Digital image nondestructive compression method and device, resolution method and image encoder
A digital image, lossless compression technology, applied in image communication, digital video signal modification, television, etc., can solve the problems of slow decompression speed, large storage space, poor real-time performance, etc., achieve high compression efficiency, improve response speed, and real-time performance Good results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
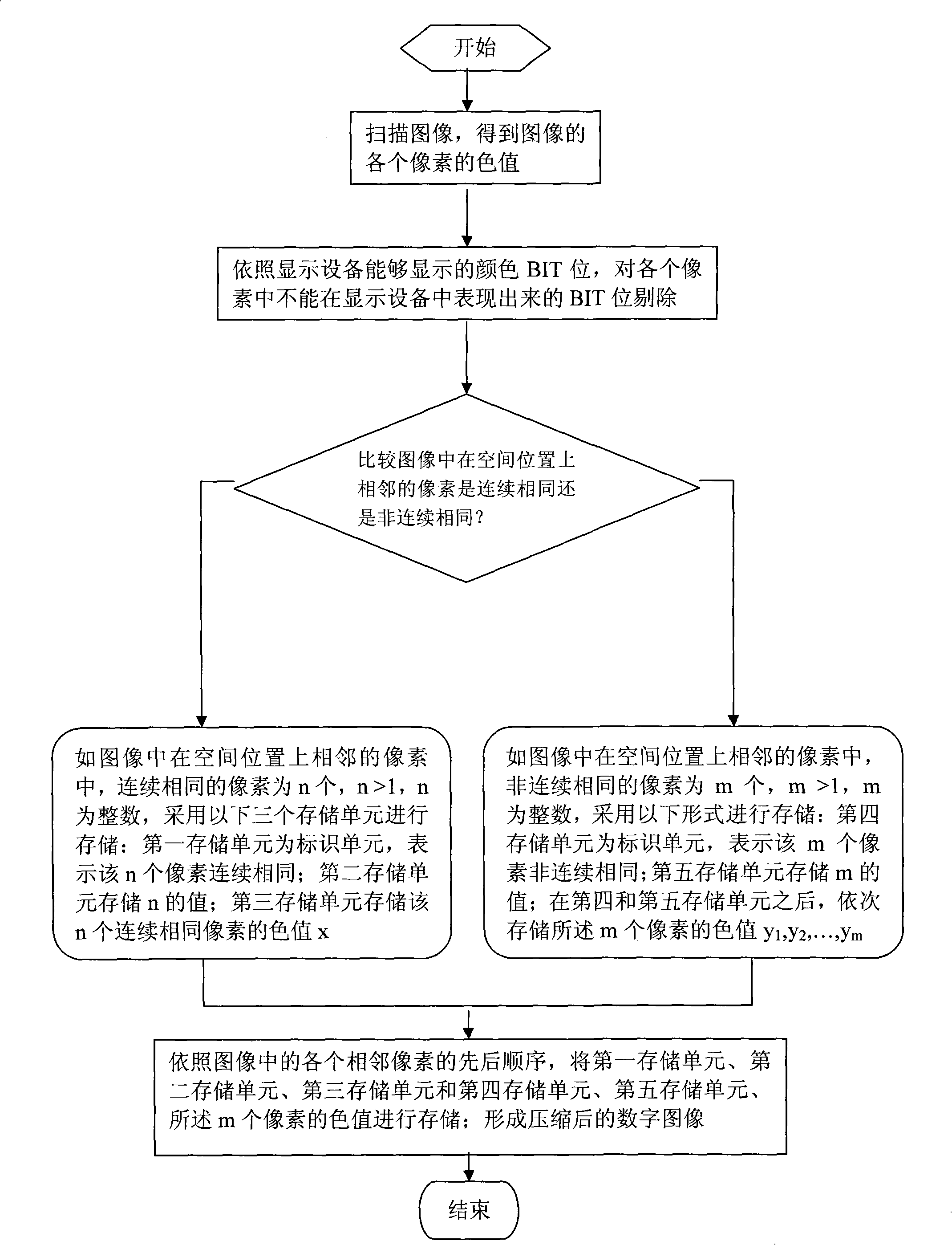
[0042] refer to figure 1 , a digital image lossless compression method mainly includes the following steps:
[0043] (1), start scanning from the first pixel of the image to obtain the color value of each pixel;
[0044] (2) Compare the scanned pixels according to their color values, and perform the following compression and storage operations:
[0045] (2.1), as in the adjacent pixels in the image, there are n consecutive identical pixels, n>1, n is an integer, and the following three storage units are used for storage: the first storage unit is the identification unit, Indicates that the n pixels are continuously identical; the second storage unit stores the value of n; the third storage unit stores the color value x of the n consecutive identical pixels;
[0046] (2.2), if there are m non-consecutive identical pixels in the adjacent pixels in the image, m>1, and m is an integer, the following format is used for storage: the fourth storage unit is an identification unit, i...
Embodiment 2
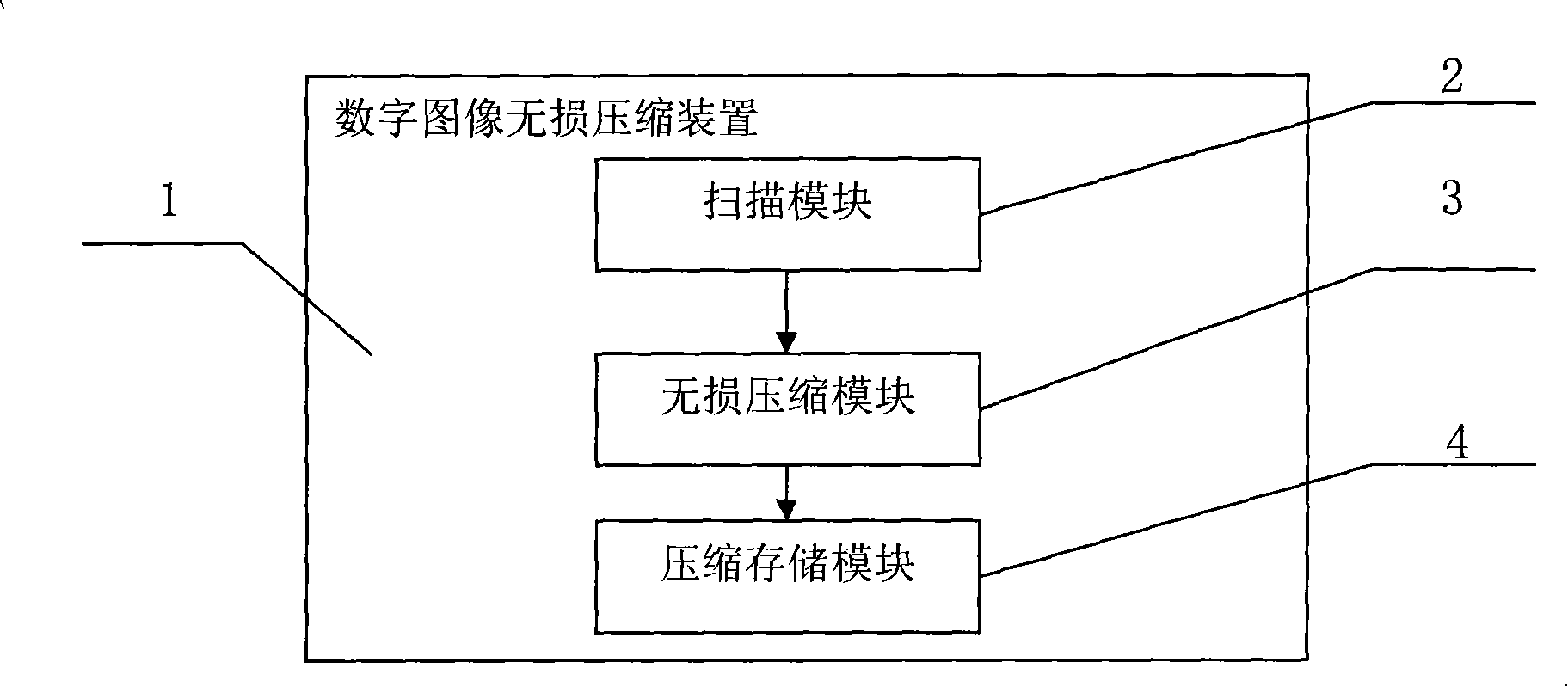
[0071] refer to figure 1 , image 3 , a device for implementing a digital image lossless compression method, comprising: a scanning module 2, which is used to scan from the first pixel of an image until the last pixel of the image to obtain the color value of each pixel; the digital image is lossless The compression device also includes: a lossless compression module 3, which is used to compare the scanned pixels: (2.1) For example, in the adjacent pixels in the image, there are n consecutive identical pixels, where n>1, n is Integer, the following three storage units are used for storage: the first storage unit is an identification unit, indicating that the n pixels are consecutively the same; the second storage unit stores the value of n; the third storage unit stores the color values of the n consecutive identical pixels x; (2.2), as in the adjacent pixels in the image, there are m non-continuous identical pixels, m>1, and m is an integer, which is stored in the followin...
Embodiment 3
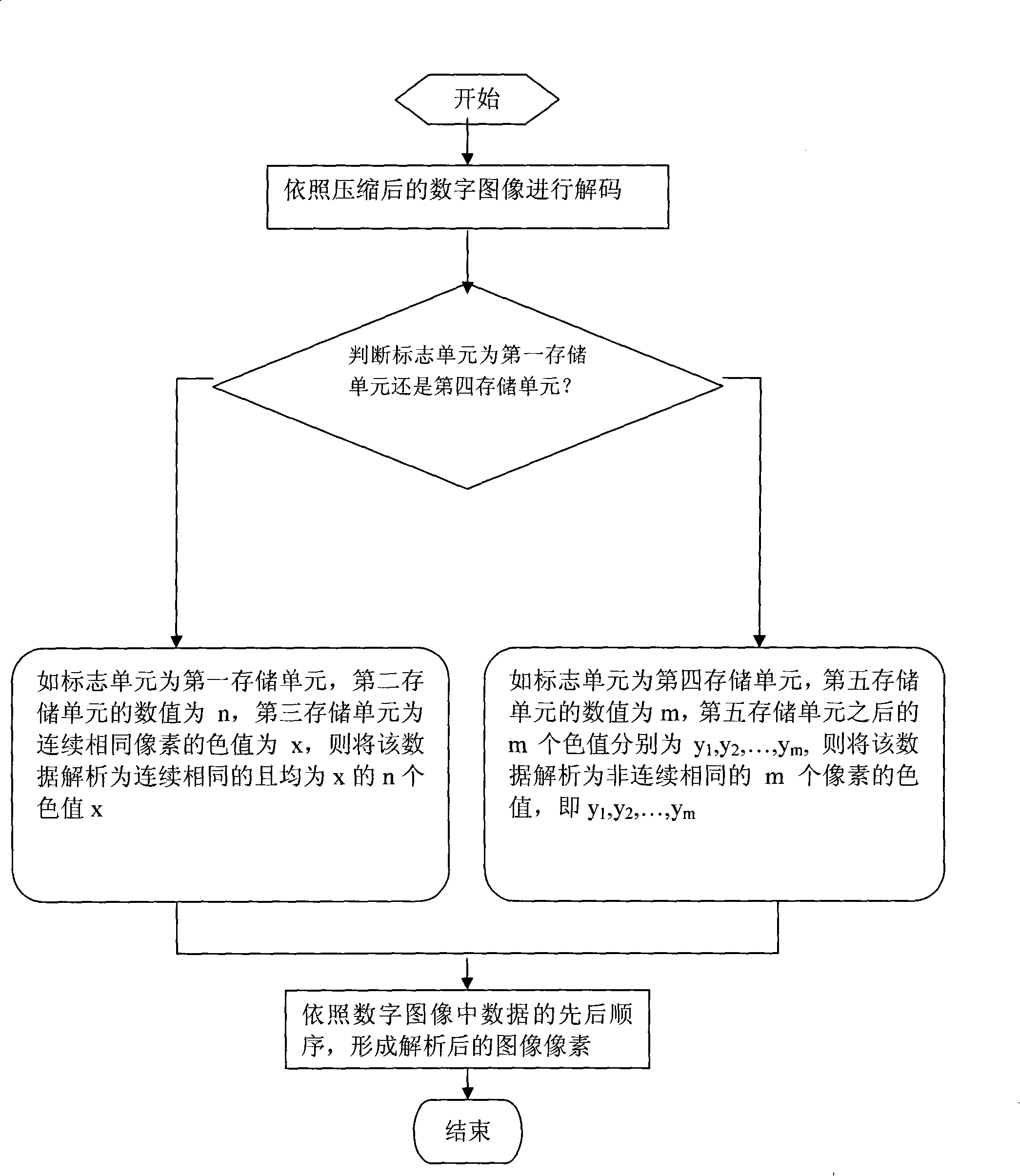
[0075] refer to figure 1 , figure 2 A digital image analysis method coordinated with a digital image lossless compression method mainly includes the following steps:
[0076] (1) Decoding according to the compressed digital image, if the flag unit is the first storage unit, the value of the second storage unit is n, and the third storage unit is the color value of consecutive identical pixels x, then analyze the data It is n color values x that are consecutively the same and are all x; if the flag unit is the fourth storage unit, the value of the fifth storage unit is m, and the m color values after the fifth storage unit are respectively y 1 ,y 2 ,...,y m , then parse the data into the color values of non-consecutive identical m pixels, that is, y 1 ,y 2 ,...,y m ;
[0077] (2) According to the sequence of data in the digital image, the analyzed image pixels are formed.
[0078] The analysis method of this embodiment is: perform reverse analysis on the compress...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com