Formulae neighborhood based data dimensionality reduction method
A data dimension reduction and neighborhood technology, applied in the field of information processing, can solve problems such as parameters and external noise are too sensitive, dimension reduction performance failure, etc., to achieve the effect of broadening the applicable neighborhood, maintaining consistency, and good aggregation effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0015] As shown in the figure, a data dimensionality reduction method based on rule neighborhoods includes the following:
[0016] 1. Formal description of data dimensionality reduction
[0017] Establish a five-tuple model: FO = (X, D, δ, d, Y),
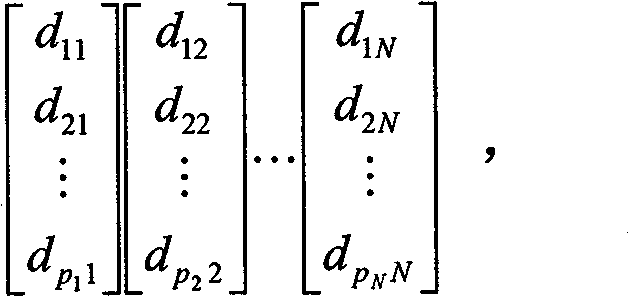
[0018] Among them: D is the dimension of the high-dimensional space; d (d X = { x → 1 , x → 2 , . . . , x → N } , Is a high-dimensional space R D N D-dimensional real number vectors in ( x → i = ( x → i 1 , x → i 2 , . . . , x → i D ) T , i = 1,2 . . . , N ) ; Y is the output sample set of the model FO, expressed as: Y = { y → 1 , y → 2 , . . . , y → N } , Is a low-dimensional space R d N d-dimensional real number vectors in ( y → i = ( y → i 1 , y → i 2 , . . . , y → i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com