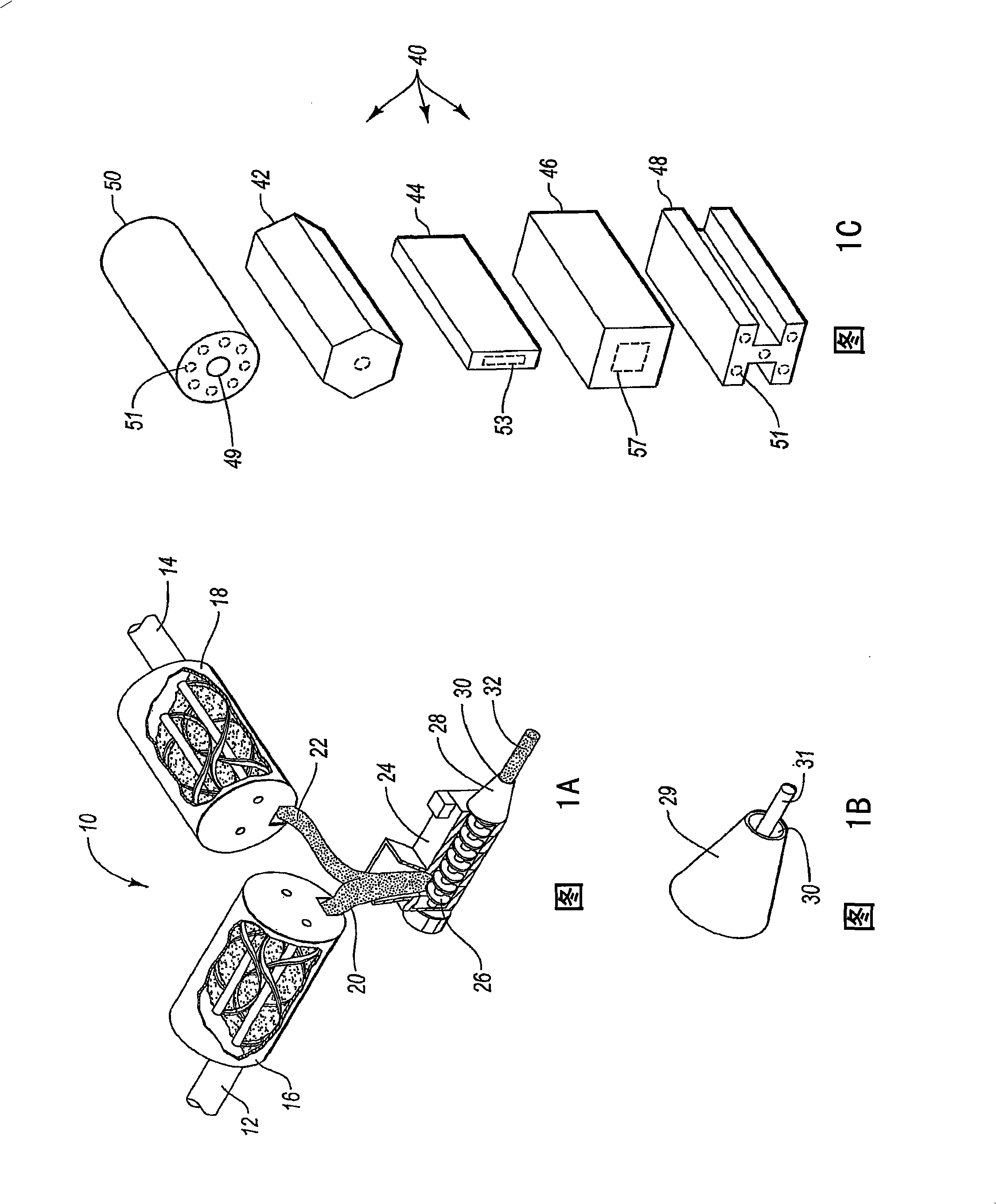
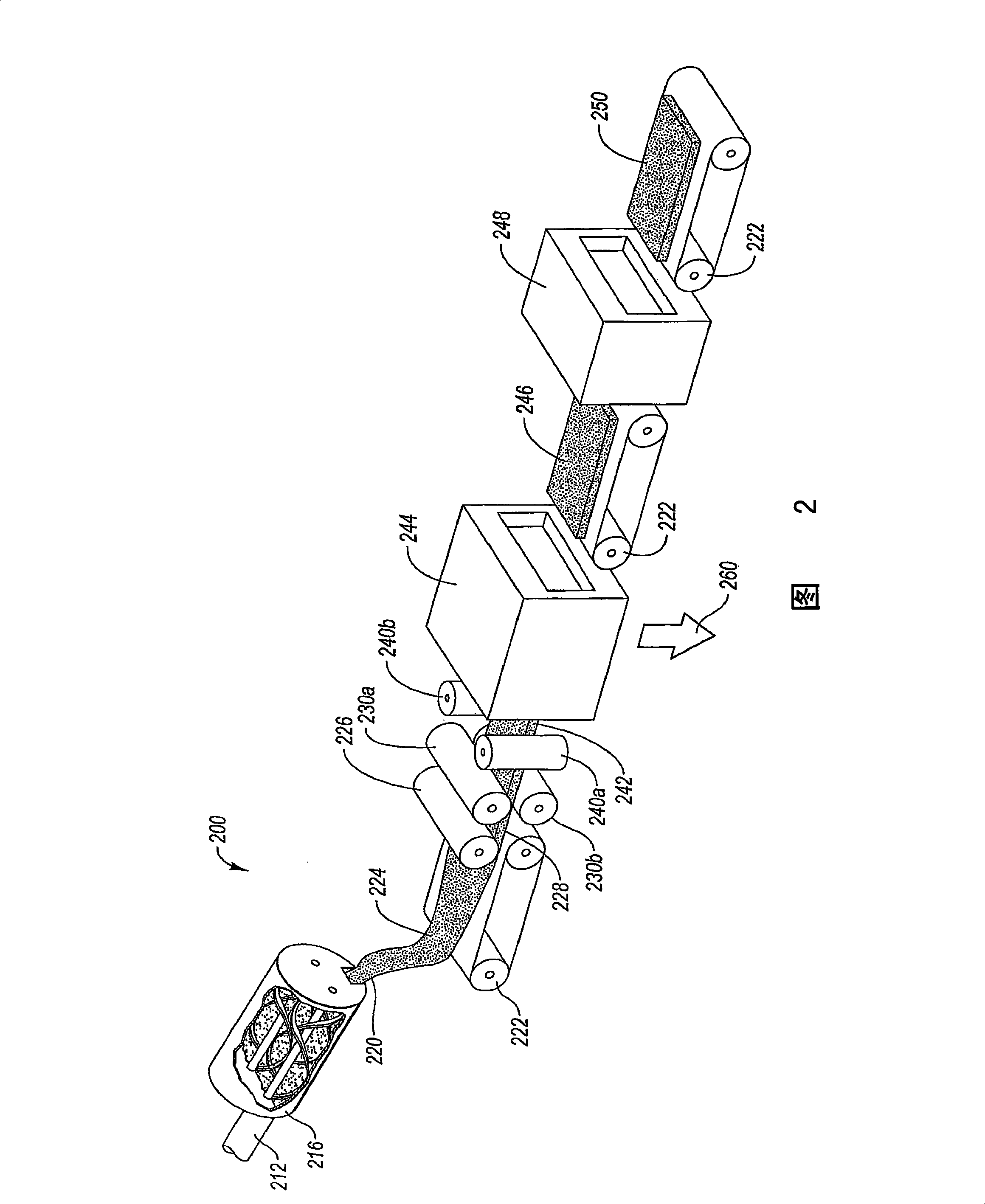
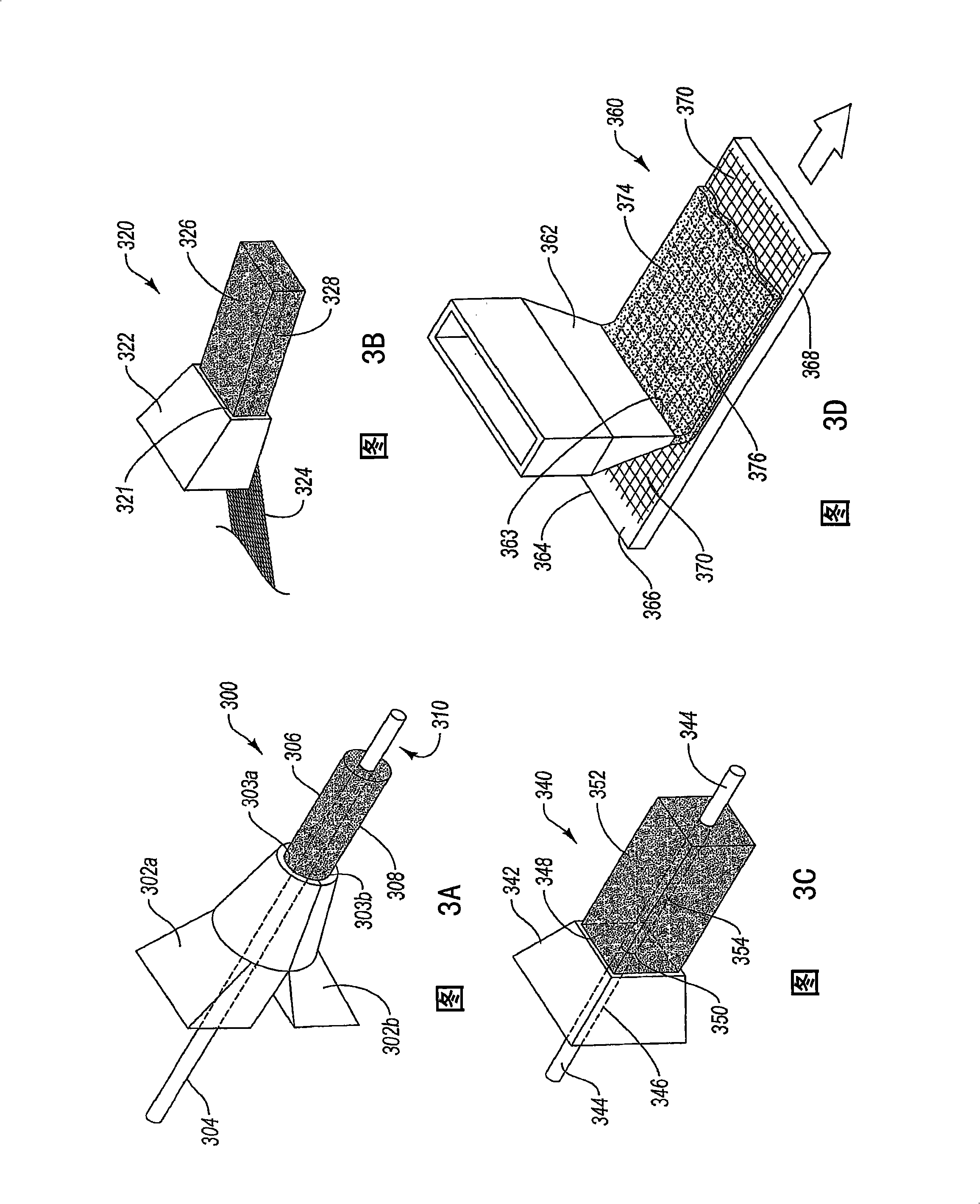
Cementitious composites having wood-like properties and methods of manufacture
A cohesive composition and cohesive technology, applied in the field of cohesive building products and cohesive building materials
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0197] Various extrudable compositions were prepared in accordance with the present invention having different concentrations of the components. All mixtures were mixed according to the normal mixing procedures described above and in the references incorporated herein. Briefly, the fibrous mixture of fibers, rheology modifier and water was mixed for 1 hour, then the other components were added and mixed for an additional hour. Extrudable compositions were formulated as shown in Tables 1-6.
[0198] Table 1
[0199] substance (wet)
Mixture 1
mixture 2
Mixture 3
Mixture 4
Mixture 5
Mixture 6
fiber type
HW
HW
SW
SW
SW
SW
461
790
933
1227
1627
1755
Portland cement (grams)
910
910
910
910
910
910
50
50
50
50
50
50
Starch (grams)
219
219
219
219
219
...
Embodiment 2
[0218] Various extrudable compositions were prepared according to Example 1 with different component concentrations. Extrudable compositions were formulated as shown in Tables 7-8.
[0219] Table 7
[0220]
[0221] Table 8
[0222]
[0223] The cementitious compositions exemplified by Mixtures 1-6 are extruded into building products and cured (eg, by incipient heating). The amounts of each component were then calculated on a dry basis and are provided in Tables 9-10.
[0224] Table 9
[0225]
[0226] Table 10
[0227]
Embodiment 3
[0229] The flexural strength of extruded cementitious building products is tested and compared to wood. More specifically, flexural strength was tested as a function of displacement (inches) versus applied force (lbs). In this way, the displacement of timber (x) is compared with that of unreinforced extruded composites (solid diamonds - ◆ ), glass fiber reinforced extruded building products (solid squares - ), and extruded plain steel bars (steel rebar) reinforced. Comparing the displacement of the building product (solid triangle-▲), as shown in Figure 8. As shown, the displacement of the extruded cementitious building product and wood was similar up to a force of about 275 lbs. Additionally, extruded building products reinforced with fiberglass rebar and conventional rebar exhibit greater displacement than wood under the same force. Thus, extruded bonded building products can be compared to wood with less end force, and steel-reinforced bonded building products actually ha...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com