Routing method for avoiding dead lock in fault tolerance mesh based on channel overlapping
A technology to avoid deadlock and routing, applied in data exchange networks, digital transmission systems, electrical components, etc., can solve the problem that a node cannot be used as a source node or target node of a message, so as to reduce transmission delay, improve transmission performance, and improve practicality. The effect of traffic
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
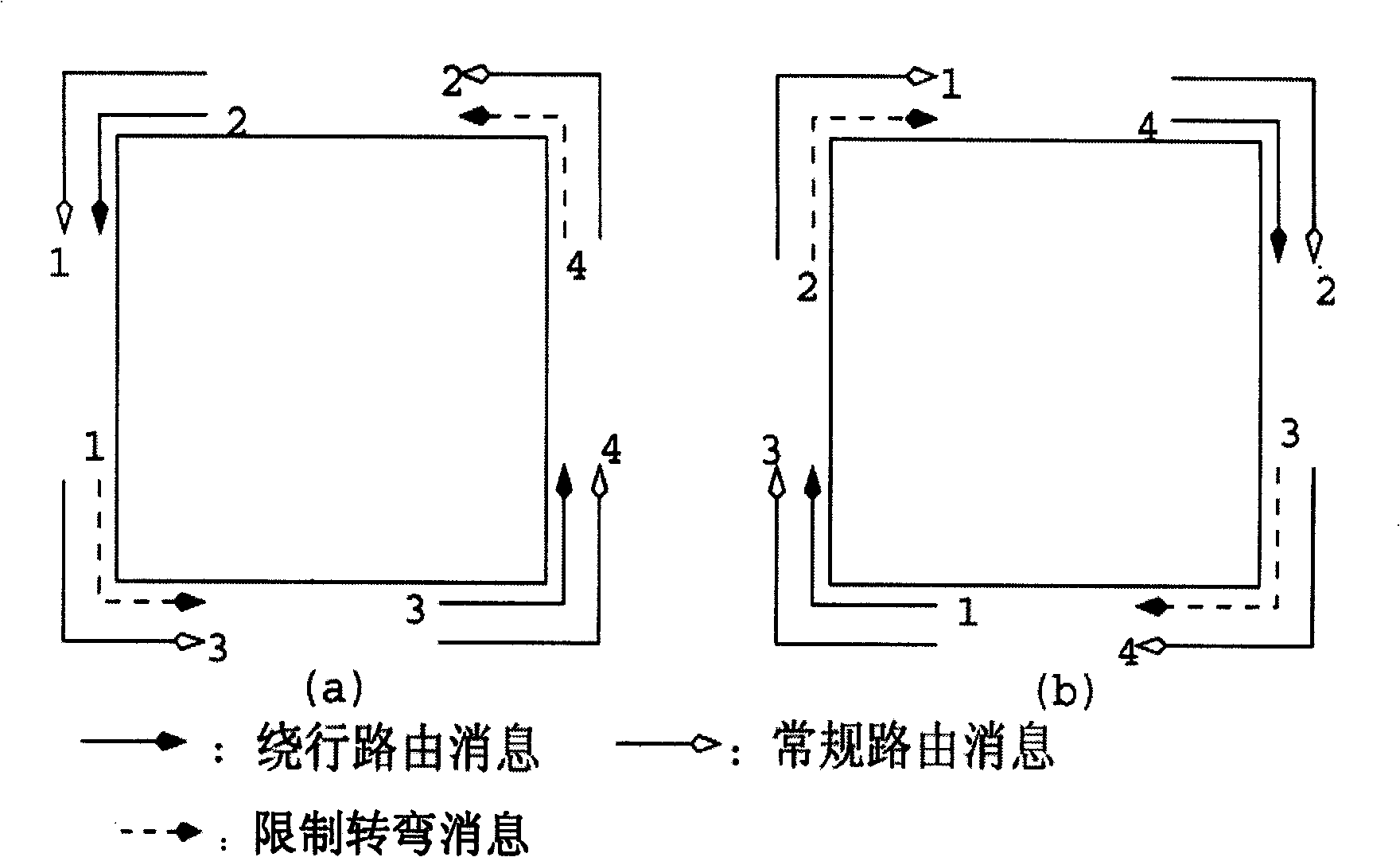
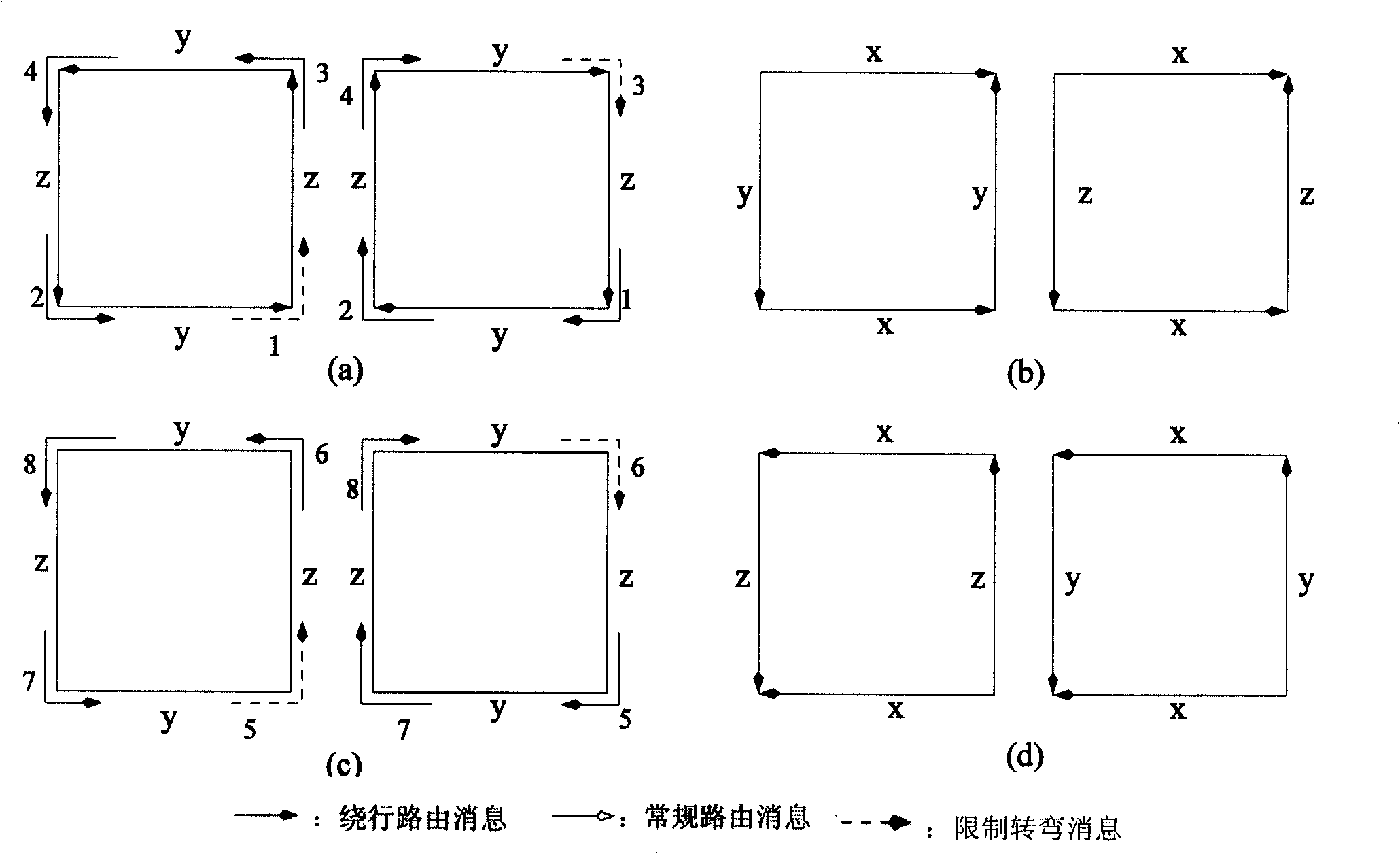
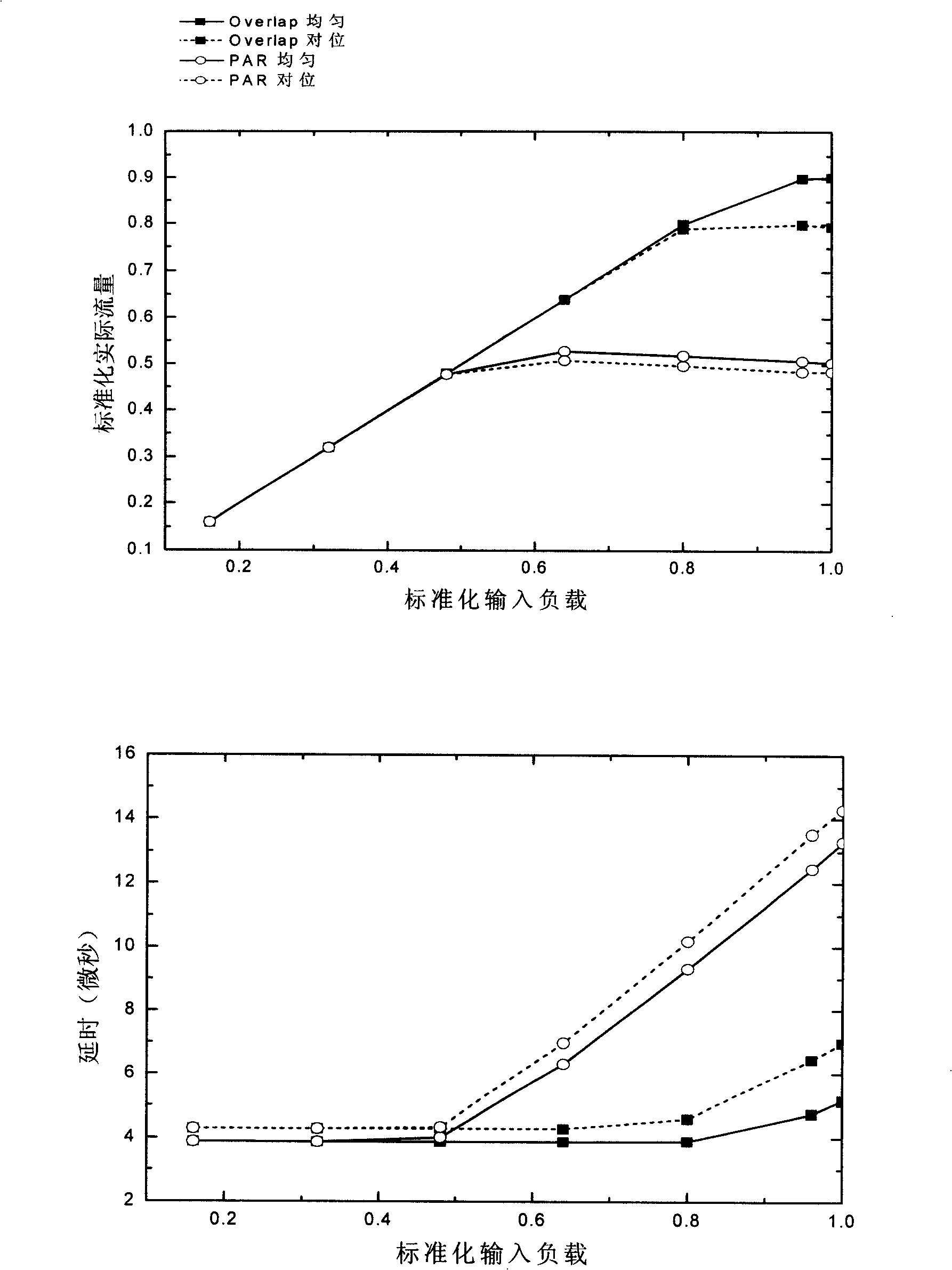
[0064] A physical network can be divided into several virtual subnets. Messages inserted into the network are restricted to routing within a certain virtual subnet. As long as there is no deadlock in each virtual subnet and there is no deadlock between virtual subnets, it can be guaranteed that no deadlock will occur in the entire network. The partitioning method proposed in this paper is mainly for two-dimensional and three-dimensional mesh networks, and this method can also be extended for higher-dimensional networks.
[0065] A two-dimensional mesh network can be divided into the following four virtual subnets: 1.x-y-, 2.x-y+, 3.x+y-, 4.x+y+. we use c i Indicates the i-th virtual channel in a physical channel. In the above four virtual subnets, 1 and 2, 3 and 4 can be combined in pairs to obtain two virtual subnets, x-y * (c 1 -, c 1 ) and x+y * (c 1 +,c 2 ). The labels in parentheses indicate the virtual channels assigned to each virtual subnet, for example, x+y ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com