Electro-magnetic braking device for controlling molten metal flow in continuous cast crystallizer
A technology of liquid metal flow and casting mold, which is applied in the field of continuous casting, can solve the problems of large volume and weight of the device, achieve the effects of volume and weight reduction, simple form, and weaken the degree of influence
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
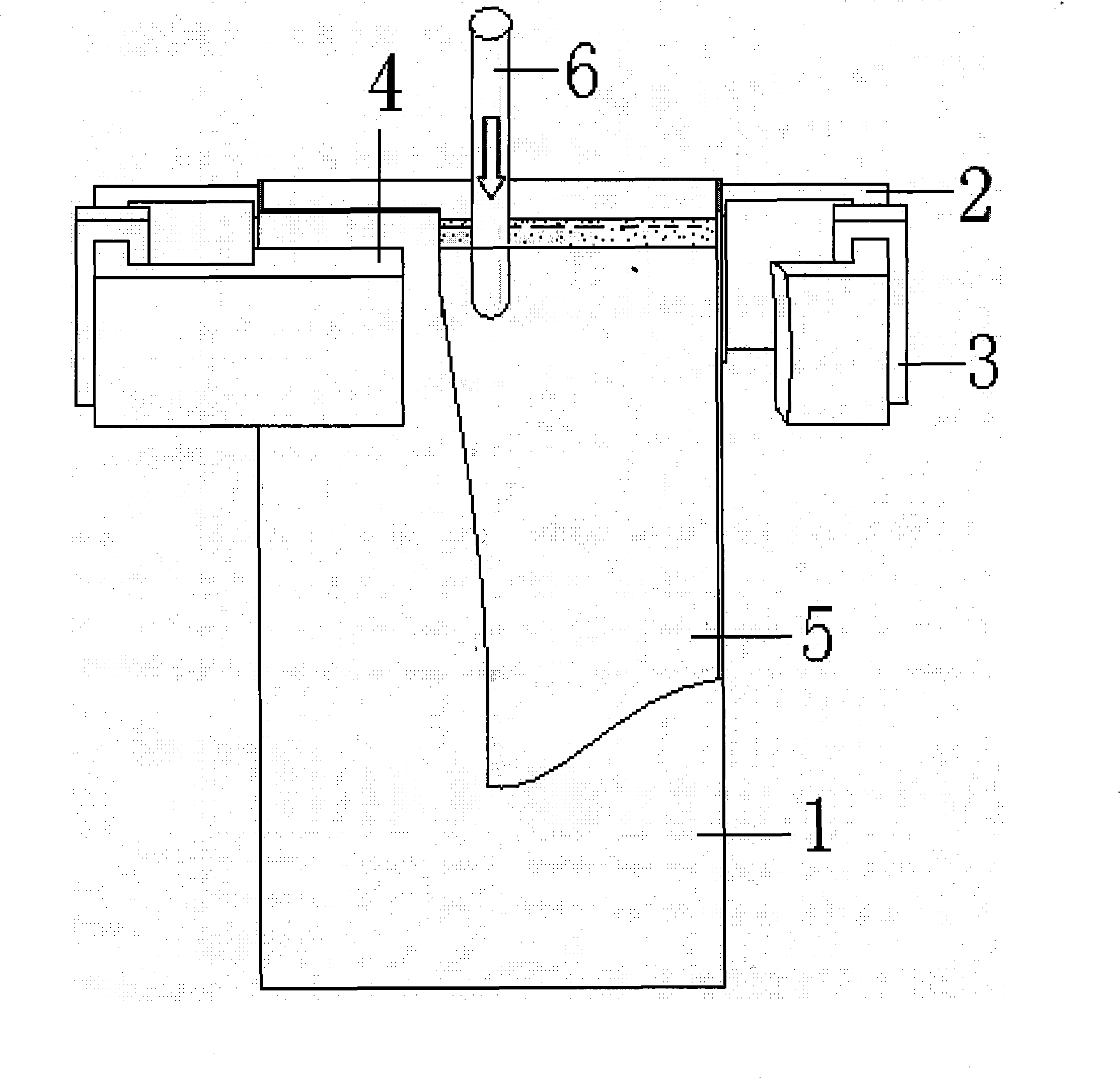
[0017] Such as figure 1 As shown, the electromagnetic braking device of the present invention is composed of a magnetic core 2 half-surrounded on the side wall of the crystallizer 1, an exciting coil 3 and a magnetic pole 4. The magnetic pole 4 is arranged on the narrow surface area biased to the mold 1, and the magnetic pole 4 is in height Simultaneously cover the surface area of the molten metal 5 near the narrow face of the crystallizer 1 and the impact point area where the nozzle 6 flows out. By applying current to the excitation coil 3, a static magnetic field is generated between the two pairs of magnetic poles 4. The two groups of excitation in this embodiment The coils 3 are respectively arranged at the center of the magnetic core 2, on one side of the narrow side of the crystallizer.
[0018] For a mold with a cross-sectional size of 1400×230mm, a nozzle immersion depth of 150mm, and a nozzle side hole inclination angle of -15 degrees, the magnetic pole of the elect...
example 2
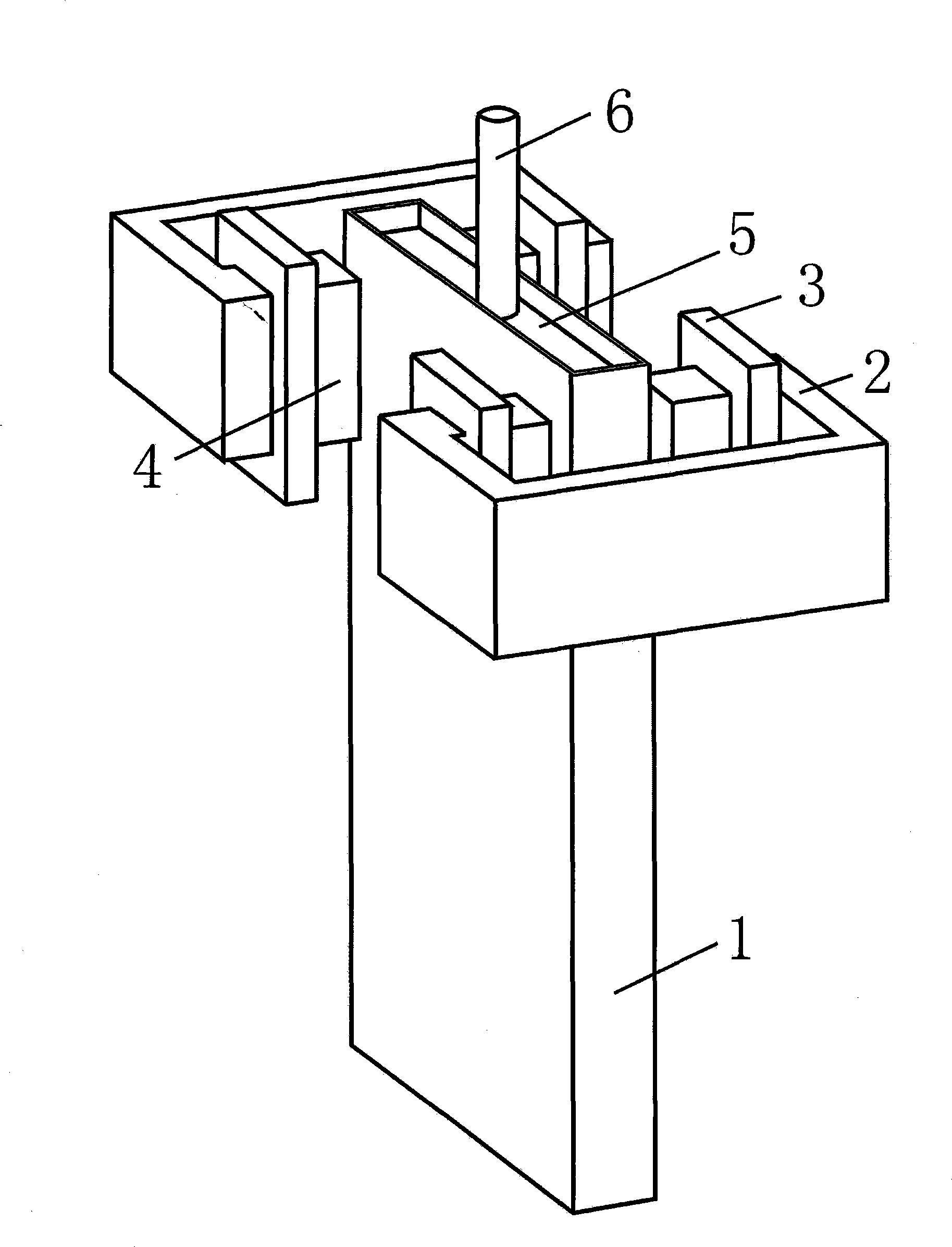
[0020] according to image 3 The arrangement scheme of magnetic poles, magnetic cores and excitation coils of the electromagnetic brake shown, and the connection method of magnetic poles and magnetic cores. For a mold with a cross-sectional size of 1400×230mm, a nozzle immersion depth of 150mm, and a nozzle side hole inclination angle of -15 degrees, the electromagnetic brake magnetic pole is placed near the narrow surface of the continuous casting mold. In the height direction, the top of the magnetic pole is located within the range from 50mm up to 500mm down from the molten steel surface of the mold; in the width direction, the magnetic pole is located within the range of 180mm inward from the side wall of the mold. That is, the cross-sectional size of the magnetic pole is 180×500mm, so that the magnetic pole simultaneously covers the surface area of the molten metal near the narrow surface of the mold and the impact point area of the outlet flow. When the width of the...
example 3
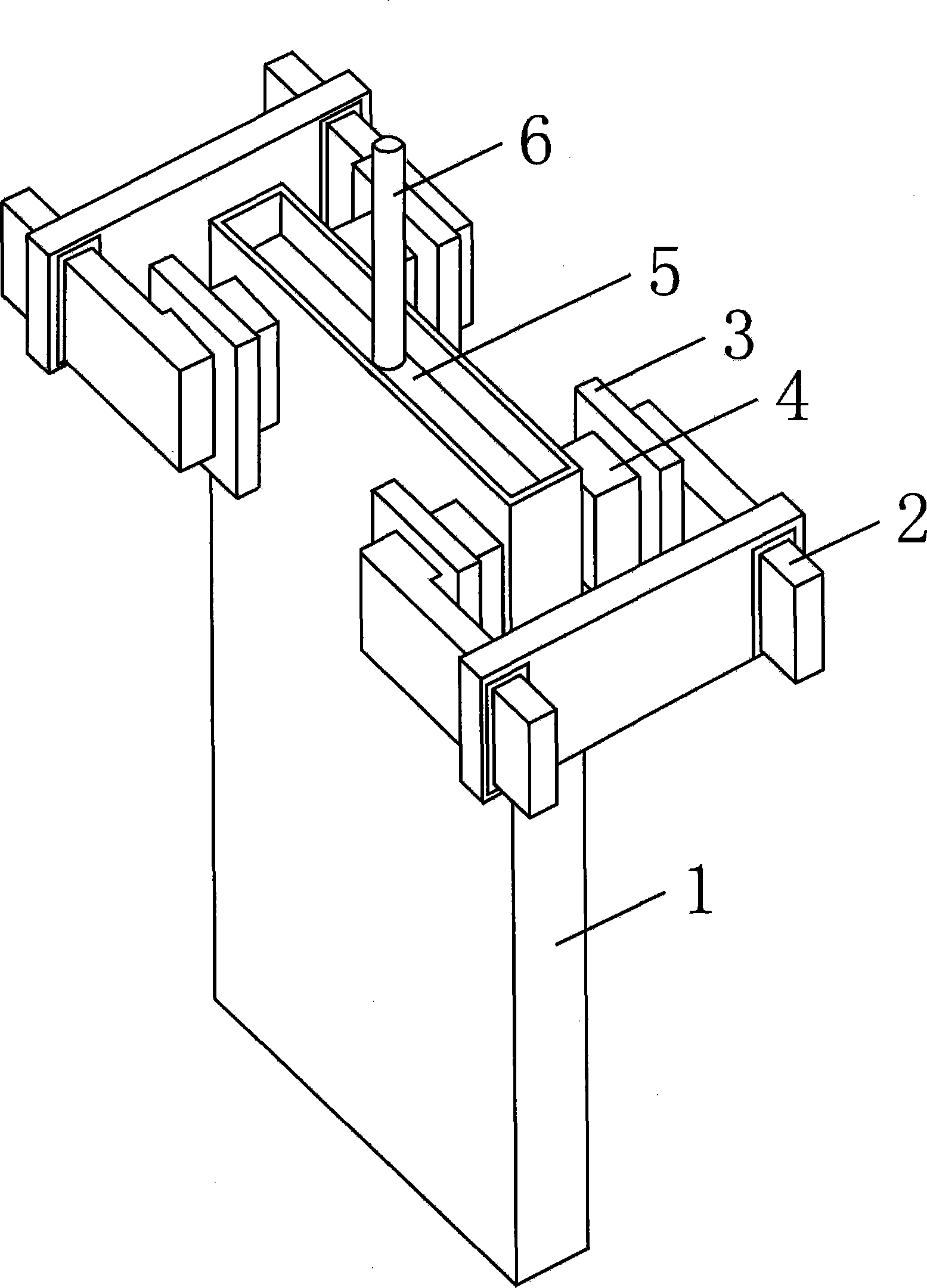
[0022] The structure of the device is the same as Example 1, the difference is that for a mold with a cross-sectional size of 1400×230mm, a nozzle immersion depth of 150mm, and a nozzle side hole inclination angle of -15 degrees, the magnetic pole of the electromagnetic brake is placed near the narrow surface of the continuous casting mold. In the height direction, the top of the magnetic pole is located within the range from 50mm up to 800mm down from the molten steel surface of the mold; in the width direction, the magnetic pole is located within the range of 400mm from the side wall of the mold. That is, the cross-sectional size of the magnetic pole is 400×800mm, so that the magnetic pole simultaneously covers the surface area of the molten metal near the narrow surface of the mold and the impact point area of the outlet flow. The magnetic core and the magnetic poles are integrally connected.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| magnetic flux density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com