Cotton breeding method utilizing exogenous self-incompatibility
A cotton-friendly technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, botany equipment and methods, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., can solve the problems of difficult control of application concentration and application time, unstable effect, cumbersome operation, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0048] First of all, it needs to be explained that the main technical idea of this application is to drive the exogenous PrSI stigma-determining gene by constructing a cotton expression vector and using the cotton stigma and pollen tube specific promoter PrsS1 and pollen-determining genes PrpS1 to express. After transforming the expression vector into recipient cotton and obtaining stable homozygous transgenic lines Gh-PrpS and Gh-PrsS, combined with the upland cotton standard line TM-1, reciprocal crossing was carried out by pairwise pairing, and the development of pollen tubes was observed And the statistics of the number of bells, and the actual verification of self-incompatibility.
[0049] In the process of exogenous gene expression, a cotton stigma and pollen tube specific promoter needs to be used, that is, the upstream about 2000 bp sequence of the cotton stigma and pollen tube specific expression gene. Therefore, in this embodiment, a brief introduction to the p...
Embodiment 2
[0063] On the basis of Example 1, the inventors used the plasmid pBI121 as the backbone vector (a commonly used publicly available plasmid), and the exogenous poppy self-incompatibility determining gene pair as the target gene, combined with the obtained in Example 1 Two expression vectors were constructed: the cotton stigma-specific promoter Ghstp was fused with poppy poppy self-incompatibility stigma-determining gene PrsS to construct the stigma-incompatibility expression vector Ghstp-PrsS-pBI121; the pollen tube-specific promoter Ghpop and Pollen incompatibility expression vector Ghpop-PrpS-pBI121 was constructed by fusing the pollen tube determinant gene PrpS of poppy self-incompatibility. The specific construction process is briefly introduced as follows.
[0064] (1) Preparation of poppy self-incompatibility-determining gene pairs
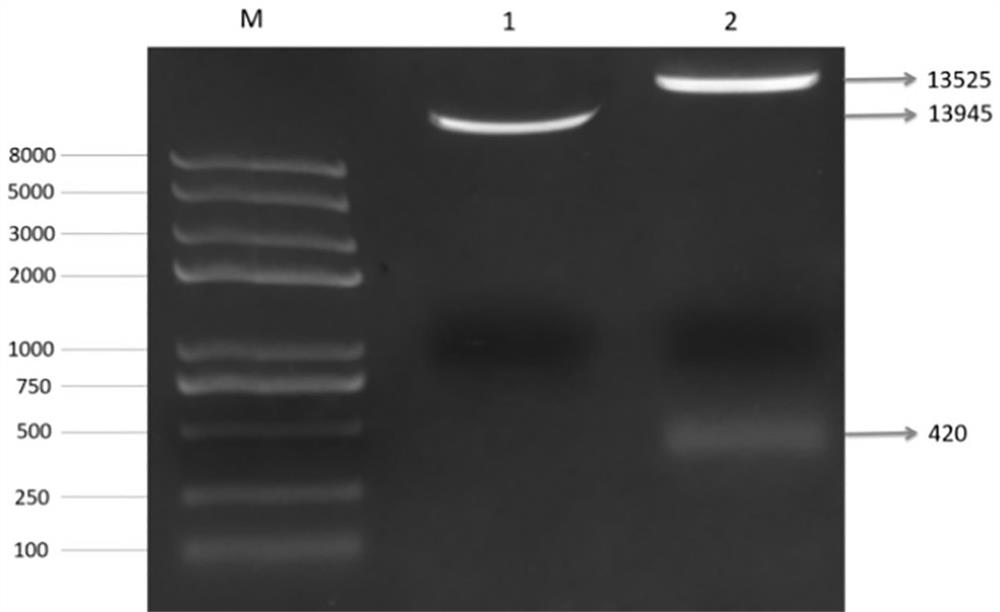
[0065]The PrsS1 (full length 420 bp) and PrpS1 (full length 579 bp) used in this application can be obtained by existing methods such as PC...
Embodiment 3
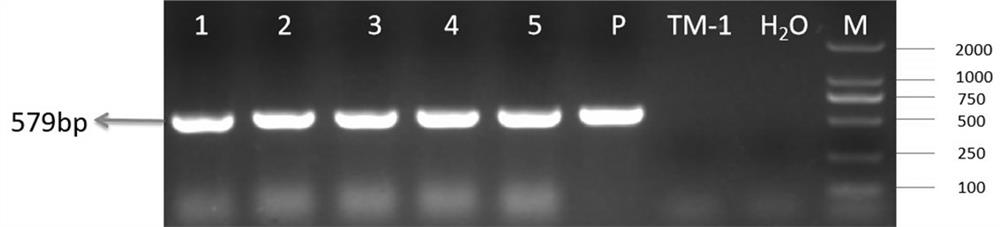
[0087] On the basis of Example 2, the inventors used the Agrobacterium-mediated transformation technology to further convert the cotton stigma-specific expression vector Ghstp-PrsS1-pBI121 and pollen-incompatible expression vector Ghpop-PrpS-pBI121 in Example 2 into Agrobacterium-mediated The transfer technology was introduced into the recipient cotton Z24, and two groups of stable homozygous self-incompatibility stigma-determining gene and pollen-determining gene transgenic lines Gh-PrpS and Gh were obtained through PCR detection of the target gene and detection of self-fertilization offspring segregation. -PrsS. The specific experimental process is briefly introduced as follows.
[0088] (1) Preparation of transgenic seedlings
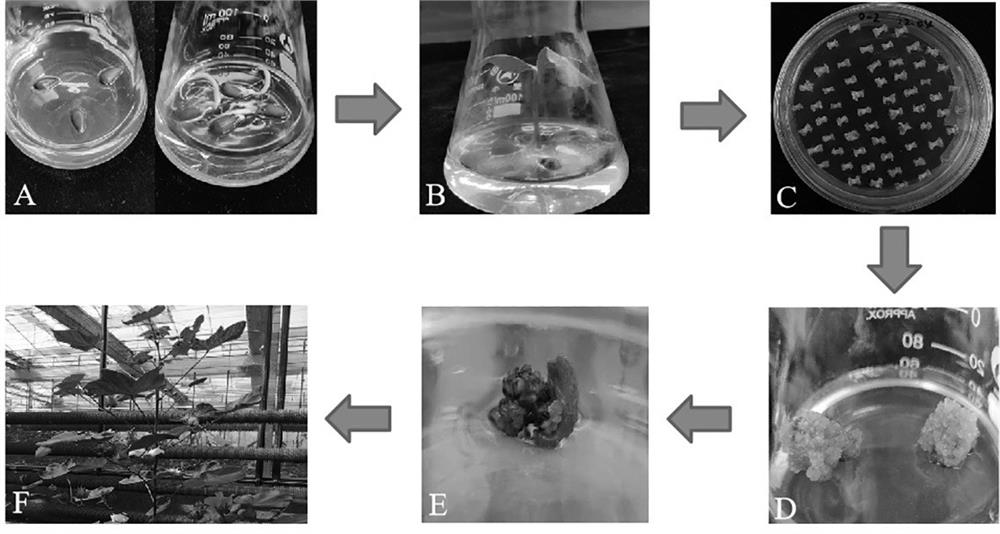
[0089] Refer to the existing technology (the specific process is as follows figure 2 shown), cotton seeds (Z24) were germinated and cultured aseptic seedlings, and then the hypocotyls were cut into small sections and then transformed with the stig...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com