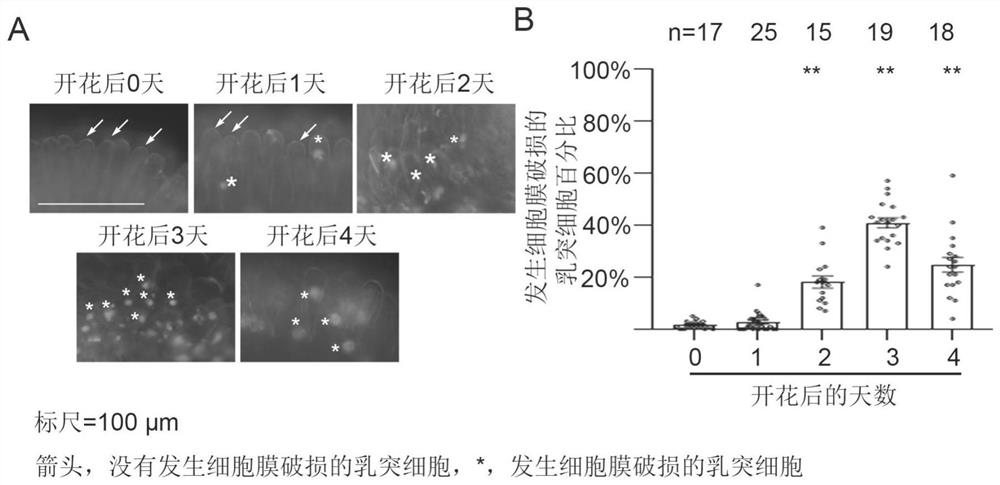
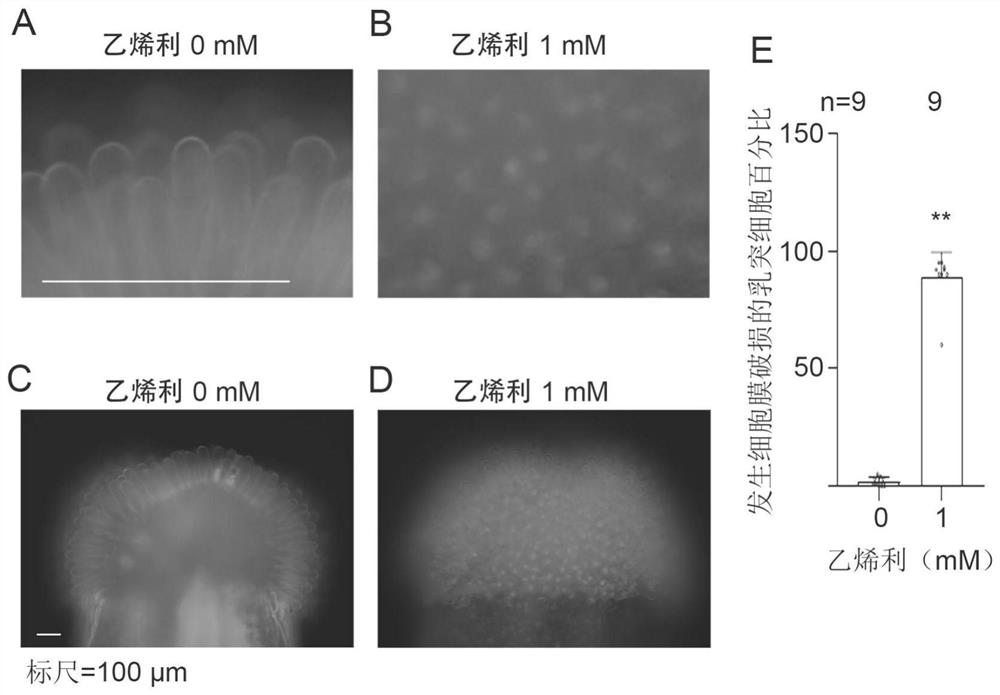
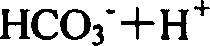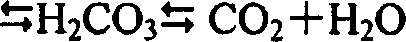Patents
Literature
78 results about "Self-incompatibility in plants" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Self-incompatibility (SI) is a general name for several genetic mechanisms in angiosperms, which prevent self-fertilization and thus encourage outcross and allogamy. It should not be confused with genetically controlled physical or temporal mechanisms that prevent self-pollination, such as heterostyly and sequential hermaphroditism (dichogamy).
In-vitro regeneration culture method for tea clones
InactiveCN102422810AReduce browning rateReduce browningPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsShootCamellia sinensis
Owner:ANHUI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
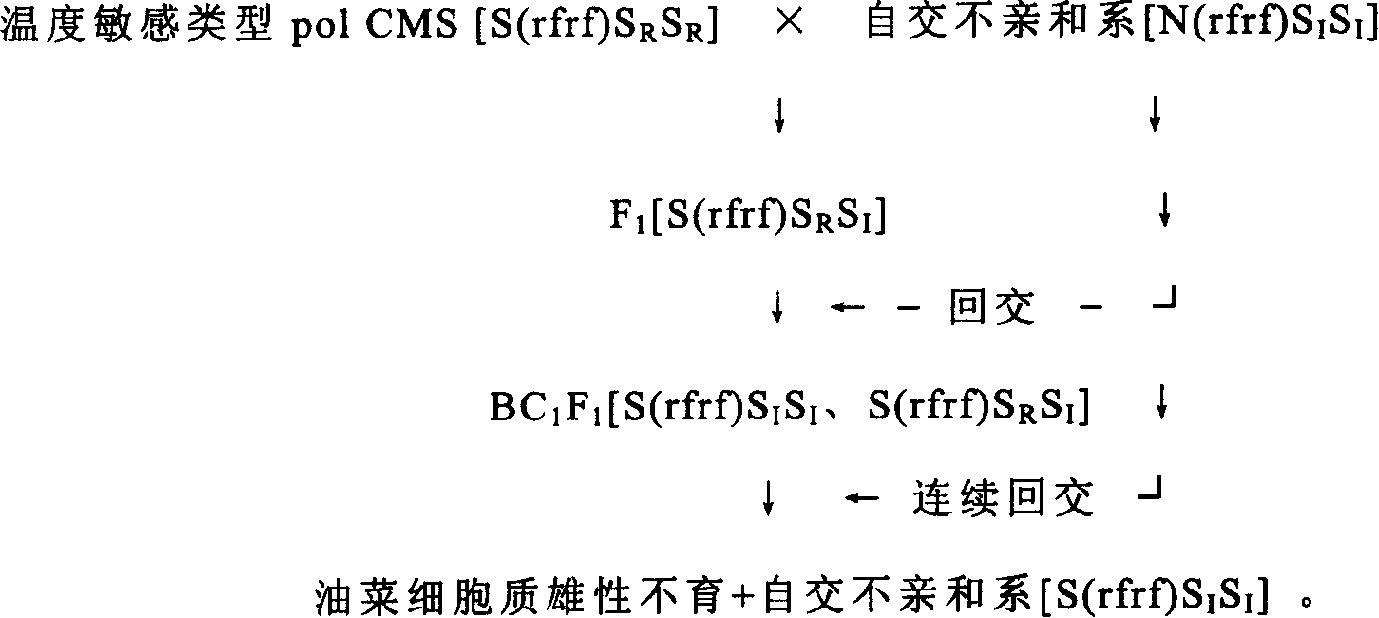
Rape cytoplasmic male sterility + self incompatibility hybrid superiority using method
InactiveCN1586160AImprove seed productionReduce the risk of seed productionPlant genotype modificationHeterosisZoology
The present invention relates to crossbreeding, back crossing, etc. with temperature sensitive polCMS as female parent and selfing incompatible line capable of maintaining its incompatibility as male parent to shift the selfing incompatibility gene into the temperature sensitive polCMS and breeding cytoplasmic male sterility+ selfing incompatible line selectively from the offspring with high temperature sterility and low temperature fine powder selfing incompatibility; top crossing and back crossing of the line with available rape variety and screening to breed maintainer line and restoring line; maintaining the sterile and selfing incompatibility of the cytoplasmic male sterility+ selfing incompatible line with the maintainer line and restoring the bearing capacity of the cytoplasmic male sterility+ selfing incompatible line with the restoring line to form the matched three lines. The present invention has low breeding cost and risk, high hybrid purity and high heterosis.
Owner:INST OF OIL CROPS RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
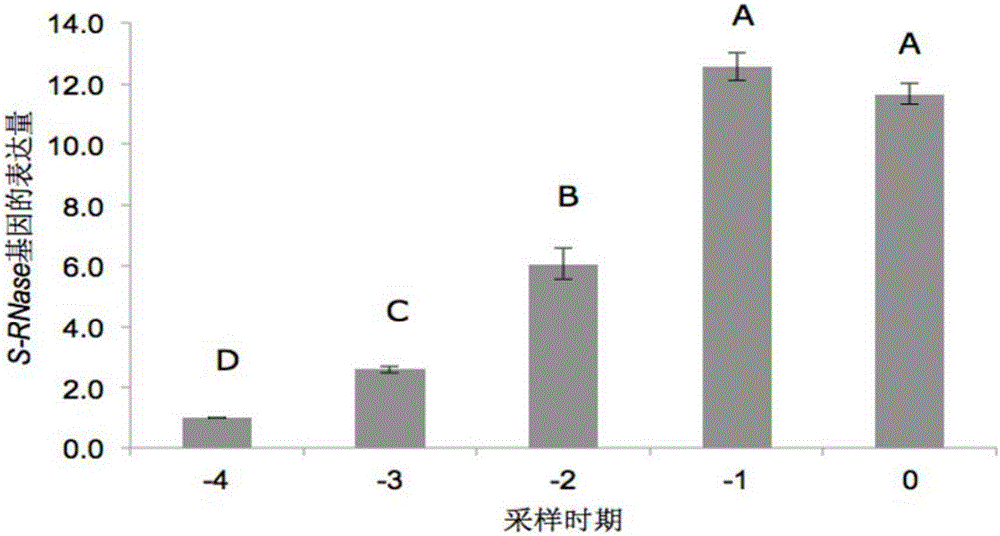
Method for improving self-pollination seed setting percentage of diploid potatoes and application of method
InactiveCN105052724AImprove self-fertilization rateOvercoming self incompatibilityPlant genotype modificationSelf-pollinationSolanum tuberosum
The invention relates to the field of plant breeding and specifically discloses a method for improving the self-pollination seed setting percentage of diploid potatoes. The method comprises: carrying out artificial self-pollination on diploid potato flower buds, preferably carrying out artificial self-pollination on the flower buds with a relatively low S-RNase gene expressive quantity. Self-incompatibility of the diploid potatoes is overcome by selecting a proper pollination time for self-pollination. The method is simple and feasible. No exogenous wild genomes are needed to be transferred while self-incompatibility is overcome, so that the obtained self-pollinated seeds can be directly applied to a process of genetic research and breeding.
Owner:INST OF VEGETABLE & FLOWERS CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Dominant SCAR molecule mark for wild cabbage type cole self-incompatibility and uses thereof
InactiveCN101255461AReduce breeding workloadShorten the breeding periodMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationNucleotideMolecular breeding
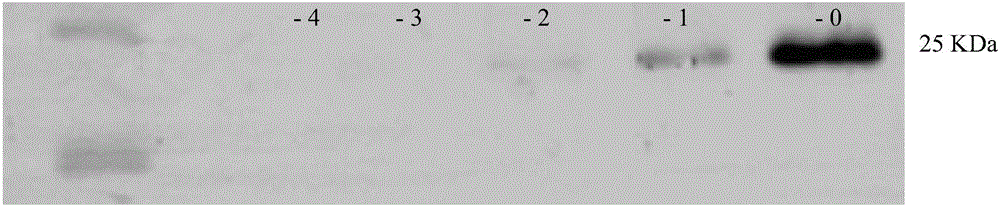
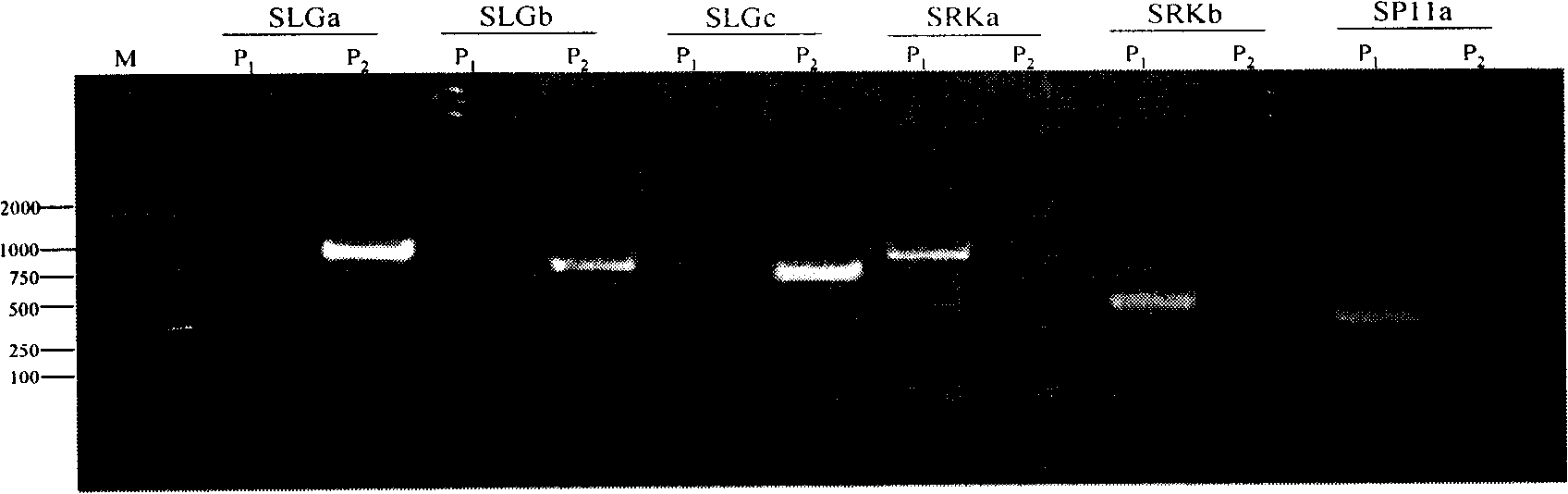
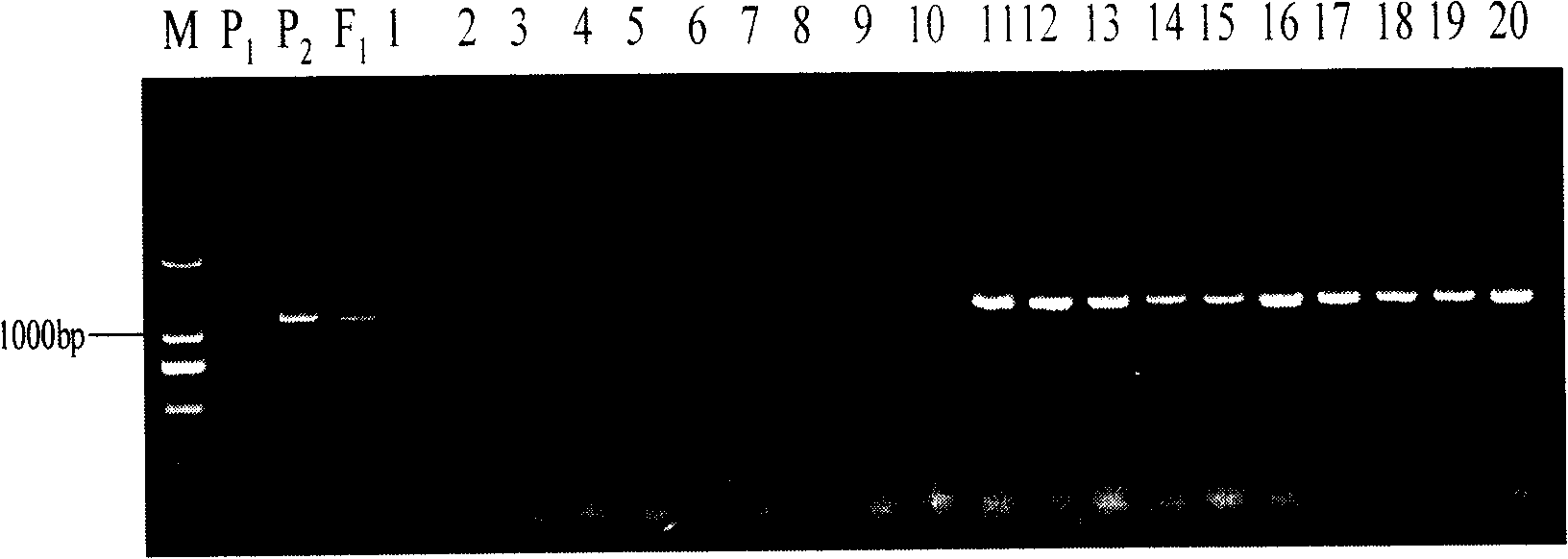
The invention belongs to the field of rape breeding, particularly relates to rape self-incompatibility complete linkage dominant SCAR labels and the application thereof. Cabbage type rape self-incompatibility S locus dominant SCAR molecular labels are produced artificially, which includes self-incompatibility S locus dominant labels and self-incompatible restorer line S locus dominant labels, wherein the self-incompatibility S locus dominant SCAR labels are named as SRKa, SEKb and SP11a, whose nucleotide sequences are displayed in sequence tables with SEQ ID NO: 1, 2, 6; the self-incompatible restorer line S locus dominant SCAR labels are named as SLGa, SLGb and SLGc, whose nucleotide sequences are displayed in sequence tables with SEQ ID NO: 3, 4, 5. The molecular labels can differentiate homozygous-compatible, hybrid-compatible and homozygous-incompatible genes. The molecular labels are used to verify the cabbage type rape self-incompatibility phenotype. The invention provides practical labels and a usage method for rape molecular breeding.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Seedling growing method for overcoming self-incompatibility of pears
InactiveCN103250573AAvoid major economic lossesCultivating equipmentsHorticultureRootstockPollination
Provided is a seedling growing method for overcoming self-incompatibility of pears. The method includes the steps of stock seedling breeding and grafting. According to the step of grafting, two varieties are selected and combined as cions, and the two varieties are different in S gene classification, synchronous in flowering phase, large in pollen quantity and strong in pollen viability; in breeding of pear variety seedlings without pollen, the pear variety seedlings need to be combined with other two varieties or three varieties as cions, and the two varieties or three varieties are different in S gene classification, synchronous in flowering phase, large in pollen quantity and strong in pollen viability; the grafting method is bud grafting, the combinations of the two varieties are Yuan Huang (S3S4)+Cui Guan (S2S5), and the like, and the combinations of the three varieties is Xin Gao (S3S9)+Yuan Huang (S3S4)+Cui Guan (S2S5), and the like. According to the seedling growing method for overcoming the self-incompatibility of the pears, problems existing in pollination variety selective breeding of the pears are fundamental solved in the seedling breeding stage, and therefore great economic losses brought to orchard workers in production and caused by the self-incompatibility of the pears can be avoided.
Owner:INST OF FRUIT & TEA HUBEI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Breeding method of primula forbesii variety
ActiveCN101790958AEffectively fixedSolving Breeding DifficultiesCultivating equipmentsPlant genotype modificationHybrid seedLoment
The invention relates to a breeding method of a primula forbesii variety, which comprises the following steps: selecting two plants as parent from primula forbesii cultivation groups with the same flower color and flow model, wherein one plant is a long stigma flower and the other plant is a short stigma flower; then carrying out emasculation, bagging, pollen acquisition, artificial pollination, bag removal and harvesting and breeding of double-cross seeds; and finally repeatedly hybridizing and breeding for 3-4 years to obtain the primula forbesii variety which has consistent phenotypic expression, stable heredity and no segregation character phenomenon. The breeding method can effectively fix the character, enable various single plants in the breed to tend to be homozygous and solve the breeding difficult problem caused by self-incompatibility; and besides main target characters (flower colors and flower models) are obtained, other fancypoints such as flower diameter and the like can be greatly improved, the progeniture flow diameter is gradually increased and the ornamental value can be further improved.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Method for overcoming self-incompatibility of brassica plant
InactiveCN1748473AIncrease humidityReduce formationPlant phenotype modificationHigh absorptionMicrogram
The present invention relates to the breeding technology for brassica plant, and especially carbonic anhydrase treatment method of overcoming self-incompatibility of brassica plant. Specifically, carbonic anhydrase solution of 2-10 microgram / ml concentration is sprayed to the blooms with just emerged stigmata in 8:30-10:30 AM every other day in the initial blooming period until blooming in 90%. The sprayed carbonic anhydrase solution is preferably in atomized form for high absorption. The said method may be used in Brassica campestris, Brassica oleracea, Brassica napus and Brassica pekenensis to raise the self-compatibility index in different degree.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Breeding method of easy-dry type self-incompatible line of Chinese cabbage anther
InactiveCN102172208AOvercoming self-incompatibilityLoose powder time is shortPlant genotype modificationRelease timePollen
The invention discloses a breeding method of an easy-dry type self-incompatible line of Chinese cabbage anther. The method comprises the following steps: (1) selecting the easy-dry type self-incompatible line of anther as breeding protospecies to plant; (2) collecting the anther of the self-incompatible line blossoming in the day and not releasing pollen at 8-10 a.m.; (3) processing the anther so that the anther is loosened and releases pollen until the pollen can be dipped; (4); manually opening the bud to blossom in 3-5 days on the self-incompatible line, and exposing the stigma; (5) manually dipping the pollen obtained in the step (3) with a finger or a rubber, and smearing the pollen on the stigma obtained in the step (4); and (6) collecting the self-pollinated seeds after hulling. As easy-dry type self-incompatible line of Chinese cabbage anther has short pollen releasing time and small pollen quantity, the method disclosed by the invention adopts a mode of in vitro pollen collection and artificial pollination, improves the pollen quantity, overcomes the self-incompatibility of Chinese cabbage, can increase the seed collection quantity by 100-200 times, and realizes high breeding efficiency and yield.
Owner:山东春秋大白菜育种研究中心
Seed selection method for cold resistant and bolting resistant brassica oleracea var
ActiveCN107432243ASelf-incompatibility weakenedEnhanced self-incompatibilityPlant genotype modificationSodium bicarbonateWarm water
The invention discloses a seed selection method for cold resistant and bolting resistant brassica oleracea var. According to the invention, original cabbage excellent self-incompatible line and (male parent) and other cabbages (fertile, female parent) are subjected to hybridization through a castration florescence, progeny is subjected to backcrossing fourth generation through the emasculation florescence, fine spraying is carried out on stigma by warm water with sodium bicarbonate having concentration being 1% at the temperature of 28-32 DEG C at florescence, the substances of the stigma such as callose is broken up, so that self-incompatibility is changed to self-compatibility, and the free pollination by honeybees among the plants at the florescence finally. On one hand, the original parent enables purification and renovation, on the other hand, through multi-generation florescence pollination, the self-incompatibility is reduced, the self-compatibility is enhanced, self-incompatibility is gradually changed to self-compatibility, for the utilization of breeding of a cytoplasmic male sterile line, the breeding efficiency is increased, the disadvantages of self incompatibility and artificial bud pollination required by line breeding can be overcome, at the same time, for the phenomena of multi-year inbred parent property degeneration, such as strong plant growth vigor, less bud abortion rate, large pollen amount, and high setting rate, the method finds a novel method for purification and renovation.
Owner:南京利华农业科技有限公司
Seed selection and application of rape environmental sensitivity nuclear sterile line with self-incompatibility characteristic
InactiveCN101595839AReduce the chance of self-fertilizationHigh purityPlant genotype modificationBiotechnologyHybrid seed
The invention discloses a seed selection method of rape environmental sensitivity nuclear sterile line with self-incompatibility characteristic. In the method, nuclear sterile rape sensitive to photoperiod, temperature and the like is selected to hybridize with self-incompatibility line, environmental sensitivity nuclear sterile line with self-incompatibility characteristic is selected from the progeny as a female parent of two-line hybrid cultivar. The rape environmental sensitivity nuclear sterile line with self-incompatibility characteristic selected by the invention is applied to production of hybrid seeds, selfing fructification probability of the environmental sensitivity sterile line in the production link can be reduced and purity of the hybrid seeds can be improved.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Simplified production method for rape male sterile hybrid F1 seeds
ActiveCN109006464AReduced risk of mixing into F1 seedsSimplify the breeding processPlant genotype modificationBiotechnologyBreeding program
The invention provides a simplified production method for rape male sterile hybrid F1 seeds. The method is a hybridization seed production method for producing the hybrid F1 seeds by selecting a cytoplasmic male sterile line (or a nuclear male sterile line) and a restorer line having a self-incompatibility characteristic. The method concretely comprises the following steps: mixing the cytoplasmicmale sterile line (or the nuclear male sterile line) and restorer line seeds having the self-incompatibility characteristic according to a specific ratio under an isolation condition, sowing the obtained uniformly-mixed seeds in the field of a rape seed production area, and harvesting the sterile line and the restorer line in a mixed manner at the time of ripening to obtain the hybrid F1 seeds. The method has the advantages of simple breeding program, saving of the labor cost, and saving of money and labor.
Owner:武汉联农种业科技有限责任公司
Method for selecting cabbage-type rape varieties and materials by rape double haploid inducing line
ActiveCN106069721AEasy accessEfficiently obtainedPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsMaterial resourcesCrossover test
A method for selecting cabbage-type rape varieties and materials by a rape double haploid inducing line includes 1), determining target traits of breeding of cabbage-type rape varieties and materials; 2), performing crossing, convergent crossing or backcrossing on at least two cabbage-type rapes with the target traits; 3), pollinating cross, convergent cross or backcross descendants by the rape double haploid inducing line; 4), inducing the descendants to overcome self-incompatibility, and verifying genetic stability of the induced descendants; 5), verifying yield, resistance and quality characters of the induced stable descendants; 6), according to the yield, the quality characters and the resistance, determining stable strains to form conventional varieties of the cabbage-type rapes; 7), inducing the genetic stable strains of the descendants to form a new variety line of the cabbage-type rapes, and test-crossing the new variety line with a sterile line to form a maintainer line or restorer line, or entering a next circle of variety and material breeding process. By the method, breeding speed and efficiency of hybrid or conventional varieties of the cabbage-type rapes can be increased greatly, and manpower and material resources can be reduced.
Owner:CHENGDU ACAD OF AGRI & FORESTRY SCI
Method for overcoming diploid potato self-incompatibility
ActiveCN109750061AShort breeding cycleEasy to operateHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementGene targetsA-DNA
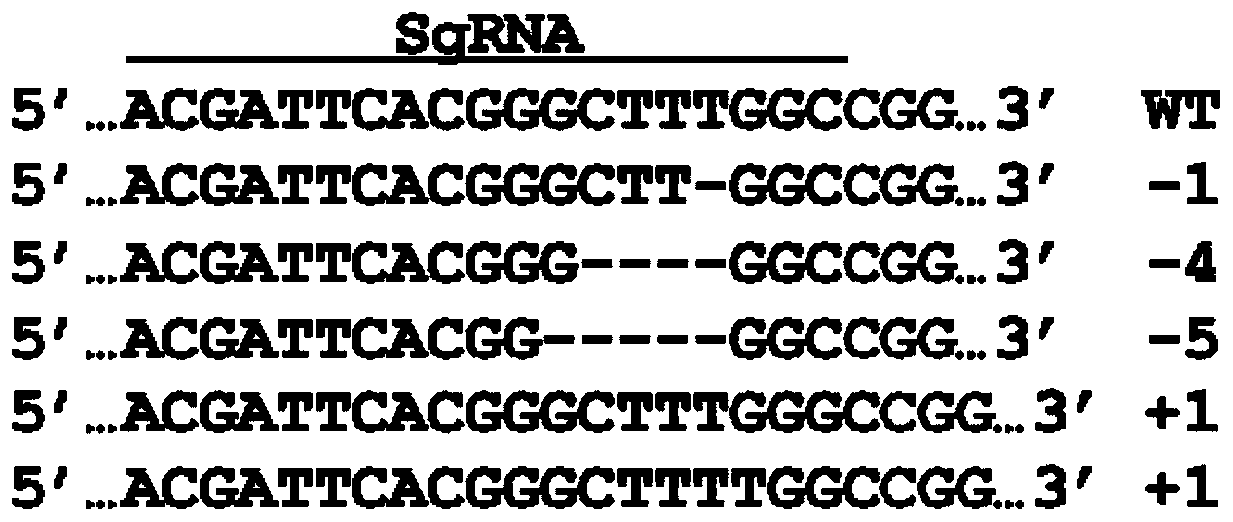
The invention discloses a method for overcoming diploid potato self-incompatibility. The method comprises the steps of 1, selecting a target fragment; 2, constructing a gene target shooting recombinant vector; 3, achieving function deletion mutation of a S-RNase gene inside a cell; 4, regenerating a plurality of potato plants; 5, specifically amplifying a DNA block containing the target fragment of the S-RNase gene in the regeneration plant; 6, selecting the regeneration plant edited by the S-RNase gene; 7, further screening out a diploid gene editing strain from the gene edited plant; 8, performing expanding propagation and planting on the gene edited strain, and performing self-incompatibility phenotype identification on the blooming stage; 9, amplifying product sequencing on the harvested self-compatible plant later generations, and detecting heredity and separation of the edited target gene for later generations. The method has the advantages that the simple, accurate and efficiency method is found for overcoming diploid potato self-incompatibility.
Owner:AGRI GENOMICS INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI +1
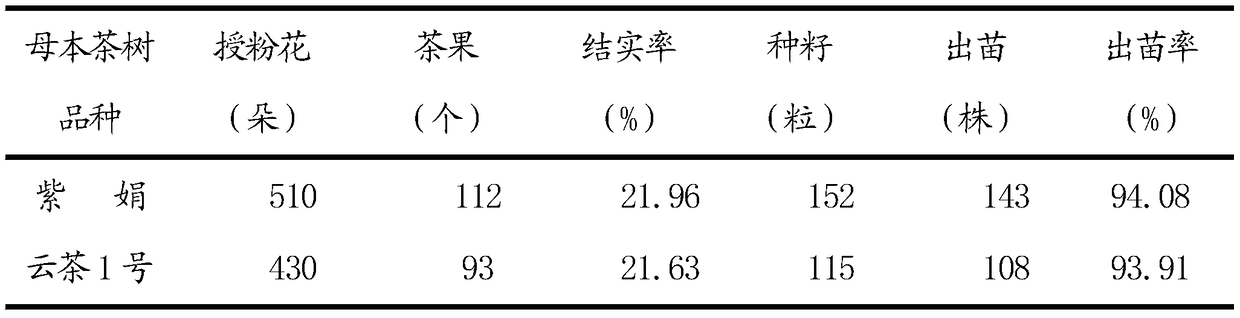
Tea tree cross-breeding method
PendingCN109122300AImproves the number of bloomsImprove seed setting ratePlant genotype modificationDiseaseThinning
The invention discloses a tea tree cross-breeding method. The tea tree cross-breeding method comprises a growth age and a bearing age and comprises the following steps of 1, parent selection, 2, planting, 3, pruning, 4, fertilizer applying, 5, greenhouse building, 6, pollination, 7, branch and leaf thinning, 8, seed harvesting, and 9, seeding. The tea tree cross-breeding method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that clear parental origins of hybrid seeds of offspring is guaranteed by using self-incompatibility of a parent, and the parental origins of the hybrid seeds of the offspring are also easy to distinguish. The tea tree cross-breeding method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that distances between plants is large; and problems such as close growing, crossing and overlapping of tree crown branches, poor ventilation and light transmission, breeding of pests and diseases, easily aged branches and less fruits can be effectively solved. The tea tree cross-breeding method disclosed by the invention can persistently obtain hybrid offspring with consistent properties, can provide a stable cultivation method for cultivation and screening works of tea tree plants and is very suitable for scientific researches and large-scale tea tree plant seedling breeding.
Owner:TEA INST YUNNAN ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Method for obtaining selfing progeny of stevia rebaudianum through embryo rescue
The invention belongs to the field of biotechnology breeding and in particular relates to a method for obtaining selfing progeny of stevia rebaudianum through embryo rescue. The method specially comprises the following steps: selecting a stevia rebaudianum variety that selfing seeds cannot be obtained because of young embryo abortion, as a parent; carrying out artificial supplementary pollinationand selfing; peeling off young embryos 5-7 days after pollination; and carrying out in-vitro culture on the young embryos so as to obtain seedlings S1; transplanting the seedlings S1, thereby obtaining complete plants. By adopting an embryo rescue technique, the self-incompatibility obstacle of stevia rebaudianum is overcome, selfing progeny of the stevia rebaudianum is obtained, a part of properties are homozygoted, homozygote and a selfing line can be obtained through multiple generations of selfing, the breeding efficiency of the stevia rebaudianum can be effectively improved, and the stevia rebaudianum variety breeding progress can be accelerated.
Owner:INST OF BOTANY JIANGSU PROVINCE & CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
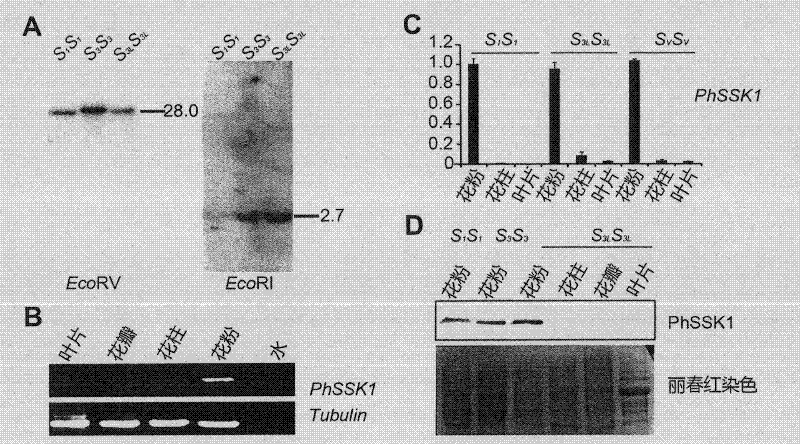
Protein involving self-incompatibility and cross-compatibility control of phanerogam pollen, coding gene thereof and application
The invention discloses protein involving self-incompatibility and cross-compatibility control of phanerogam such as Solanaceae plant pollen, coding gene thereof and an application of reducing the gene expression through transgene on aspects of preventing transgene flow and establishing a gene bank of a variety. The invention provides PhSSK1-RNAi carrier and a host cell containing the carrier. The gene of the present invention has an important theoretical significance in revealing molecule mechanism of self-incompatibility of the phanerogam such as Solanaceae plant. Through transgene RNAi, reducing the gene expression can cause pollen to loose compatibility in cross-pollination, having an important effect and meaning on preventing transgene flow of Solanaceae transgene plant and establishing a good trait control gene bank of Solanaceae economic crop such as potato, tomato and the like.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Process for overcoming self-incompatibility of plant by electrical field
InactiveCN1456045AHigh affinityImprove seed setting ratePlant genotype modificationPollenElectric field
A technology for overcoming the mating incompatibility of plant by electric field includes such steps as picking up mature anthers, drying for 1-3 hr until pollen is released, treating the pollen in electric field, and pollinating within 1-5 hr. It can increase the setting percentage by 10-40%.
Owner:NORTHEAST FORESTRY UNIVERSITY +1
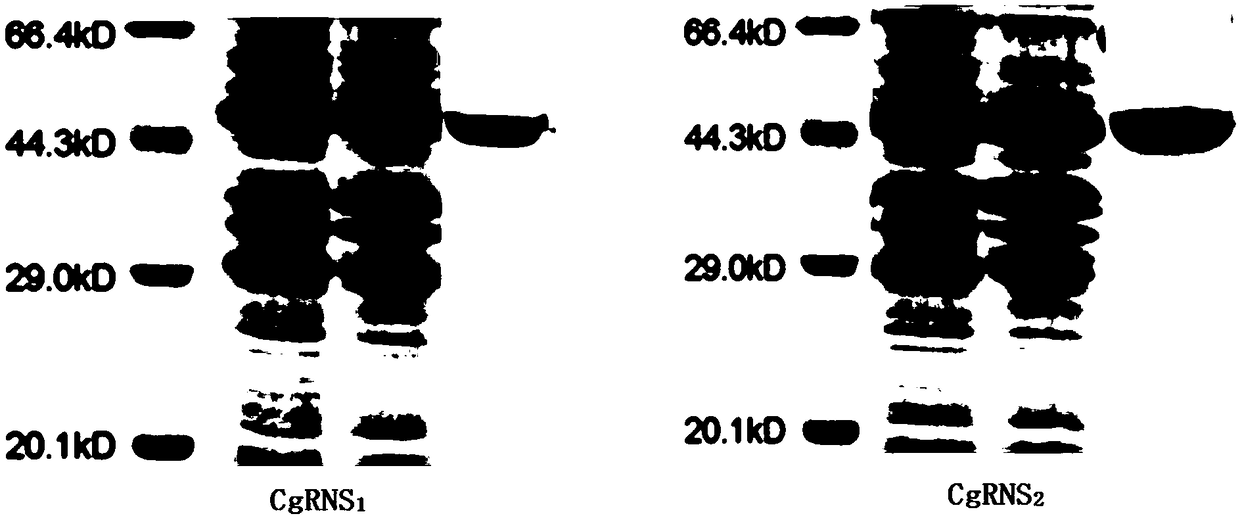
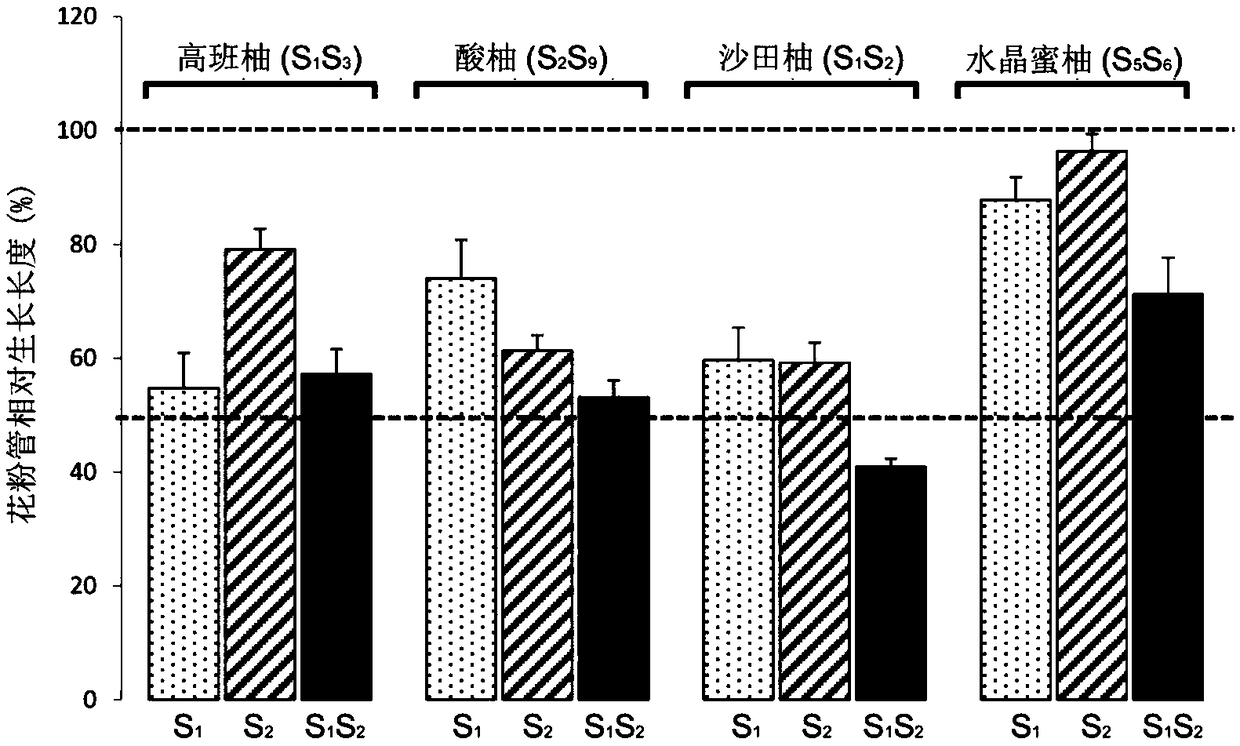
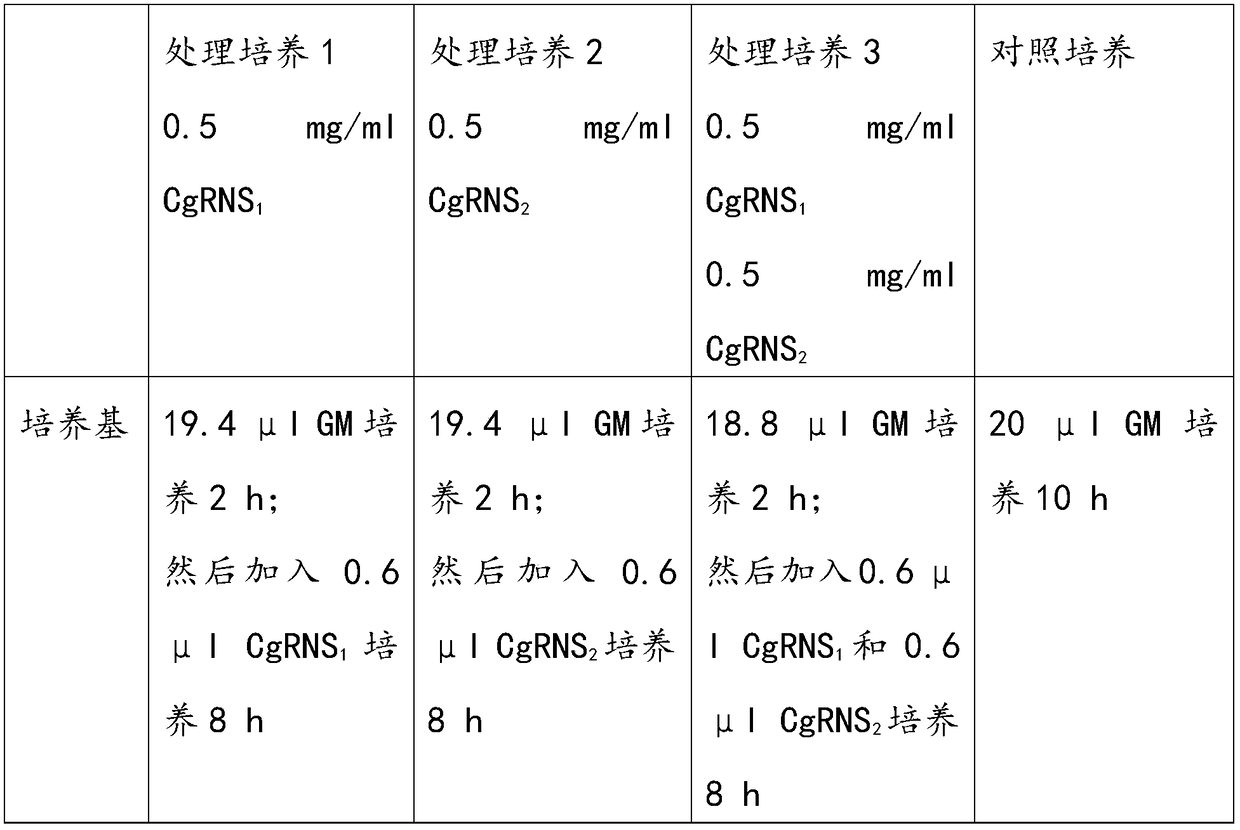
Method for in-vitro verification of self-incompatibility function of S-RNase in citrus and pomelo
The invention relates to a method for in-vitro verification of self-incompatibility function of S-RNase in citrus and pomelo. The method comprises that follow steps: step 1, obtaining an S-RNase protein; 2, collecting pollen from that donor plant; step 3: treating pollen obtained in the step 2 with S-RNase protein obtained in the step 1, and measuring the effect of the treatment of S-RNase proteinon the pollen germination pollen tube. By adopting the method of the invention, the self-incompatibility style gene of citrus can be rapidly verified in an in vitro culture mode, and the proper pollen can be treated with a recombinant protein with an appropriate concentration, which can cause a self-compatibility or incompatibility reaction, thereby avoiding the problem of transgenic verificationof the citrus S gene.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Process for overcoming self-incompatibility of plant by laser
InactiveCN1456044AImprove biological activityEarly germinationPlant genotype modificationPollenAgronomy
Owner:NORTHEAST FORESTRY UNIVERSITY +1
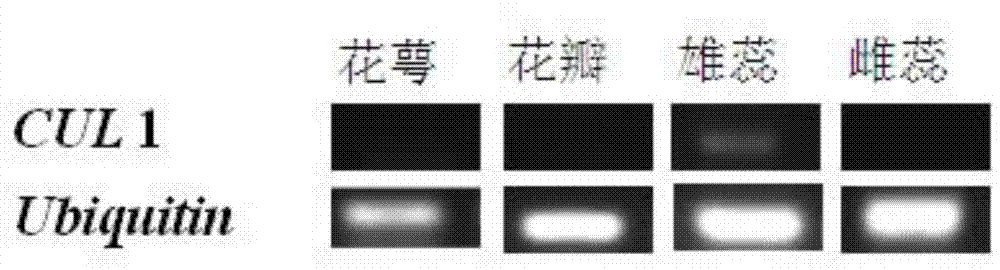
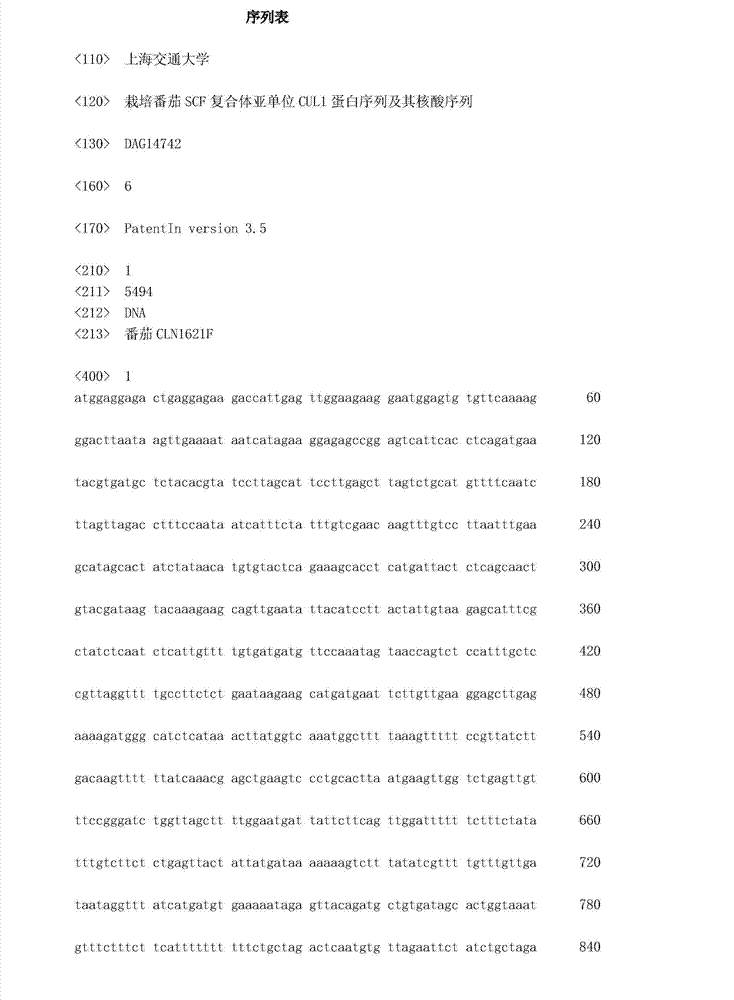
Cultivated tomato SCF complex subunit CUL1 protein sequence and nucleotide sequence thereof
The invention relates to a cultivated tomato SCF complex subunit CUL1 protein sequence and a nucleotide sequence thereof and belongs to the technical field of molecular biology. Concretely, the invention relates to a cultivated tomato SCF complex subunit CUL1 protein sequence shown as SEQ ID NO.3 and the nucleotide sequence which codes the CUL1 protein sequence. The CUL1 protein gene is utilized to screen out correlated or interactive substances, receptors, inhibitors, and antagonists. The CUL1 protein gene can be over-expressed or low-expressed through genetic engineering means, and furthermore the self-incompatibility mechanism mediated by S-nuclease is researched, so as to provide important theoretical foundation for obtaining wild tomato varieties which can overcome the incompatibility of distant hybridization and improving the tomato varieties.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Cotton breeding method utilizing exogenous self-incompatibility
ActiveCN111808860ASelf-incompatibility realizationHigh purityPlant peptidesFermentationBiotechnologyGenotype
The invention belongs to the technical field of cotton breeding, and particularly relates to a patent application of a cotton breeding method utilizing exogenous self-incompatibility. According to theinvention, an exogenous corn poppy self-incompatibility gene pair PrsS / PrpS is utilized and is introduced into cotton in combination with a genetic engineering technology. The invention proves that:a corn poppy self-incompatible system is introduced into cotton, the cotton self-incompatibility phenotype can be realized, which indicates that the self-incompatibility can be successfully realized in the cotton (the self-incompatibility of the cotton can be realized by taking a transgenic strain Gh-PrsS as a male parent and Gh-PrpS as a female parent, cotton bolls cannot be normally generated, namely, the conversion of the cotton from self-incompatibility to self-incompatibility can be realized). By utilizing the method, different cotton self-incompatible new materials can be successfully created, so that the labor cost is greatly saved, the purity and the efficiency of seed production are improved, the genotype limitation of the materials can be broken through, and the strong-advantagehybrid cotton cultivation of efficient seed production is realized.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY
Method for propagating self-incompatible line of non-heading Chinese cabbage
ActiveCN107743837AReduce constraintsLabor savingLeaf crop cultivationHorticulture methodsHigh concentrationPollination
The invention discloses a method for propagating a self-incompatible line of non-heading Chinese cabbage. According to the method, in the flowering period of the self-incompatible line, high-concentration CO2 is used for treatment for a long time for breaking the self-incompatibility and overcoming the self-propagating difficulty of the self-incompatible line, and the propagating of the self-incompatible line of the non-heading Chinese cabbage is efficiently carried out through combination of CO2 automatic application, entomophilous pollination, later-stage screening and the like, rapid utilization of a self-incompatible hybrid of the non-heading Chinese cabbage is promoted, and large-scale propagating difficulty of the self-incompatible line of the non-heading Chinese cabbage in the priorart is overcome, thereby limiting the problem of rapid application of the self-incompatible hybrid.
Owner:NANJING INST OF VEGETABLE SCI
In-vitro identification method for gramineal self-incompatibility phenotype
InactiveCN108901824ASimple methodEasy to masterPlant genotype modificationAniline blue stainMicroscopic observation
The invention belongs to the technical field of plant biology, and discloses an in-vitro identification method for gramineal self-incompatibility phenotype, which comprises the following steps: (1) inflorescence arrangement: the inflorescences of a paternal plant are pruned at the full-bloom stage, removing bloomed spikelets; (2) artificial flower forcing: the inflorescences are inserted into Hoagland nutrient solution, and flower forcing treatment is carried out under a completely dark condition for 8 to 12 hours; (3) in-vitro pistil culture: mature spikelets are chosen from the maternal inflorescences, and the pistils are intactly cut off under a stereoscopic microscope and inserted into 0.5 to 1 percent of agarose solid medium for in-vitro culture; (4) indoor pollination: in the morningof the next day, paternal pollen is used for pollinating the pistils; (5) pistil softening: the pollinated pistils are softened with 8 to 10mol / L of NaOH for 3 to 4 hours; (6) pistil dyeing: the softened pistils are dyed with 0.1 to 0.5 percent of aniline blue; (7) microscopic observation: the growth of the pollen tubes on the pistil stigmas are observed in an inverted fluorescence microscope. The method is simple and easy to master, the accuracy is high, and the method is suitable for being applied in the genetic analysis and crossbreeding research of miscanthus.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
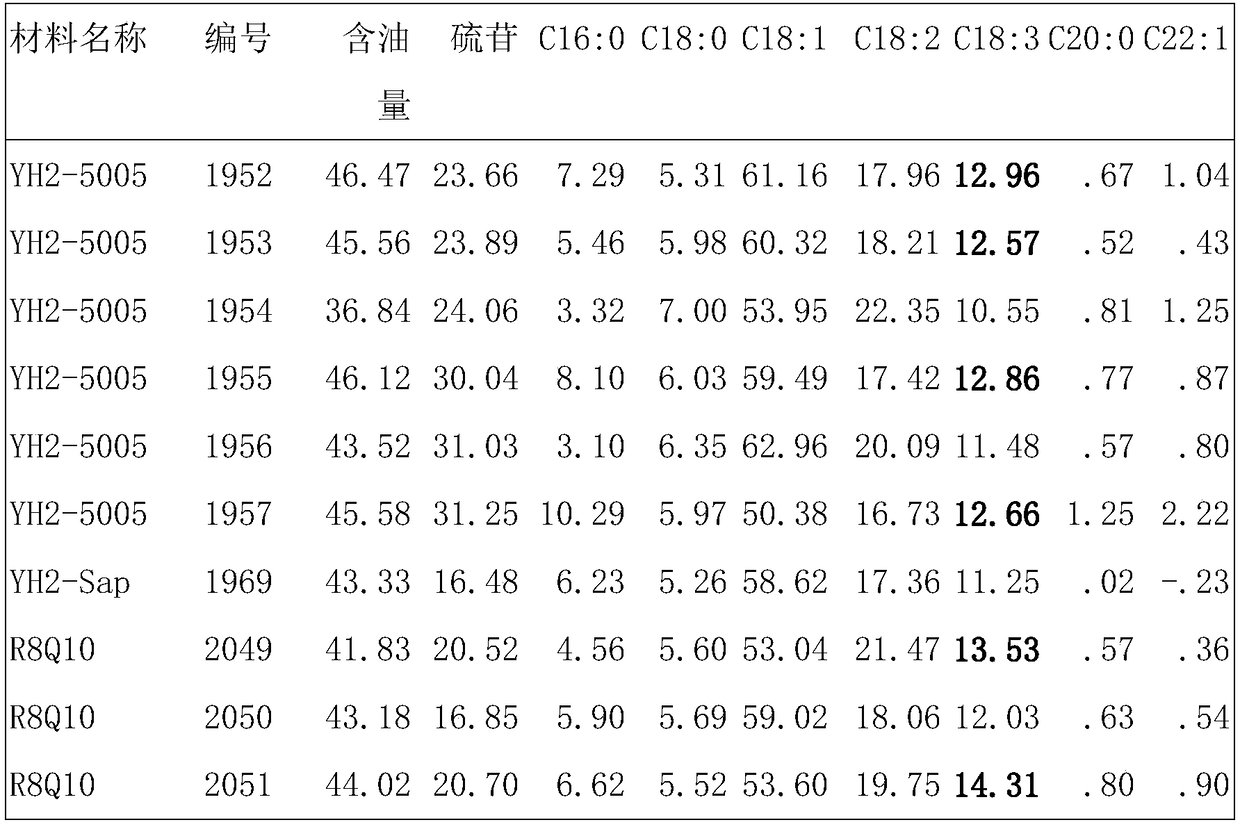
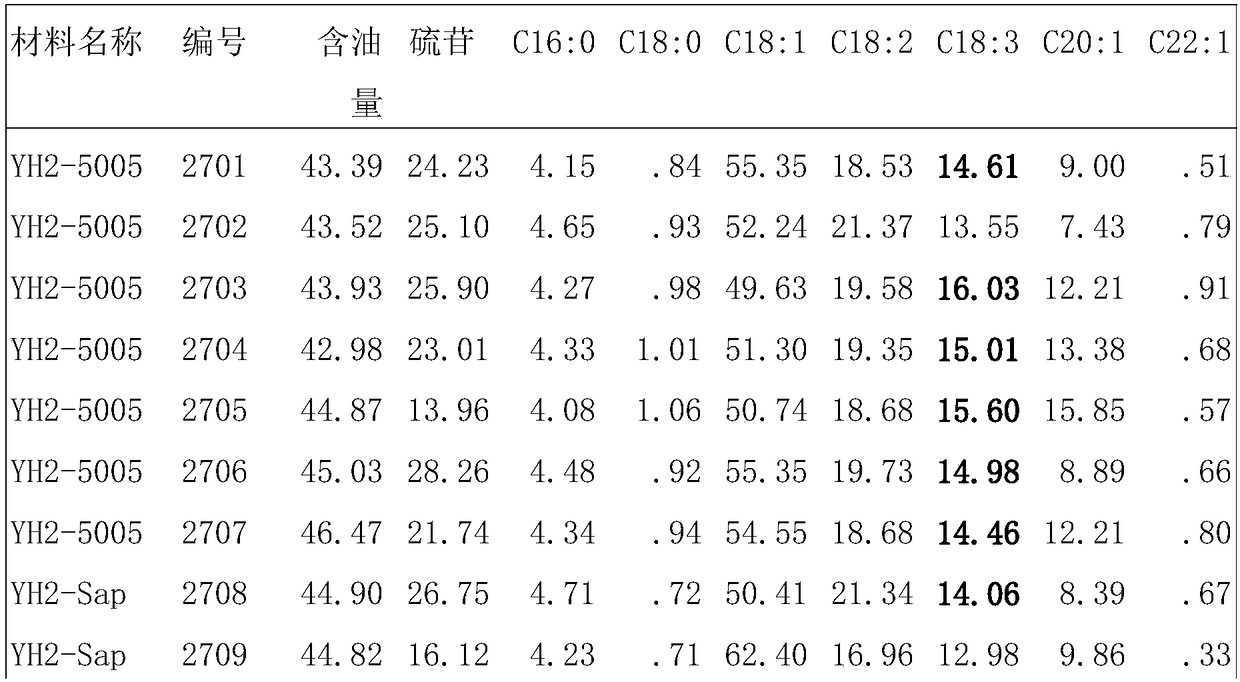
High-linolenic acid rape gene donor and application thereof
ActiveCN109496829AImprove food qualityComply with management policyPlant genotype modificationAngiosperms/flowering plantsBrassicaControl system
The invention discloses a high-linolenic acid rape gene donor. The high-linolenic acid rapeseed gene donor is named cabbage type rape Brassica napus high-linolenic acid rape R8Q10 in China center fortype culture collection, and a preservation number is CCTCC NO:P201820. The high-linolenic acid rape gene donor is used for breeding novel rape varieties, from pedigrees obtained through selfing, hybridization, backcross and the like, a novel high-linolenic acid strain is separated out, and is used for a conventional variety, or pollination control systems of self-incompatibility, male sterility and the like are used for breeding a hybrid so that the high-linolenic acid rape gene varieties with the linolenic acid content in fatty acid reaching 15%-17% or above can be obtained.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Alleles related to self-cross-compatibility characters of non-heading Chinese cabbages and obtained through gene editing and application of alleles
ActiveCN112575004AImprove breeding efficiencyReduce the cost of seed productionMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant peptidesNucleotideNucleotide sequencing
The invention relates to the technical field of gene engineering, in particular to alleles related to self-cross-compatibility characters of non-heading Chinese cabbages and obtained through gene editing and application of alleles. The nucleotide sequence of the allele provided by the invention is as shown in SEQ ID No. 1, SEQ ID No. 2, SEQ ID No. 3 or SEQ ID No. 4. The invention further providesa molecular marker of the allele, and applications of the allele and the molecular marker. The self-compatible non-heading Chinese cabbage material is successfully obtained through the technical meansof gene editing, distant hybridization, continuous backcross, molecular marker-assisted selection and the like. Therefore, the self-incompatibility of the non-heading Chinese cabbages is broken through, and the self-compatible material created by the method can greatly improve the breeding efficiency and reduce the seed production cost.
Owner:WUHAN ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Method for overcoming self-incompatibility of radish plants
InactiveCN112005879AOvercoming self incompatibilityMprove inbreedingPlant growth regulatorsBiocideBiotechnologyBrassicaceae
The invention relates to a method for overcoming self-incompatibility of radish plants, and belongs to the technical field of breeding. The method comprises the following steps: spraying an ethephon solution mixed with Tween-20 on stigmas which are just unfolded to be cross-shaped at the beginning of an initial flowering stage, and completely drying fog drops on the stigmas after spraying and performing pollinating from pollen of plant self. The method disclosed by the invention is low in cost, high in efficiency, convenient to operate and suitable for the self-incompatible line of the radishplants, can overcome the self-incompatibility of other cruciferae crops or other family crops caused by stigma mastoid cell disorders, and has important value for breeding and seed production of the cruciferae crops.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY +2
Method for overcoming self-incompatibility of brassica plant
InactiveCN100364389CIncrease humidityReduce formationPlant phenotype modificationHigh absorptionMicrogram
The present invention relates to the breeding technology for brassica plant, and especially carbonic anhydrase treatment method of overcoming self-incompatibility of brassica plant. Specifically, carbonic anhydrase solution of 2-10 microgram / ml concentration is sprayed to the blooms with just emerged stigmata in 8:30-10:30 AM every other day in the initial blooming period until blooming in 90%. The sprayed carbonic anhydrase solution is preferably in atomized form for high absorption. The said method may be used in Brassica campestris, Brassica oleracea, Brassica napus and Brassica pekenensis to raise the self-compatibility index in different degree.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Engineering of plants to exhibit self-compatibility
InactiveUS20110265202A1Improve featuresPreventing self-pollinationOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationBiotechnologyTransmembrane protein
Owner:THE UNIV OF BIRMINGHAM
A kind of breeding method of self-incompatibility two-line hybrid of Brassica napus
InactiveCN101422133BSimplify the breeding processShorten the breeding cyclePlant genotype modificationBrassicaHeterosis
The invention belongs to the technical field of rapeseed breeding, and in particular relates to a method for breeding self-incompatible two-line hybrids of Brassica napus. It is characterized in that the present invention aims at the problem that self-incompatible hybrids of Brassica napus cannot be widely promoted in production because of the shortcomings of existing methods for breeding self-incompatible hybrids of Brassica napus, and proposes a cabbage A method for breeding self-incompatible two-line hybrids of Brassica napus, including breeding and breeding of self-incompatible lines of Brassica napus, breeding and breeding of self-incompatible restorer lines of Brassica napus, Brassica napus Breeding of self-incompatible two-line hybrids of rapeseed and methods for producing seeds thereof. The invention provides an effective method for the breeding of self-incompatible hybrids of Brassica napus, which is beneficial to the large-scale popularization of self-incompatible hybrids of Brassica napus and promotes the utilization of heterosis of Brassica napus.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Method for improving self-incompatibility Wuta-tsai hybridization efficiency
InactiveCN105815211AImprove hybridization efficiencyAvoid accessPlant genotype modificationBiologySelf-incompatibility in plants
The invention discloses a method for improving the hybridization efficiency of wutah, which belongs to the field of horticultural technology. It mainly aims at the labor-intensive, time-consuming and low-efficiency characteristics of artificial hybridization of Wutaicai, and improves the hybridization efficiency of Wutaicai through isolation, reasonable assembly, bagging, and removal of shriveled seeds. The invention has the characteristics of simple operation, low cost, good effect and the like.
Owner:ANHUI SCI & TECH UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com