Method for detecting trisomy 13 and down syndrome by non-invasive maternal blood screening
A technology of maternal blood and blood, applied in the direction of material inspection products, special data processing applications, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as poor quality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
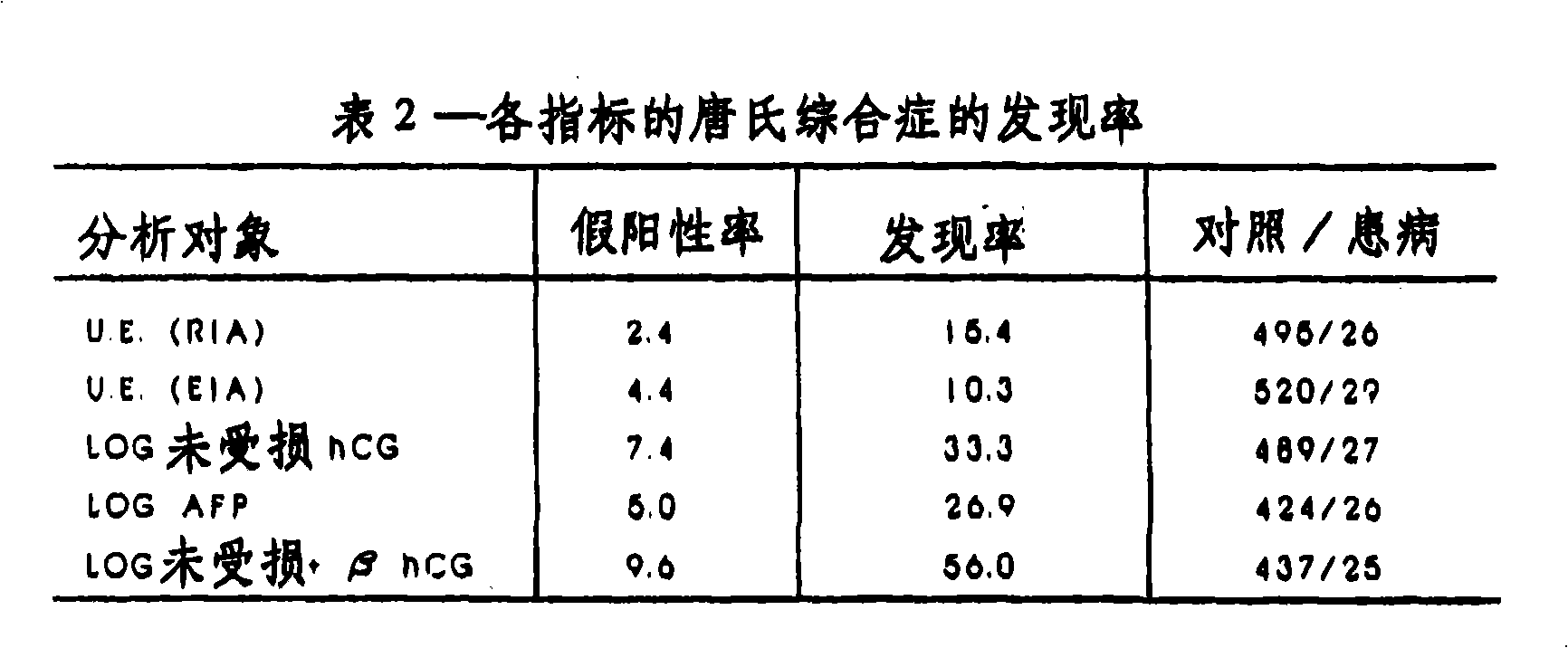
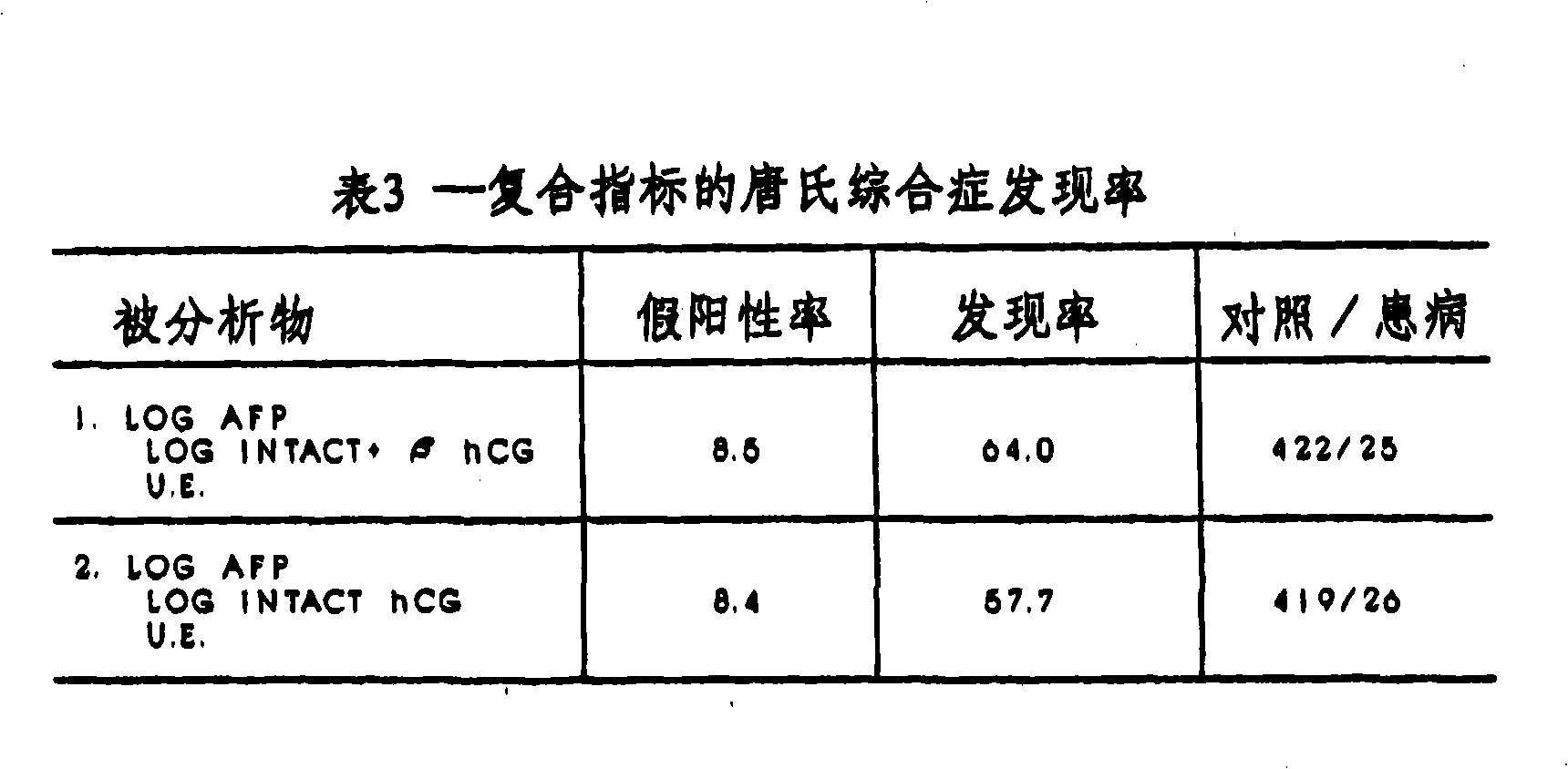
[0068] More than 400 case samples were used to study the relationship between fetal Down's syndrome and free β-HCG content in maternal blood as well as AFP content (MSAFP), UE and undamaged HCG in maternal serum. The samples included samples from 25 pregnant women known to be carrying fetuses with Down syndrome and control samples from the affected cases.
[0069] For each blood sample, the content values of AFP, undamaged HCG molecules, free β-HCG and UE (hereinafter referred to as "indices") are determined by the following assay methods:
[0070] index test methods
[0071] MSAFP enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)
[0072] UE radioimmunoassay
[0073] Undamaged HCG Bead ELISA
[0074] Free β-HCG ELISA
[0075] The value of each index becomes a variable in the step-by-step discriminant processing and linear discriminant processing on the Statistical Analysis System (SAS Research Institute, Inc.), a computer software statistical software package available on t...
example 2
[0095] More than 550 patient samples were used to study the relationship between fetal Down's syndrome and the level of free β-HCG in maternal blood. First, blood samples obtained from 29 pregnant women known to be pregnant with fetuses with Down syndrome were used to control gestational age (same number of weeks), maternal age (difference within 3 years) and frozen storage time (difference within one month). 520 unaffected samples were analyzed. All samples were obtained from non-diabetic white singleton pregnant women.
[0096] In order to avoid a fixed bias with a certain tendency in the estimated detection rate, the concept of effective group was adopted. The effective set is a set of data that is independent of the baseline data. Results from patients in the cohort were not used to establish baseline data, but were compared to baseline data to determine detection rates. This additional valid set included 26 additional cases identified as trisomy 21 (total of 55 cases) ...
example 3
[0120] The following examples illustrate the preparation of a one-step assay and a two-step assay for free β-HCG and their use in the method of the invention.
[0121] Preparation of one-step free β-HCG assay
[0122] 1. Overlay a 96-well microtiter plate with a "capture" antibody specific for the free beta subunit of the human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG) molecule. Antibodies can be monoclonal or polyclonal. The antibody concentration used to coat the plate was 0.8 micrograms per well, but could be varied if desired. Plates were incubated at 4°C for at least 16 hours.
[0123]2. Rinse the plate with pH 7.2 phosphate buffer containing 0.05% Tween 20, other suitable washing buffers can also be used. The plates were then "blocked" with pH 7.2 phosphate buffer containing 3% hydrolyzed animal protein and 0.05% Tween 20. Other solutions familiar to those skilled in the art may also be used, such as 1% bovine serum albumin solution. Add 300 microliters of septum solution to eac...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com