A kind of breeding method of self-incompatibility two-line hybrid of Brassica napus
A technology of Brassica napus and hybrids, applied in the direction of botany equipment and methods, applications, plant genetic improvement, etc., can solve the problem of not breeding self-incompatible hybrids of Brassica napus, and achieve low seed production costs , Improve breeding efficiency, simple breeding method
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
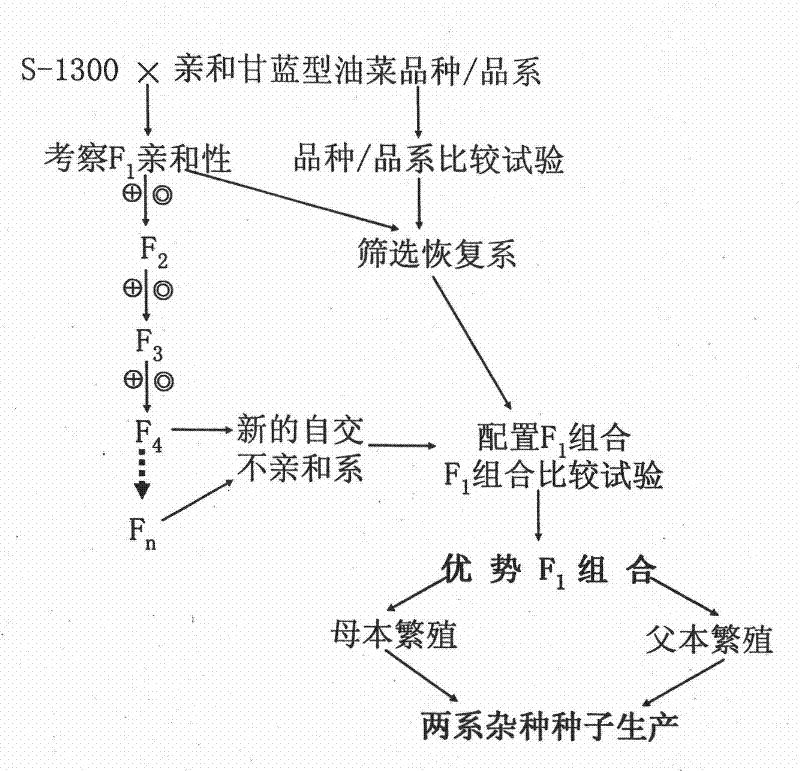
[0025] 1. The selection and breeding of Brassica napus self-incompatibility line, the steps are as follows:
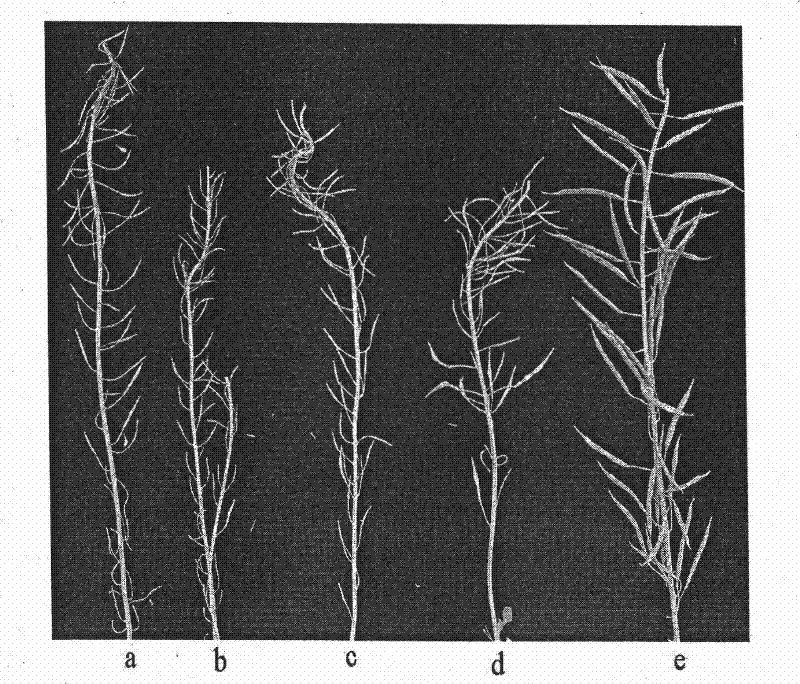
[0026] (1) The self-incompatible line S-1300 of Brassica napus was used as the female parent, and it was crossed with the self-compatible Brassica napus line Huashuang 3 to obtain the first generation hybrid (F 1 )seed.
[0027] (2) F of seeding step (1) 1Seeds, at flowering stage of Brassica napus, on hybrid F 1 The main inflorescence of the plant is bagged and self-crossed, and its compatibility is judged, if F 1 If it shows self-compatibility, it will be bagged and self-crossed, if F 1 If it shows self-incompatibility, it will be self-breeded by peeling off the buds, and F will be obtained. 2 Seed;
[0028] (3) F of planting step (2) 2 Seeds; flowering stage of Brassica napus, for each F 2 The plants were bagged and selfed; the self-incompatible plants were selected, and the buds were manually stripped for selfing; the individual plants were harvested. 2 Pla...
Embodiment 2
[0053] Embodiment 2 (test comparison)
[0054] Specific steps are as follows:
[0055] 1. Use the affinity index method to judge the affinity of Brassica napus:
[0056] Carry out the main branch bagging of the investigated Brassica napus plants at the initial flowering stage, when there are 3-5 flowers blooming on the main branch, knock off the flowers on the main branch, and knock off some small buds on the top of the inflorescence center , Then cover the main branch and two side branches with a sulfuric acid paper bag and fasten them with paper clips. Extract the paper bag upward every other day, and pat the paper bag with your hands during the extraction process to scatter the pollen, which is beneficial to the pollination of the flowers and plays a role in assisting pollination. If there are flowers or flower buds on the side buds protruding out of the bag when extracting the paper bag, it should be knocked out in time to avoid the collected seeds from being impure. Af...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com